













Preview text:
HRM chapter 1: What is HRM ?
-> Human Resource Management is the process of recruiting, training, appraising and employess Five basic functions: + Planning + Organizing + Staffing +Leading +Controlling
The personnel aspect of management
- Conducting job analyses (determining the nature of each employee’s job)
- Planning labor needs and recruiting job candidates - Selecting job candidates
- Orienting and training new employees
- Training employees, and developing managers
- Managing wages and salaries (compensating employees)
- Providing incentives and benefits - Appraising performance
- Communicating (interviewing, counseling, disciplining)
- Building employee relations and engagement Chapter 4: The basic of Job Analysis ?
->The procedure for determining the duties and skill requirements of a
job and the kind of person who should be hired for it Information: + Human requirement:
• Job-related knowledge and skills Education ➢ Certificates ➢ Work experience ➢ • Personal attributes Aptitudes ➢ Physical characteristics ➢ Personality ➢ Interests ➢ + Job context:
+Information about such matters: • Working conditions • Schedule • Organizational context • Social context +Performance standars:
Information about the job’s performance standards: Quantity levels ➢ Quality levels ➢ + Work activities:
Information about the job’s actual work activities, such as: • Cleaning • Selling • Teaching • Painting
• How, why and when the activities are performed + Skills
Information about skills the job requires: • Sensing • Communicating • Decision making • Writing • Job demands Lifting ➢ Walking long distances ➢
+ Machines, Tools, Equipment, Work Aids • Tools used • Materials processed • Knowledge applied • Services
Method of Collecting job Analysis information + Observation:
▪ Observation may be combined with interviewing ▪ Take complete notes
▪ Talk with the person being observed – explain what is happening and why ▪ Ask questions + Interview( Widely used)
• Individual interviews with each employee
• Group interviews with groups of employees who have the same job
• Supervisor interviews with one or more supervisors who know the job +Participants’ diary: • Time-consuming • Self-reporting
• Remembering what was done earlier
• Can use dictating machines and pagers +Questionnaire:
• Use a specific questionnaire
• Structured or unstructured questionnaires may be used to obtain job analysis information
• List duties in order of importance or frequency of occurrence • Review and verify the data Writing Job Descriptions: 1. Job Identification: • Title
• Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) • Date • Approvals • Supervisor’s title • Salary • Grade level 2. Job Summary: • General nature
• Major functions or activities
• Includes general statements 3. Relationships:
4. Responsibilities and Duties: • Examples
Establishes marketing goals to ensure share of market ➢
➢Maintaining balanced and controlled inventories
• Defines the limits of job holder’s authority Purchasing authority ➢ Discipline ➢ Interviewing and hiring ➢ 5. Standards of Performance
Duty: Meeting Daily Production Schedule
• Work group produces no fewer than 426 units per working day
• Next workstation rejects no more than an average of 2% of units
• Weekly overtime does not exceed an average of 5%
6. Working Conditions and Physical Environment Writing Job Specifications
The specification should specify the person’s Skills on the job ❑ Knowledge of and for the job ❑
Length of experience for the job ❑ Attitude for the job ❑ Preferences ❑ Presentability ❑
Job Specifications for Trained and Untrained Personnel Writing Job Specifications
• For trained personnel – focus on traits, such as: Length of previous service ➢ Quality of relevant training ➢ Previous job performance ➢
• For untrained personnel – specify qualities, such as: Physical traits ➢ Personality ➢ Interest ➢ Sensory skills ➢
Specifications Based on Judgment Writing Job Specifications
• Review job’s duties then deducing the human traits and skills the job required
• Using competencies listed on Web-based Job Specifications
Specifications Based on Statistical Analysis
Writing Job Specifications
• Refer to the process of using statistical data and analysis to identify the
key skills, qualifications, and characteristics required for a particular job.
