














Preview text:
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system... za
************************************* I. Study Guide: 2010/1/6
************************************* A. General Guideline:
1. Study the summary in each chapter. 2. Study the lecture notes. 3. Study the homeworks.
4. Study those examples discussed in the class. 5. Study the textbook. 6. Study this study guide.
7. Try the quizzes at http://www.w3schools.com/.
8. Study the exercises in the textbook. B. Review for the Final Exam:
1. Understand the basis of database management. (Chapter 1)
2. Understand the relational model. (Chapter 2)
3. Understand SQL. (Chapter 3)
4. Understand advanced SQL. (Chapter 4)
5. Understand database design and the E-R model (Chapter 5)
6. Understand relational database design (Chapter 6)
7. Understand XML (Chapter 10) *************************** II. Sample Questions: *************************** A. Multiple Choice Questions:
Chapter 1 - 2: Introduction, Relational Model
1. Which is not an advantage of using a database system? (A) currency (B) data independence (C) availability (D)speed
2. Which is not a component of a database system? (A) data (B) hardware (C) software (D) none of above 3. Which statement is false?
(A) A database system may support single or many users. (B) Every user has the same view on the
database. (C) The database is integrated (D) The database is shared.
4. Which is not a level in the three levels fo the architecture?
(A) data level (B) inernal level (C) exernal level (D) coneceptual level
5. Which is not the job of a database administrator?
(A) participates in conceptual database design (B) determines how to implement conceptual schema
(C) implement security and integrity (D) maintain the computer system
6. Which is not a function of a DBMS?
(A) data definition (B) data manipulation (C) optimiation and execution (D) none of above
7. Which is not an explanation of a data dictionary?
(A) data about the data (B) metadata (C) data index (D) none of above
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
8. Which is not a component of the relational model?
(A) an open-ended collection of scalar types (B) a relation evaluator
(C) a relational type generator (D) none of above 9. Which statement is true?
(A) A tuple corresponds to a row in a table.
(B) A relation variable is inherently a specific set of values.
(C) A relation can have different values at different times. (D) none of above
10. Which is not one of transaction's ACID properties? (A) automaticity (B) consistency (C) isolation (D) durability 11. Which statement is false?
(A) Each attribute of a relation has a name.
(B) Attribute values are (normally) required to be atomic.
(C) The special value null is a member of every domain (D) none of above
12. Which is not one of six basic operators of relational algebra? (A) select (B) union (C) set intersection (D) set difference 13. Which statement is false?
(A) It is possible for tuples to have a null value.
(B) In SQL "P is null" evaluates to null if predicate P evaluates to null.
(C) null signifies an unknown value or that a value does not exist. (D) The result of any arithmetic
expression involving null is null.
14. Which is not a DDL command of SQL?
(A) create table (B) select (C) create type (C) alter table
15. Which is not a operation implemented by the SQL select command?
(A) restrict (B) project (C) join (D) none of above 16. Which statement is false?
(A) Every database has a catalog.
(B) A catalog has only a schemas.
(C) Each catalog includes one Information Schema
(D) The Information Schema is a collection of all other schemas as views.
17. Which of the following is not correct?
(A) SQL select operation may be used for data retrieval as well as for data modification.
(B) SQL may be used for data definition as well as data retrieval
(C) SQL may be used fo defining base tables as well as view tables
(D) SQL data definitions may be used for defining primary keys as well as foreign keys. 18. Which statement is true?
(A) (unknown or true) = unknown (B) (unknown or false) = false
(C) (true and unknown) = unknown (D) (false and unknown) = unknown Chapter 3: SQL 1. What does SQL stand for?
(A) Standard Query Language (B) Structured Query Language
(C) Semantic Query Language (D) Syntax Query Language
2. Which is not a category of SQL? (A) DDL (B) DML (C) DCL (D) DAL
3. Which is not a SQL command? (A) delete (B) insert (C) search (D) update
4. Which is not a DDL command? (A) alter table (B) create table (C) drop table (D) select table
5. Which is not a DML command? (A) delete (B) drop table (C) insert (D) update
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
6. Which of the following is to use alter a table? (A) DDL (B) DML (C) DCL (D) DAL 7. Which of the following
is to use update a table? (A) DDL (B) DML (C) DCL (D) DAL
8. Which is a set of commands used to update and query a database?
(A) DDL (B) DML (C) DCL (D) DAL
9. Which of the following is not a DML command? (A) insert (B) create table (C) delete (D) select
10. To delete a table, which SQL command can be used?
(A) delete (B) unpack (C) drop (D) truncate
11. How many attributes will be shown in the following query?
select student_no, name, department, address, email (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6
12. In select student_no, score from the grade_report table where course_no = 'CS02208', what is course_no = 'CS02208'?
(A) A condition (B) A list of attribute names (C) A list of the relation names (D) None of the above
13. What result set will the following query return?
select item_no from order where quantity > 20;
(A) The order_id of all orders that had more than 20 items. (B) The item_no of all orders that had more than 20 items.
(C) The order_id of all orders that had more than one item.
(D) The item_no of all orders that had 20 or more items.
14. Which can be used to select the student's number whose score is greater than or equal to 60 from the grade_report table?
(A) select student_no from report where score <= 60.
(B) select student_no from report where score > 60
(C) select student_name from grade_report where score >= 60.
(D) select student_no from grade_report where score >= 60
15. To eliminate duplicate rows in a query, the qualifier is used in the SQL Select command. (A) distinct (B) check (C) alter (D) specific 16. The SQL command
adds one or more new columns to a table.
(A) create relationship (B) create view (C) create table (D) alter table
17. Indexes are created in most RDBMSs to:
(A) provide a quicker way to store data.
(B) decrease the amount of disk space utilized.
(C) increase the cost of implementation.
(D) provide rapid random and sequential access to base-table data.
18. What result set will the following query return?
select item_no, description from item where price >= 100 and price <= 200;
(A) The item_no for all items costing between 100 and 200
(B) The item_no and description for all items costing between 100 and 200
(C) The item_no and description for all items costing less than 100
(D) The item_no and description for all items costing more than 200
19. In an SQL statement, which of the following parts states the conditions for row selection? (A) where (B)
select (C) from (D) in case 20. What does the following SQL statement do?
delete from customer where city = 'Hsinchu';
(A) Deletes all records from the customer table.
(B) Deletes all records from customer where the city is equal to Hsinchu.
(C) Removes the customer table from the database. (D) None of the above
21. DDL is typically used during which phases of the development process?
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
(A) Analysis (B) Physical design (C) Implementation (D) All of the above
22. Which of the following is the wildcard operator in SQL statements? (A) * (B) <> (C) = (D) & 23.
Which is a aggregate function that returns the number of tuples or values as specified in a query? (A) avg (B) count (C) min (D) sum
24. Which provides a condition on the group of tuples associated with each value of the grouping attributes?
(A) exit (B) in (C) having (D) with
25. Which can be used to increase the 10% interest rate for all accounts in the account table?
(A) update account where interest = 0.1; (B) update account set interest = 1.1 * interest;
(C) udpate interest * 1.1 from account (D) None of the above
26. Which of the following is true about the SQL statement Select * From Product Where Quantity = 1 Or Quantity = 2;
(A) All fields will be selected from the Product table for products that have a quantity of 1.
