
















Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194 THUONGMAI UNIVERSITY
KHOA KINH TẾ VÀ KINH DOANH QUỐC TẾ ---------- BÀI THẢO LUẬN
HỌC PHẦN: TIẾNG ANH THƯƠNG MẠI 1
Đề tài: HOW TO STAY COMPETITIVE IN JOB MARKET
Giảng viên: Bùi Thị Thu Trang Nhóm thực hiện: 03
Lớp học phần: 242_ENTI3311_28 Hà Nội, 2025 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194 MEMBER RATING TABLE No Contents/Tasks Name Comments Task completio n level 1 Introduction, Nguyễn Xuân Hưng A Conclusion, 3.3 (Leader) 2 3.4 Lê Ngọc Linh A 3 1.1 and 1.2 Phạm Thùy Linh A 4 3.1 Hoàng Minh Khánh A (Editor) 5 3.5 Lê Minh Khoa A 6 3.2 Vũ Vân Khánh A 2 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194 Contents
INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................... 3
1. The Current Labor Market Landscape in Vietnam ............................................ 4
1.1 Technological Advancements ............................................................................ 4
1.2. The impact of Free Trade Agreements (FTA) ................................................ 5
1.3 Downsizing ......................................................................................................... 7
2. Employment Barriers for Recent Graduates ....................................................... 8
2.1 The current state of youth unemployment in Vietnam and Its Causes ........ 8
2.2 Barriers ............................................................................................................... 9
3. How to stay competitive in the job market? ....................................................... 11
3.1. Develop In-Demand Skills ............................................................................. 11
3.2. Gain Practical Experience ............................................................................. 15
3.3 Cultivate a Strong Personal Brand ................................................................ 20
3.4. Effective networking strategies ..................................................................... 24
3.5. Adaptability and Resilience in Career Development .................................. 26
Conclusion ................................................................................................................. 28
REFERENCES .......................................................................................................... 29 INTRODUCTION
In today's fast-changing job market, competition is fiercer than ever. Technological
advancements such as digitalization, artificial intelligence, and automation are reshaping
industries, leading to both new career opportunities and the replacement of traditional jobs.
Additionally, Vietnam's integration into the global economy through Free Trade Agreements
(FTAs) has increased international competition, making it even more challenging for job
seekers, especially recent graduates.
Many young professionals face employment barriers, including skill mismatches, lack
of work experience, and difficulties in adapting to industry demands. To stay competitive, it
is essential to develop in-demand skills, gain practical experience, build a strong personal
brand, and adopt effective networking strategies.
In this presentation, we will explore the challenges of the current job market and
provide actionable strategies to help individuals enhance their employability and achieve long-term career success. 3 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
1. The Current Labor Market Landscape in Vietnam
1.1 Technological Advancements
Vietnam's labor market is significantly impacted by rapid technological
advancements, particularly in areas such as digitalization, artificial intelligence (AI), and
robotics. In a landscape of rapid technological evolution, the labor market is undergoing
significant transformations. These innovations are creating new professions, offering
opportunities for remote work and digital-based careers that did not exist before. According
to a report by ManpowerGroup, the Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
sectors are poised to lead recruitment trends in 2025. Roles such as programmers, AI
engineers, and cybersecurity experts are becoming increasingly vital.
Vietnam is also aligned with this trend. A report from the Ministry of Information and
Communications reveals that the Vietnamese IT market needs to supplement at least 500,000
technology workers between now and 2025 to meet the growing demand for human resources
in the information technology field, particularly in artificial intelligence, big data, and
cybersecurity. Here are some professions predicted to require additional human resources:
• Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Specialists: Artificial intelligence
continues to be one of the most promising fields. According to Regenesys, the demand
for specialists in this area is expected to grow by 35% by 2025. The number of job
postings for artificial intelligence specialists has increased by 74% annually over the
past four years (according to LinkedIn). Machine learning engineers are also among
the top-ranked jobs, with a 344% growth in recent job postings.
• Data Analysts: Data has become particularly important in the AI era. According to
Regenesys's forecast, the demand for data analysts is expected to increase by 36%, and
salaries often exceed six figures.
• Cybersecurity Specialists: As security threats increase, the role of cybersecurity
specialists becomes more critical than ever. This field requires extensive information
technology and cybersecurity knowledge to protect an organization's data from attacks.
• Digital Marketing Specialists: The e-commerce boom has also increased the demand
for digital marketing specialists. Businesses need them to build and maintain their online presence.
• Remote Healthcare Professionals: The healthcare industry is undergoing a digital
revolution. Leading this trend is telemedicine - healthcare services for remote patients
through the use of information technology.
Moreover, the rapid advancement of technologies like video conferencing, project
management software, and online communication platforms, coupled with the COVID-19 4 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
pandemic, has been a pivotal force driving the transformative shift in the remote work
technology industry. According to a recent study by Metrigy, over half of the surveyed
companies anticipate adjusting their work policies to balance internal needs with employee
desires. Remote work has become an indispensable modality in the modern work environment.