Specifications Based on Statistical Analysis
• This procedure has five steps:
1) Analyze the job, and decide how to measure job performance;
2) Select personal traits that you believe should predict performance;
3) Test candidates for these traits;
4) Measure these candidates’ subsequent job performance;
5) Statistically analyze the relationship between the human trait and job performance
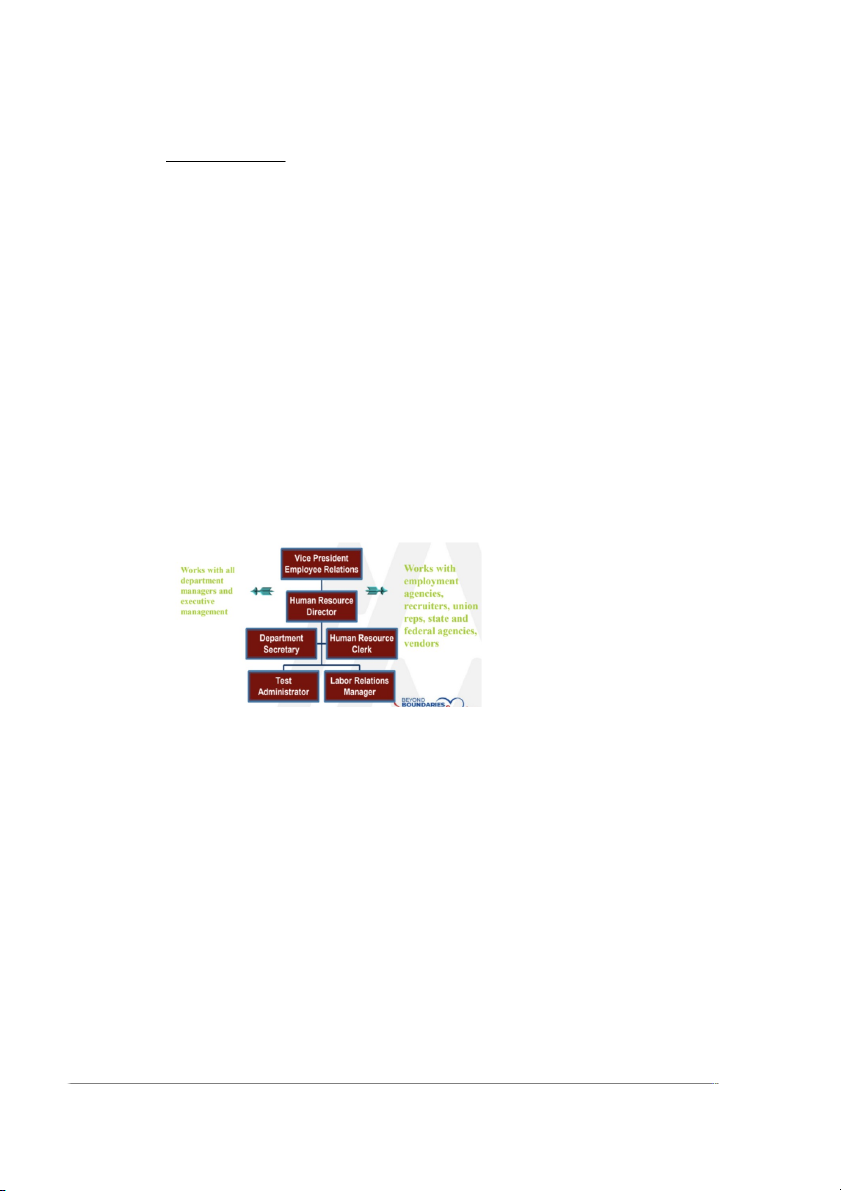
Chapter 5: Personal Planning and Recruiting
Workforce planning: Workforce planning is a process of deciding what
positions the firm will have to fill and how to fill them.
• It’s forecasting and determining the HR needs of organization, then
build the workforce plan to ensure that the organization has enough
workforce to achieve organization’s goals and optimizing labour's cost.
II. IMPORTANT OF WORKFORCE PLANNING
➢ Workforce planning is the first step in the recruiting and selecting
process. It is an important part of a company’s strategic planning process.