(B) All fields will be selected from the Product table for products that have a quantity of 1 or 2.
(C) All fields will be selected from the Product table for products that have a quantity of only 2. (D) None of the above.
27. To get all the customers from Hawaii sorted together, which of the following would be used? (A) Having
(B) Group By (C) Sort (D) Order By
28. Which of the following is a technique for optimizing the internal performance of the relational data model?
(A) Not reporting statistics to save machine resources (B) Using random index organizations
(C) Clustering data (D) Avoiding indexes on secondary keys
29. What result will the following SQL statement produce?
Select Avg(standard_price) as average from product_v;
(A) The average price of all products (B) The average of all products in product_v (C) The average
standard_price of all products in product_v (D) None of the above
30. Which of the following is true of the order in which SQL statements are evaluated?
(A) The group by clause is processed before the where clause.
(B) The select clause is processed before the order by clause.
(C) The select clause is always processed first. (D) The select clause is always processed last.
31. Which of the following can produce scalar and vector aggregates?
(A) Order By (B) Having (C) Group By (D) Sort
32. Which of the following questions is answered by the SQL statement?
Select Count (Product_Description) from Product_T;
(A)How many different columns named "product Description" are there in table Product_T?
(B)How many products are in the Product Table?
(C )How many characters are in the field name "Product_Description"?
(D) How many products have product descriptions in the Product Table?
33. What result set is returned from the following query?
Select customer_name, telephone from customers where city in ('Boston','New York','Denver');
(A) The customer_name and telephone of all customers living in Boston and New York and Denver
(B) The customer_name and telephone of all customers
(C) The customer_name of all customers living in Boston, New York or Denver
(D) The customer_name and telephone of all customers living in either Boston, New York or Denver
34. Multiple values returned from an SQL query that includes an aggregate function are called:
(A) scalar aggregates. (B) summations. (C) agates. (D) vector aggregates.
35. What results will be produced by the following SQL query?
Select sum(standard_price) as total_price from product_v where product_type = 'WOOD';
(A) The total price of all products that are of type wood (B) The total price of all products
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
(C) The standard_price of any wood product in the table (D) The standard_price of the first wood product in the table
36. What does the following SQL statement do?
Alter Table Customer_T Add Type varchar(2.;
(A) Alters the Customer_T table to be a Type 2 Varchar
(B) Alters the Customer_T table by adding a 2-byte field called "Varchar"
(C) Alters the Customer_T table to accept Type 2 Varchars (D) Alters the Customer_T table, and adds a field called "Type"
37. Indexes are created in most RDBMSs to:
(A) provide a quicker way to store data.
(B) increase the cost of implementation.
(C) provide rapid random and sequential access to base-table data. (D) decrease the amount of disk space utilized.
38. In an SQL statement, which of the following parts states the conditions for row selection? (A) Select (B) Group By (C) Where (D) From
39. Which of the following is the wildcard operator in SQL statements? (A) = (B) <> (C) * (D) &
40. DDL is typically used during which phases of the development process?
(A) Physical design (B) Implementation (C) Analysis (D) All of the above
41. Which of the following is a purpose of the SQL standard?
(A) To specify minimal and complete standards, which permit different degrees of adoption in products
(B) To specify syntax and semantics of SQL data definition and manipulation
(C) To define the data structures and basic operations for SQL databases (D) All of the above
42. A single value returned from an SQL query that includes an aggregate function is called a(n):
(A) scalar aggregate. (B) summation. (C) vector aggregate. (D) agate.
43. What does the following SQL statement do?
Delete from Customer_T where state = 'HI';
(A) Deletes all records from the customer_t table (B) Removes the customer_t table from the database
(C) Deletes all records from customer_t where the state is equal to HI (D) None of the above
44. Which of the following counts ONLY rows that contain a value? (A) Tally(*) (B) Count(*) (C) Checknum (D) Count
45. The first in a series of steps to follow when creating a table is to:
(A) create an index. (B) identify columns that must be unique.
(C) identify each attribute and its characteristics. (D) identify columns that must be null.
46. is a set of commands used to update and query a database. (A) DPL (B) DDL (C) DCL (D) DML 47. The SQL command
defines a logical table from one or more tables or views.
(A) create table (B) create relationship (C) create view (D) alter table
48. Which of the following will produce the minimum of all standard prices?
(A) Select min(standard_price) from product_v where standard_price = min(standard_price);
(B) Select standard_price from min(product_v); (C) Select min(standard_price) from product_v;
(D) Select standard_price from product_v where standard_price = min;
49. What will be returned when the following SQL statement is executed?
Select driver_no, count(*) as num_deliveries from deliveries where state = 'MA' group by driver_no;
(A) A listing of all drivers who made deliveries to state = 'MA', sorted by driver number.
(B) A count of all of the deliveries made to state = 'MA' by all drivers.
(C) A listing of each driver who made deliveries to state = 'MA' as well as the number of deliveries that
each driver has made to that state. (D) None of the above.
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
50. What does the following SQL statement do?
Update Product_T Set Unit_Price = 775 Where Product_ID = 7
(A) Changes the length of the Unit_Price field to 775 (B) Changes the price of a unit called Product_T to 7
(C) Changes the unit price of Product 7 to 775 (D) Updates the Product_T table to have a unit price of 775
51. A view may not be updated directly if it contains:
(A) the group by or having clause.
(B) the distinct keyword. (C) derived columns and expressions in the select clause. (D) all of the above.
52. What will be returned when the following SQL statement is executed? Select driver_no,count(*) as
num_deliveries from deliveries group by driver_no;
(A) A listing of all drivers, sorted by driver number
(B) A count of all of the deliveries made by all drivers
(C) A listing of each driver as well as the number of deliveries that he or she has made (D) None of the above
53. is a set of commands used to control a database, which includes security. (A) DPL (B) DCL (C) DDL (D) DML
54. What result set will the following query return? Select
item_no from order_v where quantity > 10;
(A) The order_id of all orders that had more than one item
(B) The order_id of all orders that had more than 10 items
(C) The item_no of all orders that had more than 10 items
(D) The item_no of all orders that had 10 or more items
55. What does the following SQL statement do? Select *
From Customer Where Cust_Type = "Best"
(E) Selects the "*" field from the Customer table for each row with a customer labeled "best"
(F) Selects all the fields from the Customer table for each row with a customer labeled "*" (G)
Selects fields with a "*" in them from the Customer table
(H) Selects all the fields from the Customer table for each row with a customer labeled "best"
56. The is the structure that contains descriptions of objects such as tables and views created by users.
(A) catalog (B) SQL (C) master view (D) schema
57. To eliminate duplicate rows in a query, the qualifier is used in the SQL Select command. (A) alter (B)
specific (C) check (D) distinct 58. A
view is materialized when referenced. (A) materialized (B) dynamic (C) base (D) virtual 59. What
result set will the following query return?
