




Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|46342985 lOMoARcPSD|46342985 HANOI UNIVERSITY
FACULTY OF MANAGEMENT AND TOURISM MICROECONOMICS 61ECO2MIC TUTORIAL EXERCISES Autumn 2024 lOMoARcPSD|46342985 TUT 1 - INTRODUCTION Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1.
Which of the following is correct?
a. The word economy comes from the Greek word for “rational thinker.”
b. Economists study the management of scarce resources.
c. Because economists believe that people pursue their best interests, they are not interested in how people interact.
d. All of the above are correct. ____ 2.
When the government attempts to improve equality in an economy the result is often
a. an increase in overall output in the economy.
b. additional government revenue since overall income will increase. c. a reduction in equality. d. a reduction in efficiency. ____ 3.
Mallory decides to spend three hours working overtime rather than watching a video with
her friends. She earns $8 an hour. Her opportunity cost of working is a. the $24 she earns working.
b. the $24 minus the enjoyment she would have received from watching the video.
c. the enjoyment she would have received had she watched the video.
d. nothing, since she would have received less than $24 of enjoyment from the video. ____ 4.
A rational decision maker takes an action only if the
a. marginal benefit is less than the marginal cost.
b. marginal benefit is greater than the marginal cost.
c. average benefit is greater than the average cost.
d. marginal benefit is greater than both the average cost and the marginal cost. ____ 5.
A furniture maker currently produces 100 tables per week and sells them for a profit. She
is considering expanding her operation in order to make more tables. Should she expand?
a. Yes, because making tables is profitable.
b. No, because she may not be able to sell the additional tables.
c. It depends on the marginal cost of producing more tables and the marginal revenue she will earn from selling more tables.
d. It depends on the average cost of producing more tables and the average revenue she will earn from selling more tables. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 6.
Which of the following statements exemplifies a principle of individual decisionmaking? a.
Trade can make everyone better off. b.
Governments can sometimes improve market outcomes. c.
The cost of something is what you give up to get it. d. All of the above are correct. ____ 7.
Which of the following statements does not apply to a market economy?
a. Firms decide whom to hire and what to produce.
b. The “invisible hand” usually maximizes the well-being of society as a whole.
c. Households decide which firms to work for and what to buy with their incomes.
d. Government policies are the primary forces that guide the decisions of firms and households. ____ 8.