In forming Workforce plans, managers need to forecast three factors: ➢
Workforce needs, Supply of internal candidates, Supply of external candidates. • Recruitment
• Reducing non-visible costs.
• Employee career planning and development
• Effectiveness of human resource management programs.
III. Workforce Planning Process
Step 1: Environmental scanning ✓ Step 2: Predicting HR needs ✓ Step 3: Predicting HR supply ✓
Step 4: Balancing HR supply and needs ✓ Forecasting HR needs
• Forecast revenue → estimate the number of persons needed
• Forecasting employee needs: we need to consider the following factors - Products/services - Economy - Technology - Financial sources - Absenteeism/turnover - Development - Management philosophy Forecast Techniques 1. Trend analysis 2. Ratio analysis 3. Scatter plot 4.Computer forecast 5.Managerial judgment
IV. Forecasting the supply of internal candidates
• Determining which current employees may be qualified to fill the openings. • This may look at: - Personnel skills inventory - Personnel replacement charts
- Computerized information systems • Matter of privacy
• Finding internal candidates: using job posting, HR records, and skills inventory.
INTERNAL & OUTSIDES SOURCES OF CANDIDATES
Internal Sources of Candidates Advantages
• Foreknowledge of candidates’ strengths and weaknesses
• More accurate view of candidate’s skills
• Candidates have a stronger commitment to the company • Increases employee morale
• Less training and orientation required Disadvantages
• Failed applicants may become discontent
• Time wasted interviewing inside candidates who will not be considered
• Unable to diversify human resources Finding Internal Candidates Posting open job position Rehiring former employees Succession planning Recruiting via the Internet Advantages
• Cost-effective way to publicize job openings
• More applicants attracted over a longer period
• Immediate applicant responses
• Online prescreening of applicants
• Links to other job search sites
• Automation of applicant tracking and evaluation • Disadvantages
• Exclusion of older and minority workers
• Unqualified applicants overload the system
• Personal information privacy concerns of applicants
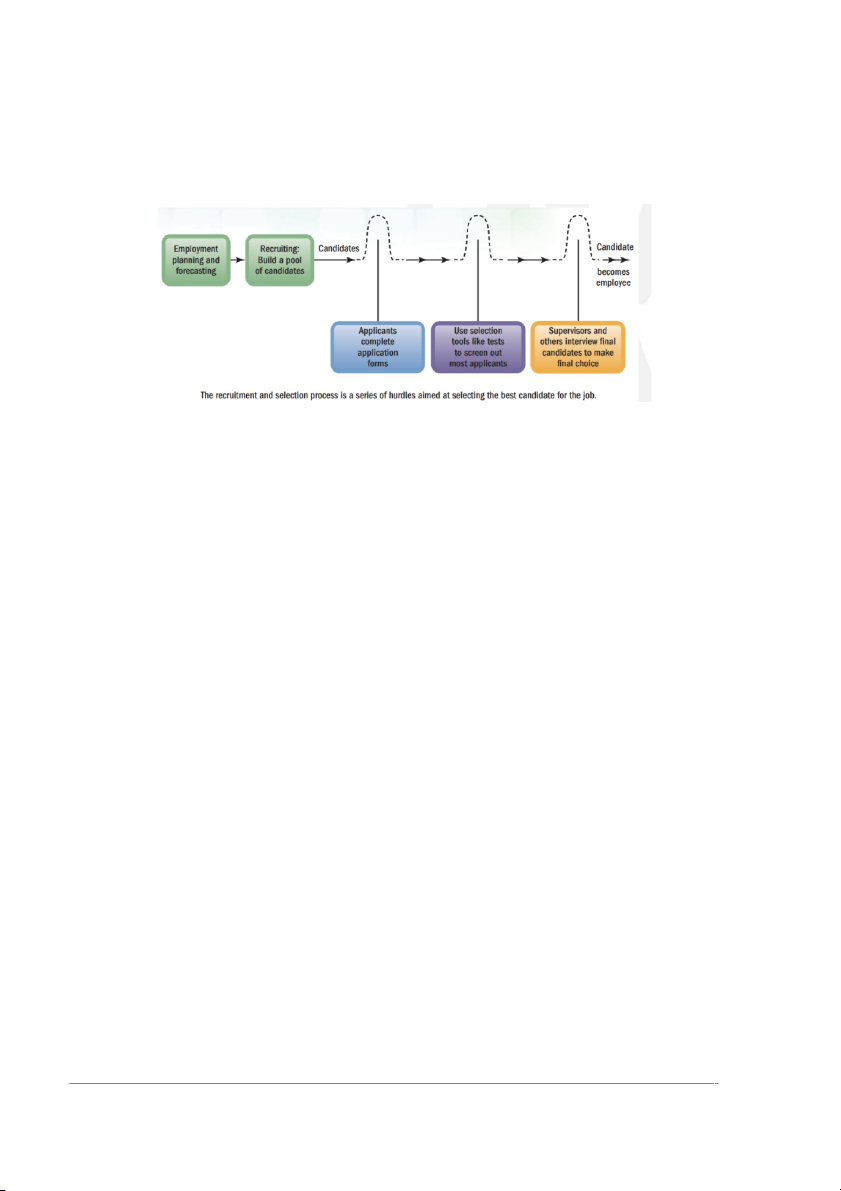
Chapter 6: Selecting Employees Types of tests
1. Tests of mental or cognitive abilities
Intelligence Tests - (IQ) Tests ➢
• Tests of general intellectual abilities that measure a range of
abilities, including memory, vocabulary, verbal fluency, and numerical ability Aptitude tests ➢
• Tests that measure specific mental abilities, such as inductive
and deductive reasoning, verbal comprehension, memory, and numerical ability
2. Tests of physical or motor abilities Tests of motor abilities ➢
