










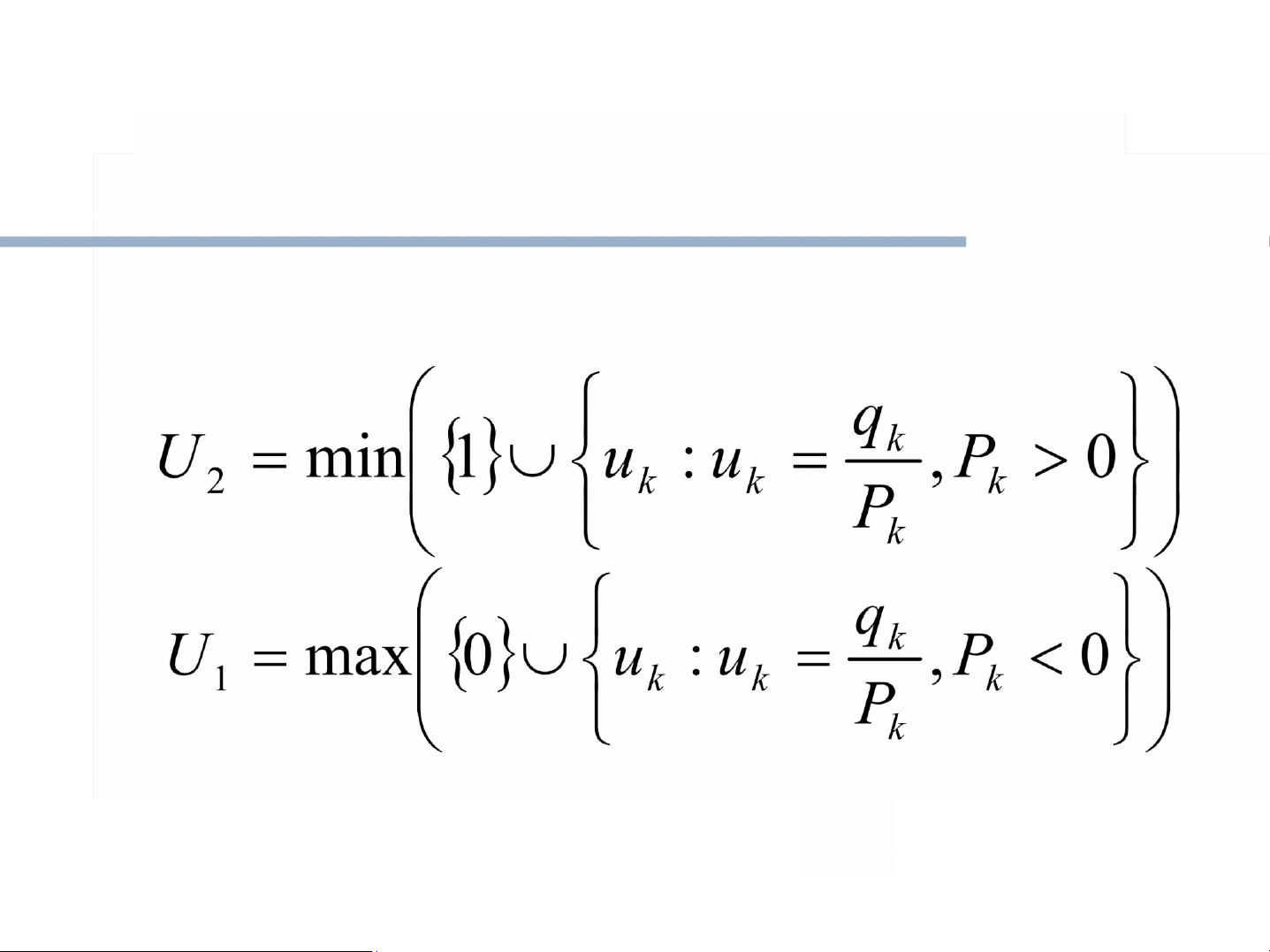


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59455093
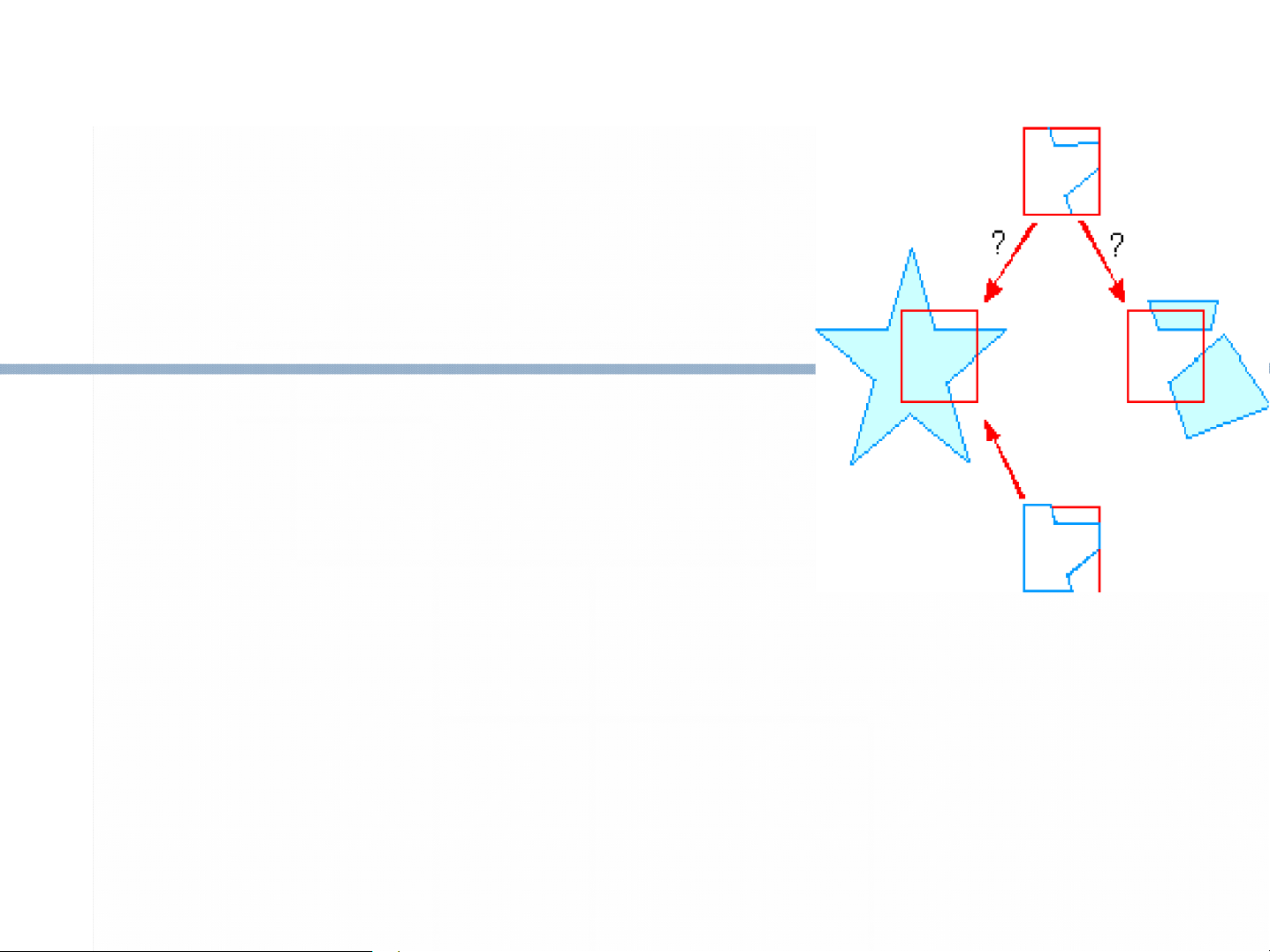
Xén tỉa - Clipping Kỹ thuật thực hành là cần thiết để nâng cao tốc độ trong thực hiện
Nhiệm vụ cơ bản trong đồ họa là giữ các
phần của đối tượng lựa chọn nằm bên nhiệm vụ ngoài đồ hoạ. Định nghĩa Clipping điểm
Xén tỉa là việc di chuyển tất cả các đối
tượng hoặc các phần của đối tượng thuộc
xmin ≤ x ≤
mô hình ngữ cảnh ra bên ngoài của sổ thế xmax ymin ≤ y ≤ ymax giới thực
Việc loại từng điểm ảnh của đối tượng
thường chậm nhất là khi đối tượng mà phần