Select item_no, description from item where weight > 100 and weight < 200;
(A) The item_no for all items weighing more than 200
(B) The item_no for all items weighing between 101 and 199
(C) The item_no and description for all items weighing less than 100 (D) The item_no and description for
all items weighing between 101 and 199
60. Which of the following finds all groups meeting stated conditions?
(A) Having (B) Where (C) Select (D) Find 61. The SQL command
adds one or more new columns to a table.
(A) create table (B) alter table (C) create relationship (D) create view
62. The benefits of a standardized relational language include:
(A) cross-system communication. (B) reduced training costs. (C) application longevity. (D) all of the above.
63. What will be returned when the following SQL query is executed?
Select driver_no, count(*) as num_deliveries from deliveries group by driver_no having count(*) > 2;
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
(A) A listing of all drivers who made more than 2 deliveries as well as a count of the number of deliveries (B) A listing of all drivers
(C) A listing of all drivers who made more than 2 deliveries
(D) A listing of the number of deliveries greater than 2 64. What will result
from the following SQL Select statement?
Select min(product_description) from product_v;
(A) The first product description alphabetically in product_v will be shown.
(B) The minimum value of product_description will be displayed.
(C) An error message will be generated. (D) None of the above.
65. Any create command may be reversed by using a command.
(A) delete (B) unpack (C) drop (D) truncate Chapter 4: Advanced SQL
1. One major advantage of the outer join is that:
(A) the query is easier to write. (B) information is easily accessible. (C) information is not lost. (D) all of the above. 2. A join operation:
(A) brings together data from two different fields.
(B) causes two disparate tables to be combined into a single table or view.
(C) causes two tables with a common domain to be combined into a single table or view.
(D) is used to combine indexing operations. 3. User-defined data types:
(A) can be a subclass of a standard type. (B) can have defined functions and methods. (C)
can behave as an object. (D) can have all of the above.
4. In order for two queries to be UNION-compatible, they must: (A) both return at least one row.
(B) both have the same number of lines in their SQL statements.
(C) both output compatible data types for each column and return the same number of rows. (D) all of the above. 5. The MERGE command:
(A) allows one to combine the INSERT and DELETE operations. (B) joins 2 tables together.
(C) allows one to combine the INSERT and UPDATE operations. (D) none of the above.
6. Explicit commands to manage transactions are needed when:
(A) multiple SQL commands must be run as part of a transaction.
(B) a transaction consists of just one SQL command.
(C) autocommit is set to off. (D) none of the above.
7. All of the following are advantages of SQL-invoked routines EXCEPT: (A) flexibility. (B) security. (C) sharability. (D) efficiency. 8. A procedure is:
(A) stored within the database. (B) called by name. (C) given a unique name. (D) all of the above.
9. A join in which the joining condition is based on equality between values in the common columns is called
a(n): (A) equi-join. (B) uni-lateral join. (C) natural join. (D) both A and C.
10. A type of join implemented in SQL-1999 and by extension SQL-2003 that returns all of the data from each
table that is joined is called a(n):
(A) union join. (B) inner join. (C) outer join. (D) intersect join.
12. A join in which rows that do not have matching values in common columns are still included in the result table is called a(n):
(A) outer join. (B) equi-join. (C) union join. (D) natural join.
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system... 13. Embedded SQL consists of:
(A) SQL written into a front-end application. (B) SQL translated to a lower-level language. (C) SQL
encapsulated inside of other SQL statements. (D) none of the above.
14. The UNION clause is used to:
(A) join two tables together to form one table.
(B) find all rows that do not match in two tables.
(C) combine the output from multiple queries into a single result table. (D) none of the above.
15. A join that is based upon equality between values in two common columns with the same name and where
one duplicate column has been removed is called a(n):
(A) inner join. (B) multivariate join. (C) natural join. (D) equi-join. 16. more
takes a value of true if a subquery returns an intermediate results table which contains one or rows.
(A) Extents (B) In (C) Exists (D) Having
17. Establishing IF-THEN-ELSE logical processing within an SQL statement can be accomplished by:
(A) using a subquery. (B) using the immediate if statement.
(C) using the CASE keyword in a statement. (D) using the if-then-else construct.
18. A named set of SQL statements that are considered when a data modification occurs are called:
(A) triggers. (B) stored procedures. (C) trapdoors. (D) treatments.
19. A new set of analytical functions added in SQL:2003 are referred to as:
(A) OLAF functions. (B) OLAP functions. (C) average functions. (D) MOLAP functions. 20. In SQL, a from
subquery is a type of subquery in which processing the inner query depends on data the outer query.
(A) natural (B) paired (C) inner (D) correlated
21. If the DBA wishes to describe all tables in the database, which data dictionary view should be accessed in MySQL?
(A) describe (B) list (C) show (D) depict
22. All of the following are new data types added in SQL:2003 EXCEPT: (A) MULTISET. (B) BIT. (C) BIGINT. (D) XML.
23. What results would the following SQL statement produce?
select owner, table_name from dba_tables where table_name = 'CUSTOMER';
(A) A listing of all customers in the customer table
(B) A listing of the owner of the customer table (C) An error message
(D) A listing of the owner of the customer table as well as customers
24. While triggers run automatically, do not and have to be called.
(A) selects (B) routines (C) trapdoors (D) updates
25. User-defined transactions can improve system performance because: (A) speed is improved due to query optimization.
(B) transactions are processed as sets, reducing system overhead.
(C) transactions are mapped to SQL statements. (D) all of the above. 26. A
is a temporary table used in the FROM clause of an SQL query.
(A) derived table (B) correlated subquery (C) view table (D) none of the above
27. A type of query that is placed within a WHERE or HAVING clause of another query is called a: (A) master
query. (B) subquery. (C) multi-query. (D) superquery.
Chapter 5: Database design and the E-R model
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
1. Which is the first step of database design?
(A) logic design (B) requirements collection and analysis (C) physical design (D) transaction implementation
2. Which is in DBMS-independent design process?
(A) application program (B) transaction implementation (C) physical (D) functional analysis
3. Which is not a type of attributes?
(A) Simple (B) Composite (C) Multi-valued (D) Parametic
4. are specific objects or things in the mini-world that are represented in the database.
(A) Entities (B) Attributes (C) Relationships (D) Descriptions
5. A property or characteristic of an entity type that is of interest to the organization is called a(n):
(A) relationship. (B) coexisting entity. (C) attribute. (D) cross-function.
6. A person's name, birthday, and social security number are all examples of :
(A) Entities (B) Attributes (C) Relationships (D) Descriptions
7. An attribute that can be broken down into smaller parts is called a(n) attribute.
(A) simple (B) associative (C) complext (D) composite
8. The total quiz points for a student for an entire semester is a(n) attribute.
(A) derived (B) stored (C) mixed (D) addressed
9. A(n) relationship is the relationship between a weak entity type and its owner. (A) key (B) member (C) identifying (D) main
10. is the current state of the entities of that type that are stored in the database.
