











Preview text:
Preface
Since commerce was formed thousands of years ago, many concepts of
goods have been born, but for businesses the most used concept is "goods are
created to satisfy customer needs." products, thereby creating values for businesses.
Customer behavior is not a strange concept to businesses with the most basic steps
from when a customer "perceives a need" to "decides to buy". However, in the
process of moving up the hierarchy of Maslow's hierarchy of needs, there has been
a change in customer buying behavior. Typically, customers' post-purchase
feedback behavior. This not only determines whether customers will continue to use
the product in the future but also affects how businesses reach their potential
customers. Therefore, understanding the operating principles of customer buying
behavior is essential. All of the above reasons show that researching the topic of
factors affecting customers' purchasing decisions is very necessary. Research results
from the project "Some factors affecting instant foods buying behavior of HUFLIT
students" hope to help businesses understand which factors really affect customers'
buying decisions, thereby making recommendations. Appropriate strategies to
increase competitiveness in the market and develop. Abtract
The market is witnessing a shift in consumer preferences from home-cooked
foods to instant products, due to the busy lifestyles and hectic work schedules of
working people. This change in consumer behavior is likely to significantly enhance
the market under study during the forecast period. Instant food no longer seems
strange to everyone, especially familiar to students. This research aims to identify
the factors that influence the buying behavior of instant foods among HUFLIT
students. The article provides recommendations based on the theoretical model of
planned behavior, reference models from previous research articles and the use of
quantitative research methods. Information was selected and statistically analyzed
using SPSS software, and hypotheses were tested for reliability through regression
analysis. This study aims to determine the habits, needs, preferences and buying
behavior of HUFLIT students regarding instant foods. The research results evaluate
the consumption level of instant foods and help businesses have more basis to build
the right strategy to motivate consumers to buy more products, helping companies
also position their products. We rely on various factors, including product service,
quality, taste, price, functionality, size, packaging and marketing to gain a
competitive edge in the market.
Keywords: buying behavior, instant foods, shopping decision-making stage model, HUFLIT students. 1 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUTION 1.1 Rationable
In today's busy life and increasingly developing society, people's lives are
also increasingly improving. Therefore, consumers tend to use convenient products
that save time and costs. Instant food seems to have become an essential food for
every family. The most obvious advantages of instant food in a busy life are the
savings in time, cost and effort. prepare food every day. Instead of taking many
hours to prepare and cook, consumers only need the instant food such as cereal, pho
and noodles combined with eggs, vegetables, and meat depending on their
preferences, and consumers can have a meal right away. Eat a complete meal and
gain energy for the working day. Besides, instant foods are rich in both types and
flavors, making eating new and more interesting. In 2022, Vietnam ranks first in the
world in terms of instant noodle consumption per capita. Accordingly, each
Vietnamese person eats about 85 packs of noodles/year, corresponding to the
frequency of eating 1 pack every 4 days (Statistics of the World Instant Noodles
Association - WINA, May 2023) (Hà Thái, 2023)
Human buying behavior is very diverse and changes increasingly complex
due to increasing customer awareness and understanding. Their buying behavior is
also based on different habits and needs. Therefore, understanding customer buying
behavior is very important. Currently, instant food is a very popular food and is
favored by most consumers. Especially with easy-to-use and convenient features,
instant foods have been occupying a fairly high market share in the student
segment. The report predicts a revenue growth of 28 billion USD within six years
from 2020-2026, with an average annual growth rate of 6%. The instant noodle
business has potential for growth in domestic and global markets, with global
demand increasing by 3.45% in 2019 and 14.79% in 2020 due to the Covid-19
pandemic. However, quality issues are increasingly being paid attention to adapt to
the health needs of consumers. It is always necessary to focus on food safety and
hygiene through high quality standards. (Hà Thái, 2023) 2
Mr. Truong Nhat Khue Tuong - Nutrition, teacher teaching at Ho Chi Minh
City University of Medicine and Pharmacy said that almost all foods provide energy
value. Among them, instant foods such as instant noodles, cereals... are the foods
that mainly provide carbohydrates in meals. Especially for the busy lifestyle of low-
income people like students, instant food is their savior. If you know how to
combine instant foods with fruits, you can help make the meal more nutritious.
