



Preview text:
2019 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT)
Knowledge Sharing Platform for Multi-site Organisation Ahmad Ghandour College of Business Al Ain University Abu Dhabi, UAE ahmad.ghandour@aau.ac.ae
Abstract—in today's dynamic and highly agile business
capabilities, the platform support organisational KM
environment, Knowledge Management (KM) have become strategies to increase efficiency, promote internal increasingly important factor in competitiveness and
collaboration and increase employee efficiency; a common
sustainability. Organizations are facing growing challenges in
pool of knowledge to share best practices and relevant
documenting, sharing and reusing the knowledge across teams
information across industry; community tools, such as blogs,
and geographic locations due to the absence of a collaborative
wikis, discussion forums and calendars; information
platform. Organizational knowledge accumulated over time
management and enhanced find-ability to optimize
needs to be indexed and shared among employees. In this
operations and foster innovation. Additionally, the portals
paper, a framework to design a KM platform with multiple
will be integrated with all backend systems to avail internal
portals is proposed to be implemented as internal information
e-services while community management leaders ensure
sharing platforms for a multi-site organization. A meta-
information accuracy. They also bring together different
requirements were collected from literature and then
information sources such as peoples and skills directory,
translated into design principles for efficient and effective KM
news, alerts and feeds from external sources. Another
system development for multi-site organizations
capability of the platform is to allow employees to submit
Keywords: KM, Organizational Knowledge, KM Platform,
documents that are automatically indexed according to a
Framework, Multisite Organization
well-defined industry taxonomy and reviewed by the
knowledge area owners. Overall, such platform aims to give
users better access to information to improve performance I.
and collaboration between individuals and departments INTRODUCTION across the organisation. The ability to manage knowledge in today’s
organisations in facing the growing challenges in creating,
The remainder of the paper is organised as follows.
capturing, organizing, sharing and refining information and
Section II presents the related works. Section III describes
content across teams and geographic locations is crucial.
the proposed design KM platform followed by discussion
Knowledge is embedded not only in goods and services but and conclusion.
also in highly mobile employees and it is becoming the
greatest asset in the organisation. Much of an organisation’s II. RELATED WORK
valuable knowledge walks out the door at the end of the day
A multi-site organisation is an economic actor
although many organisation have no idea how to manage this
geographically spaced multiple entities with a group of
knowledge. Not only knowledge have become increasingly
people, a bundle of resources and an accumulation of
important factor in delivering competitive, innovative and
knowledge and learning. No analysis is complete .unless it
improved services but also a major source for achieving
takes account of all these aspects at once. Issues in such
sustainable growth. This has created a strong need for a
organisation include the lack of knowledge available to
systematic approach to creating and sharing organisation’s
employees and sharing such knowledge is limited. The
knowledge base not to replace individual knowledge but to
information necessary to manage the production of the firm’s
complement it. Knowledge Management (KM) is getting the
good and services become a much greater challenge. As
right knowledge to the right people at the right time so they
stated by[1]“coordinating processes when the participants are can make the best decision.
separated by time and distance is difficult, and solutions to
problems encountered in one location must often be
In organisation that span multiple geographic regions, the
rediscovered elsewhere in the organization”.
collaboration and knowledge sharing among sites is crucial
to achieve excellence in the delivered services. Information
Although strongly related, knowledge is not another form
can be easily availed when needed for all the employees in
of information. Knowledge is actioned information which
headquarter and its different geographically spaced branches.
allow us to make better decision and provide an effective
Thus the existence of a fully-fledged knowledge
input to dialogue and creativity in organisation [2], it is
management platform is invaluable for such organisations,
useful usable information that improve the performance of
otherwise, knowledge would be rendered completely
the user of this knowledge in terms of quality and/or speed of unconnected. work.