Economists, like mathematicians, physicists, and biologists,
a. make use of the scientific method.
b. try to address their subject with a scientist’s objectivity.
c. devise theories, collect data, and then analyze these data in an attempt to verify or refute their theories.
d. All of the above are correct. ____ 9.
Which of the following statements about the circular-flow diagram is correct?
a. One must imagine that the economy operates without money in order to make sense of the diagram.
b. The diagram leaves out details that are not essential for understanding the economic transactions that
occur between households and firms.
c. The government cannot be excluded as a decision maker in a circular-flow diagram.
d. All of the above are correct. ____ 10.
When constructing a production possibilities frontier, which of the following assumptions is not made?
a. The economy produces only two goods or two types of goods.
b. Firms produce goods using factors of production.
c. The technology available to firms is given.
d. The quantities of the factors of production that are available are increasing over the relevant time period. ____ 11.
Unemployment would cause an economy to a.
produce inside its production possibilities frontier. b.
produce on its production possibilities frontier. c.
produce outside its production possibilities frontier. d.
experience an inward shift of its production possibilities frontier. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 12.
The following table contains some production possibilities for an economy for a given year: Cars Newspapers 10 400 12 360 14 ?
If the production possibilities frontier is bowed outward, then "?" could be a. 340. b. 330. c. 320. d. 310. ____ 13.
A production possibilities frontier can shift outward if
a. government increases the amount of money in the economy.
b. there is a technological improvement.
c. resources are shifted from the production of one good to the production of the other good.
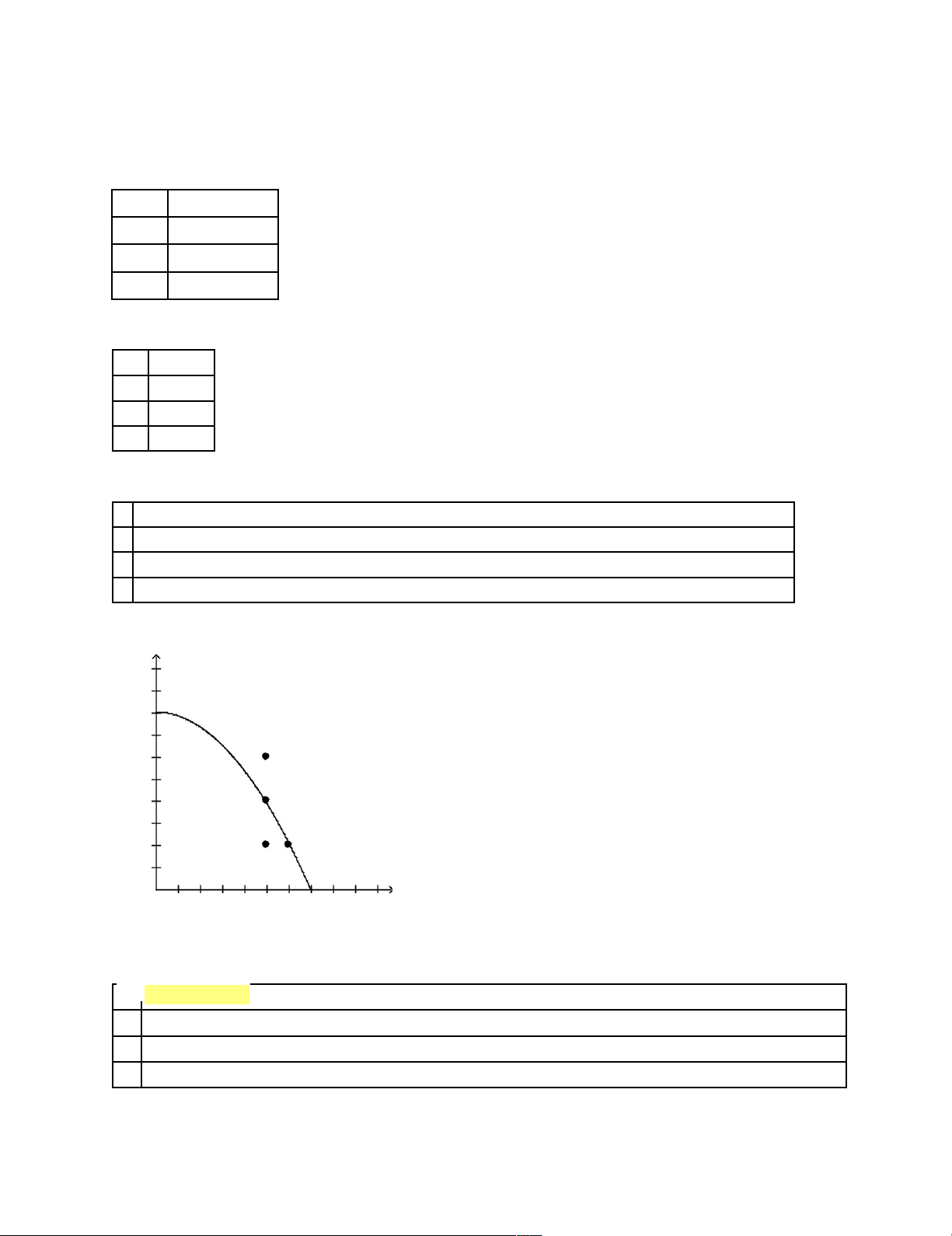
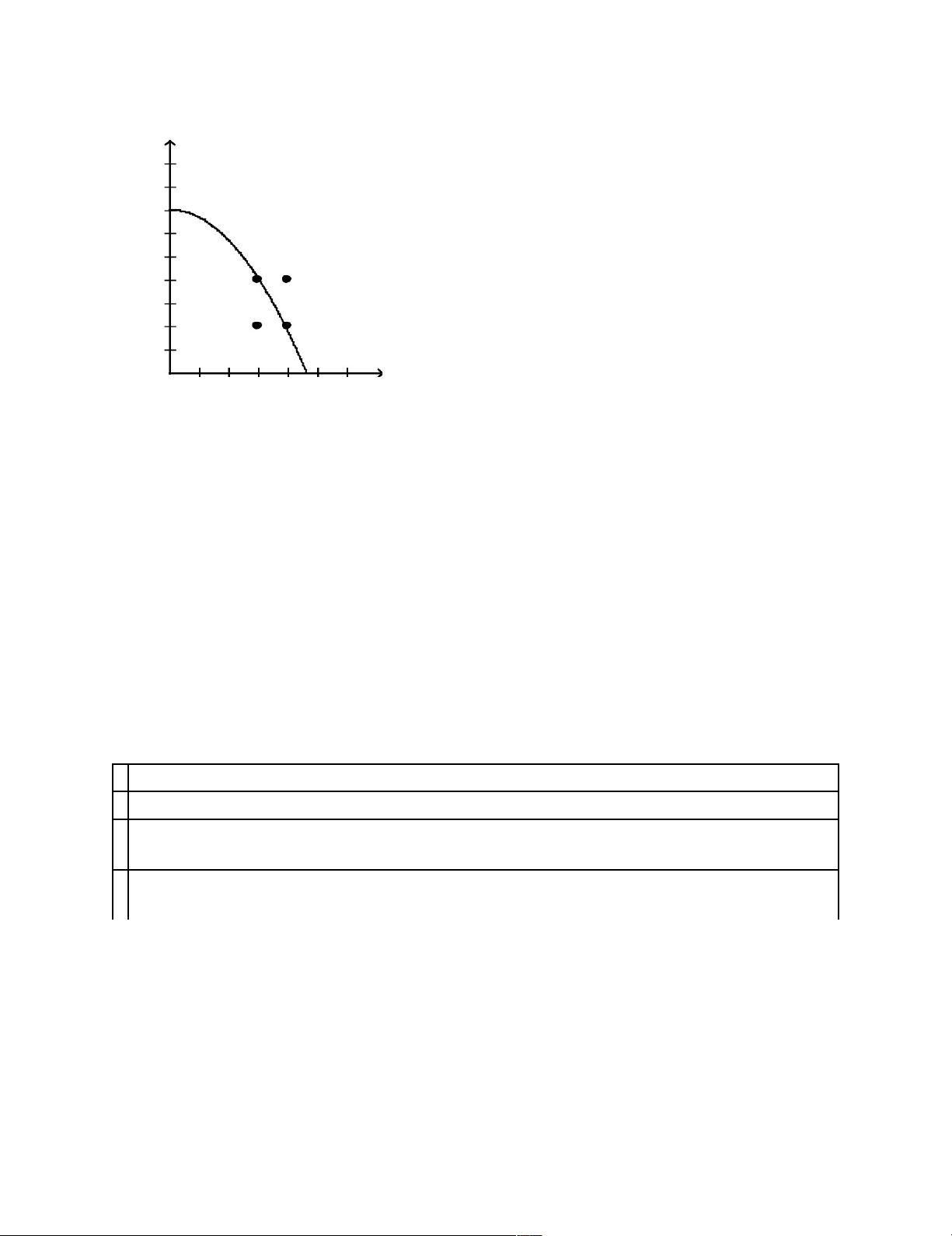
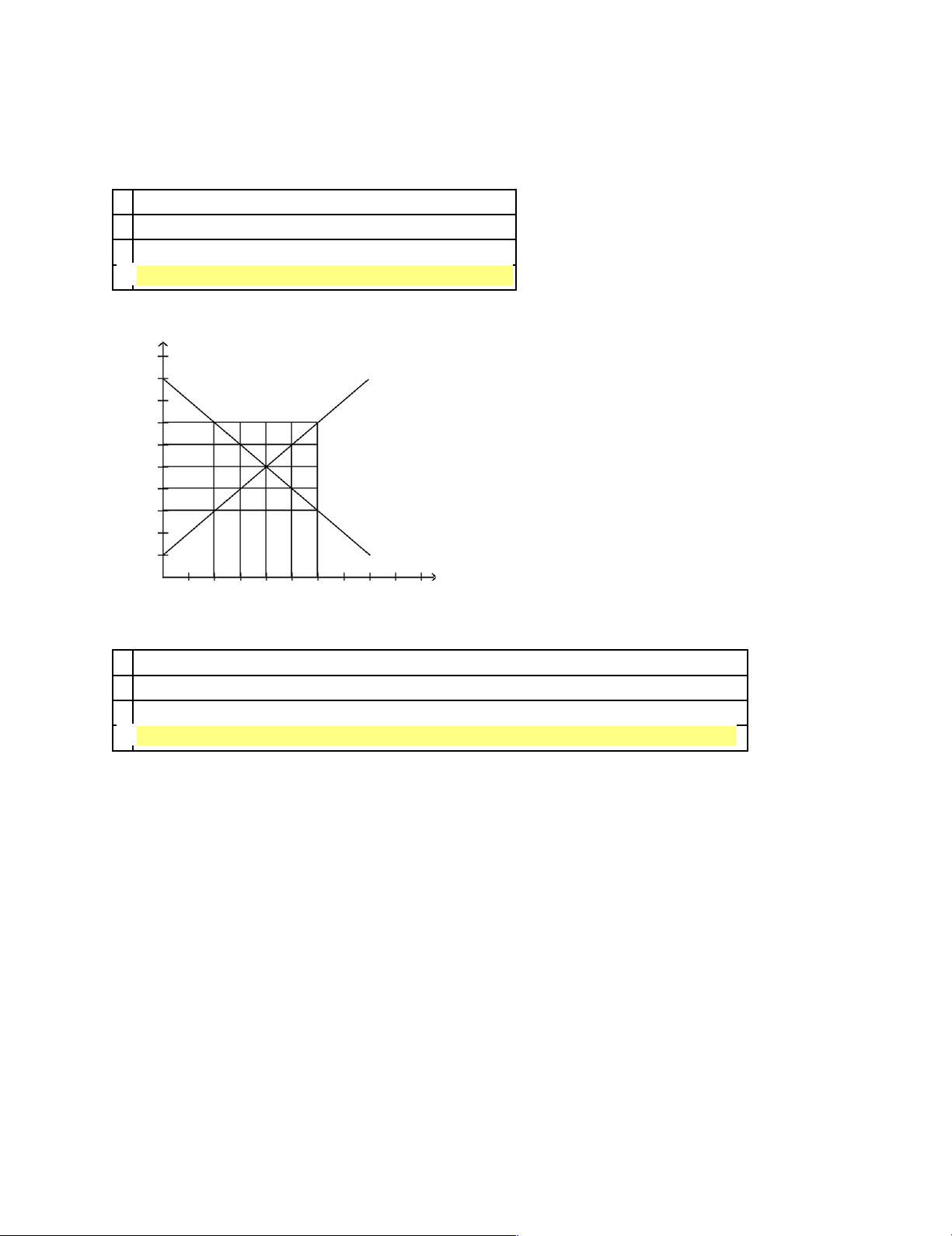
d. the economy abandons inefficient production methods in favor of efficient production methods. Figure 2-4 t o a s t er s 50 45 40 35 C 30 25 A 20 15 D B 10 5 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 t o o t h - b r u s h es ____14.
Refer to Figure 2-4. The opportunity cost of obtaining 10 additional toasters by moving from point D to point A is a. 0 toothbrushes. b. 10 toothbrushes. c. 50 toothbrushes.
d. None of the above; the economy cannot move from point D to point A. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 Figure 2-6 b a r r el s 45 40 35 A 30 D 25 C 20 B 15 G F 10 5 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 b a t h t u b s ____ 15.