Regarding food safety, currently, large, reputable instant food manufacturers have
modern production processes and very strict quality control. They have their own
team of experts to improve processes and technology, making their products richer
in nutritional value. Manufacturers have provided many instant products, suitable
for many ages and needs of everyone. (Như Quỳnh, 2023)
Grasping this key point of the instant food market, the authors decided to
choose the topic "Factors affecting the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT
students" to learn about buying behavior. and product selection priorities regarding
quality issues with this popular market of consumers in general and students in
particular. Currently, on the market, instant food products are very diverse in quality
and type. Therefore, the author provides useful information for businesses to serve
the needs of customers. From there, propose solutions to continue to maintain its position in the market. 1.2 Research objectives
Researching consumer buying behavior is a very important issue in the
business activities of domestic and foreign enterprises. Furthermore, this research
also helps managers have more basis to build the right strategy to motivate
consumers to buy goods and services and bring value to businesses. This research
focuses on understanding the factors that affect the consumption behavior of
customers, specifically HUFLIT students. This study also addresses the needs,
interests, and habits of HUFLIT students.... From there, the research will provide
some suggestions and necessary information sources for manufacturers in
identifying "Instant food buying behavior" to build business strategies suitable to
consumer needs. consumption. Helps manufacturers position instant food products, 3
improve quality, diversify products to create better products to satisfy the increasing needs of consumers. 1.3 Scope
The research scope of this article is HUFLIT students. The scope of this
survey includes all students from 8 faculties (Faculty of Foreign Languages, Faculty
of Information Technology, Faculty of Oriental Languages and Cultures, Faculty of
International Relations, Faculty of Business Administration, Faculty of Tourism -
Hotel, Faculty of Economics - Finance, Faculty of Law) and 4 courses. 1.4 Research Methods
The research is divided into 2 phases as follows:
Qualitative research: from the initial goals and theoretical foundations, the
team hypothesizes factors that can impact customers' decisions to buy instant food.
After that, the group discussed with the topic instructor the influential factors that
the group proposed to complete the interview sheet to suit the actual survey. The
information collected will be used in the research pape Quantitative research:
This study uses a five level Likert scale (ranging from 1 to 5) 1-completely disagree 2-disagree 3-neutral 4-agree
5-completely agree (as a basis for establishing the design a survey questionnaire).
Survey method: survey questionnaire using Form - Google via social network
Facebook, Google email to send the link directly to take the survey. 4
The Cronbach's Alpha coefficient is used to evaluate the reliability of each
scale component, eliminating variables with miniature or inappropriate coefficients.
Cronbach's Alpha is an index that gauges internal consistency. A scale's consistency
is higher if it has a close positive correlation between observed variables. (Hoàng
Trọng & Mộng Ngọc, 2008)
The Cronbach's Alpha coefficient value indicates the quality of a
measurement scale, with values ranging:
From 0.8 to nearly 1 showing significantly good
From 0.7 to nearly 0.8 showing suitable/good use
0.6 or higher showing eligible use (Hoàng Trọng & Mộng Ngọc, 2008)
Analyze data using EFA exploratory factor analysis (Hoàng Trọng & Mộng Ngọc, 2008):
+ Bartlett's Test of Sphericity checks the correlation in the population (sig Barlett's Test < 0.05)
+ The KMO coefficient (Kaiser-Mayer-Olkin) is crucial for assessing the
appropriateness of EFA, with a value of 0.5 or higher.
+ The Eigenvalue index measures the variance explained by factors, with any
factor with an Eigenvalue greater than 1 being included in the analytical model.
(Hoàng Trọng & Mộng Ngọc, 2008)
Linear Regression analysis analyzes the correlation of influencing factors with
Huflit students' decision to buy instant food. A statistical method that considers the
relationship between the independent and dependent variables. T-test and Anova
analysis to evaluate the difference in Huflit students' decision to buy instant food.
(Hoàng Trọng & Mộng Ngọc, 2008) 5 1.5 Structure
Includes 5 chapters, concluding as follows:
Chapter 1: Introduction - Overview of the topic. Chapter 2: Literature Review. Chapter 3: Methodology
Chapter 4: Research results - Dicussion
Chapter 5: Conclusion and Suggesstions 6
CHAPTER 2: LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Concepts và definition 2.1.1. Buying behavior
According to Philip Kotler (2004), consumer buying behavior is defined as
"A complete set of actions that take place throughout the process from recognizing
the need until purchasing and post-purchase the product". In other terms, consumer
buying behavior refers to how individuals choose how to spend their available
resources (time, money, effort) on consumer products. Buyer satisfaction is influenced
by the alignment of initial expectations with the perceived performance of the product or
service. Buyer satisfaction is influenced by the alignment of initial expectations with
the perceived performance of the product or service. (Philip Kotler, 2004)
Consumer buying behavior is the entire all the actions displayed by
consumers during the product exchange process. These actions include
investigating, purchasing, using, evaluating, and spending on goods and services to
fulfill their needs. Basically, buying behavior refers to the decision-making process
that consumers engage in when using their assets such as money, time, and effort to
purchase and use goods and services to meet their personal needs. (Tuyết Nhi, 2019)
According to the American Marketing Association, Consumer buying
behavior refers to the thoughts, feelings, and actions that customers exhibit during
the consumption process. Factors such as opinions from other consumers,
advertising, price information, product appearance, and packaging can significantly
impact customers' buying behavior. Personal, social, cultural, and psychological
factors strongly influence consumer buys. Although these factors are beyond the
control of managers, they need to be analyzed carefully, and their effects on buyer behavior considered.