However, these technological shifts also lead to technology replacing labor in
traditional sectors. Significant displacement is already evident in sectors like manufacturing,
logistics, and customer service, where automation is rapidly replacing repetitive or
noncreative tasks. Assembly line workers, cashiers, and data processors are among those
facing swift transitions. According to DeepSeek, here are seven professions that are predicted
to be at high risk of unemployment within the next six years:
• Traditional Manufacturing: The proliferation of industrial robots and AI-driven
quality control is steadily replacing manual labor on assembly lines.
• Retail and Traditional Stores: The e-commerce and live-streaming boom has
transformed shopping habits, diminishing the demand for traditional cashiers and sales consultants.
• Customer Service and Telesales: Increasingly sophisticated AI voice technology is
capable of fluent customer interaction and complex task execution.
• Auto Repair and Taxi Driving: The rise of electric vehicles is reducing the need for
traditional fuel-based car repairs, impacting traditional mechanics. Rapid advances in
self-driving technology threaten to displace taxi drivers.
• Rare Language Translation: AI translation technology, with its increasing accuracy
and cost-effectiveness, is replacing manual labor in many fundamental translation tasks.
• Traditional Accounting: Smart financial and tax systems are being widely adopted by
businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises, replacing traditional accounting practices.
• Sorting and Delivery Jobs: Robots, drones, and autonomous delivery vehicles are
being increasingly deployed in logistics, supplanting traditional roles.
1.2. The impact of Free Trade Agreements (FTA)
As globalization continues to expand, Vietnam has strengthened its economic ties with
other nations through various Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), including notable agreements
like the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP)
and the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (EVFTA). These agreements foster trade, foreign
investment, and economic growth. 5 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
According to a Ministry of Planning and Investment study, the EVFTA
(EuropeanVietnam Free Trade Agreement) is expected to create an additional 146,000 jobs
annually, primarily focusing on labor-intensive industries with high export rates to the EU
market. The expected increase in employment in various sectors is as follows: the textile and
garment industry is estimated to increase by 71,300 jobs (by 2025) and 72,600 jobs (by 2030),
representing growth rates of 1.2%, 2.3%, and 2.4%, respectively, compared to 2018. The
leather and footwear sector is projected to have employment growth rates of 4.3% and
3.8% in 2025 and 2030. Other sectors with substantial job growth include aviation (1.5% by
2025) and water transportation (0.9% by 2025). However, some sectors may experience
reduced employment, such as forestry, mining, and rice production, with annual decreases
ranging from 0.26% to 0.36%. This agreement also contributed to wage growth and improved
workers' access to social insurance. The EVFTA not only brings benefits in terms of job
creation but also has the potential to raise wages for workers through more efficient market
activities and spillover effects from foreign direct investment (FDI) enterprises. It is estimated
that the wages of FDI enterprises will be nearly 1% higher than domestic enterprises (Harvey Nguyen, 2023).
Vietnam is an attractive labor market with a large working-age population, good
professional skills, and a stable social environment. These are favorable conditions for both
businesses and workers when Vietnam joins the CPTPP (Comprehensive and Progressive
Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership). Cooperation mechanisms within the Agreement
framework will create more jobs for the labor market, increase incomes, and contribute to
poverty reduction for the people. At the same time, businesses also have an abundant, quality,
and reasonably priced labor source to serve production activities. According to research
results from the Ministry of Planning and Investment, the CPTPP can help increase the total
number of jobs by an average of about 20,000 to 26,000 workers per year. Regarding the
benefits of poverty reduction, according to a World Bank study, by 2030, the CPTPP is
expected to help reduce 0.6 million people living in poverty at the poverty standard of US$5.5
per day. All income groups are expected to benefit (Tong Thi Truc An, 2024).
However, signing free trade agreements, such as the CPTPP or EVFTA, means that
Vietnamese businesses will face more intense competition from foreign enterprises. This
competition takes place on many fronts, from price, product, and service quality to technology
and market access. Foreign businesses, with their advantages in capital, technology, and
management experience, can easily capture the market share of Vietnamese businesses,
especially in industries where Vietnam does not have a clear competitive advantage. In
addition, tariff reductions and the removal of non-tariff barriers will also create conditions for
foreign goods to flood the Vietnamese market, putting pressure on domestic manufacturers. 6 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
Similar to businesses, Vietnamese workers will also face competition from foreign
labor. The opening of the labor market under international commitments will create conditions
for foreign workers, especially highly skilled workers, to work in Vietnam. This may put
pressure on Vietnamese workers, especially those with low qualifications or skills that do not
meet the requirements of the international labor market. In addition, foreign businesses
investing in Vietnam may also bring their workforce or prioritize hiring highly skilled foreign
workers, reducing job opportunities for Vietnamese workers in certain sectors. 1.3 Downsizing
In alignment with directives from the Politburo and the Central Executive
Committee, the Ministry of Home Affairs has initiated a personnal streamlining plan for the
2022-2026 period. The goal is to ensure that personnel numbers do not exceed approved levels
while also reducing civil servant positions by 5% and state-funded public sector positions by
10%. The Ministry has also assessed and reduced nearly 18,000 positions in non-financially
autonomous public service units, representing a reduction of nearly 15% compared to 2021."
