














Preview text:
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
--------------------------- [CHAPTER 1]
Introduction to International Relations
Philosophical Foundation
Sense of belonging → Communication & Co-existence → Grouping in
different forms → Power & Conflict Historical Foundation
Prehistoric Men → CLAN → (MATRILINEAL) → (PATRILINEAL) →
TRIBE → COMMUNE → NATION STATE Definition
INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS is the study of interactions among various
actors that participate in international politics
- the most advanced form of interaction
- the most representative for humankind
- the most complicated processes
==> An interdisciplinary field
WHY STUDY INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS? Knowledge
- IR is the environment that determines the behaviours of states and people
- IR engages with the drive of interests, rights and responsibility
- IR gives the big picture of the world Skills
- IR pushes you to read more & even research more
- IR trains you to analyse, evaluate and even associate events together Attitude
- IR turns you into a more open-minded person with critical outlook
- IR helps you to engage with the current changes and calmly embrace uncertainty WHAT WILL YOU STUDY? Scope of study Motive - Interest - Power - International cooperation Behavioural patterns
- Rationality: Decision made by rational choice
- Tools: Means to achieve the goals - International system - Conflict or Cooperation Outcomes - More gains - More power - Reaction of other actors - Reaction of the system An expanding field - Main actors:
+ Nation-state => State & Non-state actors
- Main kind of relations
+ Political => Multidimensional
- Main research interest
+ Political issues => Interconnected issues [CHAPTER 2 - 3]
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS & LEVEL OF ANALYSIS
I. LEVELS OF ANALYSIS (Cấp độ chính sách phân cấp đối ngoại) - Global level:
+ all global trends, forces and factors need to be taken into account
+ Toàn cầu: Các quốc gia đều phải hợp tác toàn cầu.
+ VD: VN, Khủng hoảng 2008 - 2009: Mĩ ảnh hưởng -> tất cả quốc gia ảnh
hưởng, Mĩ chi phối thương mại thế giới. - Interstate level:
+ Interactions among states need to be taken into account in the formation of
state’s motive, behaviors, and results.
+ Lợi ích nhóm quyền lực khác nhau chi phối quốc gia - nội bộ hoặc giữa các quốc gia với nhau.
+ VD: đẩy mạnh chiến tranh Trung Đông, Hợp tác châu Á - TBD, Joe Biden đại
điện cho Đảng Dân chủ,… - Domestic level:
+ All domestic forces and interest groups’ influences on one state’s relations with others.
+ Trong nguồn kte có sức mạnh quốc gia - Individual-level:
+ Psychological features, personal awareness, choice decision-making process,
and personal activities of individuals involved in international relations.
+ Người có ảnh hưởng lớn đến quốc gia đó: Donald Trump, Obama,… II. MAJOR THEORIES
“A theory is a collection of propositions that combine to explain phenomena by
specifying the relationships among a set of concepts. It is a story of “why” a relationship
exists between those concepts.” (p.68)
Lí thuyết không phải do quốc gia định hình, researchers nghiên cứu (VD: Ban cố vấn:
GS đầu ngành VH, KT,… support cho Trump,…), lí thuyết có từ thực tiến (xảy ra => tổng
hợp => phát triển => dự báo tương lai
Giải thích hiện tượng KT, CT, XH và các mối quan hệ => giải quyết các vđề thực tế,
nhân tố, bối cảnh => Hệ thống mang tính định hướng ---------------------
MAJOR THEORIES IN INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS
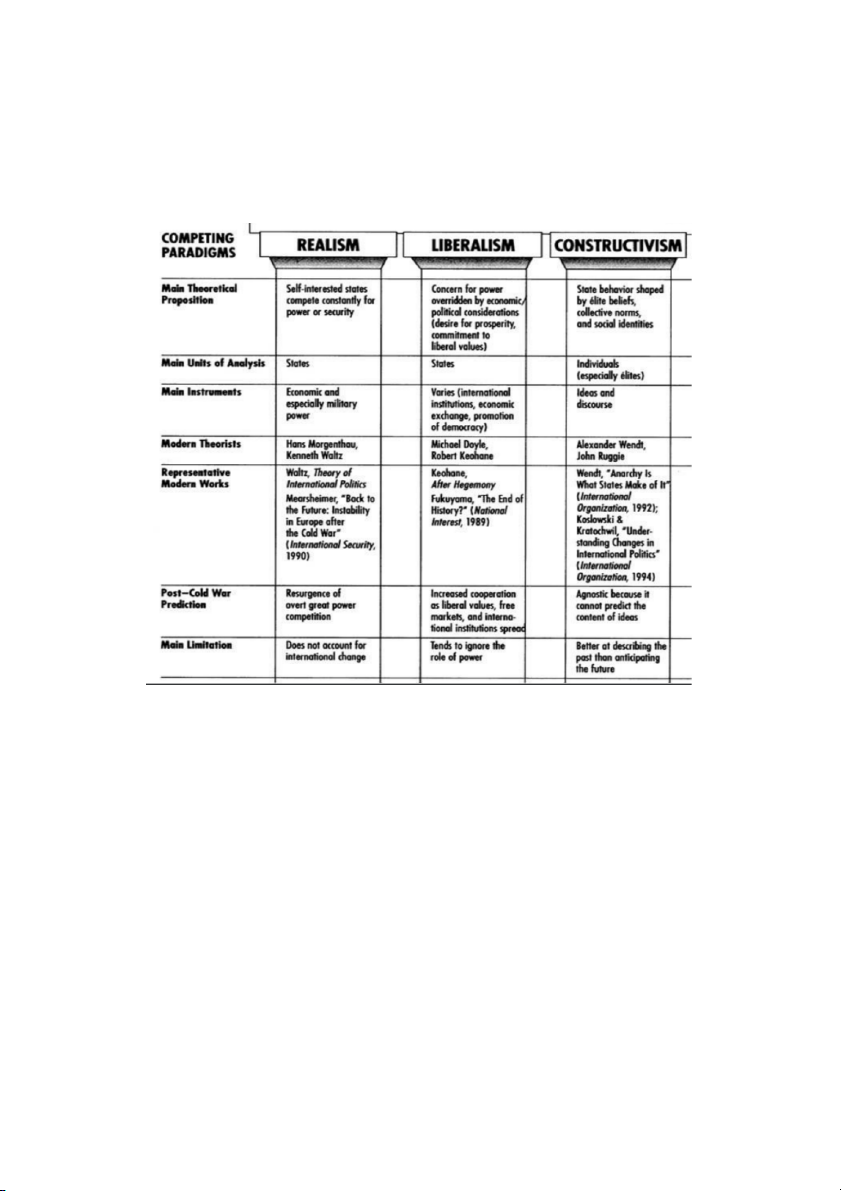
1. Realism (Chủ nghĩa hiện thực) ● Classical realism ● Neo-Realism -
Adding outside factor: emphasizing the impact of international system -
Proposing new approach: analysing IR in term of systemic level
2. Liberalism (Pluralism) ● Classical liberalism ● Neo-Liberalism -
State is not the only actor in IR existence of mix-actors (state & non-state actors) -
Anarchy of “friends” with cooperative potential: peace is achievable -