• Tests that measure motor abilities, such as finger dexterity, manual dexterity, and reaction time Tests of physical abilities ➢
• Tests that measure static strength, dynamic strength, body coordination, and stamina
3. Personality and interests tests
• Tests that use projective techniques and trait inventories to measure basic
aspects of an applicant’s personality, such as introversion, stability, and motivation Disadvantage ➢
• Personality tests — particularly the projective type — are the most
difficult tests to evaluate and use Advantage ➢
• It may be useful for helping employers to predict which candidates will succeed on the job INTERVIEW CANDIDATES What is an interview?
A procedure designed to obtain information from a person through oral responses to oral inquiries. Interview formats Unstructured interview
An unstructured conversational-style interview in which the interviewer
pursues points of interest as they come up in response to questions Structured interview
An interview following a set sequence of questions Types of questions Situational questions: ➢
focus on the candidate’s ability to explain what
his or her behavior would be in a given situation
Eg:“How would you react to a subordinate coming to work late three days in a row?” Behavioral questions: ➢
you ask interviewees how they behaved in the past insome situation
Eg:“Did you ever have a situation in which a subordinate came in late? If
so, how did you handle the situation?
Knowledge and background questions ➢
probe candidates’ job-related knowledge and experience
Eg:“What math courses did you take in college?" Types of interview Individual interview: ➢ Two people meet alone Sequential interview: ➢
Several persons interview the applicant, before a decision is made Panel interview: ➢
An interview in which a group of interviewers questions the applicant
➢ Telephone interview: An interview is made by telephone
Computerized interview: ➢
The applicants answer questions in
response to computerized oral, visual, or written questions or situations.
What are common interviewing mistakes?
How to conduct a more effective interview Structure your interview Prepare for the interview Establish rapport Ask questions Close the interview Review the interview
Chapter 7: Training and Developing Employees
Orientation/onboarding/induction training
• A procedure for providing new employees the basic background
information they need to do their jobs (like computer
passwords, company rules, etc..)
• Ideally, onboarding should start before the employee's first day with a
welcome note, orientation schedule, and instructions on necessary documents
Purposes of employee orientation
• Make the new employee feel welcome at home and part of the team.
