











Preview text:
AMERICAN CIVILIZATION
WEEK 1: INTRODUCTION TO AC What is civilization?
The process of educating a society so that its culture becomes more developed
. Human society with its well-developed social organizations, or the culture and way of life
of a society or country at a particular period in time
Some specific characteristics:
National memorial to four great American presidents: George Washington, Thomas Jefferson,
Theodore Roosevelt, and Abraham Lincoln.
Washington Monument in Washington, D.C commander-in-chief of the Continental Army
in the American Revolutionary War and the first President of the United States
Martin Luther King, Jr. delivered his famous “I Have a Dreamˮ speech in
Washington. Leader of peaceful protest demanding equal rights for African Americans
Bald Eagle: national bird of America, a majestic bird that can soar high in the air
Buckingham Palace is the official London residence of the British royal family
Blue jeans: invented by Jacob W. Davis in partnership with Levi Strauss & Co. in 1871,
American casual dressing style Overview of the USA: AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 1
Italian explorer and navigator determined to find a direct water route west from Europe to
Asia, but instead stumbling upon the Americas en route in 1492
Making four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean for European exploration and colonization of
the Americas The naming of America:
Italian explorer Christopher Columbus set foot on the Bahamas in 1492.
Assuming he had reached India in the west, Columbus named the land ‘the West Indiesʼ.
Another Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci, claiming four Atlantic voyages from
1497 1504, discovered that the newly known lands were distinct continents.
In 1501, Amerigo Vespucci invented the phrase Mundus Novus, meaning the New
World. This phrase remains.
Amerigo Vespucci's first name was used for the continents he claimed to have explored.
America 1507 The United States Of America 1776
American Motto: In God we trust Flag: stars and stripes No star 1775 1777 13 stars 1777 1795 49 stars 1959 1960 50 stars July 4. 1960 present)
Anthem: The Star-Spangled Banner Large: 9,372,610 km2 Population: 341,129, 084 Neighbours: Canada, Mexico
Ocean: Arctic, Atlantic, Pacific Largest state: Alaska Smallest state: Rhode Island