(A) Entity type (B) Entity instance (C) Entity set (D) Entity
11. Which is not the main concepts in ER model? (A) Entities (B) Attributes (C) Relationships (D) Identifications 12. A
relates two or more distinct entities with a specific meaning.
(A) Entities (B) Attributes (C) Relationships (D) Identifications
13. The of a relationship type is the number of participating entity types.
(A) cardinality (B) identification (C) degree (D) participation
14. Relationship types of degree 3 are called .
(A) ternary (B) primary (C) tertiary (D) binary
15. A(n) specifies the number of instances of one entity that can be associated with each instance of another entity.
(A) degree (B) counter constraint (C) limit (D) cardinality constraint
16. In (student_no, name, address(street, city, state, zipcode)), address is
(A) a derived attribute. (B) a multivalued attribute. (C) a composite attribute. (D) a relational attribute. 17. Which is false?
(A) Relationship type is grouped by the same type of relationships.
(B) The current state of a relationship type is the relationship set.
(C) Relationship type identifies the relationship name and the participating entity types.
(D) Relationship type identifies certain relationship constraints. 18. Which is false?
(A) A relationship can have one or more attributes.
(B) A weak entity must participate in an identifying relationship type with an owner or identifying entity
type. (C) Cardinality Ratio specifies maximum participation. (D) An attribute relate two entities.
19. An entity type whose existence depends on another entity type is called a(n) entity. (A)
weak (B) codependent (C) identifying (D) strong
20. An attribute that uniquely identifies an entity is called a(n) attribute.
(A) weak (B) relationship (C) identifying (D) key
Final Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas e-system/exam/database- lOMoAR cPSD| 5850443 1 system...
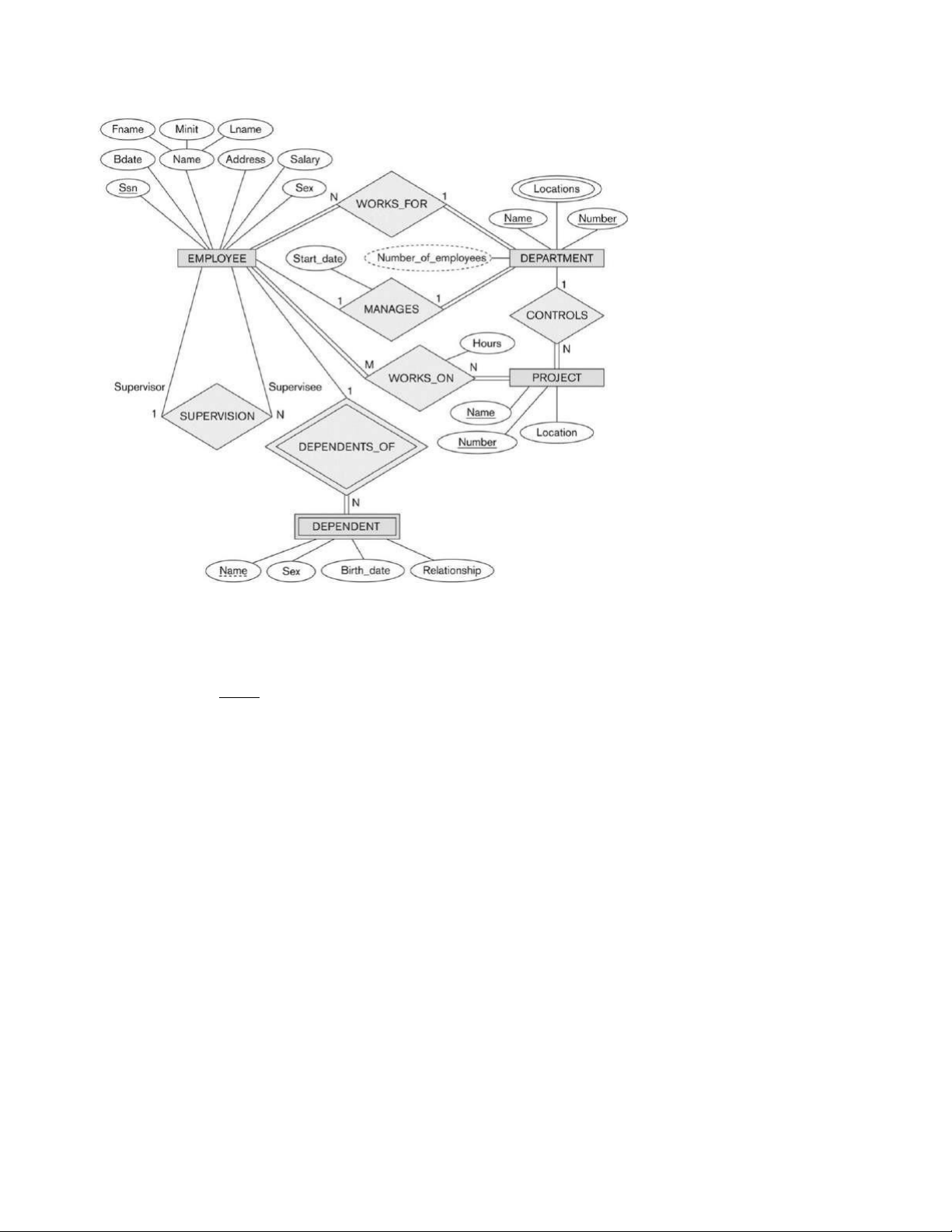
21. In the following diagram, which answer is true?
(A) Each employee can manage many departments.
(B) Each employee works in more than one department.
(C) Each employee can supervise one to many employees. (D) All of the above.
22. A student can attend 5 courses. Different professors can offer the same courses. The relationship of students to professors is a relationship.
(A) many-to-many (B) one-to-many (C) one-to-one (D) many-to-one
23. Which is not a section in a UML class?
(A) class relationship (B) class name (C) class attributes (D) class operations
24. Which is a database design tool?
(A) Visual Studio (B) Visio Enterprise (C) MySQL (D) none of the above 25. Which is false?
(B) EER stands for Enhanced ER or Extended ER.
(C) The EER can model applications more completely and more accurately.
(D) The EER is a type of implementation data models.
(E) The EER includes some object-oriented concepts, such as inheritance. 26. Which is false?
(F) The superclass/subclass relationships are also called IS-A relationships.
(G) An entity cannot exist in the database merely by being a member of a subclass. Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system..
(H) A member of the superclass can be optionally included as a member of any number of its subclasses.
(I) It is necessary that every entity in a superclass be a member of some subclass
27. is the process of defining a set of subclasses of a superclass.
(A) Specialization (B) Generalization (C) Aggregation (D) Identification 28. is the process of grouping a
set of subclasses into a superclass.
