


Preview text:
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen
VIETNAM NATIONAL UNIVERSITY – HCMC INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF BUSINESS COURSE SYLLABUSi BA016IU FUNDAMENTALS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT 2020 1. COURSE STAFF Lecturer: Dr. Tien Nguyen (Rei) Room: A1.305 E-mail: nctien@hcmiu.edu.vn
Consultation hours by appointment P a g e 1 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen lOMoARcPSD|47206417 2. COURSE INFORMATION 2.1 Prerequisite courses: NA
2.2 Teaching times and Locations Lecture Week Day Time Venue Dr. Tien Nguyen Wednesday 10:30 – 12:45 A2. 601
2.3 Units of Credit: 3 credits
2.4 Parallel teaching in the course: N/A
2.5 Relationship of this course to others
BA016U – Fundamentals of Financial Management provides students with basic concepts of financial
management. The course is provided based on foundation knowledge of financial accounting and economics.
This course may fulfill requirements of curriculum for students majoring in business administration in general;
however is the foundation for students majoring in finance, banking and accounting. For those students that
major in finance, banking and accounting, they can take higher level of courses in finance after this course, to
count for some, Corporate Finance, Financial Institutions and Market, Portfolio Theory and Investment Analysis,
International Finance, Business Analysis and Valuation, etc.
2.6 Approach to learning and teaching
The lecturer will utilize the following methods of instruction: lecture, on-class tutorial, end-of-chapter activities,
and self-study. Students are also encouraged to seek assistance outside class from the lecturer / tutor or through
group tutoring. The lecture materials will be uploaded in Blackboard to help the students to preview the materials
and to concentrate on listening and critical thinking during the lecture. This will help students to interact with
the lecturer during the classroom. 3. COURSE AIMS AND OUTCOMES 3.1 Course Aims
The aim of this course is to expose students to and familiarize them with the theoretical frameworks and practical
matters of financial management… The learning experience will include: an introduction to financial
management; time value of money; techniques of pricing of financial instruments such as bonds and stocks;
evaluation of major projects; the relationship between risk and return; an introduction to Capital Asset Pricing
Model (CAPM) and Portfolio theory; and cost of capital and capital structuring. P a g e 2 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen 3.2 Student Learning Outcomes
After completing the course, students should be able to:
• Explain the purpose, goals, and importance of financial management;
• Understand the relationship between risk and return;
• Understand time value of money and possess skills to convert financial time values;
• Make basic valuation of bonds, stocks, and investment projects;
• Evaluate capital budgeting alternatives, using the firm’s cost of capital in conjunction with internal rate of
return and net present value techniques; Compute cost of capital and capital structure.
4. STUDENT RESPONSIBILITIES AND CONDUCT 4.1 Workload
It is expected that the students will spend at least eight hours per week studying this course. This time should be
made up of reading, researching, working on exercises and problems, and attending classes. 4.2 Attendance
Students are expected to attend class regularly, and are responsible for materials covered during their absences.
Although it is the responsibility of the student for non-attendance, the lecturer has full authority to drop a
student for excessive absences. Exemptions may only be made on medical grounds.