In this paper, a framework to design a platform with three
KM deemed inevitable to achieve goals such as: identify
portals is proposed to be implemented as internal information
and deliver relevant knowledge to relevant users; capture and
sharing platforms for a multi-site organisation. With the right
classify knowledge; maintain the information life cycle
technology tools for collaboration and self-service 113
978-1-7281-3010-1/19/$31.00 ©2019 IEEE
2019 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT)
through processes and policies; and ensure information • New Items
security through policies and processes. [3]. • Spotlight
According to Dalkir [2], KM when properly harnessed,it
helps drive organisation strategy, solve problems quickly and
Designing a KM framework requires taxonomy
build organisational memory. Diffuses best practices,
management and automatic classification to be utilized and
improve knowledge embedded in products and services,
according toAlfaki& Ahmed [3], it will achieve the
increases opportunities for innovation, and it fuels successful following objectives:
organisation. Pugh &Prusak[4], discerned four type of goals •
Improving the employees collaboration by opening
for knowledge networks, coordination, learning/innovation,
several collaboration channels for cross and intra
translation/local adaptation, and support of individual organisation communication
members. Hence, many organizations are devoting
considerable resources to the development of knowledge •
Creating user friendly knowledge sharing tools management platform (KMS) •
Structuring and organizing the organisation
KMSis an IT-based system developed with tools aimed at
knowledge base via automated knowledge supporting knowledge management behavior. Sucha
classification tools and based on a well-defined
platform is usually equipped with tools that provide specific
industry ontology that fits within the organisation’s
functions related to communication (email and discussion context
forums); coordination (shareable calendars and task lists);
collaboration (shareable artefacts and workspaces); and •
Automating the business processes through a
control (internal audit trails and automatic version control).
complete E service solution that is integrated within
User-centred KMSs contribute to an organizational culture of
the knowledge management framework
sharing by providing a sense of belonging to a community of
III. KNOWLEDGE SHARING PLATRFORM
users and by supporting reciprocity among users [5]. KMS
which connects an organisation, enabling employees to share
The purpose of this article is to design a knowledge
knowledge and collaborate instantly in a secure and social
sharing platform and describe the technologies utilized to environment.
enable employees across the dispersed organization to
retrieve information required for their task to be performed.
KMS is the behaviour, standards and solutions that allow
The key characteristics of such platform are: to support for
to share and use information to support your sector, division
communication among various users, coordination of users'
and personal goals. It sets on four pillars: people, processes,
activities; collaboration among user groups on the creation, information and systems [6].
modification and dissemination of artifacts and products; and
The KMS help share and use information and knowledge
control processes to ensure integrity and to track the progress
in a way that improves day to day working. It will enable the of projects.
organisation and its entities to share information and
knowledge with each other, so that they can learn from their
own best practices and from world-class knowledge. The
organisation becomes More Efficient, Higher Quality, Entity KM
Improved Skills and Customer-Centric. [6, 7]. Base 1
According to Edmonds and Pusch[8],KMS provide
support for many information functions, including: Shared
• Acquiring and indexing, capturing, and archiving KM • Finding and accessing Base • Creating and annotating Entity KM Entity KM Base 3 Base 2
• Combining, collating, and modifying • Tracking.
According toAhmed &Elhag[9], KM system allow us to
Fig. 1. Shared KM Base versus Entities KM Bases
capture and store knowledge through the following mechanism:
Figure 1 shows the high level architecture of the platform
which include a shared knowledge base that represents all the •
Document store on KMS:The documents to be
information shared across the organisation and its branches,
populated in the KMS and shared across the
organisation include: processes, reports, best
and entity specified knowledge base that represents the
practices, templates, forms, strategic documents,
information that is localised to a certain branch.
experiences, statistics, to mention a few
In the course of analysing, designing and implementing
theplatform, system development life cycle (SDLC) is used. •
Communities of practices and interest –wikis,
The business needs are transformed into system requirements
discussion forum, blogs, document library and
and system specifications. While the analysis of the system collaborative workspace
establishes the system proposal, the design of the system • Infomediaries
answers how the system will operate in terms of hardware,
software, and the infrastructure that will be in place. The 114
2019 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT)
system proposal is the initial deliverable describing the
external sources and are automatically classified
requirements the new system should satisfy. The design of
according to the industry taxonomy.
the system decides how to build it and determines the overall
system architecture that lead to the system blueprint.
• The frequently asked questions (FAQ) is also another
feature that help employees especially the ones
The standard organizational KM architecture comprised
interacting with customers to find answers to critical
of at least three levels: the data layer, which is the unifying
questions they might face. They are divided into topics
abstraction across different types of data with potentially
of questions which are of interest to all the entities
different storage mechanisms (e.g., database, text documents,
employees. Each topic will have its list of questions and
video, audio); the process layer, which describes the logic their corresponding answer.
that links the data with its use and its users (other people or
other systems who use that data); and the user interface,
• Electronic Newsletter: act as a means of pushing
which provides access to the information assets of the
important information about a certain topic that
company via the logic incorporated in the process layer[2].