Refer to Figure 2-6. Efficient production is represented by which point(s)? a. A, B b. A,B,C,F,G c. C,F,G d. D ____ 16.
Refer to Figure 2-6. If this economy moved from point C to point F, then
a. it still would not be producing efficiently.
b. there would be no gain in either bathtubs or barrels.
c. it would be producing more barrels and more bathtubs than at point C.
d. It is not possible for this economy to move from point C to point F without additional resources. Figure 2-7 r i b eye s t ea ks 2800 2400 A C 2000 1600 1200 800 D 400 B 400 800 1200 1600 b o o ks ____ 17.
Refer to Figure 2-7. Point B represents an outcome in which a. production is inefficient.
b. some of the economy’s resources are unemployed.
c. the economy is using all of its resources to produce books.
d. the economy is using all of its ribeye steaks to produce books. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 18.
A microeconomist — as opposed to a macroeconomist — might study
a. the effect of borrowing by the federal government on the inflation rate.
b. the effect of rising oil prices on employment in the airline industry.
c. changes in the nation’s unemployment rate over short periods of time.
d. alternative policies to promote higher living standards throughout the nation. ____ 19.
Economists view positive statements as a.
affirmative, justifying existing economic policy.
b. optimistic, putting the best possible interpretation on things. c.
descriptive, making a claim about how the world is.
d. prescriptive, making a claim about how the world ought to be. ____ 20.
Which of the following is an example of a normative, as opposed to positive, statement?
a. The price of gasoline came down sharply during the second half of 2006.
b. If the government were to set a maximum legal price on gasoline, then there would be a shortage of gasoline.
c. Income taxes should be reduced.
d. The federal government obtains much of its revenue from income taxes. True/False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 21.
Economics is the study of how society allocates its unlimited resources. ____ 22.
Choosing not to attend a concert so that you can study for your exam is an example of a tradeoff. ____ 23.
Efficiency means everyone in the economy should receive an equal share of the goods and services produced. ____ 24.
An increase in the marginal cost of an activity necessarily means that people will no longer
engage in any of that activity. ____ 25.
Trade with any nation can be mutually beneficial. ____ 26.
Economists usually have to make do with whatever data the world happens to give them. ____ 27.
Economists often find it worthwhile to make assumptions that do not necessarily describe the real world. ____ 28.
In the circular-flow diagram, households and firms are the decision makers. ____ 29.