4.3 General Conduct and Behavior
Beepers, cell phones, and pagers need to be turned off before entering the classroom. The students are expected
to conduct themselves with consideration and respect for the needs of the fellow students and teaching staff. 4.4 Keeping informed
The students should take note of all announcements made in lectures or on the course’s Blackboard. From time
to time, the university will send important announcements to their university e-mail addresses without providing
a paper copy. The students will be deemed to have received this information. 5. LEARNING ASSESSMENT 5.1 Formal Requirements
In order to pass this course, the students must: P a g e 3 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen lOMoARcPSD|47206417
• achieve a composite mark of at least 50; and
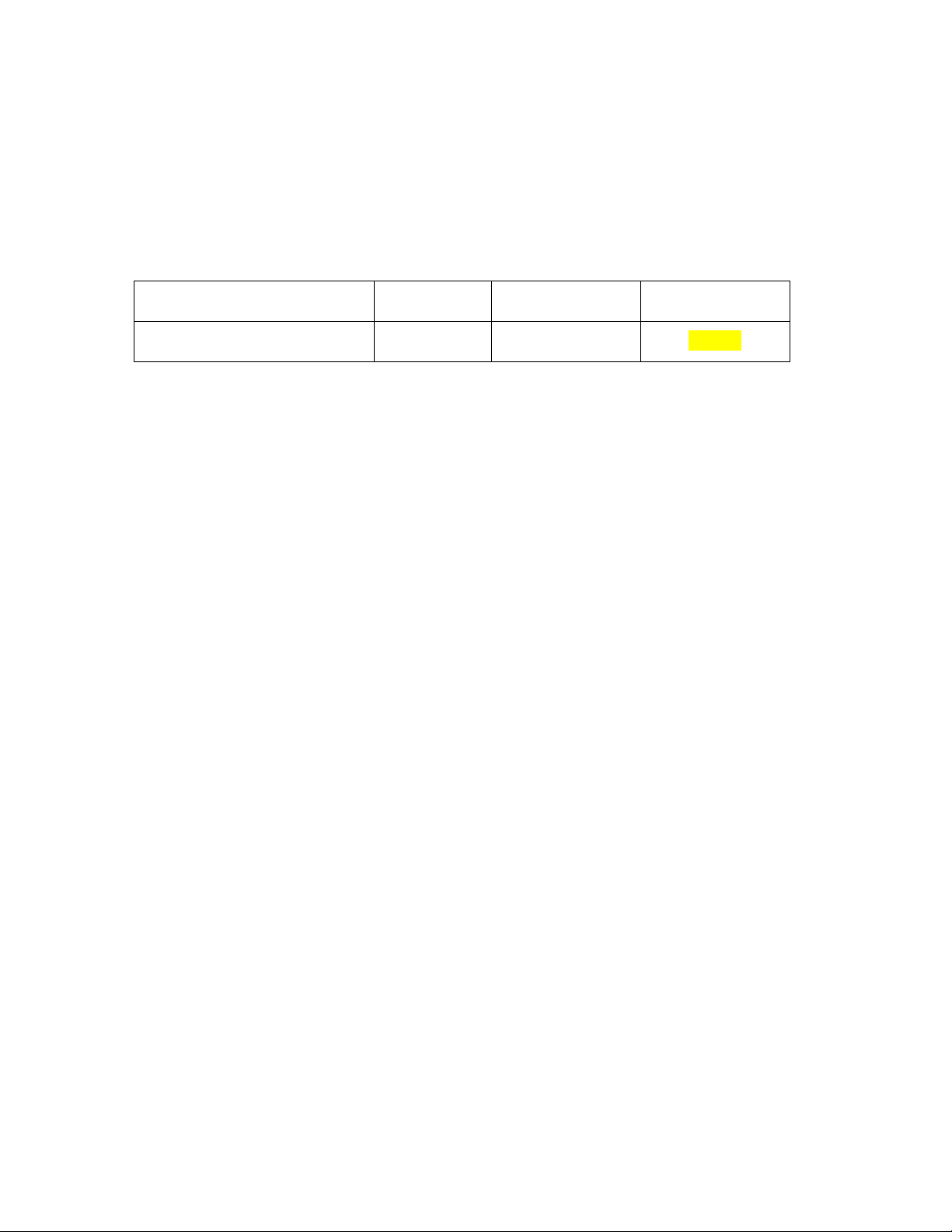
• make a satisfactory attempt at all assessment tasks (see below). 5.2 Assessment Details Two Class Tests 20% In-class Exercises 10% Mid-Term Exam 30% Final Exam 40% Total 100%
Test 1 and 2 will be multiple choice questions and will be held during class time, while mid-term and final
exam will be a combination of short answer questions, application problems and multiple-choice
questions. All of the tests and exams are closed book, but students are allowed to bring one A4 – paper into the exam room. 5.3 Special Consideration
Request for special consideration (for final examination only) must be made to the Office of Academic
Affairs within one week after the examination. General policy and information on special consideration
can be found at the Office of Academic Affairs.