lớn nằm ngoài cửa sổ hiển thị. (c) SE/FIT/HUT 2002 3 Clipping đoạn thẳng
Lines are defined by their endpoints, so it should be
possible just to examine these (in a similar way to points) and
determine whether or not to clip without considering every pixel on the line
We often have windows that are either very large, i.e. nearly
the whole scene fits inside, or very small, i.e. most of the scene lies inside the window
Hence, most lines may be either trivially accepted or rejected
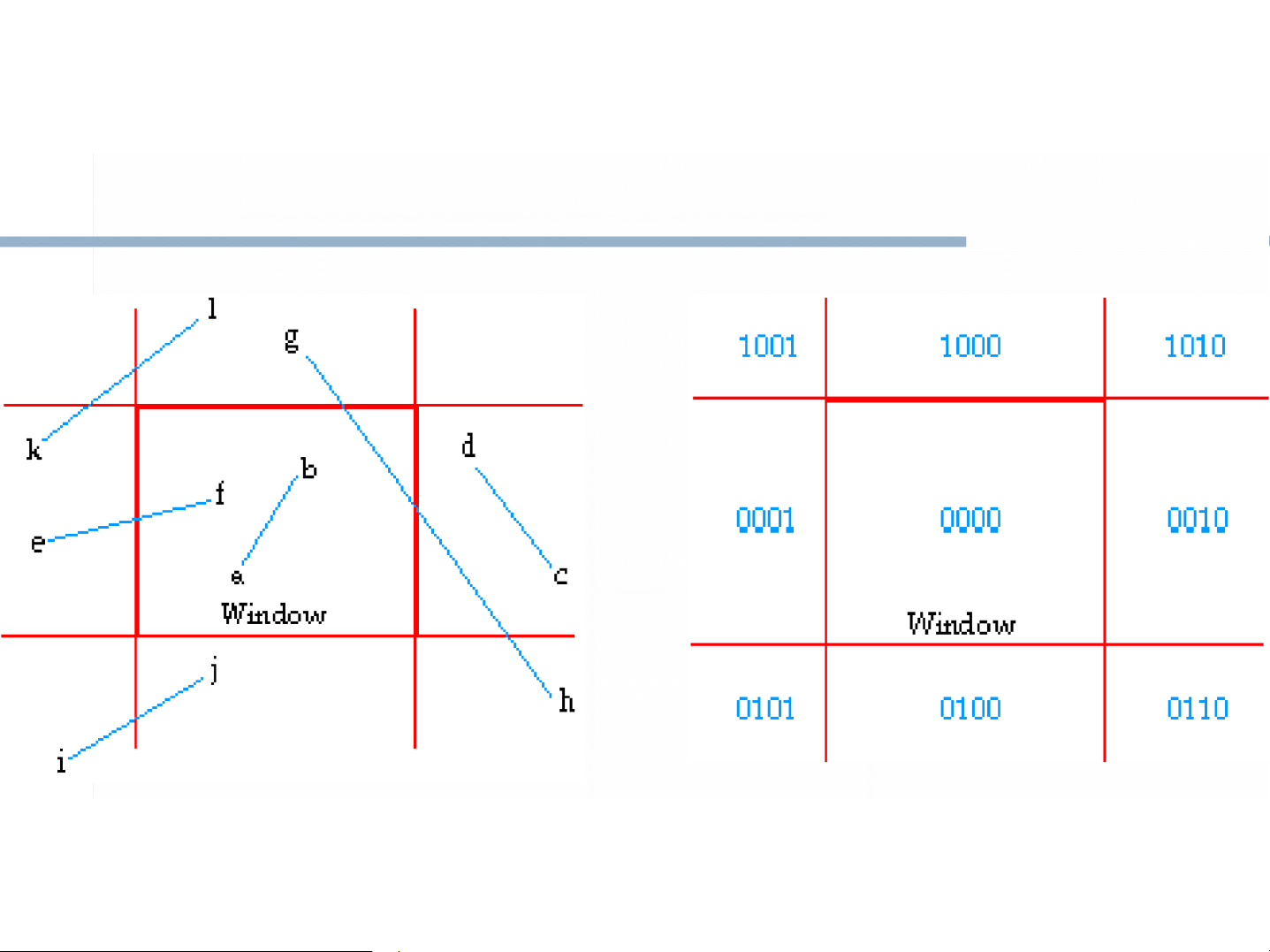
Giải thuật Cohen Sutherland Outcode
The Cohen-Sutherland line-clipping algorithm is particularly