• Make sure the new employee has the basic information to function
effectively, such as e-mail access, personnel policies and benefits, and
expectations in terms of work behavior.
• Help the new employee understand the organization in a broad sense (its
past, present, culture, and strategies and vision of the future).
• Start socializing the person into the firm’s culture and ways of doing things. What is training?
• Training is the process of teaching new or current employees the basic
skills they need to perform their jobs
• Training is used to focus mostly on technical skills
• In addition, training is also used to provide soft skills
ADDIE Five-steps Training process ADDIE training process model:
1. Analyze the training need
2. Design the overall training program 3. Develop the course 4. Implement training
5. Evaluate the course’s effectiveness
Overview of the Training process Training need analysis
There are 3 main ways to identify training needs:
Strategic training needs analysis: ➢
Strategic goals (perhaps to enter
new lines of business) often mean the firm will have to fill new jobs.
Strategic training needs analysis identifies the behaviors, skills, and
training that employees will need to fill these new future jobs. Performance analysis: ➢
is the process of verifying that there is a
performance deficiency and determining whether the employer should
correct such deficiencies through training or some other means (like transferring the employee). Task analysis: ➢
assessing new employees’ training needs. It is a
detailed study of the job to determine what specific skills and knowledge the job requires.
Other ways to identify training needs:
• Individual employee daily diaries
• Observations by supervisors or other specialists
• Interviews with the employee or his or her supervisor
• Tests of things like job knowledge, skills, and attendance • Assessment center results Training methods 1. Lectures
• Lecturing is a quick and simple way to present knowledge to large
groups of trainees, as when the sales force needs to learn a new product’s features.
2. Audiovisual-based training
• Film, audiotape, videotape, PowerPoint slides, etc. • Advantages:
- Enable to stop-action, instant replay, fast-slow motion
- Enable to show special event such as tour of a factory, open-heart surgery - Company-wide training • Disadvantage:
- More expensive than lectures 3. Programmed learning
• A systematic method for teaching job skills, involving presenting
questions or facts, allowing learners to respond, and giving them
immediate feedback on the accuracy of their answers. Advantages:
- Allow trainees to learn at their own pace - Provide immediate feedback Disadvantages:
- Not learn much more than from a traditional textbook
- Costly to develop the manuals and software programmed instruction
4. On-the-job training (OJT)
• OJT means a person learns by actually doing it.
• There are several types of OJT:
Coaching by supervisor or experienced worker ➢ Observing the supervisor ➢
Job rotation: move from job to job ➢ Advantages of OJT Relatively inexpensive
No need for expensive off-site quick facilities like a classroom Trainees learn while producing
Trainees learn by doing, get feedback on their performance 5. Vestibule training
• Trainees learn on the actual or simulated equipment but are trained off
the job (perhaps in a separate room or vestibule).
• Necessary when it’s too costly or dangerous to train employees on the job. 6. Apprenticeship training
• A structured process by which people become skilled workers through a
combination of classroom and OJT practice.
• The learner studies under the guidance of a master craftsman.
7. Distance and internet-based training
• Various forms of distance learning methods: - Traditional courses - Tele-training - Videoconferencing - Internet-based classes
8. Computer-Based training (CBT)
• Computer-based training uses interactive computer-
based systems to increase knowledge or skills. • Advantages:
- Interactive technologies reduce learning time
- Cost effective once designed and produced
- Instructional consistency, mastery of learning
- Increase retention and trainee motivation.
9. Simulated training and gaming
• A method in which trainees learn on the actual or simulated equipment they will use on the job.
• Training employees on special off-the-job equipment, as in airplane
pilot training, so training costs and danger can be reduced.
Chapter 8: Performance Management & Appraisal What is performance appraisal?
• Performance appraisal is an activity used to determine the extent to
which an employee performs work effectively Purposes for appraisal - Motivation - Communications
-Legal compliance (promotion, transfer, reward, discharge) -Tranining&Development
-Human resource and employment planning.