6. ACADEMIC HONESTY AND PLAGIARISM
Plagiarism is the presentation of the thoughts or work of another as one’s own (definition proposed by
the University of Newcastle). The university regards plagiarism as a form of academic misconduct, and has
very strict rules regarding plagiarism.1 P a g e 4 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen 7. STUDENT RESOURCES
7.1 Course Resources Required textbook:
Brealey, R.A., Myers, S.C. and Marcus, A.J. Fundamentals of Corporate Finance, McGraw Hill (any recent edition)
Note: the course will cover Chapter 1 - 12
Recommended readings: Recommended
website: www.finance.yahoo.com
www.bloomberge.com www.reuters.com Other recommended books:
Brigham, E. F. and Houston, J. F. Fundamentals of Financial Management, South-Western
Ross, S. A., Westerfield, R. W., and Jordan, B. D. Fundamentals of Corporate Finance - McGraw Hill.
Additional materials provided in Blackboard
The lecturer will attempt to make lecture notes and additional reading available on Blackboard. However
this is not an automatic entitlement for students doing this subject. Note that this is not a distance learning
course, and you are expected to attend lectures and take notes. This way, you will get the additional benefit
of class interaction and demonstration.
7.2 Other Resources, Support and Information
Additional learning assistance is available for students in this course and will be made available in
Blackboard. Academic journal articles are available through connections via the VNU - Central Library.
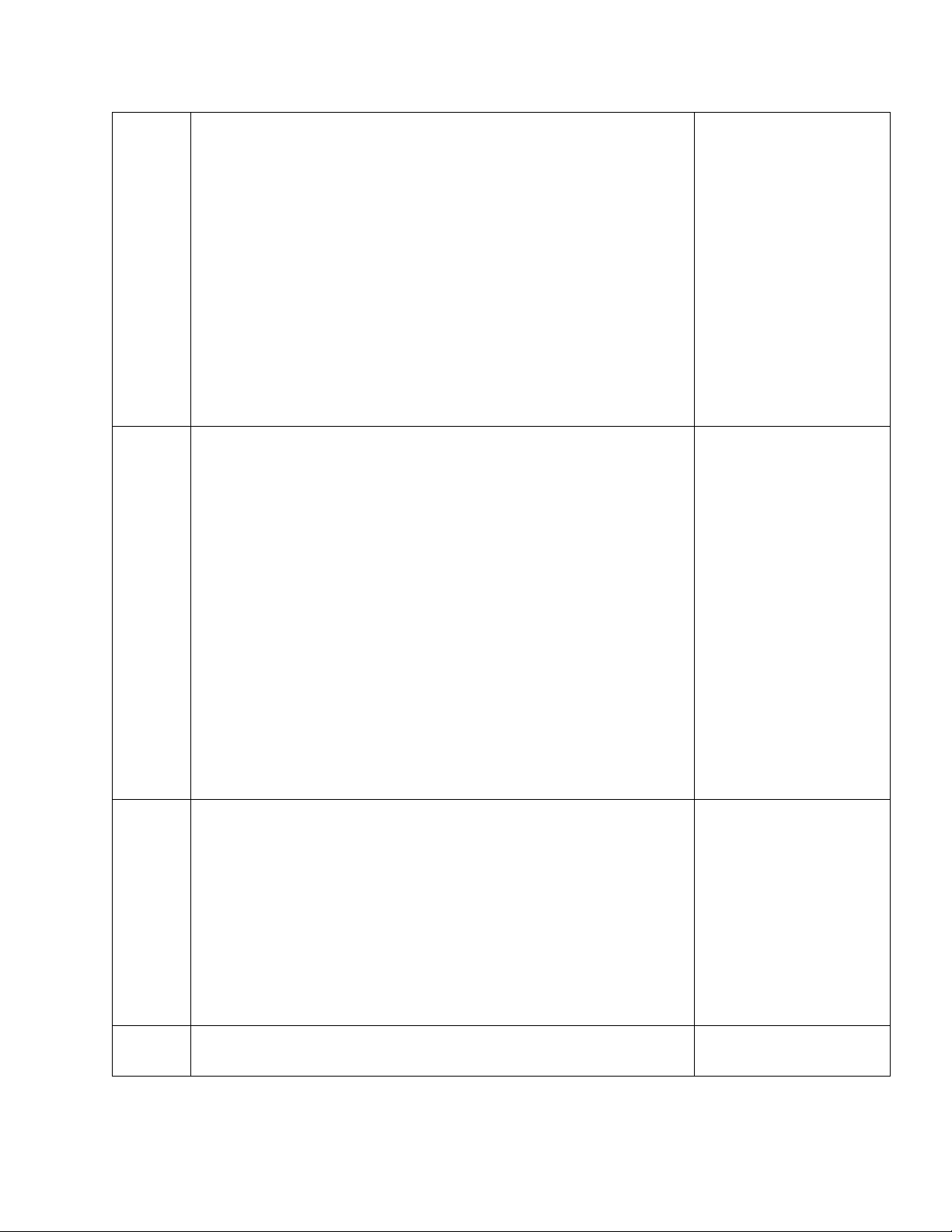
Recommended articles will be duly informed to the students. 8. COURSE SCHEDULE: Week Topic Learning materials P a g e 5 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen 1 Textbook, Chapter 1
Introduction to corporate finance Introduction