In the circular-flow diagram, one loop represents the flow of goods, services, and factors
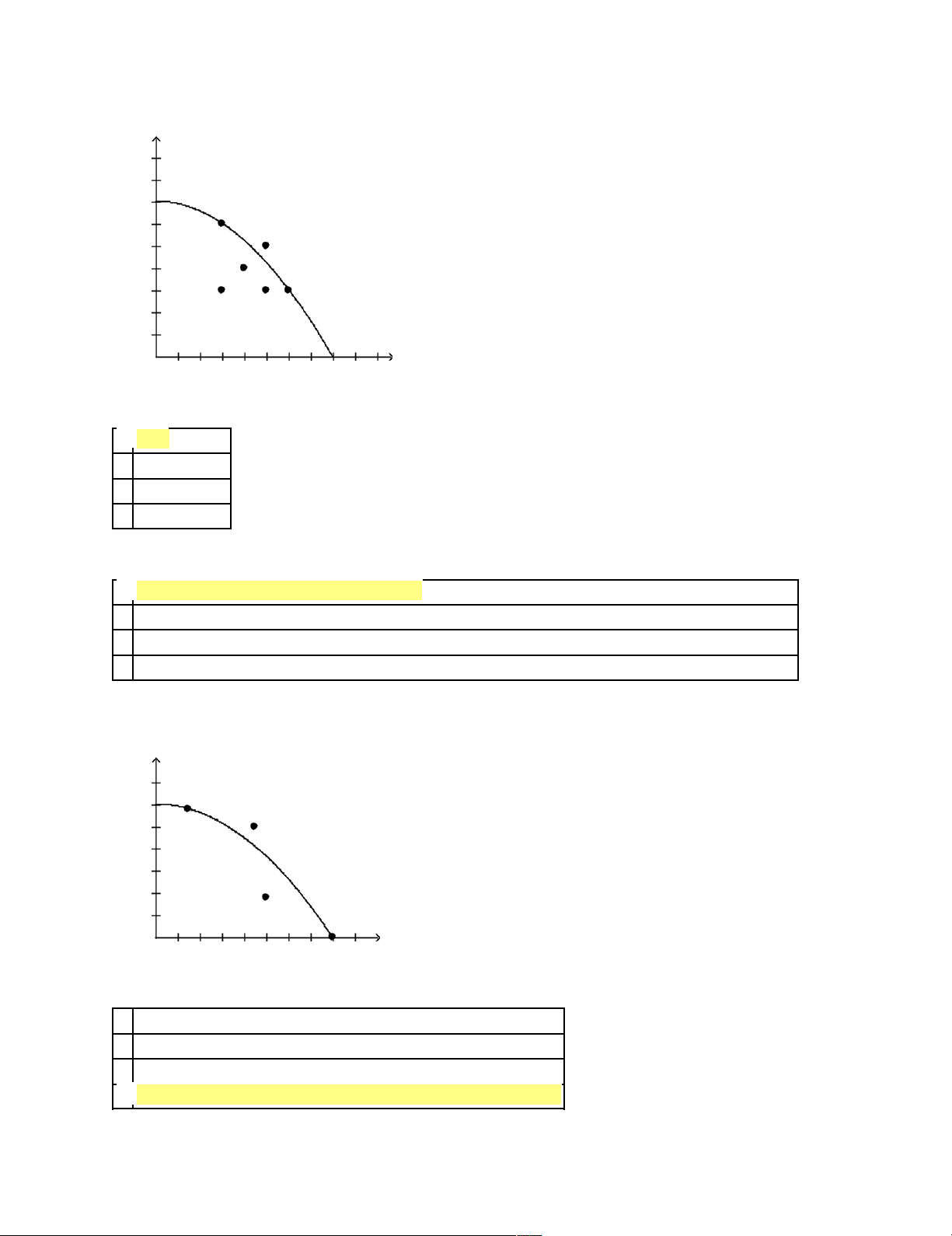
of production, and the other loop represents the corresponding flow of dollars. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 Figure 2-14 d i s h wa s h er s 45 40 35 30 25 A C 20 15 B D 10 5 1530456075 d o g - h o u s es ____ 30.
Refer to Figure 2-14. Is it possible for this economy to produce 75 doghouses. Short Answer 31.
With the understanding that people respond to incentives, outline the possible outcome
for teachers if the K-12 school year is extended to 11 months per year instead of the existing 9 months per year. 32.
Using the outline below, draw a circular-flow diagram representing the interactions
between households and firms in a simple economy. Explain briefly the various parts of the diagram. 33.
Draw a production possibilities frontier showing increasing opportunity cost of
hammers in terms of horseshoes.
a. On the graph, identify the area of feasible outcomes and the area of infeasible outcomes.
b. On the graph, label a point that is efficient and a point that is inefficient.
c. On the graph, illustrate the effect of the discovery of a new vein of iron ore, a resource needed to make
both horseshoes and hammers, on this economy.
d. On a second graph, illustrate the effect of a new computerized assembly line in the production of hammers on this economy. lOMoARcPSD|46342985
TUT 2 _ THE MARKET FORCES Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1.
In a competitive market, the quantity of a product produced and the price of the product are determined by a. a single buyer. b. a single seller.
c. one buyer and one seller working together. d. all buyers and all sellers. ____ 2.
In a perfectly competitive market, at the market price,
a. buyers cannot buy all they want and sellers cannot sell all they want.
b. buyers cannot buy all they want, but sellers can sell all they want.
c. buyers can buy all they want, but sellers cannot sell all they want.
d. buyers can buy all they want and sellers can sell all they want. ____ 3.
The quantity demanded of a good is the amount that buyers a. are willing to purchase.
b. are willing and able to purchase.
c. are willing and able and need to purchase. d. are able to purchase. ____ 4.
A downward-sloping demand curve illustrates
a. that demand decreases over time. b. that prices fall over time.
c. the relationship between income and quantity demanded. d. the law of demand. Table 4-1 Price Aaron’s Angela’s Austin’s Alyssa’s Quantity Quantity Quantity Quantity
Demanded Demanded Demanded Demanded $0.00 20 16 4 8 $0.50 18 12 6 6 $1.00 14 10 2 5 $1.50 12 8 0 4 $2.00 6 6 0 2 $2.50 0 4 0 0 lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 5.
