










Preview text:
BỘ GIÁO DỤC VÀ ĐÀO TẠO
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC HOA SEN
KHOA KINH TẾ VÀ QUẢN TRỊ SUBJECT REPORT CHANGE MANAGEMENT TOPIC
The change of Vinfast business Lớp: Change management
Giảng viên hướng dẫn: Bùi Thị Vân Quỳnh Thành viên thực hiện:
Nguyễn Ngọc Yến Nhi-22001165
Nguyễn Tường Nhân-22000442 Nguyễn Trung Dũng-2175241 Lê Vĩ Khang-22002730 Nguyễn Thu Ngân-22012357 Nguyễn Tống Phong-22008244 Nguyễn Đức Nhân 22003473 MỤC LỤC
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY.........................................................................3
CHAPTER 1 - RATIONALE FOR CHANGE THROUGH MODELS
OF CHANGE AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION................................4 1.1.
DEFINITION..............................................................................................................4 1.2.
8 STEPS CHANGE MODEL OF JOHN KOTTER’S AND 3 STEPS OF KURT
LEWIN....................................................................................................................................5 1.3.
ADVANGTAGES AND DISADVANGTAGES.........................................................8
CHAPTER 2 - RATIONALE FOR CHANGE THROUGH MODELS
OF CHANGE AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION...............................11 2.1
VINFAST BACKGROUND.....................................................................................11 2.2
VINFAST THE SITUATION OF THE CHANGE FROM THE ORIGINAL.....15 3.1
Comments and evaluations:.....................................................................................19
3.2 Proposing a complete solution:......................................................................................19
Bibliographic references:..........................................................................21 2 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Change initiatives are expensive and time-consuming. They
have a significant impact on the motivation of an
organization with a vision towards success. Andal of them
ended up failing. As is well known , change is inevitable and
therefore, organizations must learn to sustain and adapt to change.
In all organizations, strategic changes are brought about
because of projects and programs. Successful businesses
can quickly adapt to change through effective management
of their programs and projects.
The nature of change in the business, in supporting the
creation of change is to implement the organization's
strategies successfully , forcing businesses to require
program and project managers who are skilled in driving
and navigating change. in accordance with the original goal.
They do this while ensuring that the changes are
strategically aligned with the goals of the business. Since a
change initiative fails or succeeds, it is not just because of
the start, implementation, but it involves evaluating,
monitoring, or planning the project that drives the change.
Change is inevitable, and therefore organizations that can
effectively manage it, have the potential to transcend the
formulas they apply to their business 3
CHAPTER 1 - RATIONALE FOR CHANGE THROUGH MODELS OF CHANGE AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION 1.1. DEFINITION
Change means to make the form, nature, content, future, course, etc.…
of something different from what it is or from what it would be if left
alone. Change management: Is a set of strategies, processes, and
procedures companies use to manage organizational changes involving
people. Refers to a set of basic tools or structures intended to keep any
change effort under control. Is a systematic approach to dealing with
the transition or transformation of an organization’s goal, prosses or
technologies. Is the overarching approach take in an organization to
move from the current to a future desirable state using a coordinated
and structured approach in collaboration with stakeholders. What is transition?
Transition is redefining what something is the current state. It being by
first assessing the present to the desired future. Change does not happen
instantaneously, and the effect of change can only be seen after a certain
time so that the organization learns how to fulfill the necessary conditions
to achieve the vision of the future. A shift in behavior A shift in values
Change is doing things differently.
Transition is a new way of being. 4 1.2.
8 STEPS CHANGE MODEL OF JOHN KOTTER’S AND 3 STEPS OF KURT LEWIN
JOHN KOTTER’S 8-STEPS CHANGE MODEL
John Kotter developed his model of change after observing many
leaders and organizations before, during, and after the transition.