As of October 2024, ministries, sectors, and localities have reduced over 16,000 civil
servant and public employee positions following government regulations. The Ministry of
Home Affairs has guided units to implement personnel streamlining in conjunction with
approving job positions and restructuring the cadre, civil servant, and public employee
workforce. Overall, ministries, sectors, and localities have adhered to assigned personnel
numbers and actively developed personnel streamlining plans, ensuring the quality of the
cadre, civil servant, and public employee workforce.
In Bac Ninh, the province streamlined 26 personnel positions in 2024, following
Government Decree No. 29. In Thanh Hoa, the province allocated nearly 17 billion VND to
implement personnel streamlining in the first phase of 2025, resulting in a reduction of nearly
10,000 officials, public employees, and non-specialized commune-level workers.
The government's implementation of personnel streamlining presents several notable
challenges for the labor market. The downsizing resulted in many workers losing their jobs,
increasing unemployment, and putting pressure on the social security system. According to
Associate Professor Dr. Bui Hoai Son, Standing Member of the National Assembly's
Committee on Culture and Education, some people may face difficulties when losing their
jobs or having to change jobs, leading to psychological pressure, anxiety about the future, and
difficulty in maintaining daily life. (Nguyen Viet, 2024) 7 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
2. Employment Barriers for Recent Graduates
2.1 The current state of youth unemployment in Vietnam and Its Causes
According to the International Labour Organization's (ILO) 'Global Employment
Trends for Youth 2024' report, the global youth unemployment rate in 2023 was 13% and is
projected to decrease to 12.8% in 2024 and 2025 (Nhat Duong, 2025). Specifically, the youth
unemployment rate in Vietnam (aged 15-24) in 2024 is 7.83%, an increase of 0.30 percentage
points compared to the previous year. Of this, the urban youth unemployment rate is 9.35%,
a decrease of 0.45 percentage points; the rural rate is 6.97%, an increase of 0.61 percentage points.
According to the Ministry of Labour, Invalids and Social Affairs, youth unemployment,
especially among those aged 15-24, continues to be a challenge for the Vietnamese labor
market. A report by the Ministry also indicates that on average, 1 in 10 young people is
unemployed. Young workers are also three times more likely to lose their jobs compared to other age groups.
The General Statistics Office also assesses that the youth unemployment rate and the
rate of young people not in employment, education, or training (NEET) in Vietnam remain
high, reflecting the difficulties faced by students in finding jobs after graduation. (Phuc Minh, 2024).
The recent state of Vietnam's labor market highlights several factors contributing to
high unemployment. Prominent among these are limited career guidance, low technical and
professional skills, and the impact of natural disasters and epidemics. With the rise of modern
technology and techniques, machine-driven production offers higher labor productivity and
cost-effectiveness, leading to the gradual replacement of manual labor. The growth of e-
commerce and the sharing economy also reshapes business practices and company demands,
creating new needs for diverse skills and professions.
Vietnam possesses an abundant labor force, but its quality remains suboptimal.
Consequently, in the context of globalization and technological advancements, the technical
and professional proficiency of Vietnamese workers often falls short of requirements. While
many young individuals graduate from universities, not all possess the necessary skills to
work in emerging fields. This results in employers struggling to find candidates with the
requisite skills to meet job demands, underscoring the importance of vocational training for
young people. Domestic labor market salaries are unappealing, leaving many workers
struggling to find positions that match their qualifications. (Minh Ha, 2024). 8 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194 2.2 Barriers
2.2.1. Mismatch Skill
Several of the informants have matched their academic qualifications and their first or
current job, however, the others indicate differently. The Fresh graduates are well aware of
the mismatch of their academic qualifications with their first job. The skill mismatch occurs
due to several reasons: the changes in industry demands, evolving job roles, or the field of
interest among the graduates are too general to fit with various fields of work. One of the
reasons behind youth unemployment in Indonesia is the mismatch between the skills
possessed by university students and the labor market skills demand, referred to as the skill
gap (Dewanto & Pritasari, 2023). This becomes a crucial gap highlighted by higher education to overcome.
The competitive job market can make fresh graduates stand out and secure employment
that matches their academic qualifications. The advancement of technology can make
employment more challenging among the fresh graduates to find suitable job opportunities in
their respective field. Due to the skill mismatch, it leads to difficulties in finding suitable jobs.