employees across the different entities are interested in
Figure 2 shows the KM organizational architecture
it. It is published for all employees belonging to all the
entities. Any employee belonging to any entity will be
able to subscribe to newsletters topics that interest them
or view the list of all issues under different topics in the User Interface layer
global newsletters repository. Keywords Serach Indexing & Knoledge Maps Locate Experts Gateways Engine Classifications
• Collaborative space: A space for members of common
interest or certain domain of expertise coming from
different entities (forming communities) to share ideas
and transform useful information about their interest or
Process Layer (Application functions for KM)
expertise domain. Such communities have a powerful Document
membership management tool to make sure that each Import Keyword Security Metadata Find Knowledge Map Management Management Dictionary Associations Management Management
community includes the appropriate members with the
right privileges. Popular tools for these communities
include wikis, blogs, and discussion forum, to mention a few. Data Layer (Metadata)
• People & skills directory: the people and skills directory Database Video Audio Text
is a directory of profiles for all employees belonging to
the different entities. This directory will focus on
Fig. 2. KM Organizational Architecture: source [2]
people’s skills and experience. The purpose of this
directory is to help employees find domain experts or
In the case of multisite organisation, the system is
formulate a new team with members having a specific
dispersed across the sites which requires seamless integration
skill which is an important enabler for knowledge
of the shared knowledge base with each entity knowledge sharing.
base. All information in the shared knowledge base are read
• Business Intelligence (BI) features: The purpose BI is to
to the relevant section of the local KM portal of each entity
provide decision makers with a tool to help them make
with the same look and feel of the entity KM portal. This will
informed decisions. Such feature enables decision
make the user experience homogenous and let the employee
makers to have a better option about quality of service
focus on getting the appropriate information from the
offered in each branch and the progress of knowledge
different knowledge bases (the shared knowledge base and sharing among employees.
the local entity knowledge base).
For the entities knowledge bases (which is represents
The shared knowledge base form the knowledge map
through localized knowledge management portals that
that shall include the following features:
are only viewed and accessed by members of this specific
• Document repository: This document store acts as the
entity (e.g. Branch 1 KM Portal) they mainly consist of:
main document repository where all entities employees
• People & skills directory: this could be shown with the
can publish important documents for sharing across the
structure of the entity i.e. the organization chart
organization. Uploaded documents go through first, an
interleaved with the people and skills directory of people
efficient approval cycle (Figure 3) to incorporate
under entity for each of finding expertise in the entity.
important and accurate data and to guarantee up to
standard documents. Second, automatic indexing and
• Local repository; which is a repository for the entity
classification under the appropriate knowledge class values and codes of ethics
using a classification engine and according to a well-
defined industry taxonomy that is appropriate to the
• Local News; these are new of interest to the entity
organisation context. The knowledge champions (who
• Collaborative tools: such as discussion forums, polls,
are specific employees responsible for enhancing
surveys, RSS feeds, alerts etc.
knowledge sharing and structuring across all entities) can edit the classification.
• Collaborative space; A workspace for each employee that
summarizes his requests, their status, the tasks pending
• News: of interest to all the entities employees, the news
on his action and the actions of the his subordinates
information comes from different entities and even from 115
2019 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT)
• E-services tools; which is a process automation tool
• Integration Middleware; this is a tool that provides
enabling employees to receive notifications about their
different entities and even external organizations to
request and their delayed tasks using email and SMS
publish Knowledge Documents , KPIs related data and
notification,and other services to departments which
general content items, the data provided through the
automates most of the processes and the workflows
integration middleware are categorized and structured
related to that particular department.