Performance appraisal process Step 1
Define the job and its standards Step 2
Measure employees’ performance against these standards Step 3
Provide feedback to the employees so that they can improve their performance APPRAISAL METHODS 1. Graphic Rating Scale
A scale that lists a number of traits and a range of performance for each
that is used to identify the score that best describes an employee’s level of performance for each trait.
2.Alternation ranking method
Ranking employees from best to worst on a particular trait, choosing
highest, then lowest, until all are ranked. 3.Paired comparison method
Ranking employees by making a chart of all possible pairs of the
employees for each trait and indicating which is the better employee of the pair.
4.Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scale (BARS)
A behaviorally anchored rating scale (BARS) is an appraisal method that
combines critical incidents and quantitative ratings, by anchoring a
quantified scale with specific narrative examples of good and poor
performance expressed as specific behaviors.
5.Forced distribution method
With the forced distribution method, the manager places predetermined
percentages of subordinates in performance categories, as when a
professor “grades on a curve.” Example: 15% high performers ➢ 20% high-average performers ➢ 30% average performers ➢ 20% low-average performers ➢ 15% low performers ➢
Chapter 10: Developing Compensation Employee compensation
Employee compensation: includes all forms of pay going to employees
that arising form their employment.
Objectives of compensation management
Attracting and retaining personnel ➢ Motivating personnel ➢
➢ Optimizing cost of personnel Consistency in compensation ➢
Why use competency-based pay?
Competency-based pay is where the company pays for the employees’
range, depth, and types of skills and knowledge, rather than for the job title they hold. Definitions of compensation
❖ Salary is best associated with employee compensation quoted on an annual basis
Wages is best associated with employee compensation based ❖ on the
number of hours worked multiplied by an hourly rate of pay
Equity and Its Impact on Pay Rates
External equity refers to how a job’s pay rate in one company ➢
compares to the job’s pay rate in other companies.
Internal equity refers to how fair a particular job’s pay rate is when ➢
compared to other jobs within the same company. Job evaluation method
1.Management by objectives (MBO)
MBO involves setting specific measurable goals with each employee
and then periodically reviewing the progress made.
2. Management by objectives process
3. Management by objectives (MBO) Problems with MBO • Unclear objectives • Time consuming • Different expectations
4. Objectives and key results (OKRs)
Objectives and key results (OKR, alternatively OKRs) is a goal-setting
framework used by individuals, teams, and organizations to define
measurable goals and track their outcomes.
Appraising performance: Problems and Solutions Unclear standards Halo effect Central tendency Leniency or strictness Bias Solutions: • Unclear standards:
- An appraisal that is too open to interpretation • Halo effect:
- Occurs when a supervisor’s rating of a subordinate on one trait biases
the rating of that person on other traits • Central tendency:
- A tendency to rate all employees the same way, such as rating them all average • Strict/Lenient:
- The problem that occurs when a supervisor has a tendency to rate all
subordinates either high or low • Bias:
- The tendency to allow individual differences such as age, race, and
gender to affect the appraisal ratings.
Chapter 11: Pay for Performance and Employee Benefits Individual Incentive plans
Incentive plans, which are known as “pay-for-performance” plans,
motivate employees to exceed expectations and grow the business.
❖ Types of incentive plans:
Incentive plans for employees Individual incentive plans • Piecework plan
A pay system based on the number of units produced by individual ➢ workers such as units per day
• Merit pay (Merit raise)
Any salary increase awarded to an employee based on hi ➢ s or her individual performance • Merit guidelines Guidelines for awarding ➢
Incentive plans for employees ➢
Organizational-Wide Variable Pay Plans ➢ •Profit Sharing
– A plan whereby employees share in the company's profits – Challenges:
•Agreement over division of profits between company and employees
•Possibility of no payout due to financial condition of company.
