








Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Chapter 1: The Importance of Business Ethics
- Business Ethics:
+ Comprises principles and standards that guide behavior in the world of business
+ Right or wrong, acceptable or unacceptable behavior within the organization
+ Determined by you and key stakeholders - Benefits: + Better ethical climate
+ Employee commitment and trust + Investor loyalty and trust
+ Customer satisfaction and trust + Long term profits
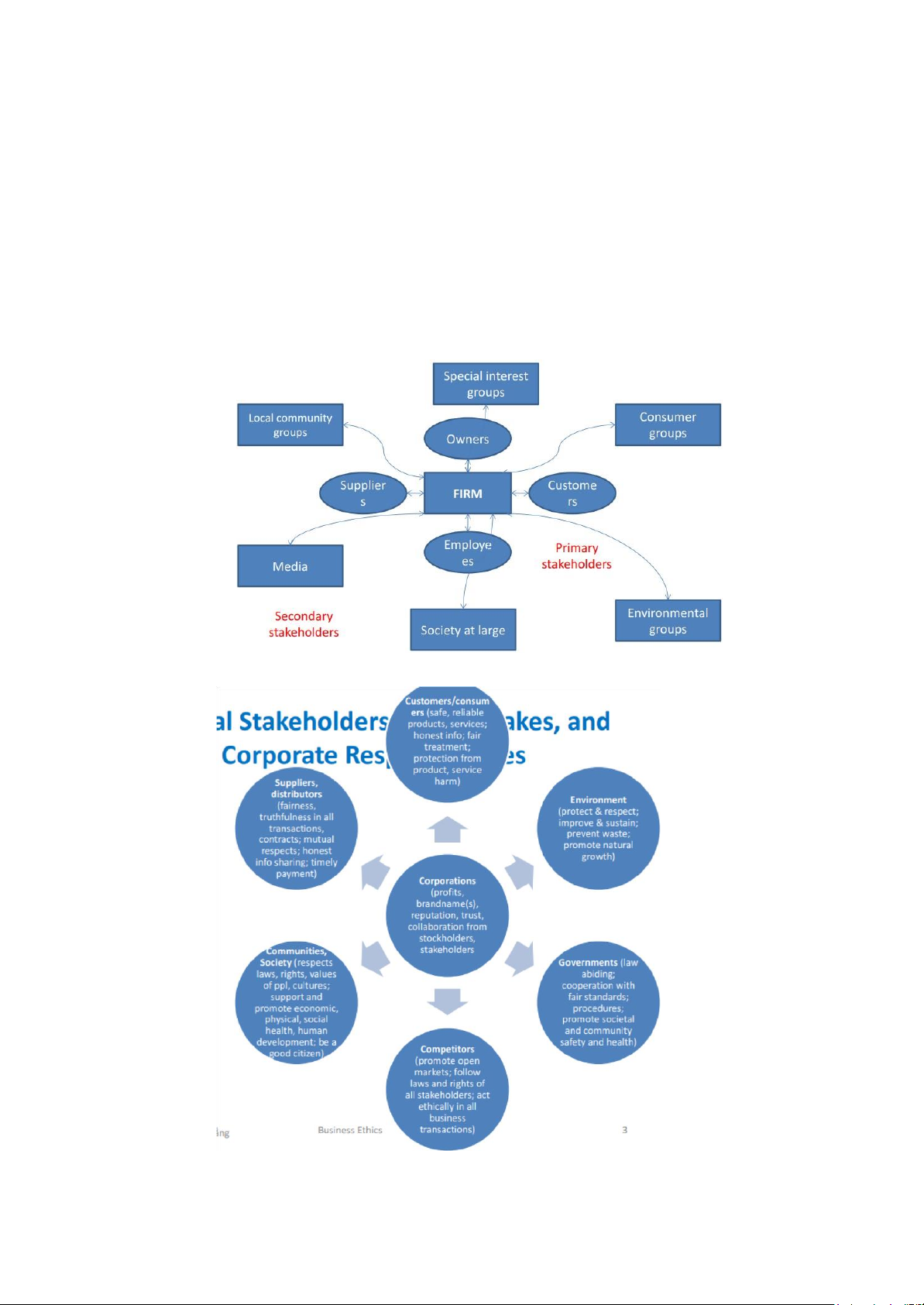
Chapter 2: Stakeholder Relationships, Social Responsibility and Corporate Governance
- Stakeholder framework
+ Helps identify internal and externalstakeholders
+ Helps monitor and respond to needs, values, and expectations of stakeholder group +
Primary SH: those who continued association is necessary for a firm’s survival (employees,
customers, suppliers, and creditors)
+ Second SH: not essential to a firm’s survival (media, government agencies, and unions)
- Social Responsibility: Can be viewed as a contract with society (economics, legal, ethical, philanthrophic)
- Business ethics: involve carefully though-out rules of conduct that guide decision making
- Corporate governance: involves the development of formal systems of accountability, oversight, and control.