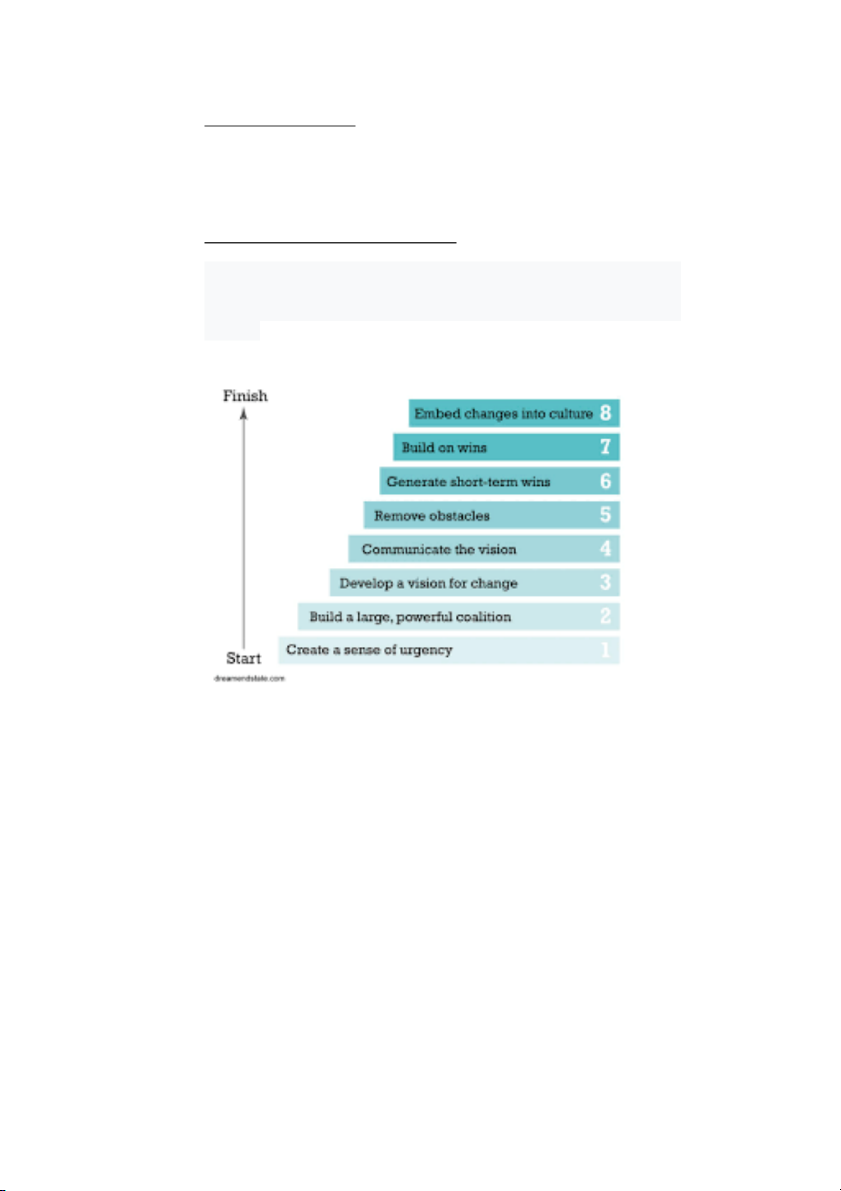
Kotter's model breaks down organizational change into eight steps: -
Step 1: Create a sense of urgency
For change to happen, every member of the company must truly
understand the need for change, have a sense of urgency about this
change so that the company can thrive. Step 2:
Build a large, powerful coalition
To succeed in the coming change, we will need allies and
stakeholders. Having supportive leadership and management
members creates strong pervasive support throughout the organization.
Step 3: Develop a vision for change
When we think about the change needed, we can have a lot of ideas
and solutions going around. Link these ideas and solutions together
into a clear and understandable vision that can be easily remembered
by everyone. A clear vision helps people understand why we want to
make a change, why they need to do something. Step 4:
Communicate the vision
The way of the vision is communicated will determine to the success
of the change. Its usually use multiple channels and models of
communication to explain the vision often and strongly through repeating every opportunity. Step 5:
Remove obstacles
By the time we get to this step, , things do not always go so smoothly
as you think it’s different between reality and theory, there will be
individuals who are resistant to change, or there are certain processes
that are hindering successful change. To stay motivated, we must actively remove obstacles. Step 6:
Generate short-term wins
Nothing is more motivating than seeing results that are worth the
effort the whole organization put in. Every time a small goal is 5
achieved, create a sense of success and victory for employees. This
will motivate them also allow individuals who are skeptical or
opposed to change to see our vision. 6 Step 7: Build on wins
Feelings of victory and short-term success are not enough to sustain
change. Sometimes this factor can deceive us that the change process
is complete, but we must continue to build and work on the next goals. Step 8:
Embed changes into culture
Ultimately, for the change to be complete, it must become part of the
company's corporate culture. Otherwise, over time people can easily
forget the change, losing the impact of both the quick and easy process. Hình 1.