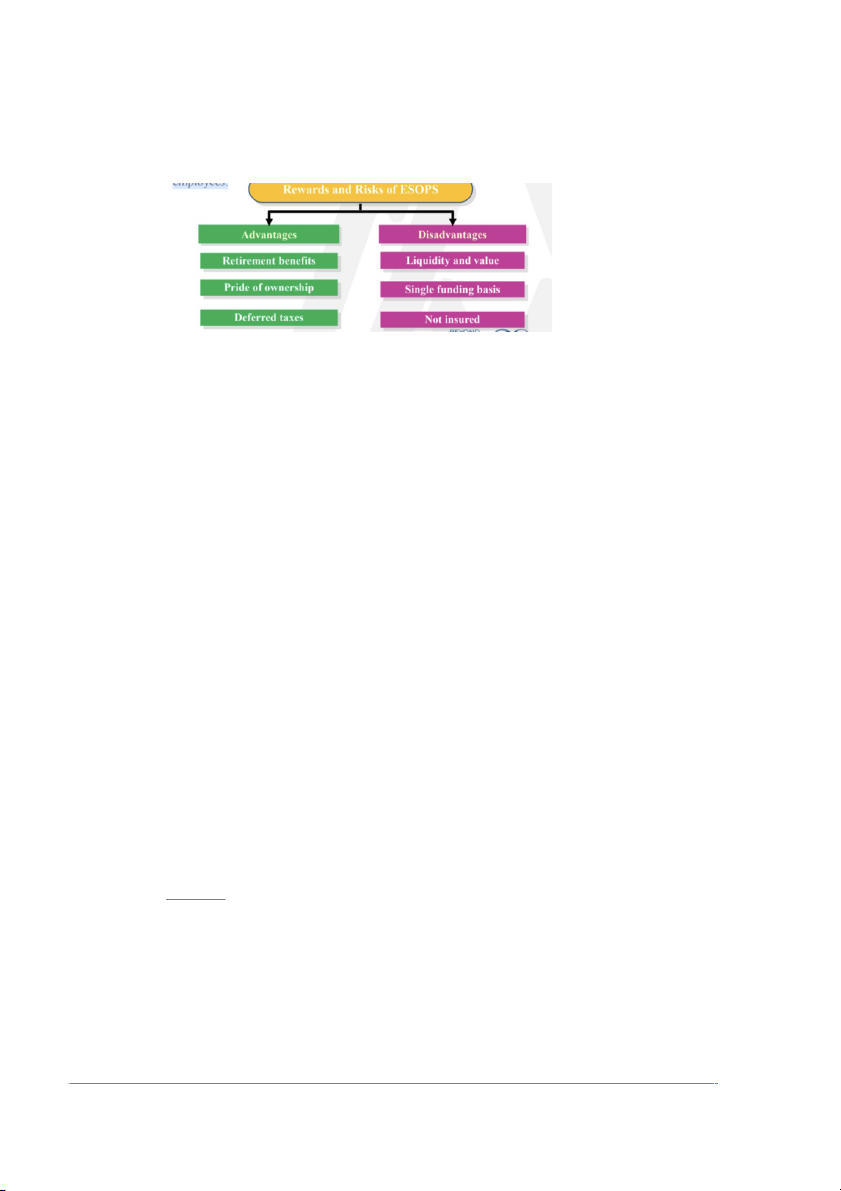
•Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs)
–Stock plans in which an organization contributes shares of its stock to
an established trust for the purpose of stock purchases by its employees. Scanlon Plan:
Rewards come from employee participation in improving productivity and reducing costs. Why do incentives fail?
❖ Performance pay cannot replace good management ❖ You get what you pay for
❖ “Pay is not a motivator” ❖ Rewards punish
❖ Rewards rupture relationships
❖ Rewards have unintended consequences
❖ Rewards may undermine responsiveness
❖ Rewards may undermine intrinsic motivation.
Chapter 12: Maintaining Positive Employee Relation WHAT IS EMPLOYMENT RELATIONS?
It implies a long-term partnership among people, and each partner plays a
different role in the organization and works collectively to achieve the
organization’s goal and to improve the quality of work life.