- Utilizing the stakeholder framework to manage responsibility and business ethics: assessing
the corporate culture, (2) identifying stakeholder groups, (3) identifying stakeholder issues, (4)
assessing organizational commitment to social responsibility, (5) identifying resources and
determining urgency, and (6) gaining stakeholder feedback
OPENING CASE (Megan Jones) 1.
If tracking employees through technology is not illegal, why should Megan be concerned
if she is not involved in any misconduct?
Because it raises ethical issues related to privacy and confidentiality. Monitoring employees' personal
activities, such as visiting a hospital or sharing confidential information, may infringe upon their right
to privacy. Even if legal, such practices can still be morally questionable. 2.
At this point, what are Megan’s alternatives to resolve her current dilemma about her
involvement and knowledge about GAC’s tracking employees? -
Megan could express her concerns to her supervisor, Debbie, seeking clarification on the ethical
implications of the employee tracking activities. -
She might consult with HR colleagues or legal experts within the organization to gain a better
understanding of the legal and ethical aspects of the situation. -
Megan could propose ethical guidelines or policies that ensure a balance between monitoring
for legitimate reasons (such as preventing confidential information leaks) and respecting employees' privacy rights. -
If Megan finds the practices to be clearly unethical or illegal, she may consider escalating the
issue to higher management or external authorities.
3. Who should have a stake or an interest in how GAC tracks and monitors its employees? lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 -
Employees: Have a stake in their privacy and the right to conduct personal activities without unwarranted surveillance. -
Megan: Has a stake in maintaining her ethical integrity and deciding whether to comply
with or resist the potentially unethical practices. -
Debbie and GAC Management: Have a stake in maintaining organizational security,
preventing information leaks, and ensuring compliance with legal and ethical standards. -
Legal Experts and HR Colleagues: Have a stake in providing guidance on the ethical and legal aspects of employee tracking. -
Competitors and External Entities: May have a stake in understanding how GAC monitors
its employees to gain a competitive advantage.
CLOSING CASE (Demarco Texas University)
1. How should Demarco approach this issue when he meets with the tribal leaders? -
Demarco should approach the issue with transparency, honesty, and empathy when meeting with the tribal leaders. -
Clearly communicate the potential benefits and drawbacks of the strip mining project,
considering the impact on their traditional way of life and the environment. -
Listen actively to the concerns and feedback from the tribal leaders and ensure they understand
the potential consequences for their community.
2. What should be the priorities in balancing the various stakeholder interests? -
Prioritize open communication and collaboration among all stakeholders, including the
indigenous tribes, Xeon employees, the Brazilian government, and surrounding communities. -
Consider the long-term impact on both the indigenous population and the company's future,
weighing economic benefits against potential cultural and environmental harm. -
Explore alternatives and compromises that could address the concerns of different stakeholders
while still allowing for the extraction of niobium.
3. Can the CEO and board of directors of Xeon continue operations and maintain a
stakehholder orientation -
Considering the interests of all parties involved, including the indigenous tribes, employees, and the broader community. -
Conduct a thorough assessment of the potential social, environmental, and economic impacts of the strip mining project. -
Implement responsible and sustainable practices, such as environmentally friendly extraction
methods and measures to mitigate negative impacts on the indigenous communities. -
Foster a culture within the company that values ethical decision-making, social responsibility,
and environmental sustainability.
Chapter 5: Ethical Decision Making
- Ethical decision making process:
+ Ethical Issue Intensity: Relates to perceived relevance or importance of an ethical issue to the
individual, work group, and/or organization lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
- Individual factors:
- Organizational factors:
+ Corporate Culture: a set of value, belief, norms, ways of solving problems share by member of the
organization (ethical culture reflects the integrity of decisions made and is a function of many factors,
including corporate policies, management’s leadership on ethical issues) leadership on ethical issues,
the influence of coworkers, and the opportunity for unethical behavior
+ Significant others: Those who have influence in a work group, including peers, managers, coworkers, and subordinates
- Opportunity: describes the conditions in an organization that limit or permit ethical or unethical behavior +
Relates to individuals’ immediate job context —where they work, whom they work with, and the nature of the work. + Also comes from knowledge
+ The opportunity for unethical behavior cannot be eliminated without aggressive enforcement of codes and rules
CLOSING CASE (CrudeOil)
1. Describe the organizational culture at CrudeOil. How does it contribute to the current situation? -
The organizational culture at CrudeOil appears to be toxic, characterized by a harsh and
unpredictable management style under Jim Stone's leadership. -
The focus on achieving results and increasing sales and profits seems to override the importance
of employee well-being and a respectful work environment. -
There is a lack of transparency and open communication, as evidenced by Jim's arbitrary and intimidating behaviors.