automatically under the relevant sections of the shared
knowledge base according to the industry taxonomy
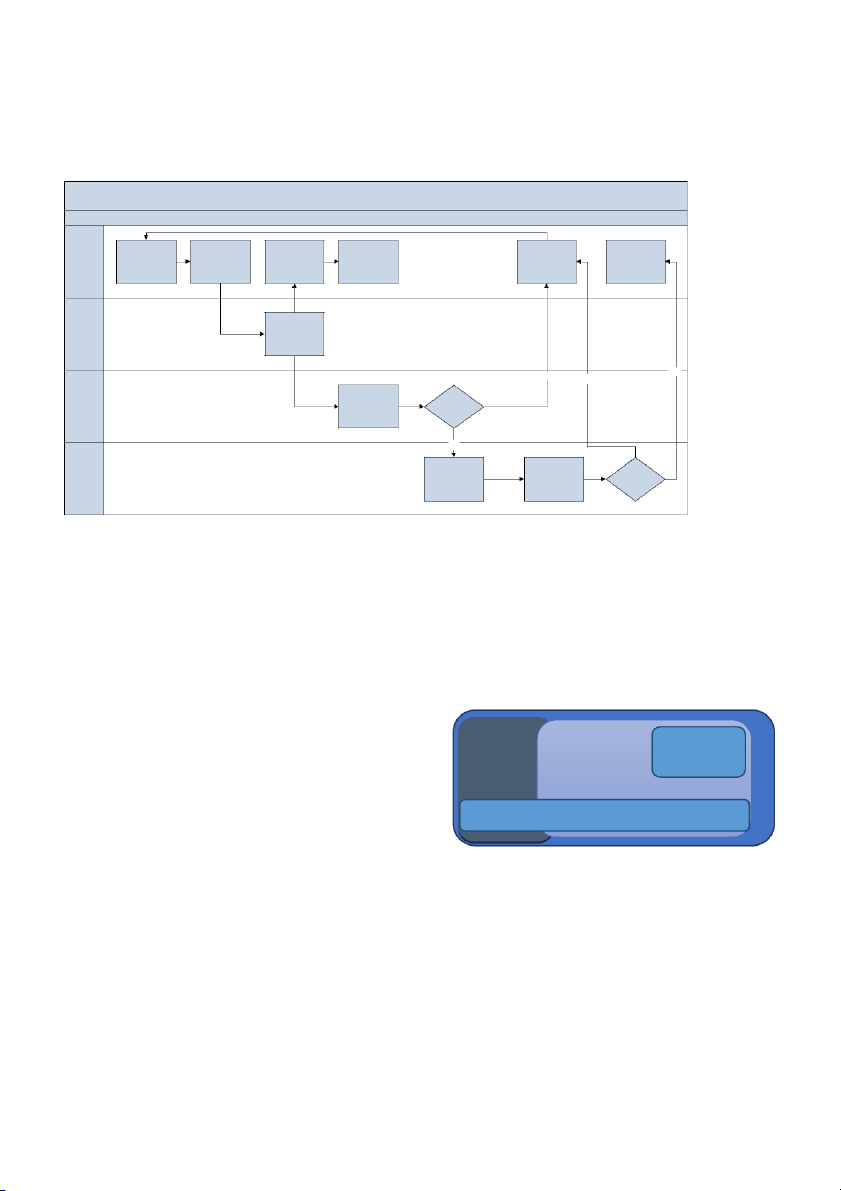
used for the organisation and its entities e Receive a Receive Review the offered Notification that oye Prepare & Upload Notification to Edit Add document taxonomy and Submit the the document was pl the knowledge the document to meta data & tags mark the relevant document published under document be of a better items Em the appropriate quality category r ledge ifie s Classify the s Document Know la according to the C Industry taxonomy Yes No No n ge io p Review the document & Edit wled m Approve a the meta data & h Edit the taxonomy Kno C Yes e r g to d a Review the Review the le in document & Edit document & Edit Approve w rd o o the meta data & the meta data & o Edit the taxonomy Edit the taxonomy n K C
Fig.3. Document Store Publishing Workflow: Source [3]
KM Platform Physical Architecture
The design of the system decides how to build it and
• External connectivity to other sites and other organisation
determines the overall system architecture that lead to the
systems (ERP, e-services, extranet etc.) enable system
system blueprint. It converts logical architecture to physical
intelligent and can provide reports on customer,
architecture. Physical architecture design is a very complex supplier, projects, etc.
process and begins with the non-functional requirements
(refer to behavioural properties that the system must have,
The below diagram (Figure 4) represents the physical
such as operational, performance, security, cultural and
technologies structure of the proposed solution
political) [10]. The resulting platform will provide one stop
shop, process support and customer service through push C & In la d
pull. It will enable users cross entities to Access documents, s e s x Active Directory i Integration
mail, SMS, video and the World Wide Web; and learn, share f in ic g SharePoint a Middlewar
and improve through Wikis and forums. t io SQL n s
The platform will also be empowered with the following physical technologies: FAST SEARCH
• Directory service (Access and identity management
system) to add new user, modify, remove, specify
privileges, assign policy etc. and Database ( MS Active
Fig. 4: Technologies structure directory, SQL, SharePoint) IV. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
• Classification engine based on industry taxonomy such as a semaphore classification.