Main reason why workers join a union
Higher wages and better working conditions Job security Social need Upgrading of skills Peer group pressure Self-fullfillment The ethical organization:
The employment relation issues in some Asian countries Vietnam Employment contract
▪ Employers must sign employment contracts with their employees
▪ Types of employment contract Definite period ➢ Indefinite period ➢
A seasonal job of less than a year ➢ Collective agreement Types of enterprise ▪ State-owned enterprise
▪ Enterprise employing 10 or more employees
▪ Enterprise with foreign capital
▪ Enterprise in industrial zone or export processing Japan
▪ Lifetime employment and the seniority-based systems
▪ Labor contracts are applied when the number of union members exceeds
75% of the total number of regular employees in the company.
▪ Spring struggle (Shunto): an annual wage increase drive conducted from March to May. China
• A tripartite system was introduced in the early 1990s
• Chinese trade union exists two basic types of economic systems Public economic system ➢ Private economic system ➢ CÂU HỎI:
1. Distinguish between Job Description & Job specification. Provide
examples of JD & JS for positions such as: a secretary, a
receptionist, a sales representative, a waiter,…
2. What is Job Analysis? Explain how information gathered through
a job analysis can be used in different ways.
3. What are sources of candidate (recruitment tools)? Describe them.
4. Which recruitment tools/ methods that are low-cost?
5. How many basic types of question that can be used in an interview?
Provide at least 02 examples for each type.
6. What is employee orientation? Why do we need to provide orientation for employees?
7. What are 3 training methods that we can use to train sales employees at a fashion store?
8. What is performance appraisal? Describe performance appraisal process.
9. Why do we need to conduct performance appraisal? Who should do the appraising?
10.Practise using appraisal methods to appraise your HRM-team
members performance (graphic rating scale, alternation ranking,
paired comparison, forced distribution, behaviorally anchored rating scale).
11.What is employee compensation? Compare direct financial
payment and indirect financial payment, examples?
12.How many types of equity in determining pay rate? What are they? CÂU TRẢ LỜI
câu có trl low cost là referal and work-in
employee orientation là đào tạo hội nhập
câu 7 3 kĩ năng bán hàng trong fashion store thông tin sản phẩm
kĩ năng giao tiếp, bán hàng -on the job training
câu 8 đánh giá hiệu suất
Performance appraisal is an activity used to determine the extent to which
an employee performs work effectively 3 bước3
1.Define the job and its standards
2.Measure employees’ performance against these
standards đo lường hs thực tế và tiêu chuẩn
https://adecco.com.vn/vn/knowledge-center/detail/danh-
gia-hieu-suat-quy-trinh-phuong-phap
3.Provide feedback to the employees so that they can improve their performance
câu 9 tại sao phải đo lường hiệu suất
tạo động viên đánh giá đúng năng lực khen thưởng góp ý cho nv
đào tạo những kiến thức kĩ năng cần thiết, bồi dưỡng phát
triển họ, nâng họ lên vị trí cao hơn và ngược lại3
ai là ng đánh giá hs là người cấp trên gần nhất qản lí trực tiếp
câu 10 đặc điểm là có hoàn thành ko, tính sáng tạo, tốc độ làm việc…
-graphic rating scale là một hình thức đánh giá nhân viên
mà nhà quản lý chỉ cần sử dụng và điểm theo một thang
điểm được chia thành 3 hoặc 5 cấp độ từ rất kém, kém,
bình thường, tốt cho đến rất tốt
-alternation ranking method phương pháp đánh giá luân
phiên Ranking employees from best
to worst on a particular trait, choosing highest, then lowest, until all are ranked
-paired comparison so sánh theo cặp Ranking employees
by making a chart of all possible pairs of the employees for each trait and
indicating which is the better employee of the pair
-forced distribution method Phân bố thành quả
With the forced distribution method, the manager places predetermined percentages of
subordinates in performance categories, as when a
professor “grades on a curve.”
gán tỉ lệ phần trăm trên tổng là chỉ có bao nhiêu ng đạt dc
số lượng bao nhiêu vd 15ng đạt dc hs cao tốt trung bình3