2. How is CrudeOil violating its core value of treating others with respect? What are some ways
it could reincorporate this core value into its organizational culture?
- CrudeOil is violating its core value of treating others with respect through Jim Stone's intimidating
and demeaning behaviors towards employees. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
- The discrepancy between the stated core value and Jim's actions creates a culture of hypocrisy, eroding
trust and creating a hostile work environment.
- Ways to reincorporate the core value:
+ Provide leadership training and development for managers, emphasizing the importance of
respectful communication and fair treatment of employees. +
Establish clear guidelines on acceptable behavior and consequences for violating respectful conduct.
+ Encourage an open-door policy where employees can report incidents of bullying or harassment without fear of retaliation.
+ Foster a culture that values diversity, inclusion, and collaboration, reinforcing the core value of
respect in all aspects of the organization.
3. If Madison cannot report her problems to her immediate supervisor, what are some other
ways she can handle the situation -
Seek support from HR: Madison can approach the Human Resources department to discuss her
concerns and seek guidance on how to address the situation. -
Document incidents: Keep a record of specific instances of mistreatment, including dates,
times, and details, to provide evidence if needed in the future. -
Build a support network: Connect with colleagues who have faced similar issues and
collectively discuss potential actions or approaches to addressing the problem. -
Anonymous reporting channels: If available, use anonymous reporting mechanisms within the
organization to communicate concerns about Jim's behavior to higher-ups. -
External resources: Explore external resources, such as employment law attorneys or
counseling services, for advice on how to navigate the situation. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
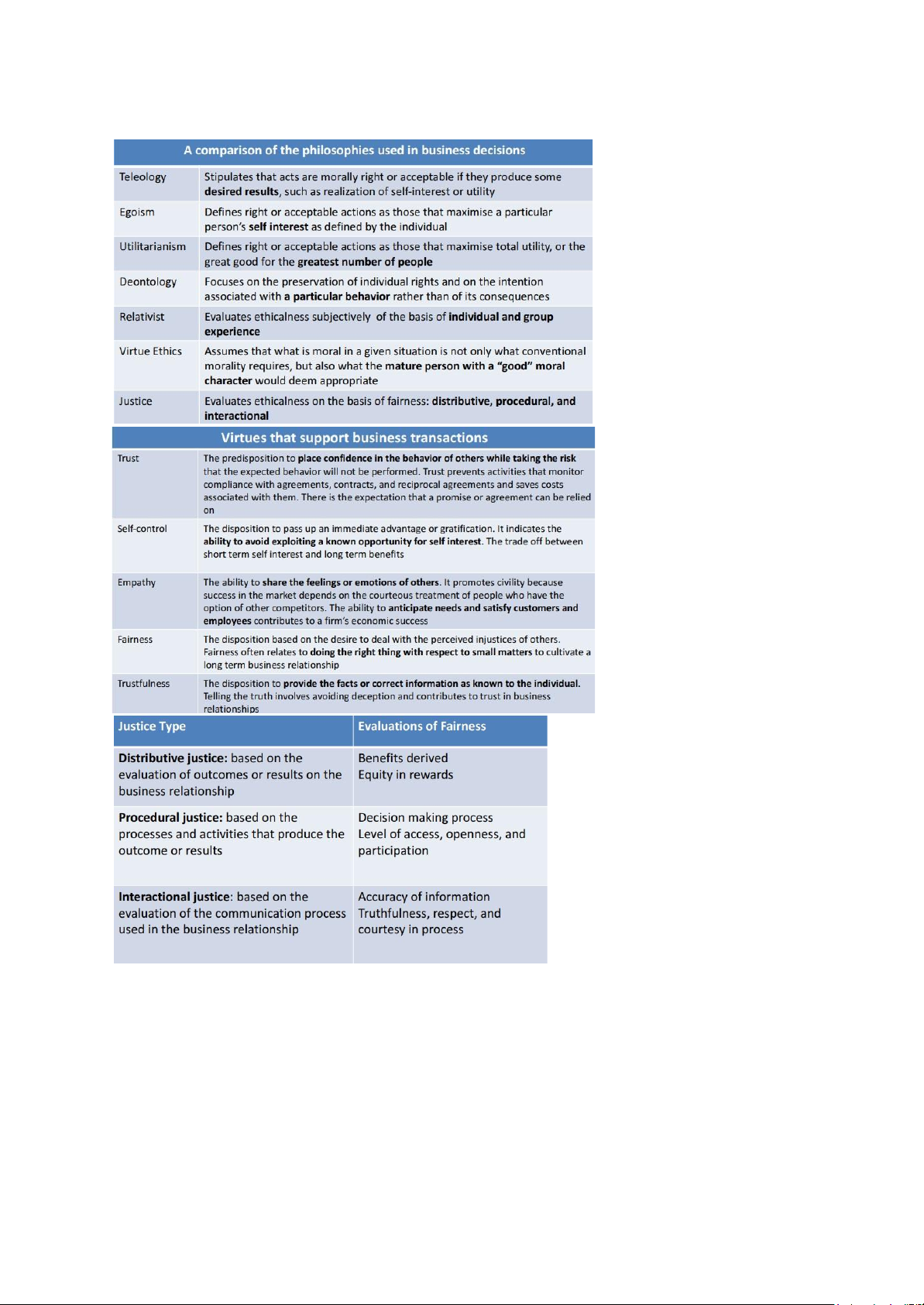
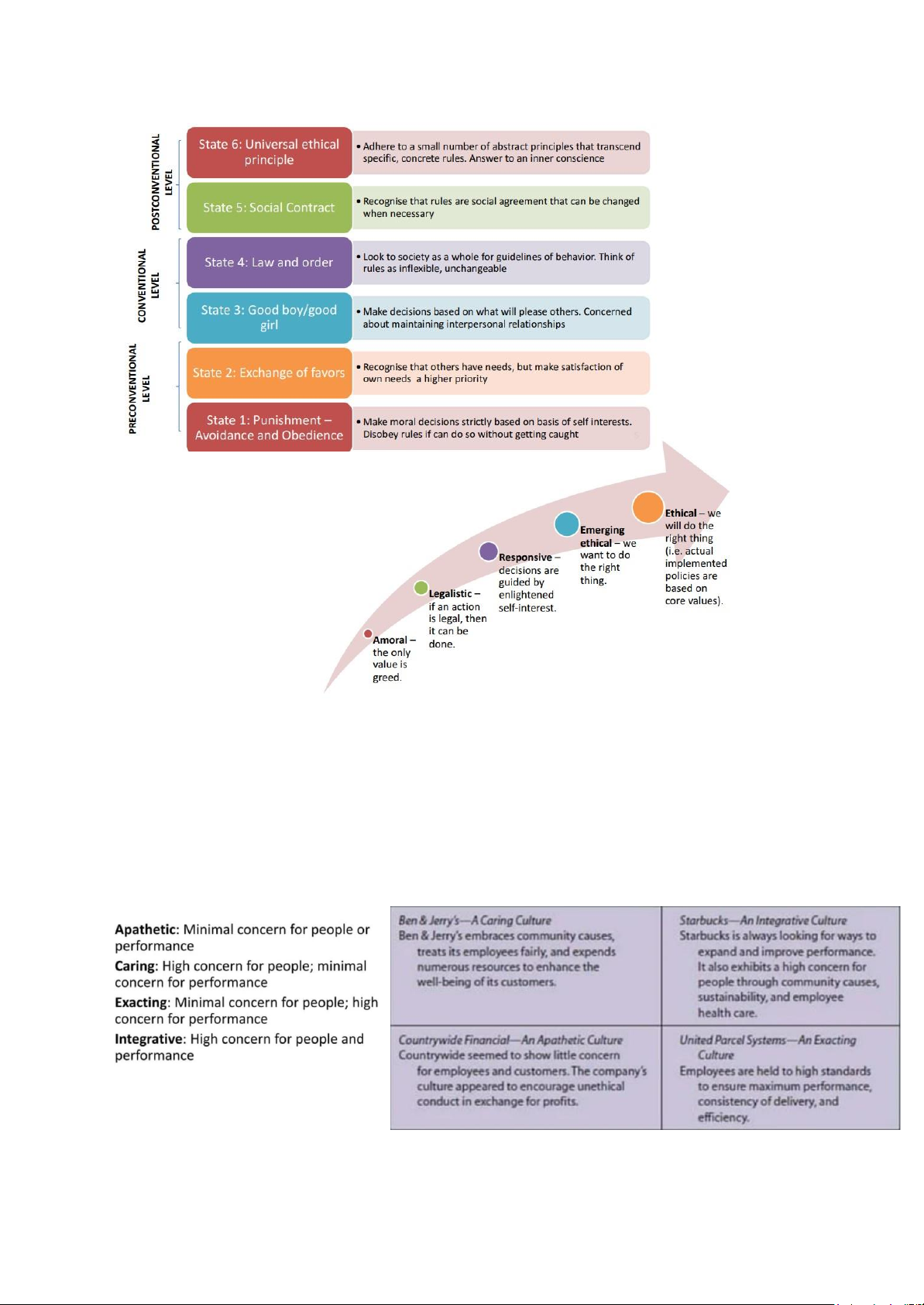
Chapter 6: Individual Factors: Moral Philosophies and Values
- Kohlberg’s Stage of Cognitive Moral Development lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
- Corporate Moral Development :
Chapter 8: Organizational Factors: The Role of Ethical Culture and Relationships 1. Definition
Organizational culture includes shared values, norms, and artifacts that influence employees and
determine behavior, including ways of solving problems that members (employees) of an organization share
- Core values form for a corporate culture: helps an organization realize its vision and achieve its goals.