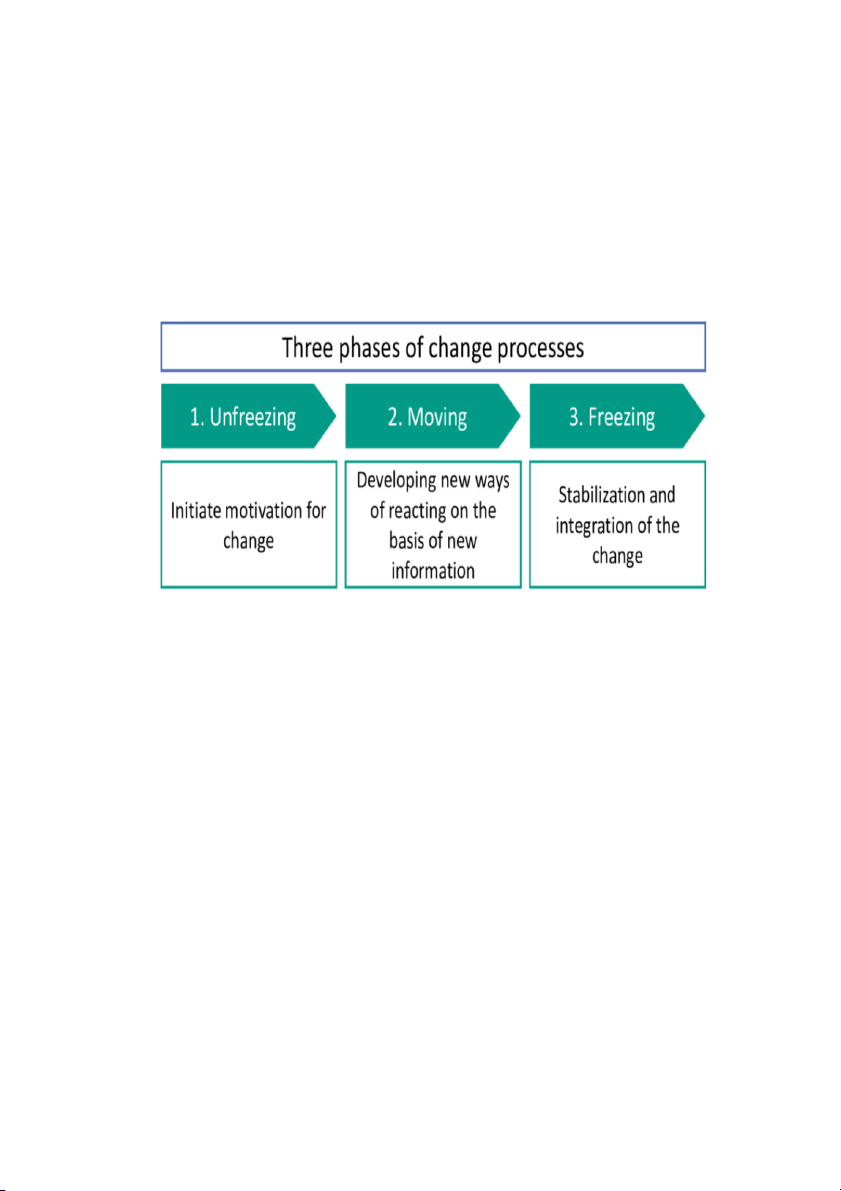
Kurt Lewin’s three-step change model
Kurt Lewin's change model is a model that represents organizational
change: creating awareness that change is needed, moving to a new
level of behavior, reinforcing the new behavior into the norm.
Kurt Lewin's model of change consists of three steps: unfreezing,
changing, and refreezing. This is a very simple and practical model 7
for understanding organizational change. Kurt Lewin's model of
change is still widely used today and forms the basis of many modern change models.
Step 1: Unfreezing
Since many people will be resistant to change, the goal of this stage
is to create the perception that the current situation is hindering the
growth of the organization. Old behaviors, ways of thinking,
processes, people, and organizational structures must all be carefully
examined to show employees the need for change to the organization
to create or maintain. competitive advantage in the market.