Dewanto and Pritasari (2023) stated further that according to experts, the high rate of youth
unemployment is frequently due to the inability of educational institutions to produce
graduates who possess employability skills.
Singh et al., (2014) stated that generic skills among graduates are important which
relate to their employability. Even though the academic background does not really match the
current job they have, yet the organisational experience, or additional experiences, have
equipped them with sufficient skill sets to start their first job.
However, some of the informants in this study have gotten jobs which fit their
academic background, and most of it related to new media. Referring to the fact that they have
to use the new technology and application, in this case social media, they still have to ensure
that what they have learned and known will fit with the work requirements or brief given to
them. In other ways, whether or not the academic background suits the job scope, individuals
have to adapt with the need of their job descriptions and requirements; updated skills as
technology rapidly changed, software acknowledgement, and so forth. This situation led to
the experience they have as the complement of their academic qualifications. Speaking about
skill mismatch, actually there are 21st century critical skills that fresh graduates could refer
to (Hartati & Riniati, 2022). To ensure that fresh graduates are equipped with adequate critical
skills, individuals, as well as a set of curriculums, should be continuously developed.
Therefore, equipping oneself with a sufficient critical skill set could accommodate the lacking
in practical skills if the company seeks for specific ones in their industry. By doing so, the 9 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
skill mismatch issue could be managed. Yet, another thing would be considered as challenges, i.e. experience.
2.2.2. Lack of work experience
As fresh graduates, most of them have minimum working experience. During their
education time, most of them could only have one opportunity for doing an internship as it is
part of the requirements in their university. As inexperienced employees, this condition leads
to the ability to cope with the work environment easily. With the new technology applied to
their particular work, they need to go the extra mile to comprehend the system to utilize it on a day-to-day basis.
The challenges in the workplace are not only regarding the work and environment
itself, but also regarding how digital technology takes part in the process of work. Due to that
matter, individualsshould be able to run side to side at the same pace with rapid technological
advancement. RN stated that technological development forces individuals to upskill
themselves continuously. This argument relates to Chandra (2021) who sees some students
engage in online courses to gain technical skills, and participate in various creative activities
by exploring new hobbies, as well as take up the available opportunities such as participating
in internships to cope with stress.
However, experience gained when they pursue their education has contributed to lessen
the challenges and gaps in doing their task during work. As a matter of fact, having the ability
to understand intercultural communication processes in a certain situation is actually the
experience that companies need to seek from their new comers in the organisation. Working
on skill development is something related to intercultural competency that is associated with
understanding culture and communication in the business environment (Tuleja, 2021),
therefore, it is an important variable that should be put into account when referring to
experience. Soft skill in communication is not less important compared to the hard skills that
are usually addressed in a job interview 2.2.3. Adaptability
Adaptability is the main key to new things in front of us. Specifically within the context
of this study, adaptability in career is one of the keys for fresh graduates to cope and survive
in their working placement (Mohammad et al., 2020). With the rapid technological
advancement, and development of society, it is important to be more adaptable for every
individual (Chen et al., 2020). Besides, the culturally diverse and changing world in the digital
era has underlined the importance of intercultural adaptation skills to handle any possible
situation in a workplace. Adaptability in this case is related to nteraction in the work 10 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
environment, and adopting and using new technology as support. Furthermore, it will relate
to adaptability in career and could help individuals adapt to changes when coping with their role in their workplace.
They could see that the mentality in the professional world is different. Therefore, they
should be able to handle pressure, stay focused, and have eagerness to learn new things.
Besides, attitude is one of the prominent requirements for them to adapt to the industry. The
working environment plays a significant role in enhancing employees' career adaptability, and
individuals need to adapt to their careers to improve their lives. Individual adaptability skills
can definitely be readiness for accepting or handling predicted work that is given by the
company. By doing so, they're participating in the whole work to be done and it is also the
method how they manage the change of working conditions. In the VUCA era, individuals
who are able to adapt with the cultural differences in their environment can quickly respond
to shifting cultural dynamics. Besides, they can also adjust with the market demands and
global trends, which in today’s world, changing is part of our daily phenomenon for
technology to keep on advancing. In the interconnected world, individuals who possess strong
intercultural communication skills are better equipped to overcome cross-cultural encounters
and eventually adapt to the work environment (Melly Ridaryanthi et al., 2024).