Refer to Table 4-1. If these are the only four buyers in the market, then the market
quantity demanded at a price of $2 is a. 0 units. b. 3.5 units. c. 6 units. d. 14 units. ____ 6.
Which of the following changes would not shift the demand curve for a good or service? a. a change in income
b. a change in the price of the good or service
c. a change in expectations about the future price of the good or service
d. a change in the price of a related good or service ____ 7.
Suppose that when income rises, the demand curve for computers shifts to the right. In
this case, we know computers are a. inferior goods. b. normal goods.
c. perfectly competitive goods. d. durable goods. Figure 4-3 p r i ce D' D q u a n t i t y ____ 8.
Refer to Figure 4-3. The movement from D’ to D could be caused by a. a decrease in price.
b. a decrease in income, assuming the good is inferior.
c. buyers expecting the price of the good to fall in the near future.
d. an increase in the price of a complement. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 9.
The line that relates the price of a good and the quantity supplied of that good is called the
a. supply schedule, and it usually slopes upward.
b. supply schedule, and it usually slopes downward.
c. supply curve, and it usually slopes upward.
d. supply curve, and it usually slopes downward. Figure 4-5 Firm A Firm B p r i ce p r i ce 20 20 18 18 16 16 14 14 S 12 12 10 10 S 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 q u a n t i t y 24
6810 12 14 16 18 20 q u a n t i t y 246810 12 14 16 ____10.
Refer to Figure 4-5. If these are the only two sellers in the market, then the market
quantity supplied at a price of $6 is a. 2 units. b. 10 units. c. 12 units. d. 22 units. ____ 11.
A leftward shift of a supply curve is called a. an increase in supply. b. a decrease in supply.
c. a decrease in quantity supplied.
d. an increase in quantity supplied. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 12.
Which of the following events would cause a movement upward and to the right along the supply curve for tomatoes?
a. The number of sellers of tomatoes increases.
b. There is an advance in technology that reduces the cost of producing tomatoes.
c. The price of fertilizer decreases, and fertilizer is an input in the production of tomatoes.
d. The price of tomatoes rises. ____ 13.
If suppliers expect the price of their product to fall in the future, then they will a. decrease supply now. b. increase supply now.
c. decrease supply in the future but not now.
d. increase supply in the future but not now. ____ 14.
Funsters, Inc., the largest toy company in the country, sells its most popular doll for
