

Preview text:
1. Distinguish between Job Description and Job Specification. Provide examples
of JD & JS for positions such as a secretary, a receptionist, a sales representative, a waiter,…
Job description: a list of what the job entails (Tasks responsibilities, duties)
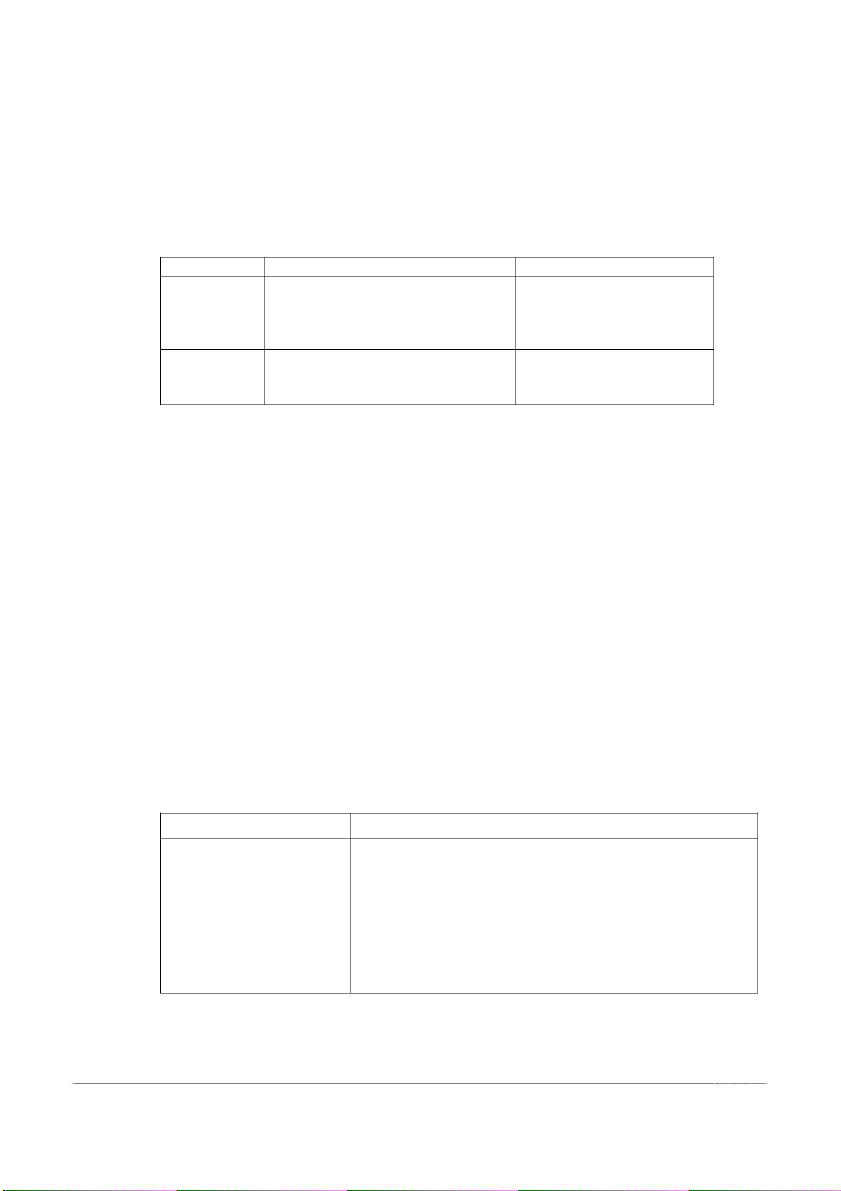
Job specification: what kind of people to hire (Skill, experience, degree, characteristics) Example Job description Job specification -Greet and welcome visitors -1 year of experience in a
-Provide information to visitors receptionist or similar role. Receptionist -Manage the reception area -Good at communicating -Could speak English -Work 8 hours a day -Ability to work in a team Waiter -Take food and beverage orders -Ability to multitask
-Serve food and drinks to customers -Attention to detail
2. What is Job Analysis? Explain how information gathered through a job
analysis can be used in different ways.