Consumer buying behavior is understood as "the mental, emotional and
physical activities that people engage in selecting, purchasing and using products
and services to satisfy desired needs". It involves purchasing, consumption, and 7
other activities involving participants in the exchange process. According to
Solomon, the term as “the study of the processes involved in individuals or groups
selecting, purchasing and using products, services, ideas, or experience to meet a desired need" (Solomon, 2006)
Consumer buying behavior involves awareness, information search, purchase
evaluation, post-purchase reactions, and consumer relationships. External factors
such as product quality, price, advertising, promotions, reviews, society, workers,
and the environment all influence it. This study focuses on consumers who have
purchased products or services, highlighting the dialectical system between the
process and external factors. The study aims to understand how these factors impact
consumers' thoughts, feelings, and buying decisions.
2.1.2 Consumer decision making process
According to Philip Kotler, the customer's product purchasing decision
process includes 5 basic steps:
Needs Awareness: The buying decision is influenced by the customer's
perception of the product's use value, which can be influenced by both internal and
external factors. (Philip Kotler, 2004)
Information Search: When the need to possess use value arises, customers'
other needs, such as understanding and experiencing the product, also arise, thereby
motivating them to seek information about the product. (Philip Kotler, 2004)
Evaluating alternatives: Customers often organize information sources
collected in a specific manner in a quick group survey:
+ Personal experience: Customers rely on their experience and observations
of the product as their primary source of information when using it.
+ Feedback from acquaintances: People often consult their relatives after
obtaining information, which significantly influences their decision to continue
using a product or not. (Philip Kotler, 2004) 8
Purchase decision: Customers evaluate brands and form purchasing
intentions, but their decisions can be influenced by influential people's negative
feedback or unexpected factors. (Philip Kotler, 2004)
Post-purchase: Customers immediately respond to a purchase if the product