Communication is especially important during this stage, so that
employees are informed of the impending change, the reasons for the
change, and the benefits it will bring to each employee. The reason is
that the more people know about a change, the more necessary and
urgent people will feel about it, and the more motivated they will be to accept the change. Step 2: Changing
Lewin recognized that change is a process in which an organization
must transform or transition to a new state. This is when the change
becomes a reality. Therefore, this is also the time when most people
struggle with the new reality. This is a time filled with uncertainty
and fear, and therefore the most difficult step to take. In the change
step, people begin to learn new behaviors, processes, and ways of
thinking. Throughout this process, employees should be reminded of
the reasons for the change and how they will benefit them once fully implemented.
Step 3: Unfreezing
Lewin calls the final stage of his change model freezing, but many
calls it refreezing to symbolize consolidating and stabilizing the new 8
state after the change. Lewin finds this step especially important to
ensure that people don't fall back to old ways of thinking or doing
things before making the change. The organization shall make every
effort to ensure that change does not disappear; rather, it needs to be
embedded in the organization's culture and maintained as an
accepted way of thinking or behaving. Organizations often use
rewards to reward individual efforts to reinforce the new status quo;
because it is believed that people tend to repeat behaviors that receive positive feedback. 1.3.
ADVANGTAGES AND DISADVANGTAGES
John Kotter’s change model advantages & disadvantages: Advantages:
Kotter's theory is drawn from the study of changes that occur with
the subject of research being businesses in the US. Therefore, this
doctrine of a series of 8 action steps is very useful for businesses,
helping to support the successful process of strategic change. The
advantage of Kotter's theory is that it is people-centered, people in
his theory play an active role, which is clearly shown in the 9
empowerment step. The theory shows details and specific steps in
accordance with big and complex changes in the enterprise.
Here are some other outstanding advantages of the Kotter doctrine:
- Create urgency to form a consensus among employees in the
organization, making them want to change and willing to contribute.
On the other hand, creating urgency is creating motivation for the
seeds of change to appear in the organization, to assess the current
situation and competitive environment in the market, besides,
businesses also identify opportunities. its business in the market and
the challenges that the business must go through.
- Establishing a guiding group is to create a sense of solidarity and
coordination among members of the organization. Because one
individual can hardly make a big change.
- In the development of vision and strategy, Kotter helped businesses
define their own prospects. It is the vision that will make individuals
work together effectively, managers and employees can take
initiative in their work, making business operations smoother and faster.
- Communicate the vision: If the vision helps to overcome inertia, then
communicating the vision will help this spread among all members of the business.
- Maximum empowerment will stimulate the development of
managers, the ability to exercise more autonomy, so the work is done
faster. For lower-level employees, empowerment will create
conditions for them to develop, thereby motivating and stimulating
them to work better, while for upper-level managers, empowering
enables them to focus on strategic issue.
- Large-scale change takes a long time, so there needs to be
convincing evidence that efforts will pay off. Understanding this,
Professor Kotter introduced the sixth step "Creating short-term
wins". This step helps to create morale and motivation among
employees, maintain the support of senior leaders, and evidence that change is on the right track.
- Any change becomes solid only when it penetrates deeply into the
behavior and attitude of all employees and permeates into the
company culture. This is the advantage of the 8th step of the Kotter model. Disadvantages:
- Besides the advantages, there are disadvantages in the steps of the
theory that are the steps in this model must follow its sequence, the 10
requirements in each step must be resolved definitively. Many steps
can take place at the same time, but just skipping a step, or a step
that has not been completely resolved, the business can be in trouble.
Another disadvantage is that this theory is only suitable for large-
scale changes or changes of a complex nature.
- Creating urgency has a disadvantage that increasing urgency requires
taking risks and creating high pressure at work, causing instability,
and creating more difficulties for businesses.
- A guiding group is a group of people who work well together and
trust each other to bring success. However, forming such a group is
not an easy thing because of personal conflicts of interest and it takes
time to find the right people for this guiding group.
- Setting a vision is always a difficult, complex, and sometimes
emotional affair. Establishing a vision requires mind and heart, and
this can take a long time and involve a lot of people. On the other
hand, the vision becomes worthless if the organization does not understand it.
- Forming and developing a vision is difficult, communicating a vision
is even more difficult. Not everyone can fully and consistently
communicate the vision so that everyone in the organization has the
same understanding of its meaning and direction.