$15. It has just learned that its leading competitor, Toysorama, is mass-producing an excellent copy and
plans to flood the market with their $5 doll in 6 weeks. Funsters should
a. “fight fire with fire” by decreasing supply of its doll for 6 weeks and then increasing the supply.
b. increase the supply of their doll now before the other doll hits the market.
c. increase the price of their doll now. d. discontinue their doll. ____ 15.
The unique point at which the supply and demand curves intersect is called a. market harmony. b. coincidence. c. equivalence. d. equilibrium. ____ 16.
If there is a shortage of farm laborers, we would expect
a. the wage of farm laborers to increase.
b. the wage of farm laborers to decrease.
c. the price of farm commodities to decrease.
d. a decrease in the demand for substitutes for farm labor. Table 4-7
The demand schedule below pertains to sandwiches demanded per week. Price Charlie’s Maxine’s Quinn’s Quantity Quantity Quantity Demanded Demanded Demanded $3 3 4 3 $5 1 2 x lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 17.
Refer to Table 4-7. Regarding Charlie and Maxine, for whom are sandwiches a normal good? a. only for Charlie b. only for Maxine c. for Charlie and for Maxine
d. This cannot be determined from the given information. Figure 4-8 p r i ce 50 45 S 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 D 100 200 300 400 500
600 700 800 q u a n t i t y ____ 18.
Refer to Figure 4-8. At a price of $35,
a. a shortage would exist and the price would tend to rise from $35 to a higher price.
b. a surplus would exist and the price would tend to rise from $35 to a higher price.
c. an excess demand would exist and the price would tend to fall from $35 to a lower price.
d. an excess supply would exist and the price would tend to fall from $35 to a lower price. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 Figure 4-13
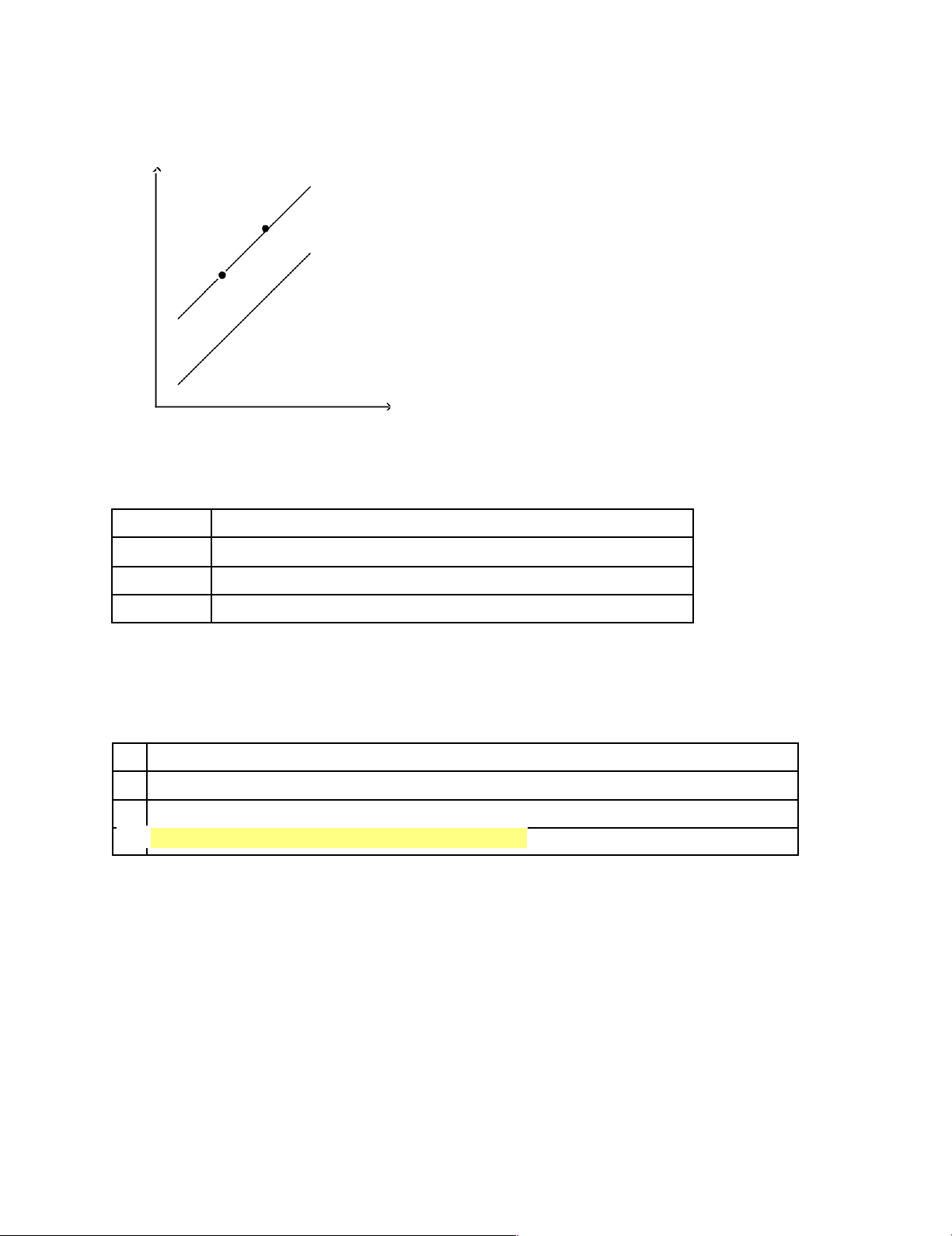
The diagram below pertains to the supply of paper in university markets. p r i ce S A y S B x q u a n t i t y ____ 19.
Refer to Figure 4-13. All else equal, a major paper company being shut down for tax evasion would cause a move a. from x to y. b. from y to x. c. from S to S . A B d. from S to S . B A ____ 20.
Music compact discs are normal goods. What will happen to the equilibrium price and
quantity of music compact discs if musicians accept lower royalties, compact disc players become
cheaper, more firms start producing music compact discs, and music lovers experience an increase in income? a.
Price will fall and the effect on quantity is ambiguous. b.
Price will rise and the effect on quantity is ambiguous. c.
Quantity will fall and the effect on price is ambiguous. d.