meets their needs, often contacting the supplier for help or complaints. If issues
aren't resolved, they may turn away or leave, causing negative feedback.
Satisfaction creates a positive image, leading to repeat shopping behavior.
Customers also act as ambassadors, connecting businesses with potential customers. (Philip Kotler, 2004)
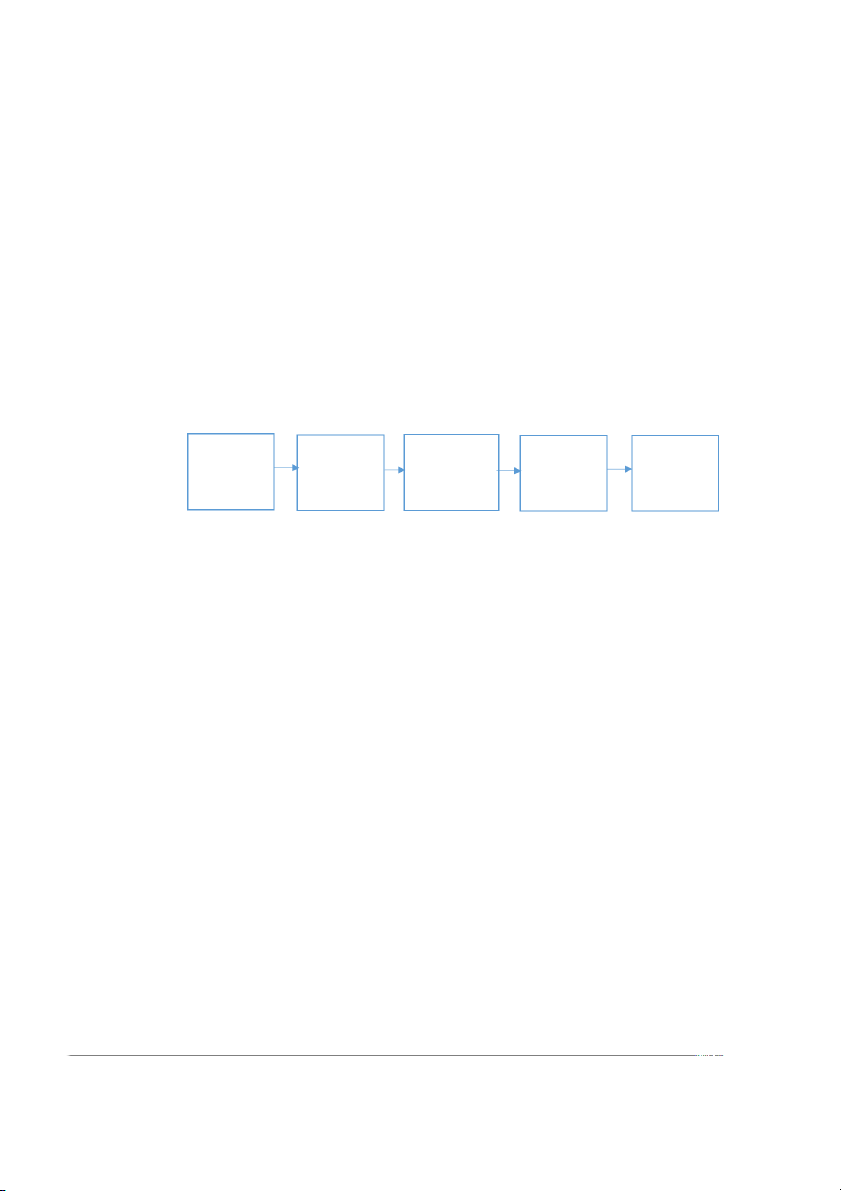
Figure 2.1: Stages of the Consumer Decision Making Process Needs Informatio- Evaluating Purchase Post- Awareness n Search Alternatives Decision Purchase (Philip Kotler, 2004)
2.2. Theoretical framework
2.2.1. Theory of Reasoned Action – TRA
The Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) is a psychological model that
suggests that behavioral intention is influenced by beliefs about the likelihood of a
particular behavior leading to a specific outcome. These beliefs are divided into
behavior and norms, with behavioral beliefs influencing an individual's attitude
towards behavior performance and normative beliefs influencing their subjective
norms. The TRA is widely used to predict behavioral intentions and strategies for
behavior change, with a recent extension, the theory of planned behavior,
incorporating perceived behavioral control as a prerequisite. (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) 9
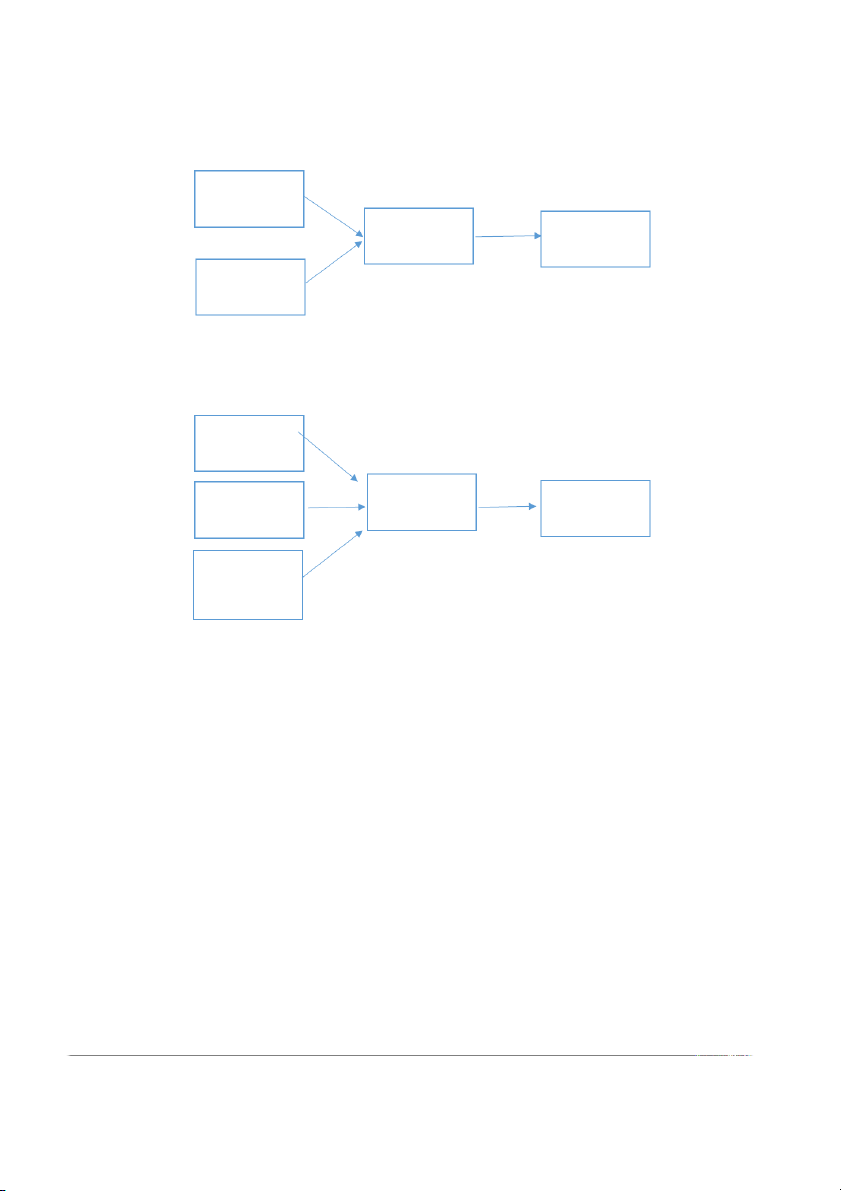
Figure 2.2 The Theory of Reasoned Action (Fishbein & Ajzen, 1975) Attitude Behavioral Intention Behavior Subject Norm
2.2.2 Theory of Planned Behavior – TPB (Proposed reasearch model)
Figure 2.3 The Theory of Planned Behavior Attitude Behavioral Subject Norm Intention Behavior Perceived Behavioral Control (Sources: (Ajzen, 1991))
The Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), introduced in 1991 by Icek Ajzen,
enhances the predictive power of the Theory of Action by highlighting the influence
of attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control on behavioral
intentions. TPB overcomes the limitations of the Theory of Action in explaining
customer behavior, with research showing that perceived behavioral control
positively affects repeat purchase intention. (Philip Kotler, 2004) 10
2.3 Reference research model
Proposed research model on "Factors affecting customers' non-carbonated
beverage consumption behavior in Ho Chi Minh City" by Tran Thi Loan - 2014.