fast for “trivial” cases, i.e. lines completely inside or outside the window.
Non-trivial lines, i.e. ones that cross a boundary of the
window, are clipped by computing the coordinates of the new
boundary endpoint of the line where it crosses the edge of the window
Each point on all lines are first assigned an “outcode”
defining their position relative to the clipping rectangle Giải thuật Cyrus-Beck Lyang Barsky
The Cohen-Sutherland algorithm requires the window
to be a rectangle, with edges aligned with the coordinate axes
It is sometimes necessary to clip to any convex
polygonal window, e.g. triangular, hexagonal, or rotated.
The, and Liang-Barsky line clippers better optimise the
intersection calculations for clipping to window boundary
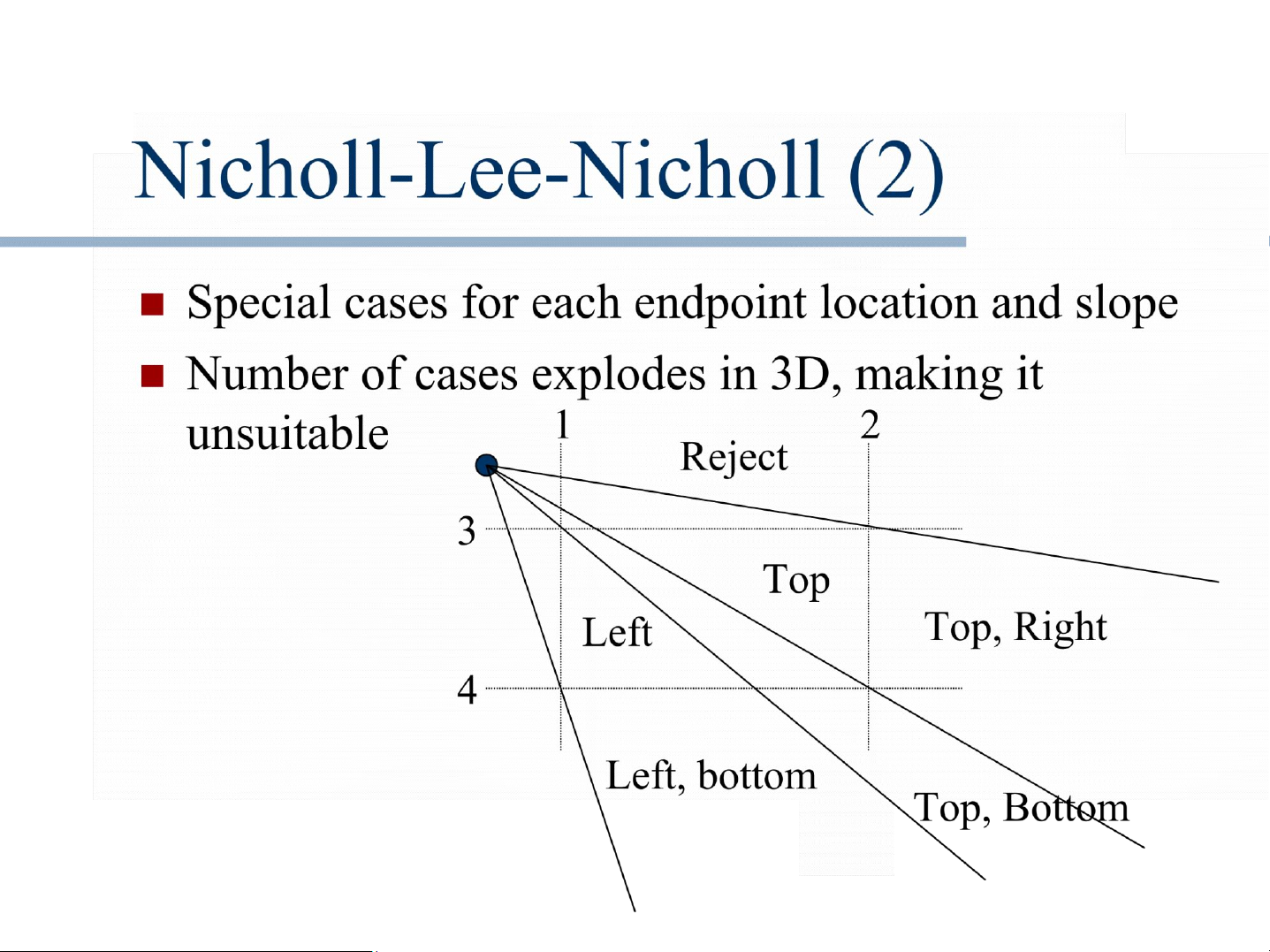
Nicholl-Lee-Nicholl reducing redundant boundary
clipping by identifying edge and corner regions
Nếu Pk = 0 : điều đó tương đương với việc
đoạn thẳng đang xét song song với cạnh thứ
k của hình chữ nhật clipping.
a) Nếu qk < 0 ⇒ vô nghiệm)
b)Nếu qk >= 0 thì bất phương trình luôn thoả mãn. cạnh k. Nicholl-Lee-Nicholl clipping
Some edges are irrelevant to
clipping, particularly if one vertex a lies inside region. Cases: x1 in
x1 in corner region a x1 in edge region
For each case, we generate specialized test regions for x2,
which a use simple tests (slope, >, <), and tell which edges to clip against.
Giải thuật đường biên (Boundary - File Algorithm)
Giải_thuật_đường_biên ( x, y ) Color : biến mầu Begin Color = Readpixel ( x, y );
If ( Color = mầu tô ) or ( Color = mầu đường biên ) Kết thúc vì chạm biên hoặc chạm phần đã tô Else
Giải_thuật_đường_biên ( x+1, y );
Giải_thuật_đường_biên ( x-1, y );
Giải_thuật_đường_biên ( x, y+1 );
Giải_thuật_đường_biên ( x, y-1 );
// Thực hiện lại giải thuật với các điểm lân cận End.