Administrative Structure: Federal State County
Cultural Symbol: melting pot, salad bowl, mosaic AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 2
WEEK 2 - THEME 1: THE COUNTRY The Early Inhabitants
Approximately 30,000 years ago, the
earth experienced the Ice Age.
North America was covered in glaciers.
As the oceans froze, the ocean floor became uncovered and dry.
At least 14.000 years ago, the first American immigrants were Asian hunters
getting to North America across a land bridge where Bering Strait is today.
Archaeologists call this period Paleoindian, meaning ancient Indian AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 3
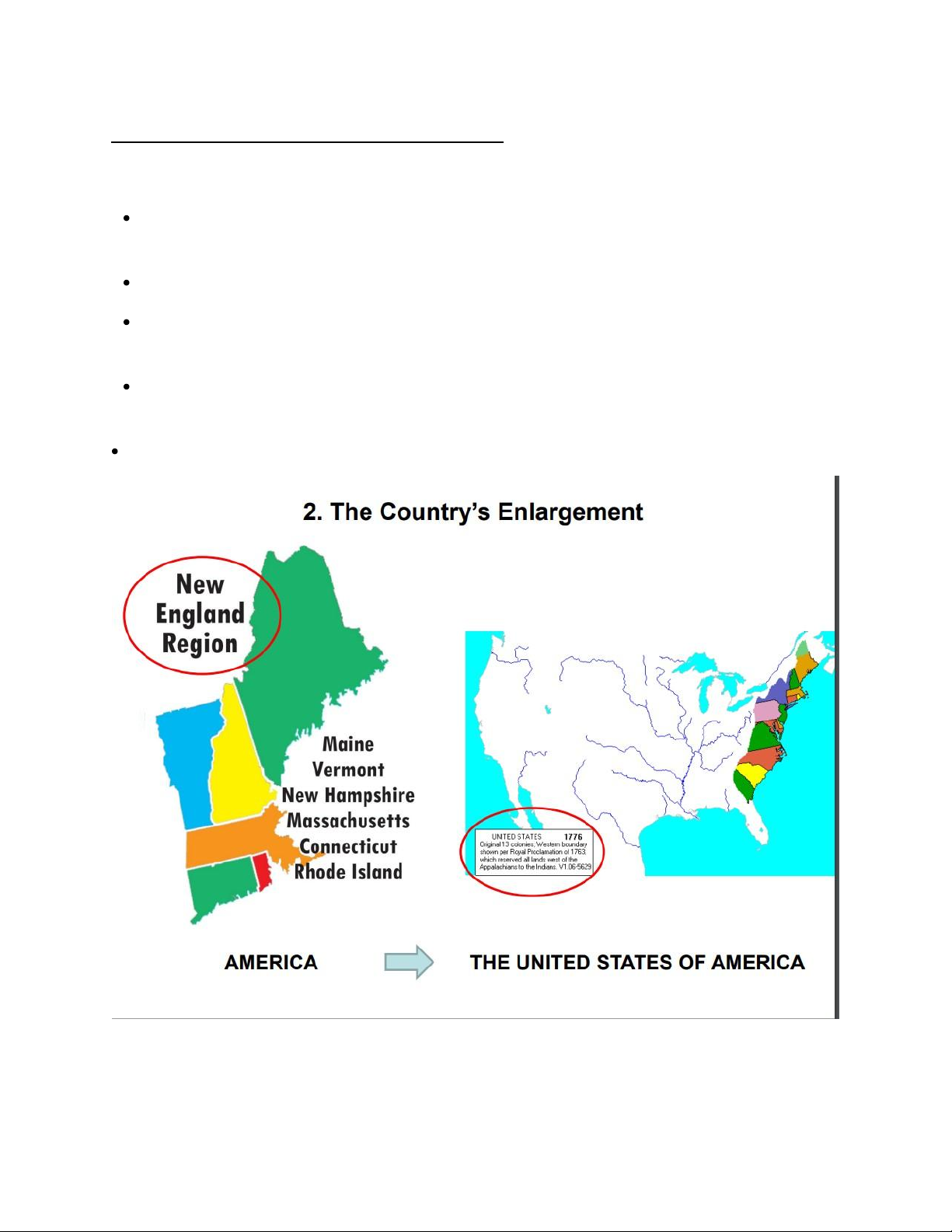
The countryʼs enlargement
1776 13 states and territory that extended west to the Mississippi River
1782 1783 Treaties with the UK establish the U.S. as an independent country,
bound on the north by Canada, south by Spanish Florida, west by the Mississippi
River, and east by the Atlantic Ocean
1803 Louisiana Purchase at $15 million from France in Napoleon time,
extending west to the Rocky Mountains, doubling the size of the U.S.
1819 Florida purchased from Spain
1845 The independent Republic of Texas was annexed from Mexico
1846 Oregon added (from a treaty with Britain)
1848 Arizona, California, Nevada, New Mexico, Texas, Utah, and western Colorado AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 4 added (brought from Mexico)
1853 Southern Arizona and southern New Mexico added Gadsden Purchase)
1861 1865 West Virginia established with help from Congress
1867 Alaska purchased from Russia
1898 Hawaii was annexed into the United States AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 5 AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 6
The countryʼs mountains system
Appalachian Mountains: great highland system of North America, 3,200 km long from the
Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador to central Alabama in the U.S., forming a natural
barrier between the eastern Coastal Plain and the vast interior lowlands; combining
a heritage of natural beauty and a distinctive regional culture
Rocky Mountains: backbone of the great upland system in the west; stretching
4,800km from northern Alberta and British Columbia southward to New Mexico;
bordered on the east by the Great Plains and on the west by the Basin of the U.S.