Figure 2.4. Model "Factors affecting non-carbonated beverage consumption
behavior of customers in Ho Chi Minh City" Quality Price Productive Availability Consumer Behavior Health Safety Concerns Faith Health consciousness 11
Proposed research model "Analyzing factors affecting customers' instant
noodle buying behavior in Ho Chi Minh City" by Pham Thi Tu Linh in 2016.
Figure 2.5 Model "Analyzing factors affecting customers' instant noodle
buying behavior in Ho Chi Minh City" Price Distribution Channel Feature of Product Buying Behavior Health Safety Brand Marketing 12
Proposed research model "Factors affecting the decision to buy Trung Nguyen
coffee powder in Ho Chi Minh City" by Nguyen Quoc Viet in 2016
Figure 2.6 Model "Factors affecting the decision to buy Trung Nguyen coffee
powder in Ho Chi Minh City" by Nguyen Quoc Viet in 2016 Quality of Product Price Location Decide to buy Promotion Coffee Taste Culture 13
2.4 Research model and hypothesis 2.4.1 Research model
From the theoretical basis of customer behavior and referring to the above
models. The research team has built the model "Some factors affecting instant foods
buying behavior of HUFLIT students”. Include 5 factors: Price, Brand, Product
Quality, Health Safety, Distribution Channel. This is a reasarch model:
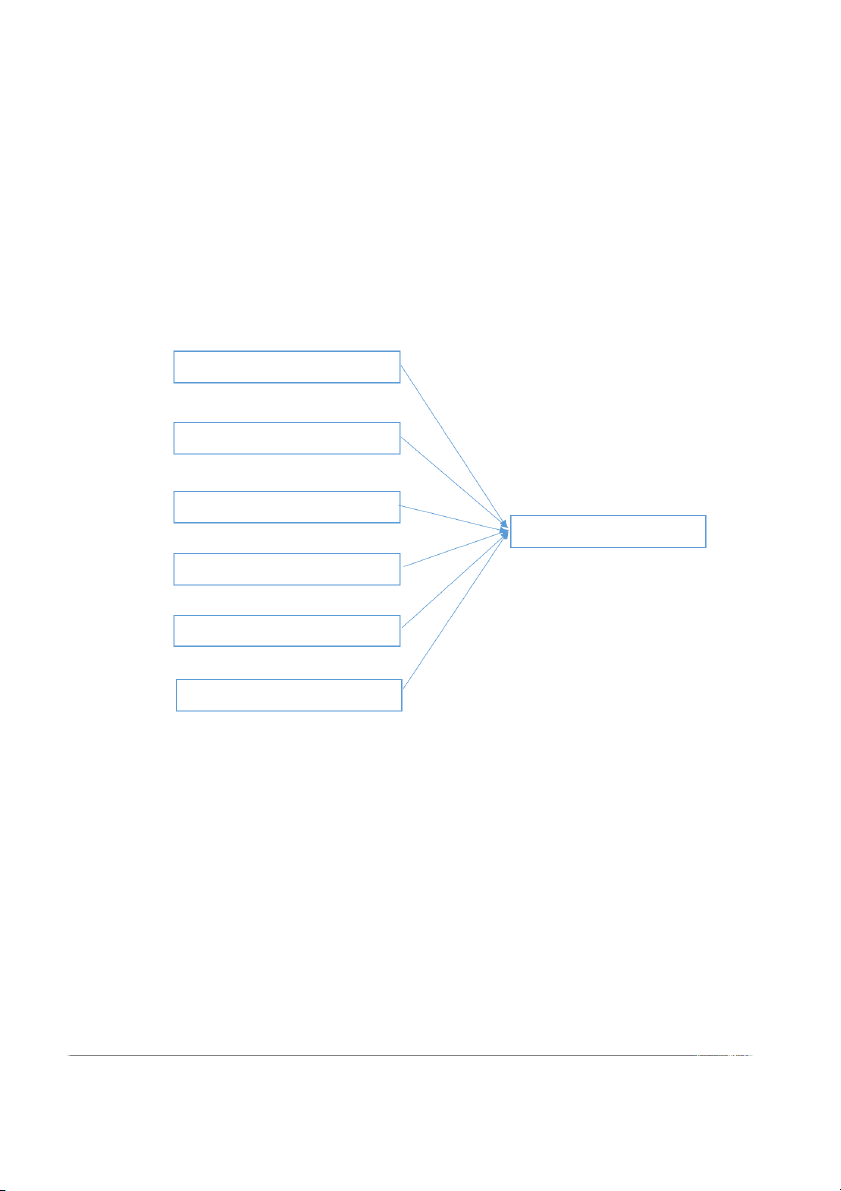
Figure 2.7. Model "Some factors affecting instant foods buying behavior of HUFLIT students" Price H1 H2 Brand Some factors H3 affecting instant food Product Quality buying behavior of HUFLIT students H4 Health Safety H5 Distribution Channel (make by author) 14 *Note:
Independent variable (x): Factors (Price, Brand, Product quality, Health safety, Distribution channel)
Dependent variable(y): Buying behavior of instant food of HUFLIT students
2.4.2 Research hypothesis
Propose the following hypothesis based on the literature analysis and propose an idea description:
H1: Product price affect the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT students
H2: Brand affect the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT students
H3: Product quality affect the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT students
H4: Health safety affect the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT students
H5: Distribution channels affect the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT students
The author uses theoretical models and reference models from their studies
on buying behavior to develop research models and hypotheses. A research
hypothesis provides a theoretical framework for the research process, leading to the
formulation of specific assumptions and proposed methods to test it. It limits the
study's scope and directs research questions. Once the hypothesis is determined,
data is collected and appropriate research methods are used to test it. The results are
based on accepting or rejecting the initial hypothesis and making scientifically
based assertions. A research hypothesis is a preliminary assumption about the
nature of things or the relationship between research variables, not an absolute truth.
Through research and data analysis, the author proves or disproves the hypothesis,
generating new conclusions and recommendations. 15 CHAP 3: METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research information
Official information for research includes:
Information on factors affecting the instant food buying behavior of HUFLIT
students. Includes a scale with 5 independent factors: Price, Brand, Product Quality,
Health Safety, Distribution Channel. Dependent factor is "Buying Behavior".
Information on students' attitudes toward purchasing decisions "Instant foods".
Personal information: Age, gender, frequency of use, personal income, etc. 3.2 Research Process
Based on the initial theoretical basis, research topic and preliminary research
to build a scale and conduct quantitative research using questionnaire surveys. From
the collected information, statistics and data analysis are conducted. The procedure is as follows: 16
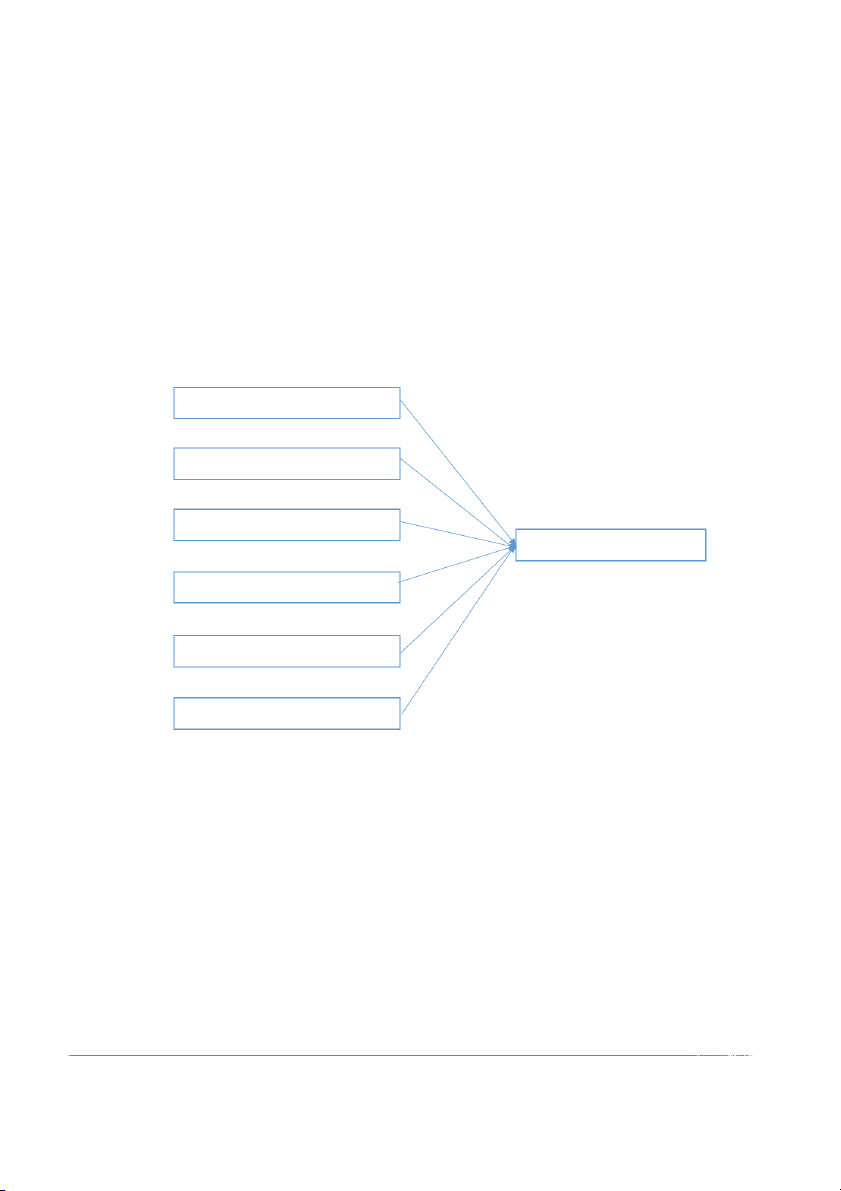
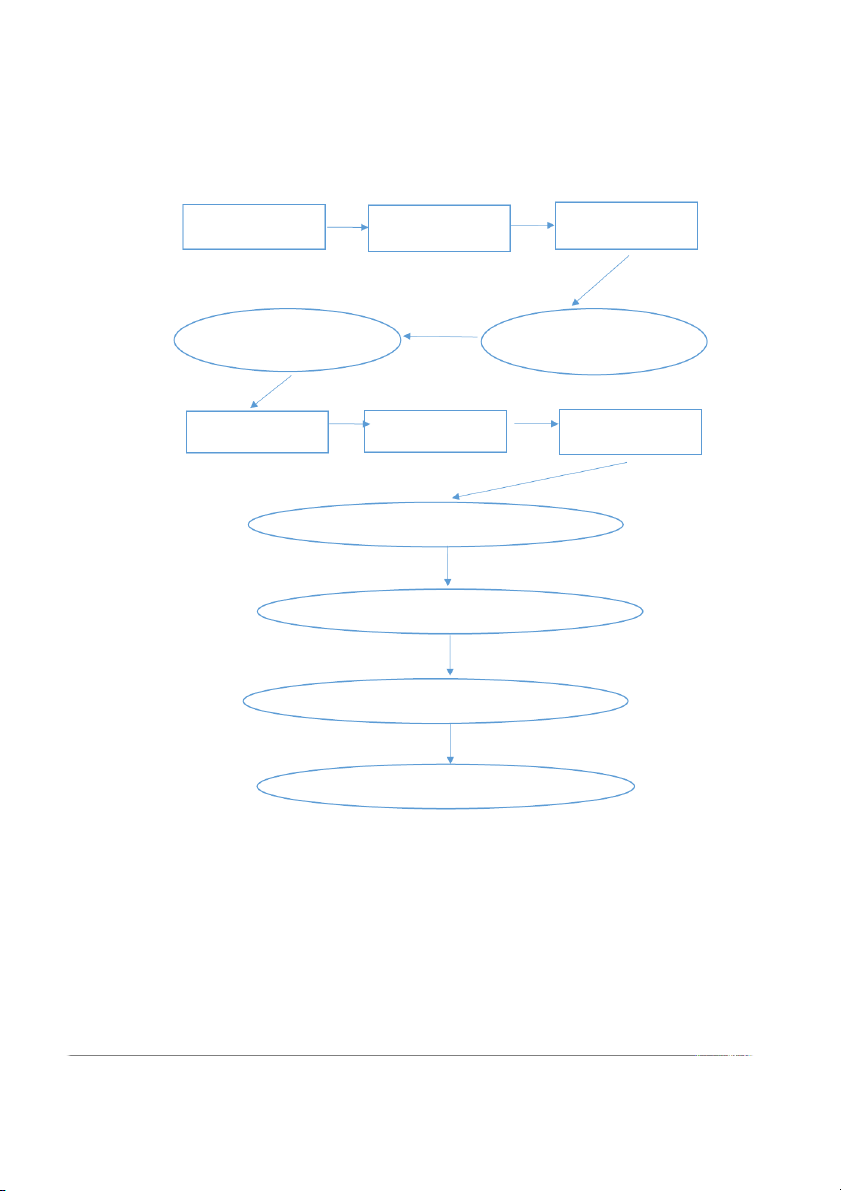
Figure 3.1 Research Process Purposes of the Theoretical ground Qualitative research research Primary survey Presented measuring scale Quantitative Alter draft scale Official scale research
Cronbach's Alpha reliability test EFA ANOVA, regression analysis Write research reports Source: Make by author 17
First, the research group will discuss factors affecting HUFLIT students'
decision to buy instant food. Secondary information source: is a source of
information obtained from survey data after they have been synthesized and
processed to meet the research objectives. The survey questionnaire was conducted
using Google forms, an online questionnaire used to survey interview participants
and was recalled after a period of time to ensure the level and quality of the survey. 3.3 Research design 3.3.1 Measurement scale