IR is interdependent process. -
Emphases on roles of Democracy, Market economy, and Institution. REALISM LIBERALISM Billiard Ball Model Cobweb Model
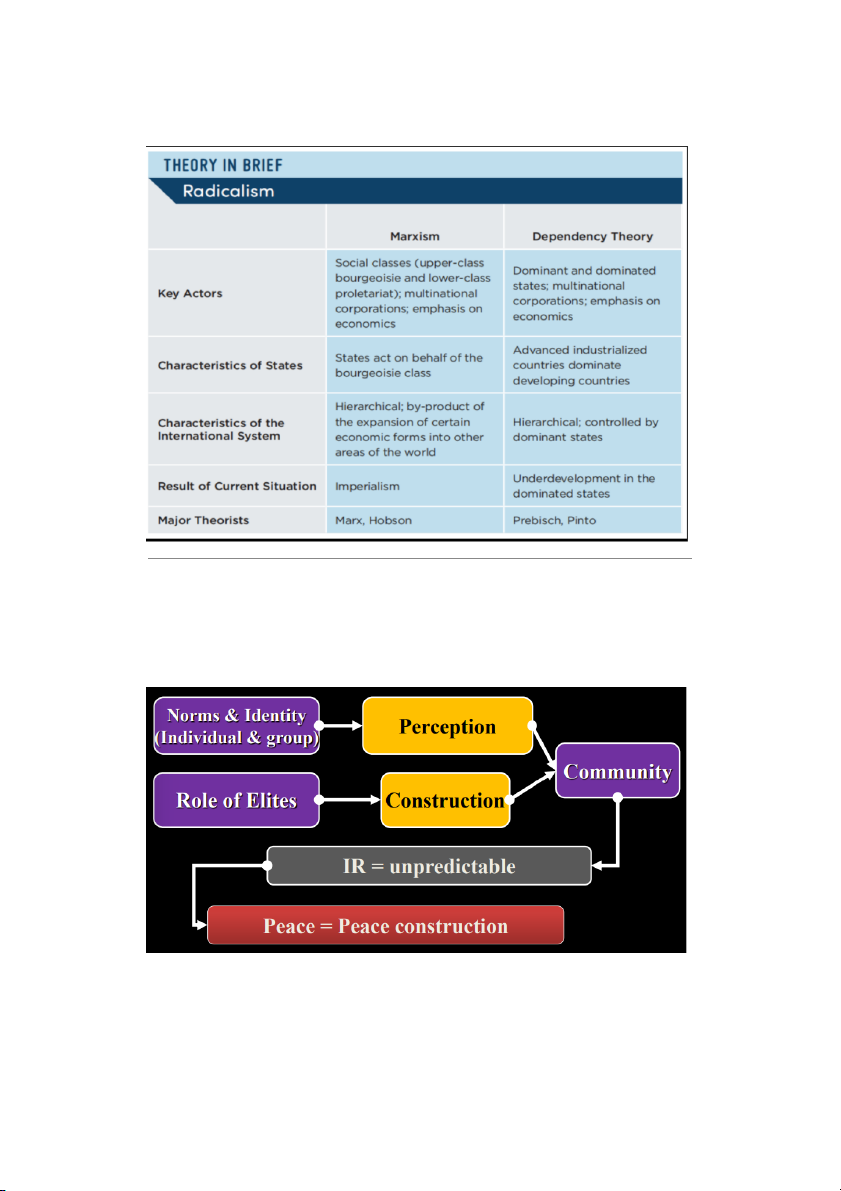
IR MODELS IN TERM OF THEORIES [3. RADICAL THEORIES] ●
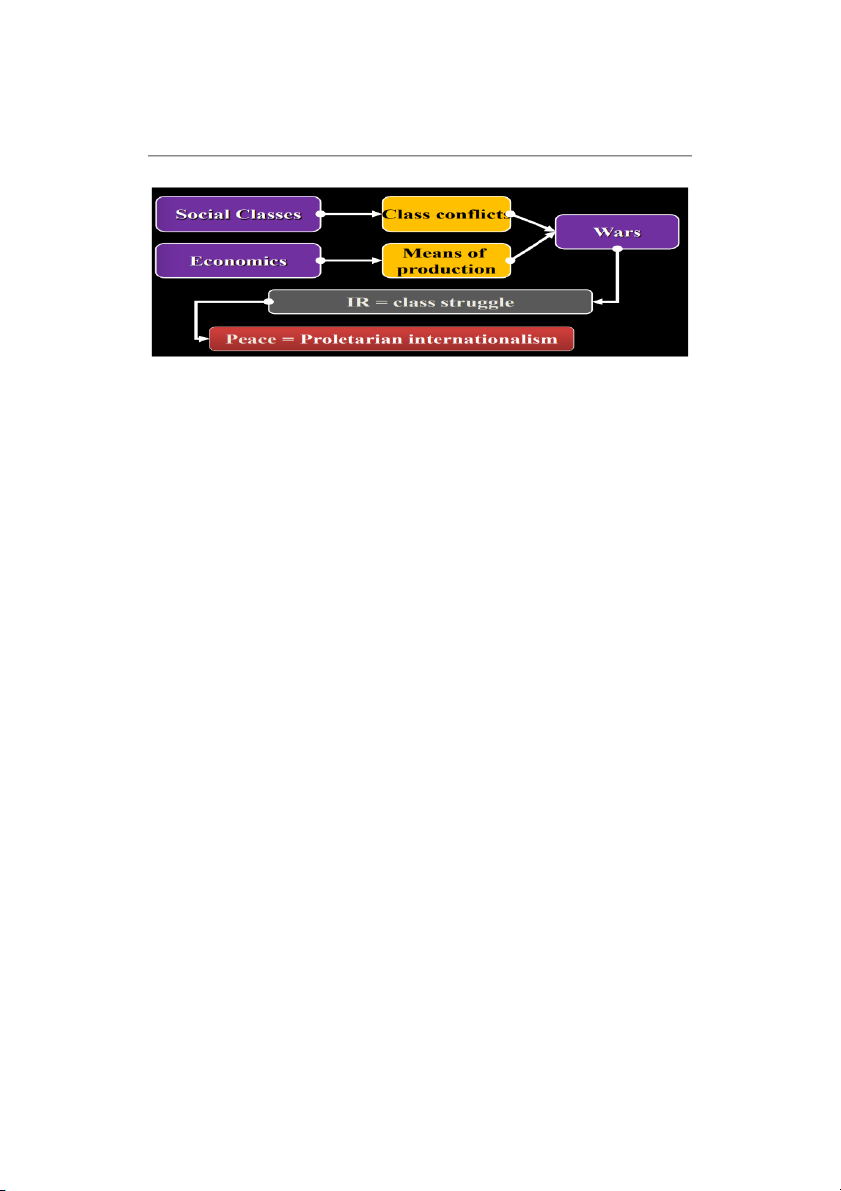
Marxism & Neo-Marxism -
Capitalism aims at economic profits → deploy the global market →
internationalizing capitalism → become dominant -
Capitalism based on class exploitation → exploiting proletarian class
internationalizing → class struggle
=> “Workers of the world, united!” (Vô sản của tất cả các nước đoàn kết lại !) ● Leninism -
Increasing confront. of imperialist powers (CN Đế quốc) → War -
Deepening class conflicts (mâu thuẫn giai cấp) → Proletarian revolution (CM vô sản) -
P. Revolution happens only at the weakest chain of capitalism -
Other ideas: states, nations, and classes
=> “Workers and oppressed peoples and nations of the world, united!”
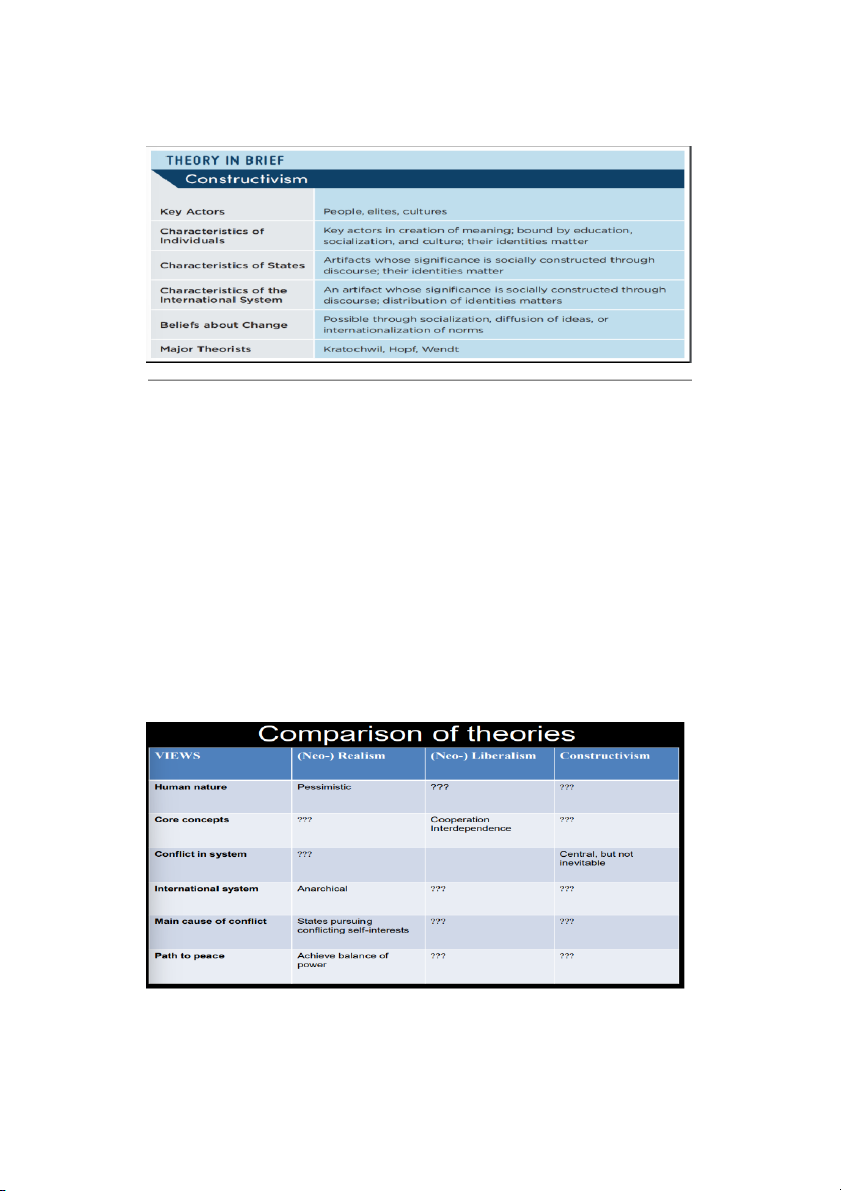
4. CONSTRUCTIVISM (Chủ nghĩa Kiến tạo)
Identity Culture (bản sắc (liên quan đến tốn giáo, văn hóa, ngôn ngữ, niềm tin của
quốc gia/dân tộc đó): Nhóm VH Hồi giáo,…
Mỗi dân tộc, mỗi cộng đồng ng có đặc trưng VH - quan điểm - suy nghĩ riêng và có
một tầng lớp tinh hoa - tinh tú (elites) riêng: tạo ra gtri kiến tạo nên nền VH đó