- Empowerment has many benefits, but it's also one that confuses
leaders. The question for them is to whom to empower and whether
these people can take over the assigned authority or not. When
giving authority to subordinates, one must trust and accept the failure
of the subordinate when the subordinate is incompetent.
- Creating short-term wins can take away the urgency that the business
tried to create in the first step. If stopped before a job is completely
completed, all previous efforts may disappear and the business. may
also have to start from scratch.
- Organizational culture has been formed for many years,
consolidated, maintained, and developed through many generations
of members of the enterprise. All members implicitly acknowledge
cultural values and are very reluctant to change to other
organizational cultures. new value. So, changing it takes time and the
process can be bumpy. The longer the business operates, the more
sustainable these factors become. It is accepted by default and
becomes a habit of everyone, so changing corporate culture is not easy.
- Sufficient time is needed to complete the entire change plan because
“Skipping a few steps will only create the illusion of speed and will
never produce satisfactory results. Make serious mistakes at any
stage. Any stage can have a destructive effect, slowing growth, and negating hard-won gains.” 11
Kurt Lewin’s change model advantages & disadvantages: Advantages: - Easy to understand:
+ Some ever-changing frameworks can take a long time to learn, and
it's easy to get lost in a sea of acronyms. Lewin's theory of change is
straightforward and divided into three main phases, each with several
steps. Force field analysis in Lewin's model of change is also a
simple concept that anyone can easily understand and apply immediately. - It focuses on behavior.
+ Behavioral psychology used in Kurt Lewin's model of change
focuses on what makes people resist or support change. This human-
centered focus is indeed consistent with many other change models
that also focus on the human element of change. - Models create feel
+ If you look at Kurt Lewin's change model, the logic of unfreezing,
changing, and refreezing makes sense to a lot of people. Its
simplicity helps people better understand change management in
general without getting bogged down in a lot of industry jargon or complicated steps. Disadvantages:
Kurt Lewin's change model is not detailed enough Some feel that
Lewin's change management model is a bit simplistic. The steps in
each phase can be interpreted in different ways. Often a different
change management model is required to "fill in the gaps". Kurt
Lewin's model of change is too rigid and does not reflect modern the
frozen phase of the Kurt Lewin model is sometimes scrutinized by
those who consider it too rigid, because its "freezes" behavior that
only needs to be unfrozen soon due to rapid technological progress.
It causes companies to constantly change to keep up with trends.
They believe that the last stage should be more flexible. People think
that Kurt Lewin's theory of change is a bit outdated. It was created 12
with comparisons to Max Weber in 1947, long before the technology
became a core part of today's workplace. Kurt Lewin's model of
change can be seen as combative rather than nurturing Lewin's three-
step model emphasizes the breaking of equilibrium during thawing,
which is essentially "wobbly" and can be seen as aggressive. Some
argue that instead of creating favorable and unfavorable
environments for change, Lewin's model of change focuses too much
on two opposing forces competing for advantage. -
CHAPTER 2 - RATIONALE FOR CHANGE THROUGH MODELS
OF CHANGE AND PRACTICAL APPLICATION 2.1VINFAST BACKGROUND About Vinfast company:
About Vin fast:-VinFast has the full name of Vin Fast Trading and
Service Business Co., Ltd., is 1 manufacturer of cars and electric
motorcycles in Vietnam established in 2017.- The head office of this
enterprise is located in Hai Phong with Ms. Le Thanh Hai as managing
director. This company is a member of Vin group created by billionaire
Pham Nhat Vuong, one of the largest multidisciplinary private economic groups in Asia.
- With the philosophy of "Customer is the center", VinFast is constantly
innovating to create high-class products with the best prices and
outstanding after-sales service, bringing opportunities to use smart
electric vehicles for everyone, contributing to creating a green, smart and sustainable future.
. The meaning behind the brand name Vin fast:-The brand name VinFast
is what makes many people feel curious about the meaning behind it.
Some people mistakenly believe that the word Fast in the brand name
refers to the speed of the car. But in fact, that meaning is not the true
meaning of this brand name.-VinFast is the company name abbreviated from the phrase "
VIETNAM – STYLE SAFE – CREA – TIVE PIONEER – ". The
meaning of this name is to express the aspirations to bring Vietnamese
brands to the international community through the production of cars.