KM is essential for the organisation to achieve
sustainable knowledge economy based. It is globally
• Search Tools; the platform could also be empowered with
recognised as essential tools to supporting the ambitious
advanced search capabilities (such as MS FAST search
growth of services within industries, and have contributed to
capabilities) enabling the user to view the highlighted
the advancement of skills and capacity of future workforce.
terms definition as per the taxonomy. The search
capability could also incorporates taxonomy navigator;
A knowledge sharing platform was designed and
having the terms and the hierarchies on the portal and
developed to connect multiple sites (three here as example)
highlight the categories that the search words are within,
under one content classification and taxonomy management
as well as similar searches and suggested items.
system to be implemented as internal information sharing
platform. The system comprised of a main node (global) and 116
2019 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT)
nodes (portals) according to the number of sites in the
In summary, the KM framework will provide the plans, organisation.
standards and disciplines to embed KM in the organisation which will help employees to:
The global node system equipped with collaboration
tools and self-service capabilities, to increase employee
• Share knowledge and experience with others across the
efficiency. A common pool of knowledge to share best organisation
practices and relevant information across industry were also
part of the design. They also bring together different
• Provide information and feedback forums to employees
information sources such as peoples and skills directory, and customers
news, alerts and feeds from external sources. The different
• Learn essential information items such as plans, report
document workflowswere also added to allow employees to and analyses
submit documents that are automatically indexed according
to a well-defined industry taxonomy and reviewed by the
• Connect with new and useful contacts knowledge area owners.
The portals include many community tools, such as
blogs, wikis, discussion forums and calendars, while R EFERENCES community management leaders ensure information
accuracy. And finally the portals would be integrated with all [1] Bowman, B.J.,
backend systems to avail internal services.
Information Systems Management, 2002. 19(3): p. Such platformaims to capture, store, distribute 32.
information and sharing knowledge assets among employees [2] Dalkir, K., . 2nd
within the organisation system, creating more collaborative
ed. 2018, Camridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press.
work ethic, where people use technology to share [3] Alfaki, I. and A. Ahmed,
information and do their jobs more effectively. .
Hence the Platform will increase the knowledge sharing 2017: Routledge.
across the organisation and within each branch through [4] Pugh, K. and L. Prusak,
interacting with theglobal document store FAQs and
MIT Sloan Management Review, 2013. 55(1): p. 79.
communities of practice interest, Global and local News, [5] Marshall, J. and A. Rossett,
RSS feeds and announcements). Thus, increasing the , in
experience of employees across the different sections and on . 2000, Springer. p. 19-34.
the long run reduce the cost of training and knowledge [6] Rinkus, S., et al.,
acquiring with the organisation and its branches. Journal of Biomedical
Moreover, the platform improves the processes handling
Informatics, 2005. 38(1): p. 4-17.
efficiency, it is expected that with the new E services [7] Weber, R. and S. Gunawardena.
introduced for each entity will reduce the time of each . in
employee working on the automated service and reduce the
human mistakes that used to happen within the course of the . 2008. IEEE. service workflow as well. [8] Edmonds, G. and R. Pusch,
And finally, the platform Increases the customer Educational
satisfaction, it is expected that through the enhanced
Technology & Society, 2002. 5(1): p. 100-104.
knowledge sharing, the advanced search capabilities, the [9] Ahmed, A. and M. Elhag,
interacted FAQs and the people and skills directory the
employees confronting the customer at the different entities
World Journal of Science, Technology and
will be easily able to respond to customer enquiries and
Sustainable Development, 2017. 14(2/3): p. 172-193. requests. [10]
Dennis, A., B.H. Wixom, and R.M. Roth,
The novelty of the system however is in the
. 7th ed. 2018: John wiley & sons. 464.
implementation. This requires to incorporate the state of art
technology in different fields. For example, the taxonomy
management and automatic classification could employ
Semaphore Ontology Editor from Smartlogic to build taxonomies and ontologies.
Additionally, capturing knowledge cannot be complete
without capturing the context of each item of knowledge.
Context makes knowledge successfully used, applied, or even understood.
The contribution of this research is two-fold. First, the
proposed system provides a systematic guidelines for KMS
designers to adopt the enabling IT and the needed KM
technical functions according to the industry standards.
Second, Enabling IT capability provide an opportunity to the
industry administrators to reengineers the industry process 117