- Job analysis is the procedure through which you determine the duties of the
company’s positions and the characteristics of the people to hire for them (produces
information for writing job descriptions and job specifications) - Steps in Job Analysis:
1. Identify the use of the information and how to collect it
2. Review relevant background information about the job
3. Select representative positions to focus on 4. Analyze the job
5. Verify information with workers and supervisors
6. Develop a job description and job specification
- The information produced by the job analysis is the basis for several HR activities
that managers engage in almost every day. Specifically: Recruitment and Selection Performance Appraisal Job Evaluation Training Requirements
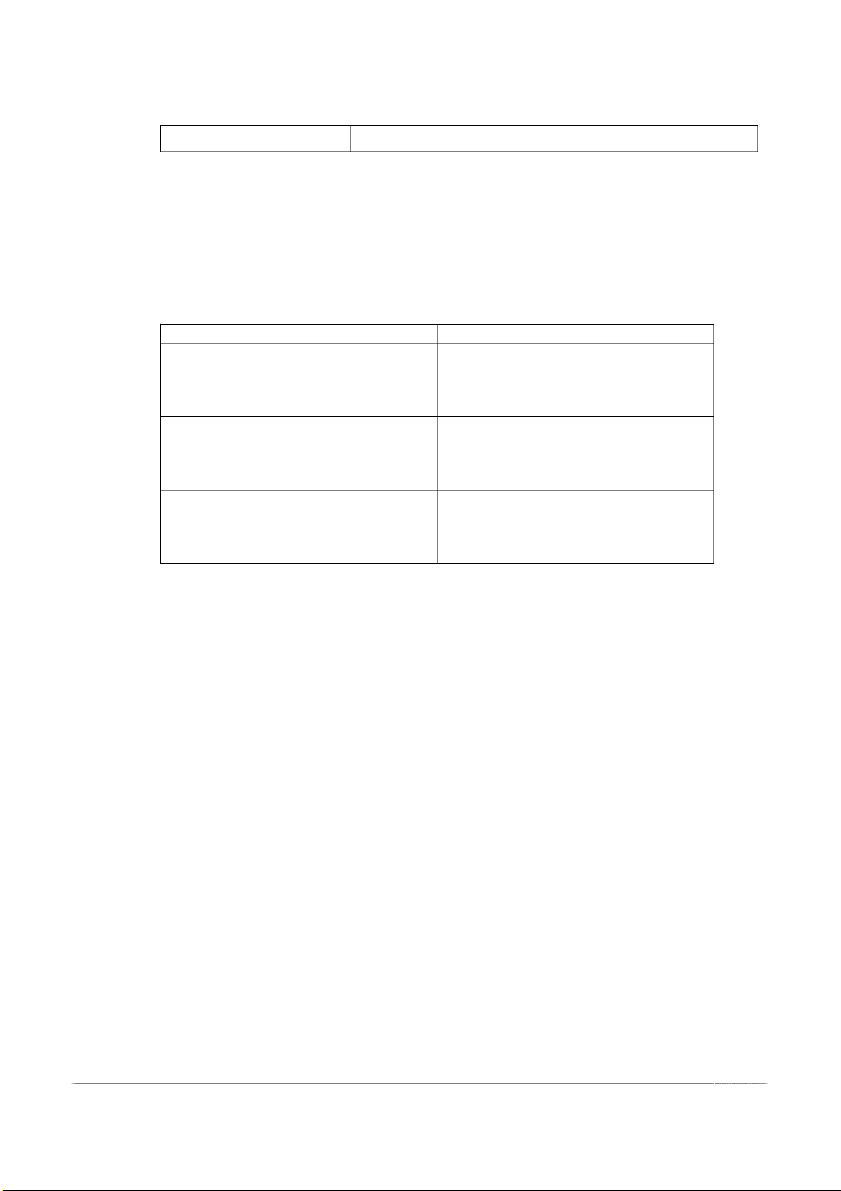
3. What are the sources of candidates (recruitment tools)? Describe them. Internal External/ Outside Job postings Word-of-mouth Internet Advertising Qualification skills Employment agencies inventories Offshoring/Outsourcing jobs Internship College recruiting
4. Which recruitment tools/ methods that are low-cost?
5. How many basic types of questions that can be used in an interview? Provide at
least 02 examples for each type. Type of question Example
- A friend comes in angry and upset.
How would you handle this situation? Situational questions
- Have you ever made a mistake? How did you handle it? Behavioral questions
Knowledge and background questions
6. What is employee orientation? Why do we need to provide orientation for employees?
A procedure for providing new employees with basic background information about the firm.
- Make the new employee feel welcome
- Make sure the new employee has the basic information
- Help the new employee understand the organization in a broad sense
- Start socializing the person into the firm’s culture and ways of doing things
7. What are 3 training methods that we can use to train sales employees at a fashion store?
- On-the-job training: Having a person learn a job by actually doing the job.
- Behavior Modeling: This will help the employee in knowing the right way to do the
task and he will mold his behavior and attitude in a similar way.
- Team Training: Teaches individuals how to listen and cooperate with each other.
8. What is performance appraisal? Describe performance appraisal process.
- Performance appraisal may be defined as any procedure that involves: 1) setting
work standards; 2) assessing the employee’s actual performance relative to the
standards; 3) providing feedback to the employee with the aim of motivating that
person to eliminate performance deficiencies or to continue the performance above par.
- The three-step performance appraisal cycle includes 1) establishing goals and
performance standards, 2) appraising the employee’s performance, and 3) feedback and to take corrective action.
9. Why do we need to conduct performance appraisal? Who should do the appraising?
- There are many reasons to appraise subordinates’ performance. Most employers still
base pay, promotion, and retention decisions on the employee’s appraisal. Also,
appraisals play a central role in the employer’s performance management process. The
appraisals also allow for correcting any deficiencies and opportunity to recalibrate the
employee’s career. Thus, it helps identify training and development needs.
- Peer Appraisals, Rating Committees, Self-Ratings, Appraisal by Subordinates, 360-
degree Feedback, Crowd Appraisals.
10. Practise using appraisal methods to appraise your HRM-team-members
performance (graphic rating scale, alternation ranking, paired comparison,
forced distribution, behaviorally anchored rating scale).
11. What is employee compensation? Compare direct financial payment and
indirect financial payment, examples?
- Employee compensation refers to all forms of pay going to employees and arising from their employment.
- Direct financial compensation includes direct payment of money to employees, such
as salaries, wages, commissions, and bonuses. Indirect financial compensation is non-
cash benefits, such as medical insurance, retirement, and employee services.
12. How many types of equity in determining the pay rate? What are they?
There are four types of equity:
1. External Equity: Compare the job’s pay rate with other companies.
2. Internal Equity: Compare to other jobs within the same company.
3. Individual Equity: Compare with what his/her coworkers earn for the same or very
similar jobs within the company.
4. Procedural Equity: Refers to the perceived fairness of the process used to make
decisions regarding the allocation of pay.