Vin Group wants to contribute to creating motivation and promoting
heavy industry, manufacturing industry, and supporting industries in
Vietnam to have development opportunities. 13 Meaning of Vin Fast logo:
If you look closely, VinFast’s logo is made up of 3 consecutive V-lines. The
meaning of the VinFast logo is to represent Vietnam, Vingroup and Rise.
Before being selected to use a stylized V-shaped logo, VinFast has
continuously edited the logo design thought. Its logo was built by 2 famous studios in the world. 14 Vin fast goals:
- VINFAST's goal is to become the leading automobile manufacturer in
Southeast Asia with a design capacity of up to 500,000 vehicles per year
by 2025, the main products are internal combustion engine cars, electric
motor cars and environmentally friendly electric motorcycles. Vinfast luxA2.0
-The entire production process is located at VINFAST Hai Phong
Factory, with a scale of 335 hectares, including 5 main workshops:
Pressing workshop; Body workshop; Paint workshop; Engine
factory; Assembly workshop. Important components such as engines
and main structural systems will be purchased from leading European
and American designers. Particularly, the car design is created by the
famous Italian studio – where luxury designs for Alfa Romeo, Aston
Martin, Audi, Bentley, BMW, Cadillac, Ferrari, Jaguar, Lamborghini,
Mercedes-Benz, Porsche, Rolls-Royce ... 15 Vinfast Lux SA2.0
-With the policy of being ahead of technology and environmentally
friendly, VINFAST will apply the world's most modern technology to
production, ensuring strict emission standards Euro 5.0 and Euro 6.0; at the
same time, prioritize the use of green energy in the production process at
the factory. The company also actively invests in used battery and battery
treatment lines to protect the environment. With rapid progress, VinFast has
launched automotive product lines: VinFast Fadil, Lux A2.0, Lux SA2.0.
Electric car VF8, VF e34,... Quickly dominate the market & be trusted by
Vietnamese people. In addition, Vinfast also develops environmentally
friendly electric motorcycles: Felix S, Klara S, Vento S,...
Felix S Electric Motorcycle Klara S 16
Vinfast's vision and mission: - Vision "To become a smart electric
vehicle brand that strongly promotes the global electric vehicle
revolution".- Mission "For a green future for everyone". 2.2
VINFAST THE SITUATION OF THE CHANGE FROM THE ORIGINAL
The situation of the change compared to the original of VINFAST company
Compared to the beginning, Vinfast only focused on gasoline-powered
cars, but VinFast has now switched from gasoline cars to electric cars and
is very successful. As of recently on 15-7, VinFast Trading and Service
Co., Ltd. announced to stop trading gasoline cars.The statement came after a
representative of the Vietnamese car company said that the last batch of Lux
and Fadhil cars had been ordered by customers. "From now until the end of
August, the company will focus on production to hand over vehicles to
contracted customers, and completely convert to producing and trading
electric vehicles," the representative said. According to the representative of
this unit, the stopping of gasoline car business took place earlier than
planned due to a sudden increase in the number of customers ordering the
above cars over the past time. “These models are always in the top of the
most popular options in the market by segment, receiving the trust and
support of a large number of customers. After producing enough vehicles to
pay the signed orders, we will officially close the gasoline car line to switch
to focusing exclusively on electric vehicle production. The representative
also emphasized that stopping the production and sale of gasoline cars will
not affect the commitments on the quality of service that the company
provides to customers. Specifically, the company has increased the genuine
warranty period for all car models to 10 years, deployed more utility
services such as Mobile Service, expanded the network of service
workshops nationwide, and prepared 1.5 times more components than the
market practice, ensure repair and maintenance until the end of the vehicle
life cycle."Customers who own our gasoline cars can also easily convert to
electric vehicles and receive an additional support of VND 30 million
through the VinFast Customer Care program," he added. The company also
said that it is promoting the construction of a system of 150,000 charging
ports for electric cars and motorcycles nationwide in 2022, thereby
completing the green mobility ecosystem in Vietnam.According to experts,
with the official cessation of production and trading of gasoline cars soon,
VinFast will become the pioneer pure electric car company in the
Vietnamese market, participating in strongly promoting the electric vehicle
revolution globally.Earlier, on 6-1, at the world's largest consumer
electronics exhibition CES 2022, VinFast officially announced its plan to
completely stop the production of gasoline cars to switch to electric cars by 17
the end of this year.This decision makes the Vietnamese car company one of
the pioneers in the world to abandon internal combustion engines and lead
the trend of switching to electric vehicles that is taking place strongly
globally. Along with the decision to stop producing gasoline cars, the
company has announced a new range of electric cars including 5 models VF
5, VF 6, VF 7, VF 8, VF 9 in all segments A-B-C-D-E. "To date, we have
received more than 73,000. globally for electric car models. It is expected
that two global models VF 8 and VF 9 will be handed over to customers by
the end of this year," the representative of this unit said. In Vietnam, VinFast
has started handing over the first electric car model VF e34 from the end of
2021. By the end of June, more than 2,200 VF e34s had reached customers,
in the context of the company facing many objective difficulties from the
disruption of the global component supply chain. Especially recently on
16/11/2022 – VinFast officially opened its first VinFast Store at Yorkdale
Trade Center, Toronto, Canada. Vinfast started from 2017 to 2019 to prove
to everyone that its vision is right and then Vinfast has received positive
feedback. In 2019, a total of more than 17,000 cars and 50,000 VinFast
electric motorcycles were ordered in the past year. Based on VinFast data,
for 4 electric motorcycle models: Klara, Klara S, Impes and Ludo, VinFast
has produced 45,118 vehicles, while orders have reached 50,000 vehicles.