3. How to stay competitive in the job market?
3.1. Develop In-Demand Skills
3.1.1. What are In-Demand Skills?
First and foremost, to understand In-Demand Skills in today's era, we must examine
the shifts in the job market. In the global economy, the transition to a digital economy and
automation has significantly altered labor demands. According to the World Economic Forum
(WEF) 2023 report, 44% of workers’ skills will change within the next five years due to the
impact of AI and digital technologies. This means that traditional skills are no longer sufficient
to secure stable employment. Instead, skills such as data analysis, critical thinking, and
innovation management are becoming increasingly vital. 11 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
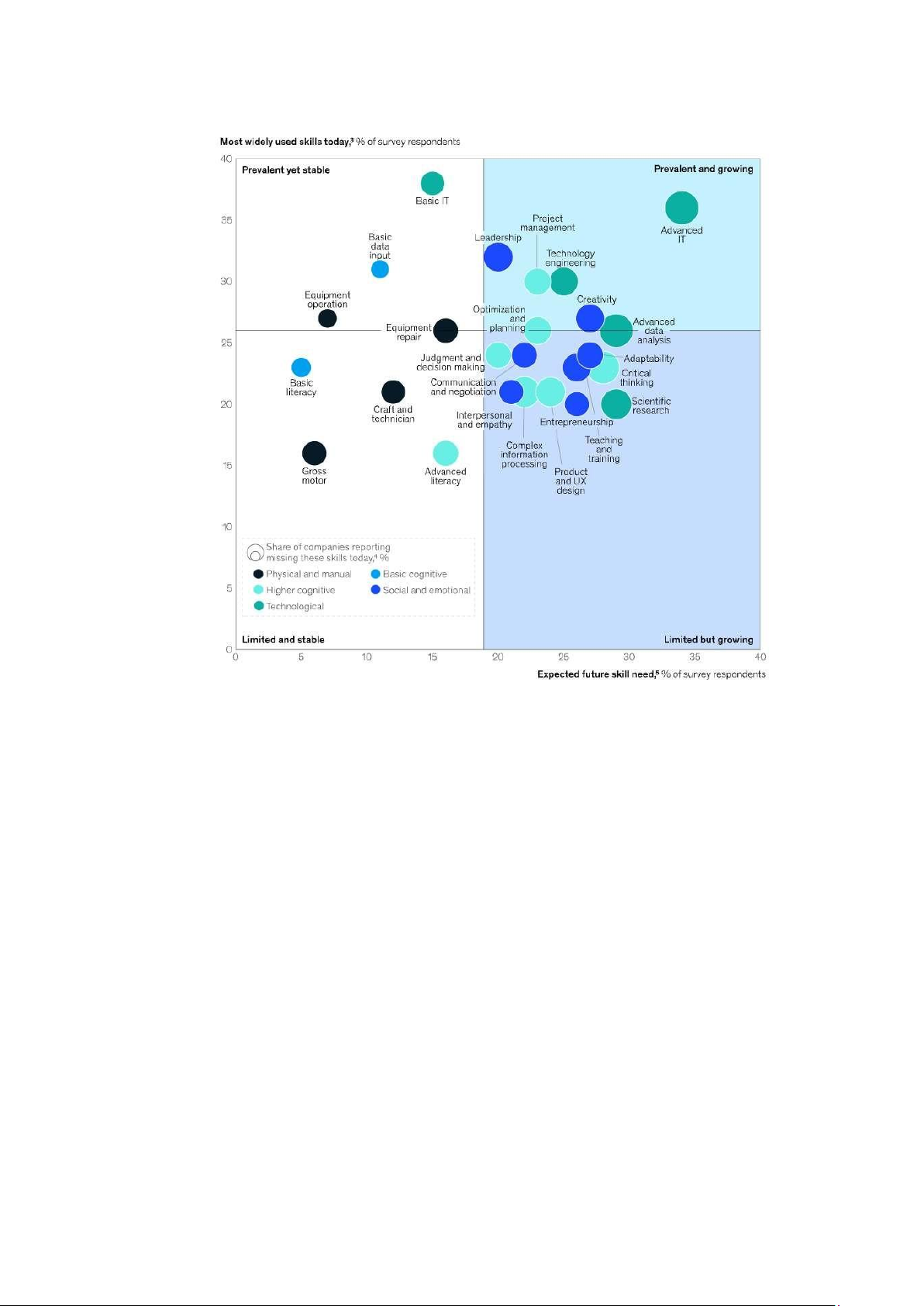
In-demand skills of today vs skills of the future in the EU and the US
These transformations illustrate that In-Demand Skills are not limited to technical
expertise but also include soft skills that enable individuals to navigate a rapidly changing job
market. Therefore, In-Demand Skills refer to both technical (hard skills) and interpersonal
(soft skills) abilities that employers highly value and actively seek in today’s job market.
These skills reflect the needs of emerging industries, technological advancements, and the
demands of modern work models.
In-Demand Skills can be categorized into technical skills and interpersonal skills. On
the technical side, skills like AI & Machine Learning, Data Analysis, Cybersecurity, and
Software Development are highly sought after due to digital transformation. Additionally,
Project Management, Business Analytics, and Marketing remain essential across industries.