(A) Specialization (B) Generalization (C) Aggregation (D) Identification
29. Which is a bottom-up process?
(A) Specialization (B) Generalization (C) Aggregation (D) Identification
30. An attribute of the superclass that determines the target subclass(es) is called the:
(A) subclass determinant (B) disjoint indicator (C) subclass identification (D) subclass discriminator
31. If an entity can be a member of at most one of the subclasses of the specialization, the specialization is said to be:
(A) discrete (B) disjoint (C) united (D) overlapping
32. If an entity can be a member of at least one of the subclasses of the specialization, the specialization is said to be:
(A) discrete (B) disjoint (C) united (D) overlapping 33. The
specialization specifies that every entity in the superclass must be a member of some
subclass. (A) total (B) partial (C) disjoint (D) discrete
34. The specialization specifies that an entity in the superclass is allowed not to belong to any of the subclasses.
(A) total (B) partial (C) disjoint (D) discrete
35. Which of the following is a completeness constraint?
(A) Partial instantiation (B) Total association (C) Partial cardinality (D) total specialization 36. The
property by which subclass entities possess all attributes of a superclass is called attribute:
(A) inheritance (B) generalization (C) aggregation (D) identification
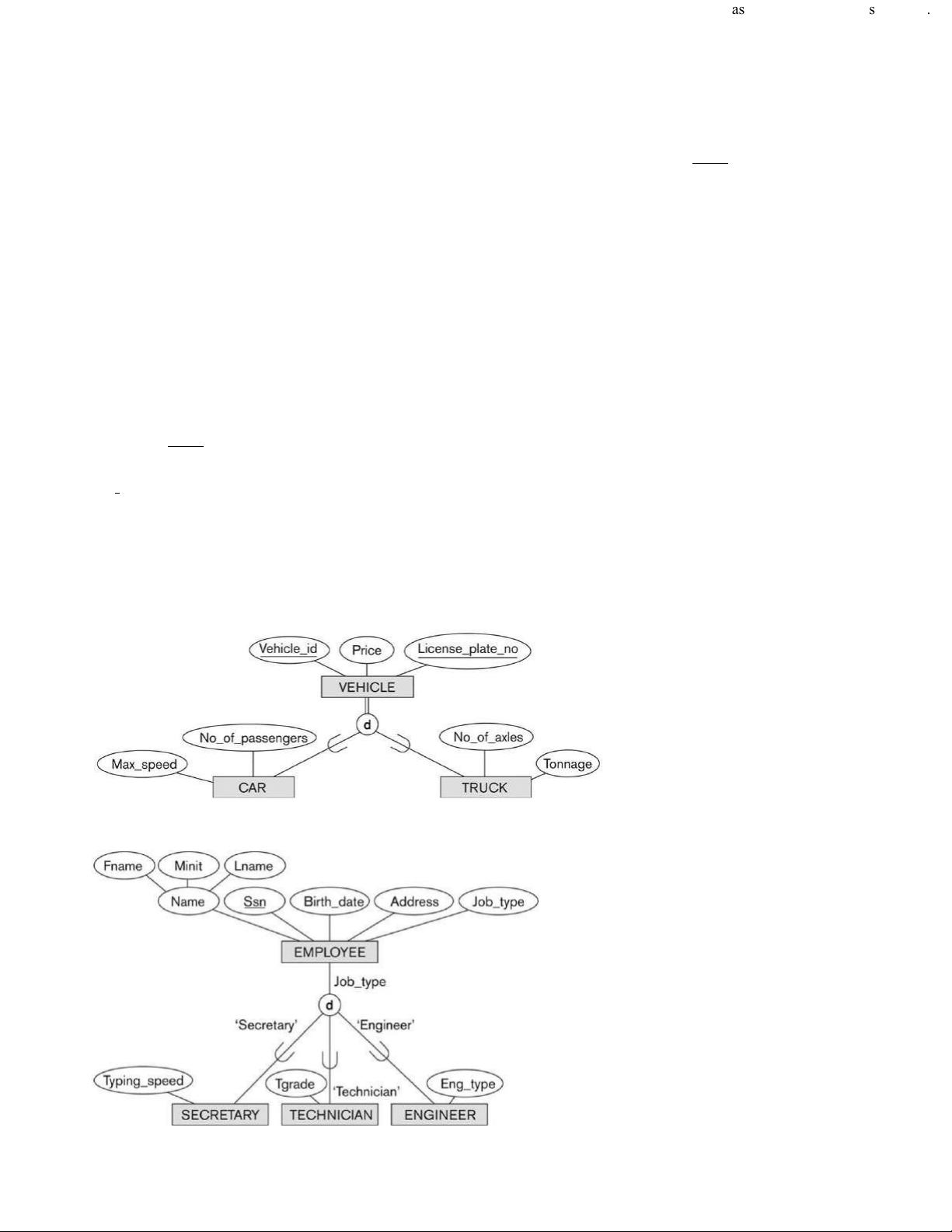
37. In the following figure, to which of the following entities are the entities "CAR" and "TRUCK" generalized?
(A) Tonage (B) Price (C) VEHICLE (D) Vehicle_id
38. In the following figure, which is true?
(A) An employee must be a secretary, a technician, or a engineer. Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system..
(B) An employee must be a secretary, a technician, and a engineer.
(C) An employee need not to be a secretary, a technician, or a engineer. (D) A secretary can be an engineer. 39. Which is false?
(A) A shared subclass have more than one distinct superclass/subclass relationships.
(B) In a shared subclass each relationship has a single superclass.
(C) ) A shared subclass leads to multiple inheritance.
(D) A shared subclass can have only one superclass. 40. A(n)
member must exist in at least one of its superclasses.