2. Organizational Culture Typologies
- A cultural audit: an assessment of an organization’s values. Communication about ethical expectations
and support from top management help to identify a corporate culture that encourages ethical conduct
or leads to ethical conflict. 3. Leadership in corporate culture lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
4. Organizational Structure -
A centralized organization: decision-making authority is concentrated in the hands of top-level
managers, and little authority is delegated to lower levels. -
A decentralized organization: decision-making authority is delegated as far down the chain of command as possible.
5. Variation in Employee Conduct
- 10 percent of employees take advantage of situations to further their own personal interests.
+ More likely to manipulate, cheat, or act in a self-serving manner when the benefits gained
from doing so are greater than the penalties for the misconduct.
+ The lower the risk of being caught, the higher the likelihood that the 10 percent most
likely to take advantage of the company will be involved in unethical activities.
- Another 40 percent of workers go along with the work group on most matters.
+ Most concerned about the social implications of their actions and want to fit into the organization.
+ Although they have personal opinions, they are easily influenced by what the people around them are doing.
+ Coupled with this philosophy is the belief that no one will get into trouble for doing what everybody else is doing.
- 40 percent of a company’s employees always try to follow company policies and rules.
+ Not only have a strong grasp of their corporate culture’s definition of acceptable behavior
but also attempt to comply with codes of ethics, ethics training, and other
communications about appropriate conduct.
+ If the company fails to communicate standards of appropriate behavior, members of this group will devise their own.
- The final 10 percent: maintain formal ethical standards that focus on rights, duties, and rules.
+ Embrace values that assert certain inalienable rights and actions, which they perceive to be always ethically correct.
+ Believe that their values are right and superior to the values of others in the company,
or even to the company’s value system, when an ethical conflict arises. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
+ Report the misconduct of others or to speak out when they view activities within the company as unethical.
6. Strong Ethical Leaders
(1) Strong personal character, (2) Passion to do right, (3) Proactive, (4) Consider SH interest, (5)
Roles model for the organization’s values, (6) transparent and actively involve in organization
decision making, (7) Competent manager who take a holistic view of firm’s ethical culture
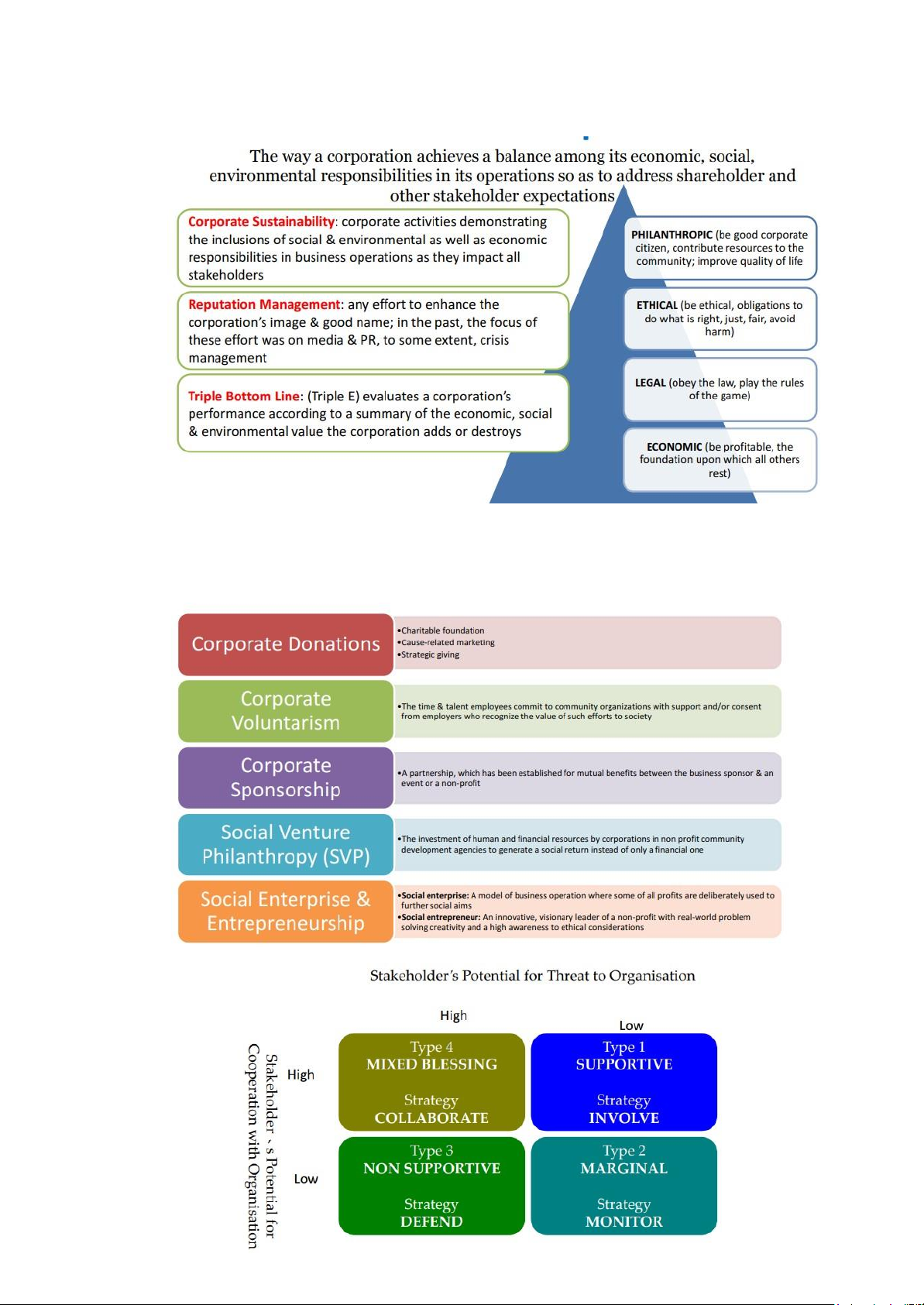
Chapter 9: Corporate Social Responsibility
- Stakeholder Management Approach: a way of understanding the ethical effects of
environmental forces and groups on specific issues that affect real time stakeholders and their welfare.