Mount. McKinley (or Denali): the highest mountain in North America, located in
south-central Alaska; 6,190m above sea level; third-highest of the seven summits (the AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 7
highest peaks on all seven continents)
Mount. Whitney: the highest mountain in the contiguous U.S. and the Sierra Nevada, 4,421m above sea level
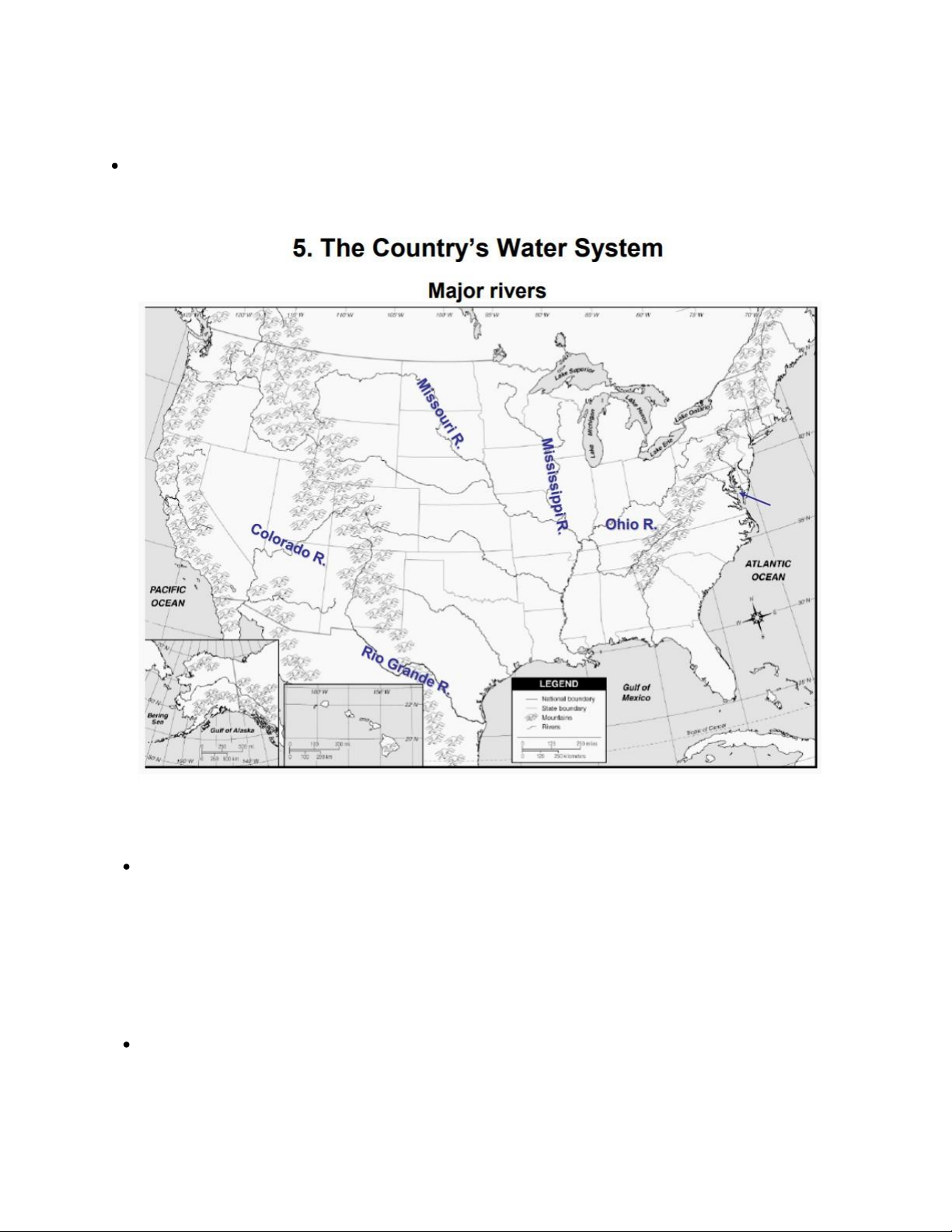
The countryʼs water system
The central U.S. river system includes the three major rivers of the central United States: the
Missouri converges with the Mississippi near St. Louis,
and the Ohio converges with the Mississippi in southern Illinois (at Cairo).