Quantity will rise and the effect on price is ambiguous. True/False
Indicate whether the statement is true or false. ____ 21.
A yard sale is an example of a market. ____ 22.
In a perfectly competitive market, the goods offered for sale are all exactly the same. ____ 23.
The demand curve is the upward-sloping line relating price and quantity demanded. ____ 24.
When Mario's income decreases, he buys more pasta. For Mario, pasta is a normal good. ____ 25.
Baseballs and baseball bats are substitute goods. ____ 26.
If a higher price means a greater quantity supplied, then the supply curve slopes upward. ____ 27.
A decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 28.
An increase in the price of a product and an increase in the number of sellers in the
market affect the supply curve in the same general way. ____ 29.
At the equilibrium price, quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. ____ 30.
When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded at the current market price, the
market has a surplus and market price will likely rise in the future to eliminate the surplus. Short Answer 31.
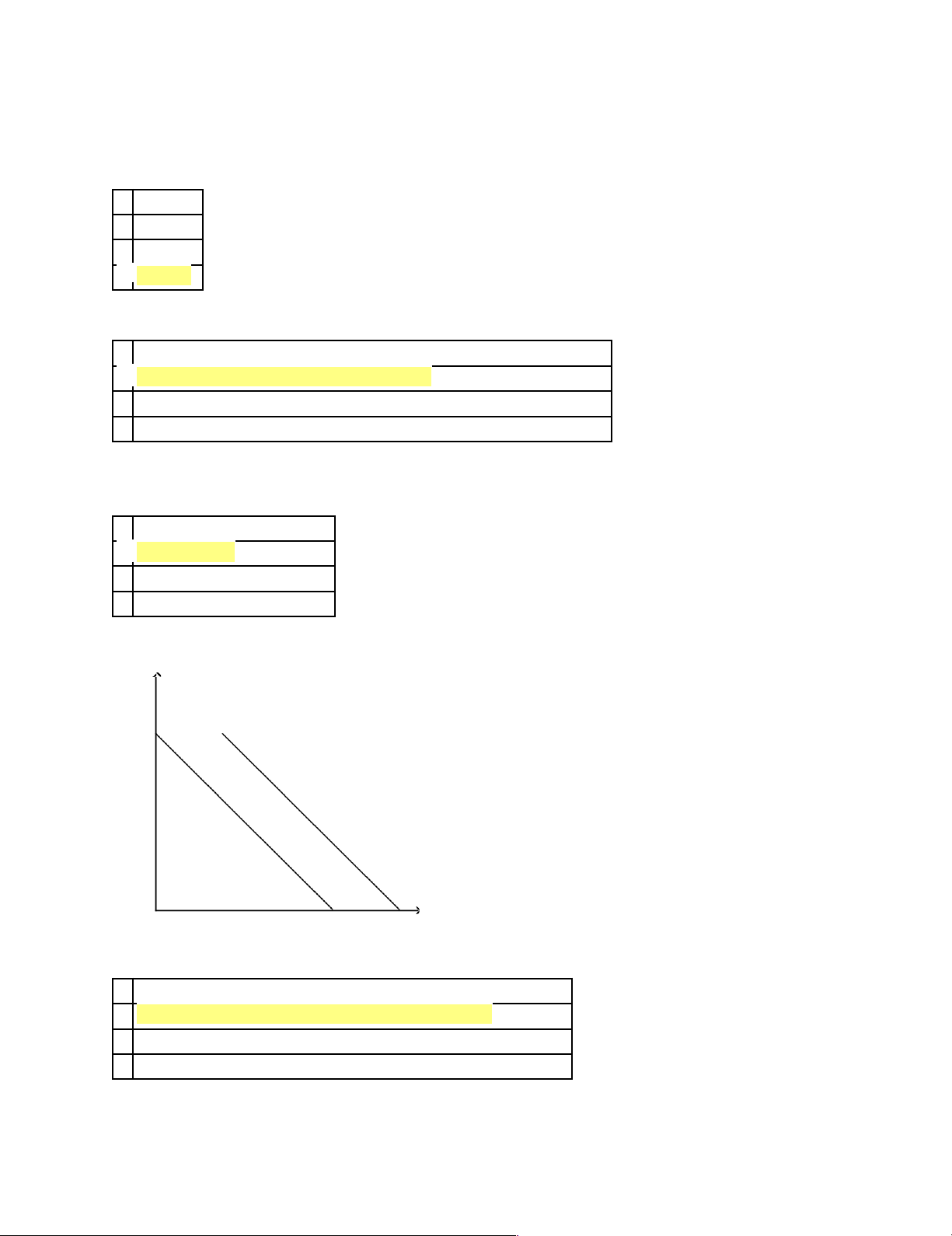
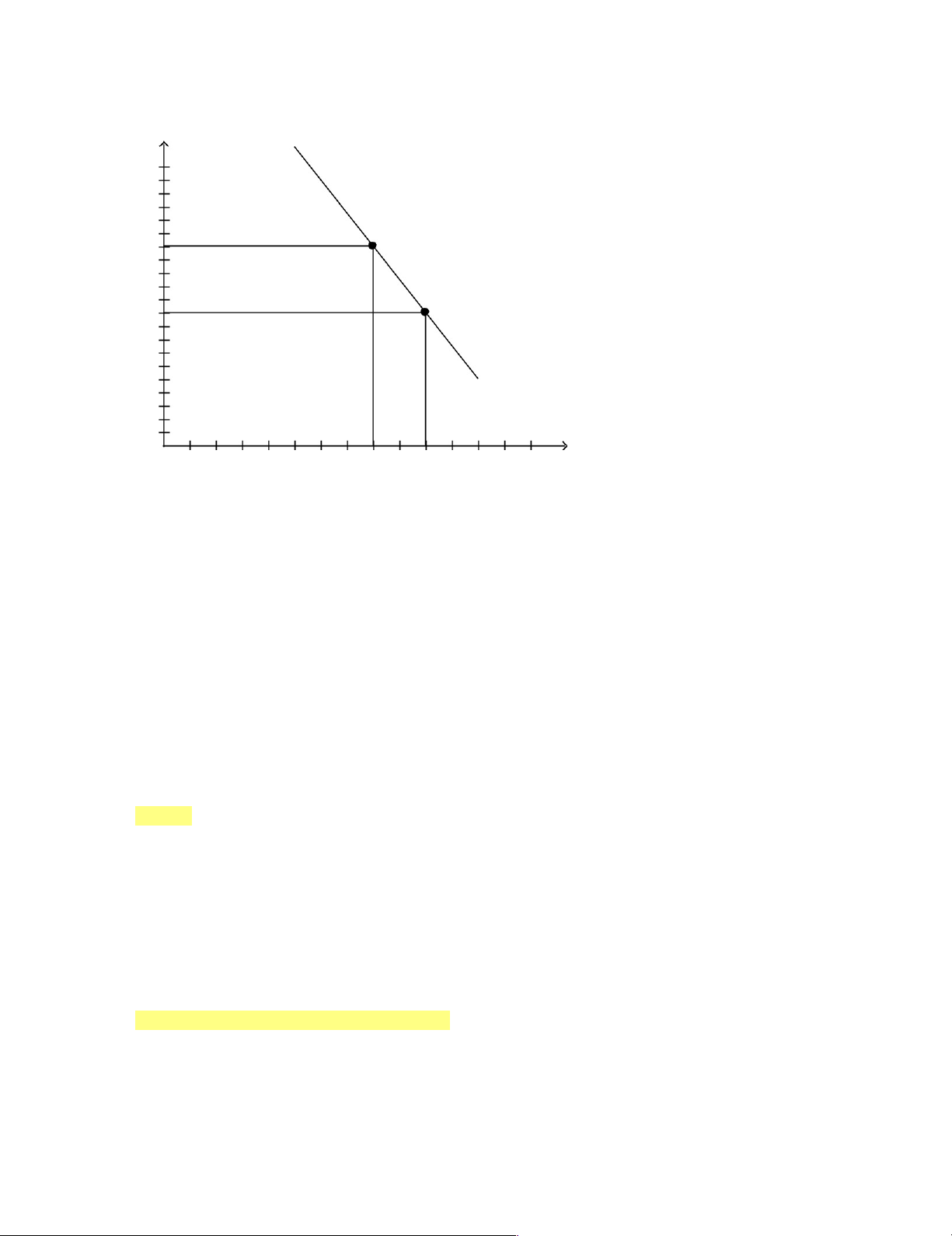
a. Given the table below, graph the demand and supply curves for flashlights. Make certain to label
the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied Per Month Per Month $5 6,000 10,000 $4 8,000 8,000 $3 10,000 6,000 $2 12,000 4,000 $1 14,000 2,000 b.
What is the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity? c.
Suppose the price is currently $5. What problem would exist in the market? What would you
expect to happen to price? Show this on your graph. d.
Suppose the price is currently $2. What problem would exist in the market? What would you
expect to happen to price? Show this on your graph. 32.
Fill in the table below, showing whether equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity go
up, go down, stay the same, or change ambiguously.
No Change in Supply An Increase in Supply A Decrease in Supply No Change in Demand An Increase in Demand A Decrease in Demand lOMoARcPSD|46342985 33.
Suppose we are analyzing the market for hot chocolate. Graphically illustrate the impact
each of the following would have on demand or supply. Also show how equilibrium price and
equilibrium quantity would change. a.
The Surgeon General of the U.S. announces that hot chocolate cures acne. b.
Protesting farmers dump millions of gallons of milk, causing the price of milk to rise. c.
Consumer income falls because of a recession, and hot chocolate is considered a normal good. d.
Producers expect the price of hot chocolate to increase next month. e.