The total order that VinFast has received for all three car models including
Fadil, LUX A2.0 and LUX SA2.0 is 17,214 units, of which the company
has only produced 15,300 cars. If combined with the sales data of car
manufacturers announced by VAMA and TC MOTOR a few days ago, the
total number of cars sold in the whole Vietnamese market in 2019 reached
417,190 units. In terms of market share, VinFast accounts for 3.66%, a
very modest figure, but remember that this is only the figure of the second
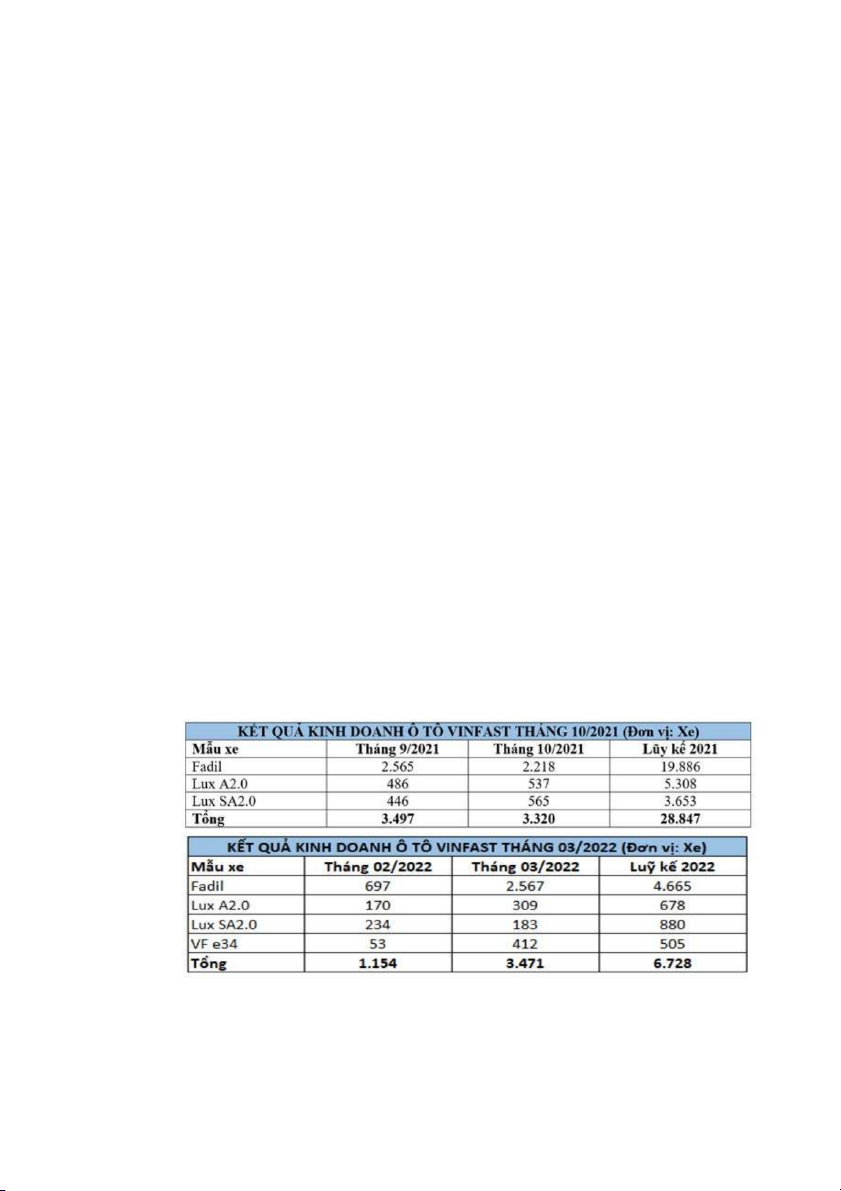
half of 2019. Here are the automotive business results of VinFast:
VinFast in October 2021 and March 2022: 18
Looking at it, it can be seen that the number of cars in March 2022
decreased significantly compared to March 2021 by 76% and in 2022,
VinFast was able to solve the problem of lack of components of VF e34 cars. 2.3 ANALYZE
Since its establishment, VinFast's vision has been set to become a
global smart electric car company as the world gradually moves to the
technological and digital era, electric cars are also produced more,
notably the electric car company Tesla developed extremely strongly
when Tesla's sales increased from 50,580 units (in 2015) to 76,230 cars
(in 2016) ... VinFast's petro cars were born, loved and really fulfilled
the mission of getting acquainted with the market. If VinFast only
produces petro cars, there are now many well-developed and long-
standing gasoline car manufacturers in the world such as Toyota,
Hyundai, Mercedes ... Therefore, VinFast is very difficult to compete
fairly with these car manufacturers because there is no reason why
customers are willing to choose a new, less famous car company in the
market like VinFast.Only when the whole industry changes its core
technology will there be an opportunity for newcomers to enter and
capture market share. Especially, VinFast's orientation is to "hit the
world market", not only Vietnam. So from the first day, VinFast's
orientation was electric cars, with the first electric motorcycle products
being well appreciated. To enter the market and win a piece of the pie,
it takes huge resources to compete with businesses that have
accumulated for a long time. For example, the mobile market was
previously dominated by Nokia, only when the market develops to
touch smartphones, businesses can have the opportunity to grow
dramatically.Before Vingroup officially entered the car market, the US
and EU governments planned a vision of 2030 to completely abandon
the production of fossil fuel cars. So VinFast's abandonment of
gasoline cars is definitely happening to catch up with the industry