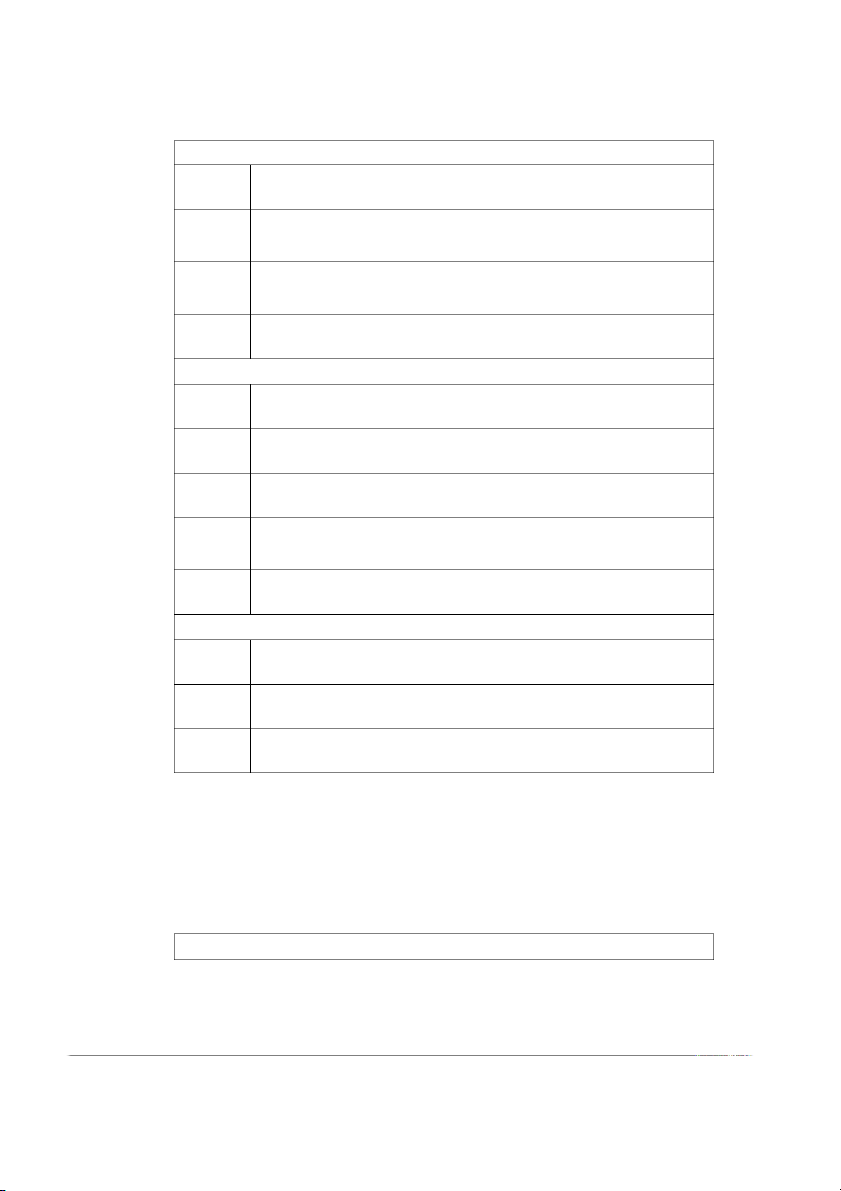
Table 3.1: Proposed scale for factors Symbol Observed variables Price P1
I tend to regard the price of the product when deciding to buy
I intend to select a different product that is less expensive but still P2
maintains a similar level of quality
I intend to use another product if the price of my favorite product P3 increases P4
I intend to pick products with more coupons Brand B1
The product is chosen due to the brand's reputation B2
The product is chosen due to its association with my preferred brand B3
The product is chosen as I had first remembered the brand B4
My family and I consistently prioritize using this product B5
The product is chosen due to its popularity in the market Product Quality 18 PQ1
The product is chosen due to its appealing taste.
I choose the product due to my curiosity about the taste of the new PQ2 product.
The product is chosen due to its visually appealing and beautiful PQ3 packaging. PQ4
The product is chosen because of its convenience and comfort of use Healthy Safety HS1
I was anxious about protecting my health while consuming instant foods HS2
I intent to choose products that are considered safe for one's health HS3
I was anxious about the product causing an increase in body heat
I was anxious about the quality and composition of the ingredients used HS4 in the product HS5
I don't intend to use instant food if it's not essential Distribution Channel DC1
I can efficiently buy instant foods from many stores DC2
I bought the product as I caught it on the top shelf DC3
I bought the instant food as it was conveniently located near my university Buying Behavior