(A) intersection (B) shared (C) category (D) selection
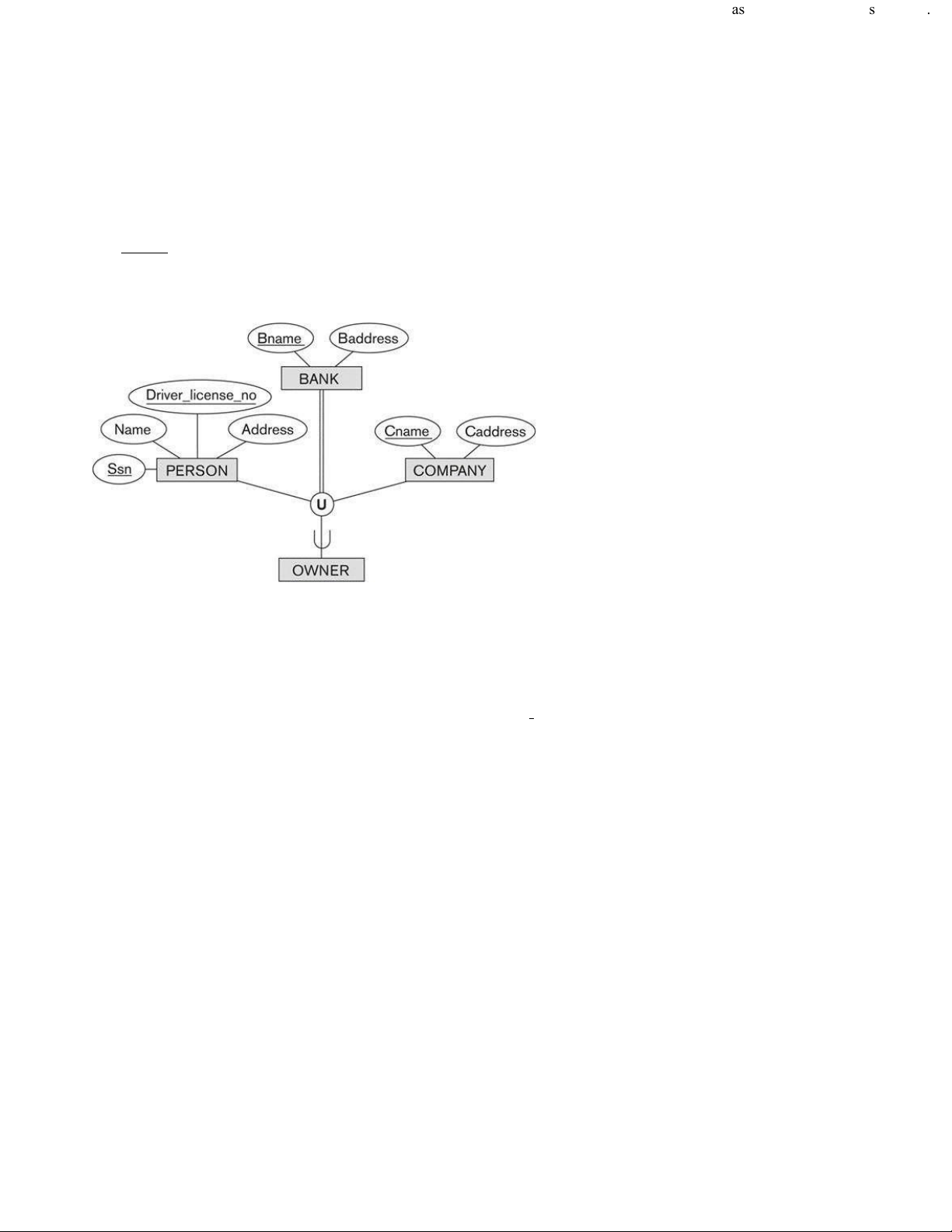
41. In the following figure, which is true?
(A) The owner class is a shared subclass.
(B) An owner must must be at least a bank, a person, or a company.
(C) An owner must be a bank, a person, and a company.
(D) An owner need not be either one of a bank, a person, and a company.
42. Which use conceptual modeling and other tools to develop "a specification of a conceptualization"? (A)
Ontologies (B) Topologies (C) Technlogies (D) Geologies 43. refers to the language and vocabulary (data model concepts) used.
(A) Assertion (B) Conceptualization (C) Generalization (D) Specification
44. refers to the description (schema) of the concepts of a particular field of knowledge and the relationships among these concepts.
(A) Assertion (B) Conceptualization (C) Generalization (D) Specification
45. What does the strength of the relational approach to data management comes from?
(A) higher adaptability and productivity.
(B) the formal foundation provided by the theory of relations.
(C) better concurrency control.
(D) ease of conversion to any new approach.
46. What mathematical concept is a relation based on?
(A) set (B) vector (C) difference (D) matrix
47. Who first proposed the relation model?
(A) Peter Chen (B) C. J. Date (C) E. F. Codd (D) None of the above 48. Which is false?
(A) A relation looks like a table of values.
(B) A relation typically contains a set of rows.
(C) In a relation rows are called tuples.
(D) Each row has a row header called an attribute. Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system..
49. In each row a value of a data item (or set of items) that uniquely identifies that row in the table is called .
(A) tuple (B) set (C) column (D) attribute
50. The key that is generated by the DBMS is called key. (A) artificial (B) automatic (C) automic (D) access 51. The attribute
is the set of values allowed in an attribute.
(A) schema (B) state (C) domain (D) scope
52. A subset of the Cartesian product of the domains of its attributes is relation . (A) schema (B) state (C) domain (D) scope 53. Which is false?
(A) All values in a tuple are considered atomic.
(B) Each value in a tuple must be from the domain of the attribute for that column.
(C) A special null value is used to represent values that are unknown or inapplicable to certain tuples. (D) The
tuples are considered to be ordered.
54. Which is not a constraint in the relational model?
(A) Key (B) Entity integrity (C) Value (D) Referential integrity
55. Which is not condition a superkey should satisfy?
(A) No two tuples in any valid relation state will have the same value for superkey.
(B) A superkey should be minimal.
(C) This condition must hold in any valid relational state.
(D) For any distinct tuples the values of superkey are different. 56. Which is false?
(A) A relation can have only one key.
(B) A key is a minimal superkey. (C) Any key is a superkey.
(D) Any set of attributes that includes a key is a superkey.
57. Which is entity integrity?
(A) The primary key cannot have null values.
(B) A relation can have only one key.
(C) If the key values are different, two tuples are different. (D) Any key is a superkey. 58. A foreign key is
(A) a key that references a primary key in other relation.
(B) a key that cannot be null.
(C) a key that uniquely identifies different tuples. (D) a superkey.
59. Which constraint involves two relations?
(A) Key constraint (B) Entity integrity (C) Referential integrity (D) Domain constraint
60. Which of the following is the action can be taken in case of integrity violation?
(B) Cancel the operation that causes the violation.
(C) Perform the operation but inform the user of the violation.
(D) Trigger additional updates so the violation is corrected. (E) All of the above
61. Which type of solutions to integrity violation does restrict or reject belong to?
(A) Cancel the operation that causes the violation.
(B) Perform the operation but inform the user of the violation.
(C) Trigger additional updates so the violation is corrected. (D) Execute a user-specified error-correction routine.
62. Which constraint may insert violate?
(A) Domain constraint (B) Key constraint (C) Referential integrity (D) All of the above 63. Which constraint may delete violate? Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system.. (A)
Domain constraint (B) Key constraint (C) Referential integrity (D) All of the above 64.
Which constraint may update violate? (B)
Domain constraint (B) Key constraint (C) Referential integrity (D) All of the above
Chapter 7: Relational Database Design
1. Which is not an approach to map binary 1:1 relationship types in the ER diagram to the relational schema? (A)
Foreign Key (B) Merged relation
(C) Cross-reference or relationship relation (D) Functional relation
2. Which is the approach to map a M:N relationship type in the ER diagram to the relational schema?
(A) A relationship relation and two foreign keys (B) Merged relation option
(C) Set of simple component attributes (D) Functional relation
3. Which is the approach to map a n-ary relationship type in the ER diagram to the relational schema?
(A) Set of simple component attributes (B) Merged relation option
(C) A relationship relation and n foreign keys (D) Functional relation
4. Which is the approach to map a composite attribute in the ER diagram to the relational schema?
(A) Foreign key (B) Set of simple component attributes
(C) A relation and foreign key (D) None of the above
5. Which is the approach to map a multivalued attribute in the ER diagram to the relational schema? (B)
Foreign key (B) Set of simple component attributes (C)
A relation and foreign key (D) None of the above 6. Which is a measure
of quality for relation schema design?