The Colorado River is a water source for seven western
states, supplying drinking water to 40 million people. AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 8
The 5th major river is Rio Grande, bordering Mexico.
The Missouri River is the longest river 3,767 km) in
North America, rising in the Rocky Mountains of western Montana and flowing east to join the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River flows 3,730 km from its source at Lake
Itasca in northern Minnesota to its mouth in the Gulf of Mexico.
The Ohio River is the gateway to the west.
The Mississippi and Missouri Rivers are the transportation arteries
for farm and industrial products in the Great Plains. They are links to
ports and other parts of the world.
The Colorado River supports $1.4 trillion 1/2 U.S. GDP in annual
economic activity and 16 million jobs in California, Arizona, Nevada, Utah,
Colorado, New Mexico and Wyoming.
The Rio Grande River forms the border with Mexico. AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 9 The Great Salt Lake Located in Utah 4,400 km2
6 times saltier than the ocean AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 10 GREAT LAKES
A group of five large freshwater lakes in central North
America, interconnected by natural and artificial channels
Four large cities Chicago, Detroit, Toronto, and Cleveland) on the shores GREAT LAKES
Hold about 20 percent of the worldʼs fresh surface water
Important recreational resources with rich sport fisheries, and numerous beaches and marinas AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 11
STATES OF THE GREAT PLAINS
The Great Plains have a wide variety of weather throughout the year.
The prairies support abundant wildlife in undisturbed settings.
The plains feature productive grain and
livestock farms and extensive petroleum and coal deposits.
THE GREAT BASIN ➢ The largest area of contiguous watersheds in North America ➢ Includes AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 12
most of Nevada, half of Utah, and sections of
Idaho, Wyoming, Oregon, and California ➢
Terrains varying from the North American lowest point at
Badwater Basin in Death
Valley to the highest point of the
contiguous U.S. at the summit of Mount Whitney CA
➢ Spans several physiographic divisions,biomes, ecoregions, and deserts
*Mojave Desert: an arid rain-shadow desert and the driest desert 124,000 km²) in North
America, within southeastern California and southern Nevada, small areas also extending into Utah and Arizona AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 13 Native Indians
THE TRAIL OF TEARS INDIAN REMOVAL
The route from Georgia to Oklahoma that was used to remove the Cherokee Nation in the 1830s.
During the forced relocation, the migrants faced hunger, disease, and exhaustion.
Over 4,000 out of 15,000 of the Cherokees died on the way. PBS AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 14
The National Park System consists of 423 sites in the U.S. and its territories.
Initially, all the park lands were inhabited, owned, occupied or claimed by different Indian tribes.
Anglo-Americans claimed "wilderness" should be only inhabited by wild animals, and AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 15
Indians were removed to limited reservations and provided with
government food rations → national parks as preserves for wild
animals (claimed to be ‘American best ideaʼ by writer and historian Wallace Stegner)
As the 1st national park established in 1872, Yellowstone was initially not for preserving
wilderness but as an ideal tourist attraction.
Native Indians lost their rights to land, hunting, water resources & fishing, medicinal &
edible plants, spiritual ceremonies and other purposes.