On the interpersonal side, employers value Critical Thinking, Adaptability, Effective
Communication, and Leadership, as they are crucial for problem-solving and teamwork in dynamic work environments. 12 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
3.1.2. How to Develop In-Demand Skills
To stay competitive in the job market, developing in-demand skills requires a strategic
and continuous learning approach. Here are key steps to build these skills effectively: - Identify Key Skills
The first step in developing in-demand skills is identifying which skills are most
valuable in today’s job market. This requires researching industry trends, job postings, and employer expectations.
According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs Report (2023), the
topgrowing skills include analytical thinking, AI and big data, and leadership & social
influence. Meanwhile, a LinkedIn 2024 report found that 86% of employers prioritize soft
skills like communication and adaptability as essential for workplace success.
To determine which skills are relevant to your career, you can: Analyze job descriptions
in your industry on platforms like LinkedIn, Indeed, or Glassdoor; Follow reports from
organizations like McKinsey, Deloitte, or the World Economic Forum and Seek advice from
industry professionals through mentorship programs or networking events.
- Take Online Courses & Certifications
Online courses and certifications offer an accessible and flexible way to gain expertise,
often taught by industry leaders and recognized by employers. According to Coursera’s 2023
Global Skills Report, job seekers who earn professional certificates increase their hiring
chances by 76%. Additionally, a LinkedIn Learning report found that employees who
regularly take online courses are 39% more likely to get promoted.
There are many platforms that provide high-quality learning resources: Coursera &
edX, Udemy & Skillshare, LinkedIn Learning and Google & Microsoft Certifications. For
example, if you want to enter the data science field, completing Google’s Data Analytics
Professional Certificate or IBM’s AI Engineering Specialization can boost your credibility.
Likewise, for project management, a PMP (Project Management Professional) certification
can significantly improve job prospects.
By leveraging online learning, you can systematically build in-demand skills and
enhance your employability in a rapidly changing job market. -
Gain Hands-on Experience
Learning theory is important, but real expertise comes from practical application.
Gaining hands-on experience allows you to apply what you’ve learned, build a portfolio, and
demonstrate your skills to employers. 13 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
A 2023 Harvard Business Review study found that 79% of hiring managers prioritize
practical experience over formal education. Additionally, a LinkedIn survey revealed that
professionals with project-based experience are 3 times more likely to land a job than those
with only theoretical knowledge.
To build hands-on experience, you can take on internships in fields like software
development or digital marketing, work on freelance projects through platforms like Upwork
or Fiverr, or participate in competitions such as Google Code Jam or Kaggle for data science.
Contributing to open-source projects on GitHub or volunteering for nonprofit initiatives can
also help demonstrate your skills. For instance, aspiring coders can showcase their projects
on GitHub, while business students can join Harvard Business School case competitions to
strengthen their problem-solving abilities. By actively working on realworld projects, you
gain valuable experience, build a strong portfolio, and improve your job prospects.
- Network & Learn from Experts
Building a strong professional network and learning from industry experts can
accelerate skill development and open new career opportunities. According to a 2023
LinkedIn survey, 85% of jobs are filled through networking, highlighting the importance of professional connections.
Engaging with experts through mentorship programs, industry events, and online
communities provides valuable insights and guidance. You can attend conferences, webinars,
or workshops to stay updated on industry trends, connect with professionals on LinkedIn, or
join networking groups and forums related to your field. For example, tech professionals can
participate in GitHub communities or AI meetups, while business students can join
organizations like Toastmasters or startup incubators. By actively networking and seeking
mentorship, you gain access to real-world knowledge, career advice, and potential job
opportunities that can enhance your skills and professional growth.
3.1.3. Benefits of Developing In-Demand Skills
Developing in-demand skills offers numerous advantages in today’s competitive job market.
Better job opportunities and career growth: Acquiring in-demand skills makes you
a more attractive candidate for employers, increasing your chances of landing highquality
jobs and advancing in your career. According to the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs
Report (2023), roles in AI, data analytics, and software development are among the fastest-
growing, with strong hiring demand across industries. 14 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
Higher income potential: Specialized skills often lead to better-paying jobs. A
LinkedIn Learning report (2023) found that employees with certifications in fields like cloud
computing, cybersecurity, and project management earn up to 20% more than those without.
Additionally, data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics shows that tech-related jobs, which
require specific expertise, offer median salaries 50% higher than the national average.
Increased adaptability in a changing job market: As technology and industries
evolve, having versatile skills ensures you remain employable. A McKinsey Global Institute
study predicts that by 2030, up to 375 million workers may need to switch careers due to
automation. Developing skills in areas like digital literacy, problem-solving, and leadership
helps professionals stay relevant and transition smoothly into new roles.
Greater confidence and professional value: Mastering high-demand skills boosts
self-confidence and enhances your credibility in the workplace. Professionals with expertise
in sought-after fields are more likely to take on leadership positions and be recognized as
valuable contributors within their organizations. According to a Harvard Business Review
study, employees who continuously upskill are 30% more likely to receive promotions and leadership opportunities.