- External SH, moral stakes, and corporate responsibilities lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 - CSR: Concept
- Corporate Philanthrophy (the effort of business to contribute to society socially, manifestet by
donations money or goods & services in kind, voluntarism, and sponsorship of events that contribute to society
- SH analysis: lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
Chapter 10: Social Entrepreneurship 1. Def
- A business operated by a non-profit that is direct involve in the production or selling of g&s
- For dual purpose: generating income and achieving social/environmental aims
2. Social Enterprise Strategy
3. Type of social entrepreneurs CLASS ACTIVITIES
1. Social Business Model Canva (Tohe)
- Key Partners: British Council, CSIP, LGT Venture Philanthropy - Key activities
+ Design and Product Development: accessories, stationery, homeware, and toys. -> core activities to
create innovative and appealing items. + Manufacturing and Production + Art and Painting Activities: + Philanthropic Initiatives + Educational Components
+ Promotional and Awareness Activities
+ Collaboration with Partners and Stakeholders lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332
+ Environmental Sustainability
+ Playground and Recreational Activities + Community Engagement"
- Vision: + Empowering Disadvantaged Children
+ Promoting Art and Creativity + Sustainable Philanthropy
+ Environmental Responsibility"
- Values (Social values): protect and preserve nature and the ecosystem by minimising and eliminating harmful factors" - Cost structure
+ Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Raw materials and supplies, Manufacturing and production costs + Labor Costs:
+ Overhead Expenses: Rent and utilities, Administrative expenses, Technology and IT costs + Marketing and Sales Costs:
+ Philanthropic Expenses: Funding for free art classes,Direct financial assistance + Educational Expenses
+ Community Engagement Expenses
+ Legal and Regulatory Compliance Value proposition Problem
Previous efforts cannot reach all one million disabled children across the country. -
The majority of assistance models have been limited to charity and short-term activities. There remains a gap
in sustainable activities and barriers exist within healthcare and education, as well as in access to entertainment, culture and sports3 . -
Disabled children also face difficulties inside the home. Many are born into poor households and are yet to
receive support so they can learn andplay as other kids. That was the context that prompted Tòhe’s creation. Solution
1. Diversification of Revenue Streams
2. Sustainable Philanthropic Initiatives
3. Balancing Social Impact and Business Operation Differentiator 1. Art and Creativity Focus 2. Social Impact
3. Environmental Responsibility 4. Community Engagement 5. Unique Product Offerings 2. - Lavondo Case Ethical, legal issues Your action lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 -
Research company's rules of conduct and get advices from lawyer (legal issue)
Abusive behavior, sexual harassment, biased - Report to higher authorities -