(A) Semantics of the attributes (B) Reducing the redundant information in tuples
(C) Reducing the NULL values in tuples (D) All of the above 7. The
of a relation refers to the interpretation of attribute values in a tuple.
(A) instance (B) semantics (C) syntax (D) ontology
8. What problems could information is stored redundantly in a database?
(A) Insertion anomalies (B) Deletion anomalies (C) Modification anomalies (D) All of the above
9. Which is not a reason for nulls?
(A) Attribute is not applicable or invalid. (B) Attribute value is unknown (may exist). (C) The value is
beyond the domain range. (D) Value is known to exist, but unavailable.
10. Which of following constraints applies to two attributes?
(A) functional dependency. (B) attribute dependency. (C) functional relation constraint. (D) functional relation. 11. Which statement is false?
(A) Functional dependencies (FDs) are used to specify formal measures of the "goodness" of relational designs.
(B) Functional dependencies and keys are used to define normal forms for relations.
(C) Functional dependencies are constraints that are derived from the meaning and interrelationships of the data attributes
(D) If the attribute X determines the attribute Y, X is functionally dependent on Y.
12. What is not a Armstrong's inference rule?
(A) Reflexive (B) Augmentation (C) Transitive (D) Associative
13. is the process of decomposing unsatisfactory "bad" relations by breaking up their attributes into smaller relations.
(A) Generalization (B) Normalization (C) Realization (D) Specialization
14. is the process of storing the join of higher normal form relations as a base relation.
(A) Denormalization (B) Generalization (C) Realization (D) Specialization 15. Which is true? Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system.. (A) A superkey is a key.
(B) Two tuples can have the same key value.
(C) A relation can have more than one candidate key. (D) None of the above
16. Which is not a property of the first normal form?
(E) There are no composite attributes. (B) There are no multivalued attributes.
(C) There are no nested relations. (D) There is no transitive functional dependency.
17. A relation that contains no multivalued attributes, and has nonkey attributes solely dependent on the primary
key, but contains transitive dependencies is in which normal form? (A) First (B) Second (C) Third (D) Fourth
18. A functional dependency between two or more nonkey attributes is called a:
(B) partial nonkey dependency. (B) partial transitive dependency.
(C) transitive dependency. (D) partial functional dependency.
19. In which normal form there is no transitive functional dependency?
(A) First (B) Second (C) Third (D) Fourth
20. In which normal form is a relation schema R if whenever an FD X → A holds in R, then X is a superkey of
R? (A) Third (B) Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF) (C) Fourth (D) Fifth B. Question and Answer: 1.
Briefly explain these terminologies. If they are acronyms, also write what they stand for.
(1) DBA (2) DBMS (2) persistent data (3) data independence (4) DDL (5) relation variable (6) primary key
(7) foreign key (8) predicate (9) true proposition (10) catalog (11) view Ans:
1. The database administrator (DBA) is the person whose job is to create the actual database and to
implement the technical controls needed to enforce the various policy decisions made by the data
administrator. The DBA is also responsible for ensuring that the system operates with adequate
performance and for providing a variety of other related technical services.
2. Persistent data is data whose lifetime typically exceeds that of individual application program
executions. In other words, it is data that (a) is stored in the database and (b) persists from the
moment it is created until the moment it is explicitly destroyed. (Nonpersistent data, by contrast, is
typically destroyed implicitly when the application program that created it ceases execution, or possibly even sooner.)
3. (Physical) data independence is the immunity of applications to changes in storage structure (how
the data is physically stored) and access technique (how it is physically accessed). Note: Logical
data independence is discussed in Chapters 2, 3, and especially 10. See also Appendixes A and D.
Logical data independence means users and user programs are immune to changes in the logical
structure of the database (meaning changes at the conceptual or "community logical" level).
Physical data independence means users and user programs are immune to changes in the physical
structure of the database (meaning changes at the internal or stored level). A good DBMS will provide both.
4. A data definition language (DDL) is a language for defining, or declaring, database objects.
5. Relation variables (relvars) are variables; they can thus be "read" and updated, by definition.
6. The primary key of a given relvar is a column or combination of columns in that relvar whose
values can be used to identify rows within that relvar uniquely (in other words, it's a unique
identifier for the rows of that relvar).
7. A foreign key is a column or combination of columns in one relvar whose values are required to
match those of the primary key in some other relvar (or possibly in the same relvar). Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system..
8. A predicate is a truth-valued function. Every relation has a corresponding predicate that defines
(loosely) "what the relation means." Each row in a given relation denotes a certain true proposition,
obtained from the predicate by substituting certain argument values of the appropriate type for the
parameters of the predicate ("instantiating the predicate").
9. A true proposition is, loosely, something that evaluates to true, unequivocally.
10. The catalog is a set of system relvars whose purpose is to contain descriptors regarding the various
objects that are of interest to the system itself, such as base relvars, views, indexes, users, integrity
constraints, security constraints, and so on.
11. A (relational) view, also known as a virtual relvar, is a named derived relvar. Views are virtual, in
the sense that they don't have any existence apart from the base relvars from which they're derived
(but users should typically not be aware that a given view is in fact virtual in this sense, though SQL
falls very short in this regard, owing to its weak support for view updating). Operations on views
are processed by translating them into equivalent operations on those underlying base relvars. 2. 1. What is a database? 2. What is a database system?
3. List two advantages of using a database system.
4. List two disadvantages of using a database system. Ans:
1. A database is a repository for a collection of computerized data files. (At least, this would be the
normal definition. A much better definition is: A database is a collection of propositions, assumed by convention
to be ones that evaluate to TRUE. See reference [1.2] for further explanation.)
2. A database system is a computerized system whose overall purpose is to maintain a database and to
make the information in that database available on demand. (As in the body of the chapter, we assume for
simplicity, here and throughout these answers, that all of the data in the system is in fact kept in just one database.
This assumption is very unrealistic in practice.)
3. Some of the advantages of using a database system are as follows: Compactness Speed Less drudgery Currency Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system.. Centralized control Data independence
4. Some of the disadvantages are as follows:
Security might be compromised (without good controls).
Integrity might be compromised (without good controls).
Additional hardware might be required.
Performance overhead might be significant.
Successful operation is crucial (the enterprise might be highly vulnerable to failure).
The system is likely to be complex (though such complexity should be concealed from the user). 3. 1. What is an entity? 2. What is a relationship?
3. What is a relational system? Ans:
1. An entity is any distinguishable person, place, or thing that is deemed to be of interest for some
reason. Entities can be as concrete or as abstract as we please.
2. A relationship (q.v.) is a special kind of entity. (As with relationships, we really need to distinguish
between entity types and entity occurrences or instances, but in informal contexts the same term entity
is often used for both concepts.)