3.2. Gain Practical Experience
3.2.1. Introduction
In today’s fast-changing job market, having a degree is no longer enough to guarantee
career success. Employers seek candidates who can do more than just understand theories -
they want individuals who can apply their knowledge, solve real-world problems, and adapt
to dynamic work environments. This is where practical experience becomes essential.
Practical experience refers to hands-on learning and direct exposure to professional tasks,
responsibilities, and challenges. It goes beyond classroom education, allowing individuals to
develop industry-specific skills, improve problem-solving abilities, and gain confidence in
their work. Whether through internships, part-time jobs, freelancing, volunteering, or industry
projects, practical experience helps students transition smoothly from academic learning to professional life.
Imagine a business student who has studied marketing strategies extensively in
textbooks. Without real-world experience, they might struggle to create an effective
advertising campaign, analyze consumer behavior, or handle unexpected challenges in a
competitive market. Theoretical knowledge provides a foundation, but practical experience
builds the skills needed to thrive in the workplace. Moreover, gaining hands-on experience
helps individuals develop essential soft skills such as communication, teamwork, adaptability,
and leadership—qualities that are just as valuable as technical expertise. It also provides 15 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
opportunities to network with professionals, gain industry insights, and increase employability.
In the following sections, we will explore various ways to gain practical experience
and discuss how it can significantly enhance career prospects.
3.2.2. Ways to gain relevant work experience
Gaining practical experience is one of the best ways for students and young
professionals to stay competitive in today’s job market. While academic knowledge provides
a strong foundation, real-world experience allows individuals to apply what they have learned,
develop essential skills, and build a professional network. Fortunately, there are several
effective ways to gain relevant work experience, including internships, part-time jobs,
freelancing, volunteering, and industry-specific certifications. Each of these paths offers
unique opportunities to grow professionally and enhance employability. Internships:
Internships are one of the most valuable ways for students to gain real-world exposure
and understand industry dynamics. By working in a professional environment, interns learn
how companies operate, develop technical skills, and build connections with industry
professionals. One of the biggest advantages of internships is that they often lead to full-time
employment. Many companies use internships as a way to identify and train potential
employees, giving interns a chance to prove their abilities and secure job offers after
graduation. According to a 2023 National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE)
report, 56% of interns receive full-time job offers from their employers, highlighting the
importance of internships for career advancement.
For example, Google’s Internship Program is known for turning interns into full-time
employees. Many students who complete internships at Google receive job offers because
they have already gained hands-on experience with the company’s projects and work culture.
Similarly, Deloitte’s internship programs provide real consulting experience, allowing
students to work on actual client projects and develop essential business skills.
Internships also help students build professional connections, which can be beneficial
for future job opportunities. Even if an internship does not lead to an immediate job offer, the
experience and industry contacts gained can open doors to other career prospects. Part-time jobs and freelancing: 16 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
Another effective way to gain practical experience is by taking on part-time jobs or
freelancing while studying. These options allow students to gain workplace experience,
develop essential skills, and earn money at the same time. Part-time jobs, even those not
directly related to a student’s field of study, help in developing transferable skills such as
communication, teamwork, time management, and customer service. A Harvard Business
Review (2023) study found that 79% of hiring managers prioritize candidates with work
experience, even if it is from part-time jobs, as it demonstrates responsibility and adaptability.
Freelancing, on the other hand, provides even greater flexibility and hands-on
experience in a specific field. Many students use platforms like Upwork, Fiverr, or Freelancer
to offer services in areas such as graphic design, writing, coding, and digital marketing.
Freelancing allows individuals to work on real-world projects, build a portfolio, and gain client management skills.
For example, a computer science student interested in web development could start
freelancing by building websites for small businesses. Over time, these projects add up to a
strong portfolio, increasing the chances of landing a full-time job in tech companies.
Likewise, a marketing student can gain valuable experience by managing social media
accounts for startups, helping them understand audience engagement and content strategies.
By working part-time or freelancing, students not only gain work experience but also
develop discipline, financial independence, and professional responsibility, all of which are highly valued by employers.
Volunteering and extracurricular activities:
Engaging in volunteer work or student organizations is another excellent way to gain
practical experience while also giving back to the community. Employers appreciate
candidates who show initiative, leadership, and commitment to personal and professional
growth-qualities that are often developed through extracurricular activities.
Volunteering helps individuals enhance teamwork, problem-solving, and leadership
skills. It also demonstrates a willingness to take initiative and a strong work ethic, both of
which are attractive qualities to recruiters. A 2023 LinkedIn Talent Trends Report found that
candidates who participate in volunteer work are 27% more likely to be hired than those who
do not, as volunteering showcases valuable soft skills.