Corporation and Goals of the corporation Agency problems Financial Decision Investment Decision Financing Decision Working Capital Management Roles of Financial Manager
Functions of financial markets and intermediates 2 & 3 Textbook, Chapter 4 Time Value of Money On-class tutorials Basic concepts
Time line/ Future values (FV)/ Present values (PV)
Simple interest rate (SR)/ Compound interest rate(CR) Multiple cash flows
Future value of Multiple Cash Flows
Present value of Multiple Cash Flows Annuity cash flow Future Value of an Annuity Present Value of an Annuity Perpetuity cash flows Present Value of a Perpetuity 4 Textbook, Chapter 4 Time Value of Money (Cont.) On-class tutorials Growing annuity cash flow
Future Value of an growing annuity
Present Value of an growing annuity Mortgage loans
Inflation and time value of money: Real versus nominal cash flows
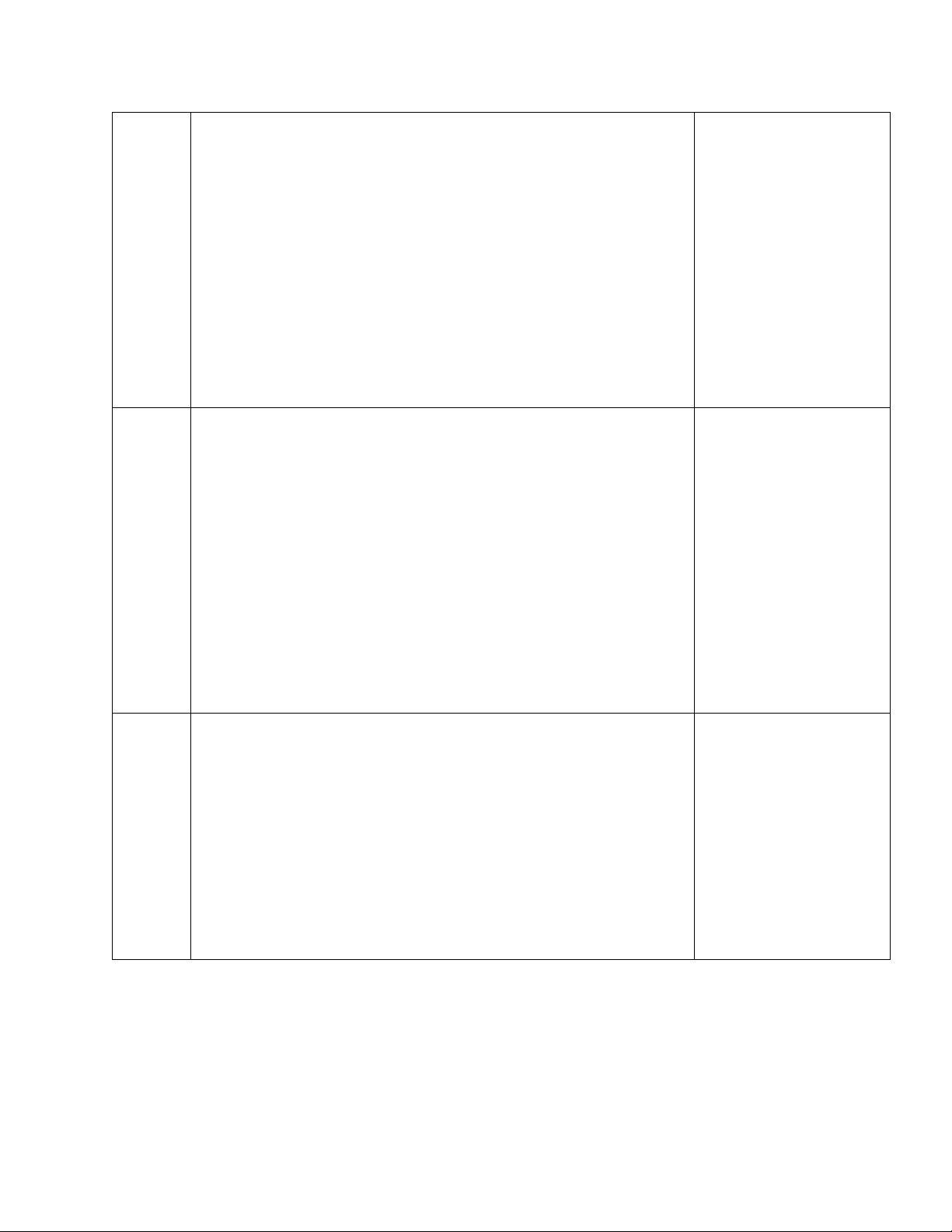
Effective annual interest rates (EAR) 5 & 6 Bonds and their evaluation Textbook, Chapter 5 P a g e 6 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen Bond characteristics On-class tutorials Bond evaluation
Coupon bonds, semi-annual coupon bonds Zero-coupon bonds Bond yield Current yield Yield to maturity (YTM) Rate of return
Relationship between market interest rate and bond price
Bond premiums and bond discounts 7 & 8 Textbook, Chapter 6 Stock and their evaluation On-class tutorials Equity versus debt
Common stocks vs. Preferred stocks
Book values, Liquidation values, and Market values
Stock valuation: Dividend Discount Model (DDM) Zero growth common stocks Constant growth common stocks
Differential growth common stocks Preferred stocks
Growth stocks and Income stocks 9 & 10 Textbook, Chapters 7
Project Investment Criteria and Capital Budgeting Decision Capital budgeting decision Capital budgeting process Project classifications