Evidence (image, message, ...) Albert Chen Case Ethical, legal issues Ethical issues: -
Insider trading: Barry's demand for inside information on IPOs raises ethical concerns about insider trading,
which is il egal and unethical. -
Misuse of company information: Albert's supervisor's request to buy stock for personal gain using non-public
information is a breach of ethical standards and potentially illegal -
Inappropriate workplace behavior: The sending of off-color jokes and nude photos through company email
is inappropriate workplace behavior, and Mary's forwarding of such messages raises questions about her conduct. -
- Professional ethics: Albert's risky trading to compensate for lost income and Mary's involvement in forwarding
inappropriate messages raise concerns about professional ethics in their brokerage careers. Legal Issues: -
Insider trading: Barry's demand for inside information potential y involves illegal insider trading, which is a violation of securities laws. -
SEC investigation: Mary's forwarding of inappropriate emails and the subsequent SEC investigation pose
potential legal consequences for her. - Lael Case Your action lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 Albert
1. Comply with Barry's demand for insider information. Consequences: -
Positive: Albert may maintain his friendship with Barry and potentially receive short-term benefits. -
Negative: This action would involve illegal insider trading, exposing Albert to legal consequences such as
fines, imprisonment, and damage to his professional reputation if caught. It could also harm the integrity of the financial markets.
2. Report Barry's demand for insider information to the appropriate authorities or Albert's supervisor. Consequences: -
Positive: Reporting the situation demonstrates Albert's commitment to ethical conduct and compliance
with regulations. It helps maintain the integrity of the financial industry and protects investors. -
Negative: There could be potential backlash or retaliation from Barry or others involved in the
misconduct. Albert may face challenges in his workplace environment or even potential threats to his own career.
3. Reflect on his own actions and reassess his investment strategies to prioritize ethical conduct and long-term sustainability. Consequences: -
Positive: By reevaluating his investment practices and focusing on ethical conduct, Albert can rebuild
trust with his clients, protect their interests, and enhance his professional reputation in the long run. -
Negative: Albert may need to adjust his investment approach and potentially face short-term financial
chal enges as he transitions to more ethical practices. Mary
1. Accept the termination and move on, seeking new employment opportunities. Consequences: -
Positive: Mary can distance herself from the e-mail scandal and potentially find a new job that aligns with
her professional goals and values. -
Negative: The termination may impact Mary's reputation, making it more chal enging to secure
employment. It could also lead to financial difficulties if she doesn't find a new job promptly.