(constructivism) => tạo ra cộng đồng COMPARISON OF THEORIES
- Realism posits that states exist in an anarchic international system. (các quốc gia tồn tại trên
một hệ thống quốc tế)
+ Each state bases its policies on an interpretation of national interest defined in terms
of power. (mỗi quốc gia có 1 chính sách khác nhau trong QHQT để xác định sức mạnh quốc gia)
+ The structure of the international system is determined by the distribution of power.
(cấu trúc của hệ thống quốc tế đc định hình bởi sức mạnh quốc gia. VD: VN bỏ phiếu trắng về vđề Nga)
- Liberalism argues that humans form states that generally cooperate and follow international
norms and procedures. (vai tro - lợi ích của con ng ở mỗi quốc gia. Hợp tác => định hình nên gtri)
- Radical theory is rooted in economics: actions of individuals are determined by their social
class. (CN cấp tiến - CN Mác - Leenin. Bản chất của nền KT liên quan đến các giai cấp trong
XH), Kte TBCN tạo nên mass struggle - đấu tranh giai cấp)
- Constructivists argue that the key structures are intersubjective and social. (cấu trúc - VH - XH) To summarise
"Without theory, we are reduced to educated guesses on how to resolve crises or how
to constructively advance human values such as justice and peace. How each of us sees
international relations depends on our own theoretical lens."