market.However, why Vinfast did not start with the production of
electric cars but had to start with the production of the first gasoline
car. If Vinfast develops electric vehicles immediately at that time, the
electric vehicle market is still far from grooming time. The level of
readiness of key component manufacturers such as batteries and
motors is not high. Even the level of consumption and acceptance of
the market is low. If making electric cars at that time, VinFast will
have to pay more when the amount of investment is extremely large,
research costs are high, operating and sales costs are high but the sales
volume is low. VinFast is not a technology unicorn to pull long-term
venture capital like Tesla. The sale of gasoline cars in advance helps 19
VinFast to take advantage of and buy existing technologies, lines and
research rooms to have products enter the market immediately.
Bringing petro car products to domestic customers also helps VinFast
build a brand and trust to a certain extent. These factors will help
VinFast more conveniently enter the electric vehicle market than
jumping right into the electric vehicle market. Especially in the context
that VinFast has no background or strengths in industrial production,
technology, battery technology, electric vehicle technology, control
technology or control software production technology. Immediately
jumping into electric cars will make VinFast need more time to prove
its capacity, prove products and technology. Although gasoline cars are
not VinFast's advantage, they play big: Using BMW engines, German
chassis, designed by the world's leading companies. And they quickly
pushed away the apprehension from customers towards the new brand.
That is the springboard, the great lever for them to be confident in the
direction from day one: electric car. Giants such as Toyota, Hyundai,
Mercedes... It is impossible to give up Petro cars in favor of electric
cars immediately but must have a long-term roadmap because the
decision to switch to electric vehicles immediately will greatly affect
the supply chain worldwide and the hundreds of millions of customers
who are using their products. Not only that, petro cars are still the
chicken laying golden eggs for these car manufacturers. This is a huge
financial source for companies to focus on researching and developing
electric cars. VinFast is different, they have just entered this big
playground and they have not been encumbered much in terms of scale
and supply chain. From the disadvantage of being a new car company,
VinFast turns that into an advantage, making a difference in the road market. 20