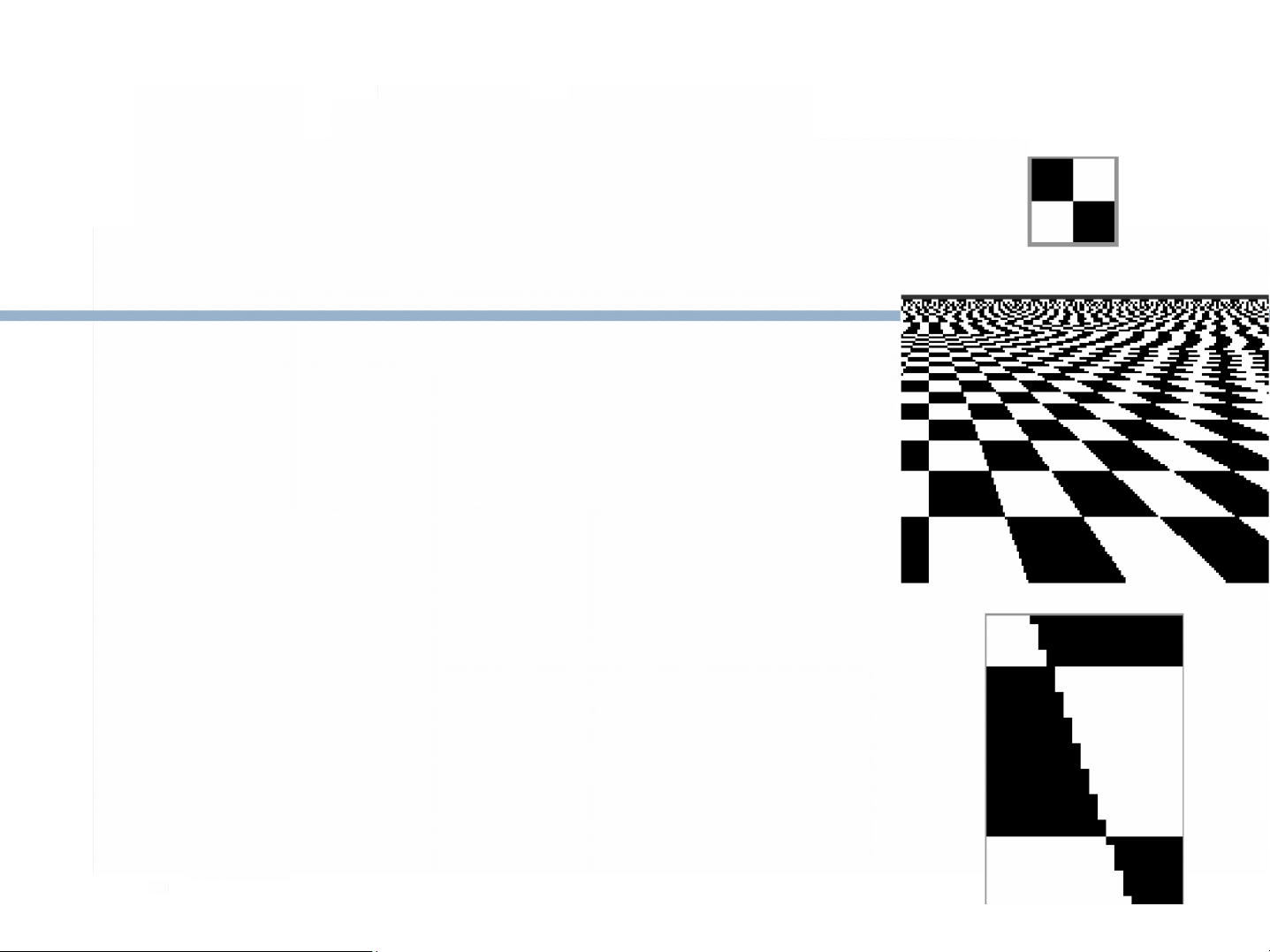
Hiệu ứng răng cưa Aliasing
SPATIAL ALIASING, IN PICTURES
moire patterns arise in
image warping & texture mapping
jaggies arise in rendering
TEMPORAL ALIASING, IN AUDIO
when resampling an audio signal at a lower sampling frequency,
e.g. 50KHz (50,000 samples per second) to 10KHz TEMPORAL ALIASING, IN FILM/VIDEO