2. Take legal action against her former employer for wrongful termination. Consequences: -
Positive: If successful, Mary may receive compensation for damages related to wrongful termination,
which can help alleviate financial burdens and restore her reputation. -
Negative: Legal action can be time-consuming, costly, and emotional y draining. There is no guarantee of
a favorable outcome, and it could strain relationships and further damage her professional reputation. lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 1. Review the Performance Records: Take a closer look at the performance records of each candidate. 2. Eliminate Bias: Ensure that personal relationships and biases do not Legal issues: unduly influence the - There isn't any decision-making potential legal issues. If process. Evaluate someone who does not each candidate based deserve the promotion on their individual gets it over the others, merits, qualifications, this may be unfair, but and performance, - Risk: Lael may get
it’s not necessarily il egal rather than factors
into trouble with some ethical just because that person
such as race, gender, issues such as discrimination Candidate: Quang didn’t deserve it. The age, or personal , favoritism, fairness and - Yeh difference between connections. Cost: + The company's Lael should unfair and il egal performance may be prioritize promotions boils down 3. Schedule affected by her decision + candidates based to how the employer Individual Meetings: on their Her reputation will be
decided who to promote. qualifications and Arrange separate damaged if others believe - Given that al 3 performance meetings with each her decision is unfaired + candidates have the records. Quang candidate to discuss Lael could break her appears to be the potential qualifications of their aspirations, personal relationship strongest candidate management, there career goals, and their - Challenge: Lael in terms of her aren't any specific views on the wants to please her recent performance indications of
and qualifications. promotion. This will colleague and upper- discrimination and
provide an opportunity management stereotypes if any of
to gain further insights individual, them get promoted into their motivations but she also has to be fair Ethical issues: and gauge their Supporting a candidate commitment to the over others may be position. regarded as discrimination on 4. Seek Input age,race, gender from Stakeholders: Consult with relevant stakeholders, such as team members who have worked closely with the candidates, to gather feedback on their performance, leadership style, and interpersonal skills. 5.Consider Diversity lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 and Inclusion: Take into account the importance of diversity and inclusion in the decision-making process. While it is crucial to evaluate candidates based on merit, considering the potential positive impact of promoting an underrepresented candidate can contribute to a more inclusive work environment. ✨SHAREHOLDERS&BOD✨ Firm Shareholders & BOD - Profit maximization - Dividend Income - Capital Gains - Capital infusion Financial - ROI - Investor relations - Share paybacks - Investment Diversification - Corporate Governance
- Ethical and Social Responsibility - Community Impact Non-financi
Stakeholder alignment (in goals, interests...) in - Innovation and Research al
order to harmonize the business environment - Reputation - Industry Leadership - Longterm Sustainability -
Fair Treatment of Shareholders (Asymmetric information)
- Ethical Investing, decisions -
Shareholders expect fair treatment - Policy
and equitable distribution of benefits, equal Potential
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) access to information. Ethics Factors Issues -
Transparency and Disclosure ⇒
- Monitoring Management ==> long term creation Avoiding + responsible in investing
Insider Trading Accountability ⇒ - Conflict of interests
Long-Term Value Creation + Responsible
Investing Conflict of Interest Moral Philosophy Moral Development Pros and Cons lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 - Pros:
+Inspires ethical behavior and Utilitarianism: Mr. societal change Khoa's actions aim for
+Sets a positive example for
societal happiness but Mr. Khoa exhibits ethical growth
Teacher might infringe on advanced moral
+ Fights against fraudulent
Đỗ Việt individual rights. Deontology: His
reasoning, prioritizing
behaviours in exams and creates
Khoa actions align with justice over personal
equality in the educational moral duty but may safety environment -Cons: lead to rigid
+ may face threats, isolation, or outcomes. even harm
+ lead to social conflicts - Pros + Consumer Awareness (alert
consumers to safety concerns -> preventing them from buying - Deontology: defective products) Engineer Tach
+ Pressure for Action: Publicizing emphasizes his moral
the issue -> put significant pressure duty to report
on the company -> Company has to production errors and
take swift and effective action to safety concerns to
rectify the error. The fear of ensure transparency reputational damage can be a and uphold ethical
strong motivator for immediate and standards
Stage 6 (Universal Ethical careful resolution. -
Utilitarianism: Principle): Engineer Tach's - Cons
Although there might be actions align closely with
+ Reputational Damage: Publicizing an element of this stage. He is motivated Tạch,
by a deep sense of duty to internal issues can harm the Toyota self-interest in his uphold ethical standards,
company's reputation -> Impact actions, especially as
ensure product safety, and sales, investor confidence, and trust he and his family may act in the best interest of in the brand. face some consumers, regardless of
+ Legal and Ethical Implications: consequences -> he personal consequences.
Legal and ethical considerations appears to be motivated surrounding the disclosure of by ethical concerns and
internal company information + the welfare of
Incomplete Information: Publicizing consumers -> He
the issue might not provide all the seems to be focused
necessary context or details -> on ethical principles rather than personal Public misunderstandings or gain. misinterpretations.
+ Affect on Family and colleagues:
Company is negatively affected -> Benefits of workers cannot be ensured lOMoAR cPSD| 58511332 - many patients - Exposing Unethical have Practices: The case has been brought to light unethical diagnosed
practices within the hospital, wrongly -
which can lead to reforms and ruin the
improved ethical standards in whole Hoài healthcare. hospital Đức - utilitarianism leading to its stage 5(6) - Patient Awareness: It hospita - justice raises awareness among fame l
patients about the importance collapse, higher rate
of ensuring the accuracy and of
integrity of their medical tests unemployme and results. nt, criticise of -
Patient Advocacy: The others and
case can empower patients to punishment be more vigilant about their of the healthcare and advocate for government' their rights and safety. s regulation