3. A relational system is a system that is based on the relational model. Loosely speaking, therefore, it is a system in which:
1. The data is perceived by the user as tables (and nothing but tables).
2. The operators at the user's disposal (e.g., for data retrieval) are operators that generate new tables from old. 4.
1. Describe the three levels of the architecture. 2. What is a DBMS?
3. List 5 major functions performed by the DBMS. Ans:
1. The internal level (storage level) is the one closest to physical storage. The external level (user logical
level) is the one closest to the users.
The conceptual level (community logical level) is a level of indirection between the other two.
2. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that handles all access to the database.
3. The major functions performed by the DBMS include: Data definition support Data manipulation support
Data security and integrity support
Data recovery and concurrency support Data dictionary support 5.
List six major steps that you would take in setting up a database for a particular enterprise.
(1) Define the high level requirements of the enterprise (this step generates a document known as the
system requirements specification.)
(2) Define a model containing all appropriate types of data and data relationships.
(3) Define the integrity constraints on the data.
(4) Define the physical level. Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system..
(5) For each known problem to be solved on a regular basis (e.g., tasks to be carried out by clerks or
Web users) define a user interface to carry out the task, and write the necessary application programs
to implement the user interface. 6. Create/initialize the database.
(6) Describe the difference between tables and views. Ans:
A table is a stored relation, while a VIEW is a virtual relation, which does not exist physically, but can be queried as if it did. 7.
1. What are 6 basic operators of relational algebra? 2.
Derive the set intersection from the six basic operations of relational algebra. 3.
Explain the natural-join operation. 4.
Explain the division operation Ans: 1. Six basic operators:
select: σ project: π union: ∪ set difference: - Cartesian product: x rename: ρ
2. The definition of set intersection is r ∩ s = {t | t ∈ r and t ∈ s}. r - (r - s) = r - {t | t ∈ r and t ∉ s} =
{t | t ∈ r and t ∈ s}= r ∩ s.
3. The natural join is a join of two tables that returns tuples for which there are matching values in the
common attributes on which the tables are joined and redundant columns are eliminated.
4. The division operation is a binary operation. The schema of the second relational variable is included
in the schema of the first relation variable. Only those tuples in the first relation which has the same
values as in the second relation for the corresponding attributes are selected but only those values in
the attributes that are additional to the second relation are projected.
8. Use the SQL command to create a table specifying a course including the following information: the course
identification, the course title, the credit hours, the instructor, the schedule, and the classroom. Ans: create table course ( course_id varchar(10), course_title varchar(25), hours integer, instructor varchar(25), schedule varchar(15), classroom varchar(19) );
9. Consider the following two database tables. Use the SQL command to get a list the first name and last name
of customers who have more than $5000 in their account. Coustomer table:
+-------------+-----------+----------+------------+
| customer_no | firstname | lastname | account_no |
+-------------+-----------+----------+------------+ | 1 | Mike | Nichols | 102 | | 2 | Jay | Leno | 202 | | 3 | John | Wayne | 302 | | 4 | Tim | Allen | 402 |
+-------------+-----------+----------+------------+ Account: +------------+---------+ | account_no | balance | +------------+---------+ | 102 | 5000.00 | Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system.. | 202 | 7000.00 | | 302 | 6000.00 | | 402 | 4000.00 | +------------+---------+ Ans:
select firstname, lastname from Customer, Account
where Customer.account_no = Account.account_no and balance > 5000;
10. Consider a banking database with the following relation schemas:
branch (branch_name, branch_city, assets)
customer (customer_name, customer_street, customer_city)
account (account_number, branch_name, balance) loan
(loan_number, branch_name, amount) depositor
(customer_name, account_number) borrower (customer_name, loan_number)
Use relation algebra and SQL to write the following queries:
Example: Find all loans of over $1200. Ans:samount > 1200 (loan) select * from loan where amount > 1200;
1. Find all loans of over $1200 at the Perryridge branch.
2. Find the names of all customers who meet the following criteria:
1. They are both a borrower and depositor.
2. Both their loan and balance are over $1200. Ans:
1. s branch_name = 'Perryridge' ^ amount > 1200 (loan) select * from loan where branch_name =
'Perryridge' and amount > 1200;
2. customer_name (s balance > 1200 (depositor |X| account )) n ?customer_name (s amount > 1200
(borrower |X| loan)) select customer_name from borrower, depositor, loan, account where
(borrower.customer_name = depositor.customer_name) and (loan.branch_name = account.
branch_name) and (loan.amount > 1200 and account.balance > 1200);
Note: |X| represents natural-join.
11. Based on the following tables answer the questions. create table Books (
isbn char(20) primary key, bname char(50),
type ENUM('technical', 'fiction', 'self-help') ); create table Authors ( idn char(9), isbn char(20), primary key (idn, isbn) );
1. How can you add an attribute - publisher into the Books table?
2. How can you drop the attribute - publisher from the Books table?
3. Write an SQL query that will return the idns of authors who have written any book that is not of TYPE 'fiction' Final lOMoAR cPSD| 58504431
Exam Review of Database Management System
http://wcla.csie.chu.edu.tw/course/databas
e - system/exam/database - system..
4. Write two significantly different SQL queries that will return the idns of authors who have not
written any book that is of TYPE 'fiction'.
5. Write an SQL query that will return the isbns of books written by more than one author.
6. Write an SQL query that will return the idns of authors along with the number of books written by each author. Ans:
1. alter table Books add publisher VARchar(20);
2. alter table Books drop publisher;
3. select idn from Authors, Books where Authors.isbn=Books.isbn and type <> 'fiction';
select idn from Authors where not exists
(select * from Authors A, Books B where A.isbn=B.isbn and B.type='fiction')
select idn from Authors where idn not in
(select idn from Authors A, Books B where A.isbn=B.isbn and B.type='fiction')
select idn from Authors except (select idn from Authors A, Books B where A.isbn=B.isbn and B.type='fiction')
4. select isbn from Authors A where exists (select * from Authors where A.isbn=isbn and A.idn<>idn)
5. select isbn from Authors AS A1, Authors AS A2 where A1.isbn=A2.isbn and A1.idn<>A2.idn)
6. select idn, count(isbn) from Authors group by idn
12. Modify the following declaration of table Authors to declare a constraint that isbn in Authors has a foreign
key which refers to isbn of Books. create table Authors ( idn char(9), isbn char(20), primary key (idn, isbn), foreign key isbn references Books(isbn) );
create table Authors ( idn char(9), isbn char(20) references Books(isbn), primary key (idn, isbn) );
13. Modify the following declaration of table Authors to declare an attribute-based check constraint that isbn in
Authors should have a value that is the same as the isbn in some tuple from Books. create table Authors (
idn char(9), isbn char(20), primary key (idn, isbn) );
create table Authors ( idn char(9), isbn char(20) check (isbn in (select isbn from Books)), primary key (idn, isbn) );
14. Consider the following relational database: employee(employee_name, street, city) works(employee_name, company_name, salary) company(company_name, city)
manages(employee_name, manager_name)
For each of the following queries, give an expression in relational algebra and SQL.