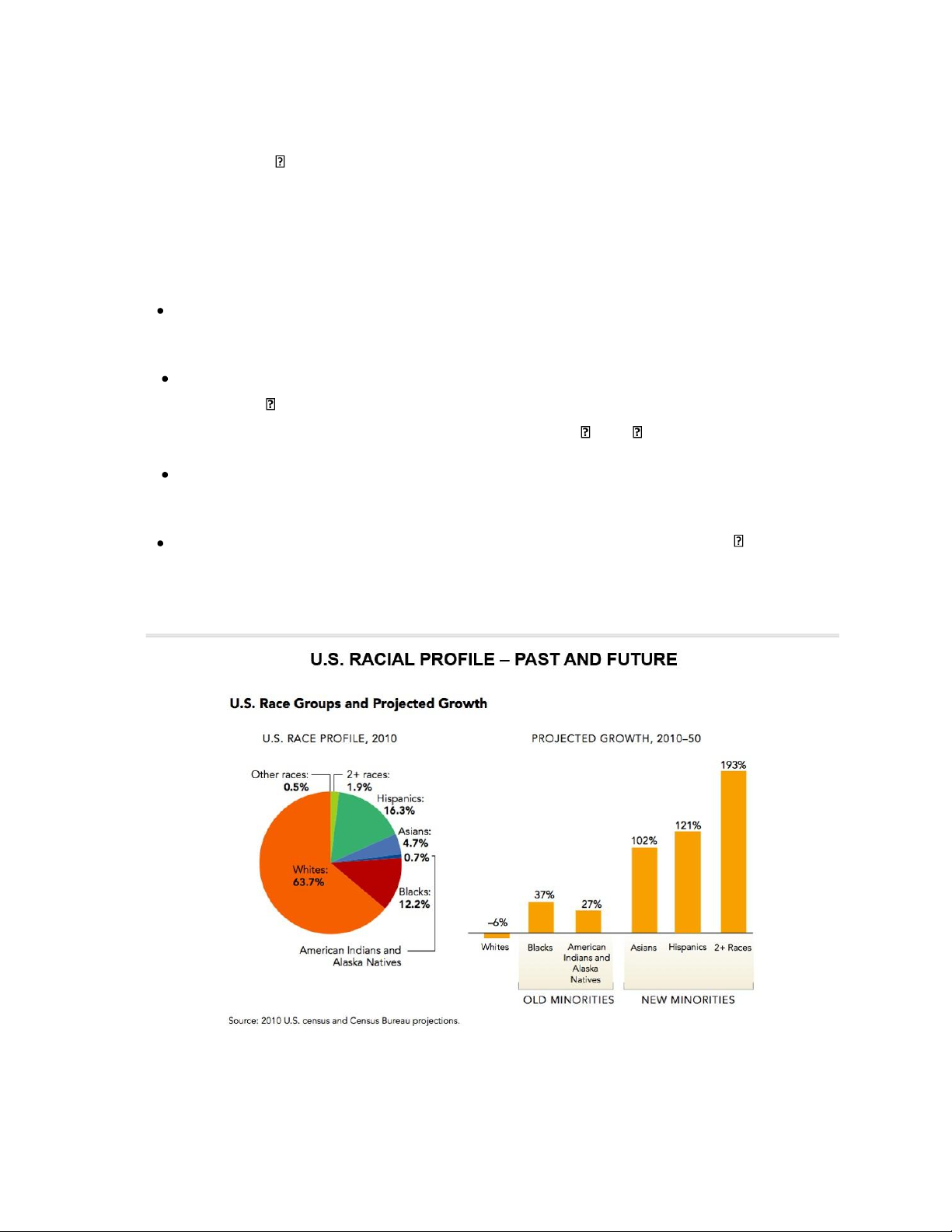
WEEK 3 - THEME 2: THE PEOPLE
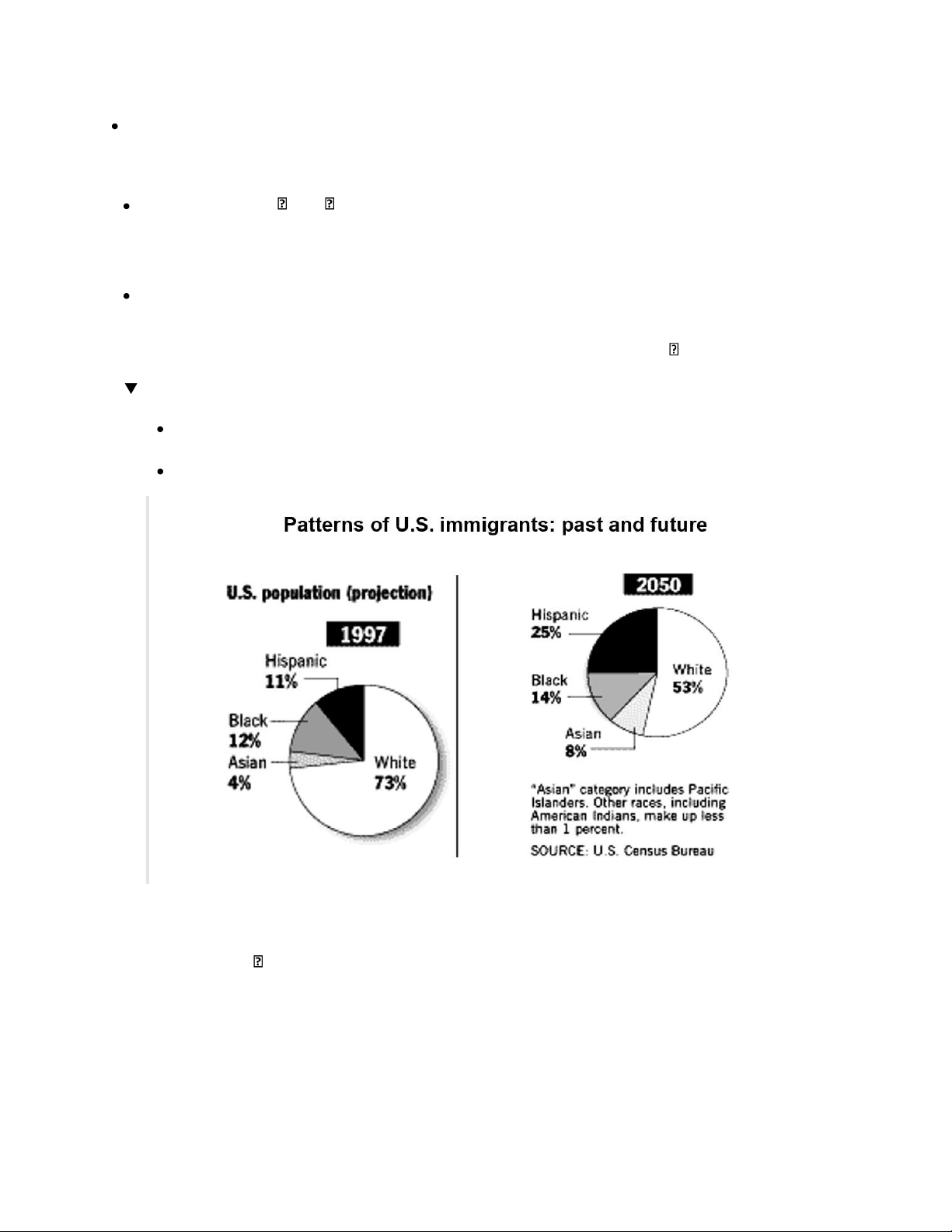
Why do people migrate or immigrate?
Refugee/asylum (religious, political, disaster, etc.) Economic difficulty at home Family AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 16 Professional development
*Much immigration occurs for economic reasons. 1. The first Americans
At least 14.000 years ago, the first American immigrants were Asian hunters getting to
America across a land bridge where Bering Strait is today.
About 1.5 million Native Americans lived in America before 1492.
Native Americans got the name ‘Indiansʼ because Christopher Columbus named the
discovered land the ‘West Indiesʼ, which means ‘India in the Westʼ.