Net Present Value (NPV) method
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) method
Payback Period (PP)/ Discount Payback period (DPP) method Profitability Index (PI) P a g e 7 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen
10 & 11 Project Investment Criteria and Capital Budgeting (Cont.) Textbook, Chapter 8
Principles of identifying cash flows Calculating Cash Flows Capital investment Operating cash flows Investment in working capital
Terminal-year incremental cash flow 12 Textbook, Chapter 10
Introduction to Risk, Return and Opportunity Cost of Capital
Introduction relationship between Risk and Return Rates of return
Measuring risk: Variance and standard deviation Risk and diversification: Diversification Asset versus portfolio risk
Variance and standard deviation of returns for a two-asset portfolio
Unique risk versus market risk 13 Textbook, Chapter 11
Risk, Return and capital budgeting Measuring market risk Concept of beta Portfolio betas Risk and return
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) Security Market Line (SML)
Capital budgeting and Project Risk P a g e 8 | 8
BA016IU – Fundamentals of Financial Management | Dr. Tien Nguyen 14 Textbook, Chapter 12
Capital Structure and Cost of Capital Measuring capital structure Market versus book weight Cost of capital Cost of debt
Cost of equity: cost of preferred stock and common stock Cost of retained earning
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) and business evaluation 15 Revision
Note: The tutorials are following Brealey, R.A., Myers, S.C. and Marcus, A.J. Fundamentals of Corporate
Finance, McGraw Hill, 5th Edition
i The syllabus is prepared following the format provided by the School of Organization and Management, University
of New South Wales, with kind permission. P a g e 9 | 8