Currently, the price of hot chocolate is $0.50 per cup above equilibrium. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 TUT 3 - ELASTICITY Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1.
A good will have a more inelastic demand,
a. the greater the availability of close substitutes.
b. the broader the definition of the market.
c. the longer the period of time.
d. the more it is regarded as a luxury. ____ 2.
Which of the following statements is correct?
a. The demand for natural gas is more elastic over a short period of time than over a long period of time.
b. The demand for smoke alarms is more elastic than the demand for Persian rugs.
c. The demand for bourbon whiskey is more elastic than the demand for alcoholic beverages in general.
d. All of the above are correct. ____ 3.
The greater the price elasticity of demand, the
a. more likely the product is a necessity.
b. smaller the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
c. greater the percentage change in price over the percentage change in quantity demanded.
d. greater the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price. ____ 4.
For a particular good, a 3 percent increase in price causes a 10 percent decrease in
quantity demanded. Which of the following statements is most likely applicable to this good?
a. The relevant time horizon is short. b. The good is a necessity.
c. The market for the good is broadly defined.
d. There are many close substitutes for this good. ____ 5.
If a 15% increase in price for a good results in a 20% decrease in quantity demanded, the price elasticity of demand is a. 0.75. b. 1.25. c. 1.33. d. 1.60. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 Table 5-3
The following table shows the demand schedule for a particular good. Price Quantity $15 0 $12 5 $9 10 $6 15 $3 20 $0 25 ____ 6.
Refer to Table 5-3. Using the midpoint method, when price rises from $6 to $9, the price elasticity of demand is a. 0.43 b. 0.67 c. 1.00 d. 1.5 ____ 7.
Refer to Table 5-3. Using the midpoint method, when price falls from $6 to $3, the price elasticity of demand is a. 0.43 b. 0.67 c. 1.50 d. 2.33 ____ 8.
Suppose the price of Twinkies decreases from $1.45 to $1.25 and, as a result, the quantity
of Twinkies demanded increases from 2,000 to 2,200. Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of
demand for Twinkies in the given price range is a. 2.00. b. 1.55. c. 1.00. d. 0.64. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 Figure 5-4 P r i ce A B Demand C Q u a n t i t y ____ 9.
Refer to Figure 5-4. Assume the section of the demand curve from B to C corresponds
to prices between $0 and $15. Then, when the price changes between $7 and $9,
a. quantity demanded changes proportionately less than the price.
b. quantity demanded changes proportionately more than the price.
c. quantity demanded changes the same amount proportionately as price.
d. the price elasticity of demand equals zero. ____ 10.
Refer to Figure 5-4. Assume, for the good in question, two specific points on the
demand curve are (Q = 2,000, P = $15) and (Q = 2,400, P = $12). Then which of the following scenarios is possible?
a. Both of these points lie on section C of the demand curve.
b. The vertical intercept of the demand curve is the point (Q = 0, P = $22).
c. The horizontal intercept of the demand curve is the point (Q = 5,000, P = $0).
d. Any of these scenarios is possible. ____ 11.
A perfectly elastic demand implies that
a. buyers will not respond to any change in price.
b. any rise in price above that represented by the demand curve will result in a quantity demanded of zero.
c. quantity demanded and price change by the same percent as we move along the demand curve.
d. price will rise by an infinite amount when there is a change in quantity demanded. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 Figure 5-9 P r i ce 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 Demand 4 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9101112 Q u a n t i t y ____ 12.
Refer to Figure 5-9. Suppose this demand curve is a straight, downward-sloping line all
the way from the horizontal intercept to the vertical intercept. We choose two prices, P and P , and the 1 2
corresponding quantities demanded, Q and Q , for the purpose of calculating the price elasticity of 1 2
demand. Also suppose P > P In which of the following cases could we possibly find that (i) demand 2 1.
is elastic and (ii) an increase in price from P to P causes an increase in total revenue? 1 2
a. 0 < P < P < $10. 1 2
b. $10 < P < P < $15. 1 2 c. P > $15. 1
d. None of the above is correct. ____ 13.
Holding all other forces constant, if increasing the price of a good leads to an increase in
total revenue, then the demand for the good must be a. unit elastic. b. inelastic. c. elastic.
d. None of the above is correct, since a price increase always leads to an increase in total revenue. ____ 14.
To determine whether a good is considered normal or inferior, one could examine the value of the
a. income elasticity of demand for that good.
b. price elasticity of demand for that good.
c. price elasticity of supply for that good.
d. cross-price elasticity of demand for that good. lOMoARcPSD|46342985 ____ 15.
Which of the following should be held constant when calculating an income elasticity of demand?
a. the quantity of the good demanded b. the price of the good c. income
d. All of the above should be held constant. ____ 16.
If two goods are complements, their cross-price elasticity will be a. positive. b. negative. c. zero.
d. equal to the difference between the income elasticities of demand for the two goods. ____ 17.
At a price of $1.00, a local coffee shop is willing to supply 100 cinnamon rolls per
day. At a price of $1.20, the coffee shop would be willing to supply 150 cinnamon rolls per day. Using
the midpoint method, the price elasticity of supply is a. 0.45 b. 0.90 c. 1.11 d. 2.20 ____ 18.
On a certain supply curve, one point is (quantity supplied = 200, price = $2.00) and
another point is (quantity supplied = 250, price = $2.50). Using the midpoint method, the price elasticity of supply is about a. 0.2. b. 0.5. c. 1.0. d. 2.5. ____ 19.
Which of the following statements is valid when supply is perfectly elastic at a price of $4?
a. The elasticity of supply approaches infinity.
b. The supply curve is vertical.
c. At a price below $4, quantity supplied is infinite.
d. At a price above $4, quantity supplied is zero. ____ 20.
If marijuana were legalized, it is likely that there would be an increase in the supply of
marijuana. Advocates of marijuana legalization argue that this would significantly reduce the amount of
revenue going to the criminal organizations that currently supply marijuana. These advocates believe that the
a. supply for marijuana is elastic.
b. demand for marijuana is elastic.
c. supply for marijuana is inelastic.
d. demand for marijuana is inelastic.