For instance, students interested in event management can gain experience by
organizing university events or charity fundraisers. This allows them to learn about budgeting,
logistics, and teamwork in a real-world setting. Similarly, those passionate about social work
can volunteer for NGOs such as Habitat for Humanity or the Red Cross, where they gain
experience in project management and community engagement. 17 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
Extracurricular activities, such as joining student clubs, debate teams, or business
competitions, also provide valuable experience. Many successful entrepreneurs and business
leaders started by participating in student-led initiatives, which helped them develop critical
thinking, public speaking, and negotiation skills.
Industry-specific certifications and projects:
In some industries, certifications and hands-on projects are essential for demonstrating
expertise. Employers often value candidates who go beyond traditional education by gaining
industry-recognized credentials or working on independent projects. According to a Coursera
2023 Global Skills Report, job seekers with industry certifications are 76% more likely to be
hired than those without them.
Many online platforms offer professional certifications in various fields, allowing
students to acquire new skills and boost their resumes. Some popular examples include:
- Google Digital Garage – A free certification in digital marketing, useful for
students pursuing marketing or business careers.
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect – A certification for IT students interested in cloud computing.
- Project Management Professional (PMP) – Ideal for students looking to enter
business and management roles.
Apart from certifications, working on independent projects or contributing to
opensource platforms is another way to gain experience. For example, software developers
can contribute to GitHub projects, showcasing their coding abilities to potential employers.
Practical experience is crucial for standing out in the job market, and there are many
ways to gain it. Internships provide industry exposure, part-time jobs and freelancing offer
hands-on work opportunities, volunteering and extracurricular activities develop leadership
skills, and certifications enhance credibility. Each of these paths helps students bridge the gap
between education and employment, making them more competitive candidates in their respective industries.
3.2.3. Benefits of gaining practical experience
Having explored various ways to gain practical experience, it's now important to
discuss why these efforts matter. Practical experience offers numerous advantages that go
beyond simply enhancing a resume. It helps job seekers stand out in the hiring process, bridge
the gap between theory and practice, build professional networks, and boost confidence and
adaptability. These factors play a crucial role in ensuring long-term career success.
• Enhances employability: 18 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
One of the biggest advantages of gaining work experience is that it significantly
increases job opportunities. Many employers prefer candidates who have already worked in
real-world environments because they require less training and can contribute effectively from day one.
For example, imagine two students applying for a graphic design job. One has an
impressive academic record but no experience, while the other has worked as a freelance
designer, creating logos and social media content for small businesses. The second candidate
is more likely to be hired because they have already demonstrated their skills in real projects
and understand client expectations. This highlights how hands-on experience can set
candidates apart in a competitive job market.
• Bridges the gap between theory and practice:
While theoretical knowledge provides a strong foundation, it often doesn’t fully
prepare students for the challenges of the workplace. Real-world situations require
problemsolving, decision-making, and adaptability-skills that can only be developed through practical experience.
As an example, an engineering student may have learned about structural design in
university, but working on an actual construction site exposes them to unexpected challenges
like material shortages or last-minute design changes. Similarly, a finance graduate may
understand financial models in theory, but handling real company budgets or market
fluctuations in an internship teaches them how to apply that knowledge effectively. By gaining
practical experience, individuals become more competent and confident professionals who
can handle workplace challenges.
• Build a professional network:
Networking is an essential part of career growth, and gaining work experience provides
a natural way to build industry connections. Whether through internships, part-time jobs, or
volunteering, interacting with professionals can open doors to future job opportunities.
For example, a student working part-time at a startup might impress their employer
with their dedication and problem-solving skills. When a full-time position opens up, they are
more likely to be considered than an outsider. Similarly, an intern at a marketing agency may
build relationships with senior managers, who could recommend them for job openings later.
These connections can be invaluable in securing employment and career advancement.
Boosts confidence and adaptability: 19 lOMoAR cPSD| 47207194
Stepping into a professional environment for the first time can be overwhelming, but
prior work experience helps individuals develop confidence and adaptability. Those who have
already worked on real projects are better prepared to handle workplace stress, interact with
colleagues, and manage their responsibilities effectively.
For example, a student who has worked on multiple freelance writing projects will be
more comfortable meeting deadlines, handling client feedback, and working under pressure
compared to someone with no experience. Similarly, a volunteer leading a charity event may
gain confidence in public speaking, teamwork, and event management-skills that are valuable
in many professional fields. By gaining hands-on experience, individuals become more
adaptable to different work environments and challenges.
In conclusion, practical experience is essential for career success. It helps job seekers
stand out in the hiring process, apply knowledge effectively, build strong professional
relationships, and develop confidence. As the job market continues to evolve, those who
actively seek work experience-whether through internships, part-time jobs, or personal
projects-will have a significant advantage. Investing in practical experience early not only
improves employability but also lays the foundation for long-term professional growth.
3.3 Cultivate a Strong Personal Brand
3.3.1. How can I build a strong personal brand? 20