We call these people the ‘indigenous people of the Americasʼ, or native American Indians. 3. European Immigrants
1st wave 16th-18th centuries): mostly settlers from the British Isles attracted by economic
opportunity and religious freedom
A mix of wealthy individuals and servants
Mostly Puritans English Protestants)
2nd wave 1840s-1850s): Irish, German, and Scandinavian immigrants AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 17
Fled famine, religious persecution, and political conflicts
Mostly Catholics Times of immigrants
1790 Naturalization Act allowing any free white person of “good characterˮ living in the U.S.
for two years or longer to apply for citizenship
1815 Immigrant influx from Western Europe
1819 Many of newcomers arriving sick or dying from their long journey across the Atlantic.
The immigrants overwhelmed major port cities, including New York, Boston, Philadelphia and
Charleston. In response, the U.S. passed the Steerage Act of 1819 requiring better conditions on ships carrying immigrants.
1849 Americaʼs first anti-immigrant political party Know-Nothing Party - formed as a
backlash to the increasing number of German and Irish immigrants
1875 Following the Civil War 1861 1865 , some states passed their own immigration
laws. In 1875 the Supreme Court declared that it was the responsibility of the federal
government to make and enforce immigration laws.
4. The enslave Africans - unwilling immigrants
Slavery in America assumedly started in 1619, when 20 African slaves seized from a
Portuguese slave ship were brought ashore in the British colony of Jamestown, Virginia.
Throughout the 17th century, the forced migration, called the Middle Passage,
brought enslaved Africans as a cheaper, more plentiful labor source for European settlers.
The years 1830 to 1860 were the worst in the history of African-American enslavement.
⇒ American Civil War 1861 1865 brought freedom to black slaves
THE UNDERGROUND RAILROAD LATE 18TH CENTURY TO THE CIVIL WAR
Many whites but pre-dominently black - who helped fugitive slaves escape to the North and to Canada
Effectively moved hundreds of slaves northward each year
The South lost 100,000 slaves between 1810 and 1850
COTTON TEARS OF NATIVE INDIANS AND AFRICAN SLAVES AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 18
Cotton was highly profitable but extremely labor-intensive
⇒ Native Indians driven out of their land and African slaves brought in
The Trail of Tears 1838 removed the native Indians from the South, resettling them to
‘Indian Territoryʼ to give the richest cotton soil to the white. This removal, following the
Louisiana Purchase, created vast lands for cotton.
The number of slaves needed in the new cotton states of Alabama, Mississippi and
Louisiana demanded slave labor traded at more than tripled price (rising from $500 in New
Orleans in 1800 to $1,800 by 1860, the equivalent of $30,000 in 2005
The dominant motto of the era: “Cotton is King!ˮ
One of the greatest periods in economic expansion and profitability in American history
Also took a costly Civil War and the loss of more than 600,000 lives to end it DACA & DREAMERS
June 15, 2012 Homeland Security announced that certain people who illegally came to
the U.S. as children and meet several guidelines may request consideration of deferred
action for a period of two years, subject to renewal. They are also eligible for work
authorization. DACA does not provide lawful status. About 800.000 applicants made their dreams in the U.S. AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 19
September, 2017: Trump moved to terminate this Obama-era policy.
January 20, 2021 President Biden issued a memorandum directing the Secretary of
Homeland Security, in consultation with the Attorney General, to take appropriate action
to preserve and fortify DACA, consistent with applicable law.
CENTRAL AMERICAN MIGRANT CARAVANS
Migrants travelling from Central America to the Mexico–United States border to seek asylum
The largest and best known of these organized by Pueblo Sin Fronteras
Village Without Borders) that set off during Holy Week in early 2017 and
2018 from the Northern Triangle of Central America NTCA
In early 2021, first migrant caravans departed for the U.S. from Honduras
International Committee for the Red Cross: "The combination of COVID 19, social
exclusion, violence and climate-related disasters that occur at the same time with a
magnitude seldom seen before in Central America raises new humanitarian challenges.'' AMERICAN CIVILIZATION 20



