


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765
PART V: FIRM BEHAVIOR & THE ORGANIZATION OF INDUSTRY
THE COSTS OF PRODUCTION ---MIC Week 9---- A. Introduction
- Market condition ( ex: town ur living in have several pizzerias but only 1 cable TV company )
How does the no. of firm affect ? B. What are costs?
1. Total revenue, total cost & profit
- All firms incurt costs as they make goods/ sevbices they sell
- A fiem costs are key determinant os its production n pricing decisions
- Caroline’s Cookie Factory – owners of the firm, Caroline + buy ingredients....
- To understand the decisios a firm make , must understand what the
firm is trying to do or firm;s objective ( Caroline started her firm,
perheps out of love for the cookie’s business, n more likely to makr money Firm’s profit :
- Amount of firm receives for the slae of its outputs called total revenue
- Amount of firm pay to buy inputs total costs
- Profit = total revenue – total cost
- Recall: opportunity cost of sth is what you give up to get it.
- When economists speak to a firm’s cost of production, they include
all the opportunity costs of makingits output of goods n services
+ Ex : Caroline pay $1.000 for flour that $1.000 is an opprtunity cost
- These opportunity cost require Caroline’s firm to pay out some money called explicit cost lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765
2. Costs as Opportunitiy Costs Explicit cost
- Is the input costs that require the firms to pay out money
- Some other costs do nmot require to pay out cash ( Caroline is
skilled with computer programming. She earns $100/ hour for that
job/ Every hour working at cookie company, she gives up $100 in
income $100 income forgone here is implicit cost, also part of her cost ) Implicit cost
- Is the input cost that do not require a cash outlay by the firm
- Total cost of her business = explicit cost + implicit cost = cost of
input materials + cost to hire workers + Caroline’s forgone income (
if she spent hour working in the other cost )
- Economists n accoutants analyse business differently
+ Economisrts study how firms make decisions of production n price
decision made based on both explicit n implicit costs
- Opportunitiy cost of the financial capital invested in the bunsiness is also important implicit cost.
+ Caroline used $300.000 of her saving to buy her cookie factory from the previoius owners.
+ If she deposited this money in a bank saving account that pay
interest rate of 5%/ year she earned: 15.000/ year.
+ To own the cookie factory, Caroline, she give up $15.000/ year in
interest income. this forgone $15.000 is also an implicit
opportunity costs of Caroline’s business.
Cost of Capital as an Opportunity cost - Case 2 :
+ Caroline didn’t have whole $300.000 to buy a factory
+ Instead, she used $100.000 of her saving n borrowed $200.000 from bank at 5% interst rate. - Mean :
+ To own cookie factory, Caroline has to give up $5.000 interest the
bank would pay ( $1.000 x 5%= $5.000), since no more $100.000 deposited in the bank, and lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765
+ Factoty has to pay out $10.000 interest/ year on that loan ( $200.000 x 5% = $10.000 )
- Explicit cost = $10.000 Implicit cost = $5.000
- Accountants will now count the $10.000 interest paid on the bank
loan every year as a cost – bcs this amount flows out of the firm, n not count $5.000.
- Economists count the opportunity cost of owning the business is
$15,000 ( = $10.000 + $5.000 ).
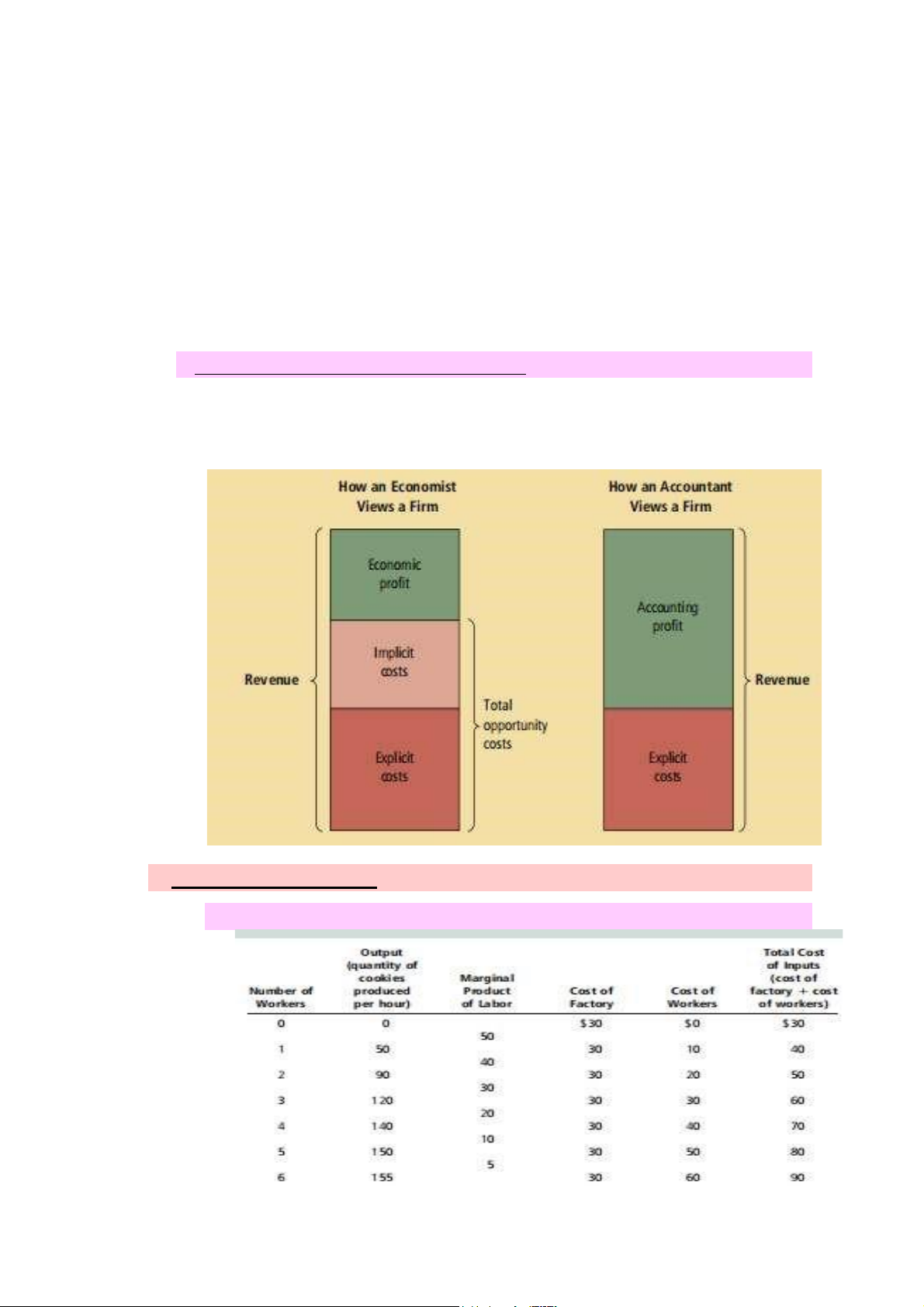
3. Economic Profit & Accounting Profit -
Economic profit = total revenue – ( explicit cost + implicit cost ) -
Accounting profit = total – explicit cost
C. Production and Costs 1. Production Function lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765
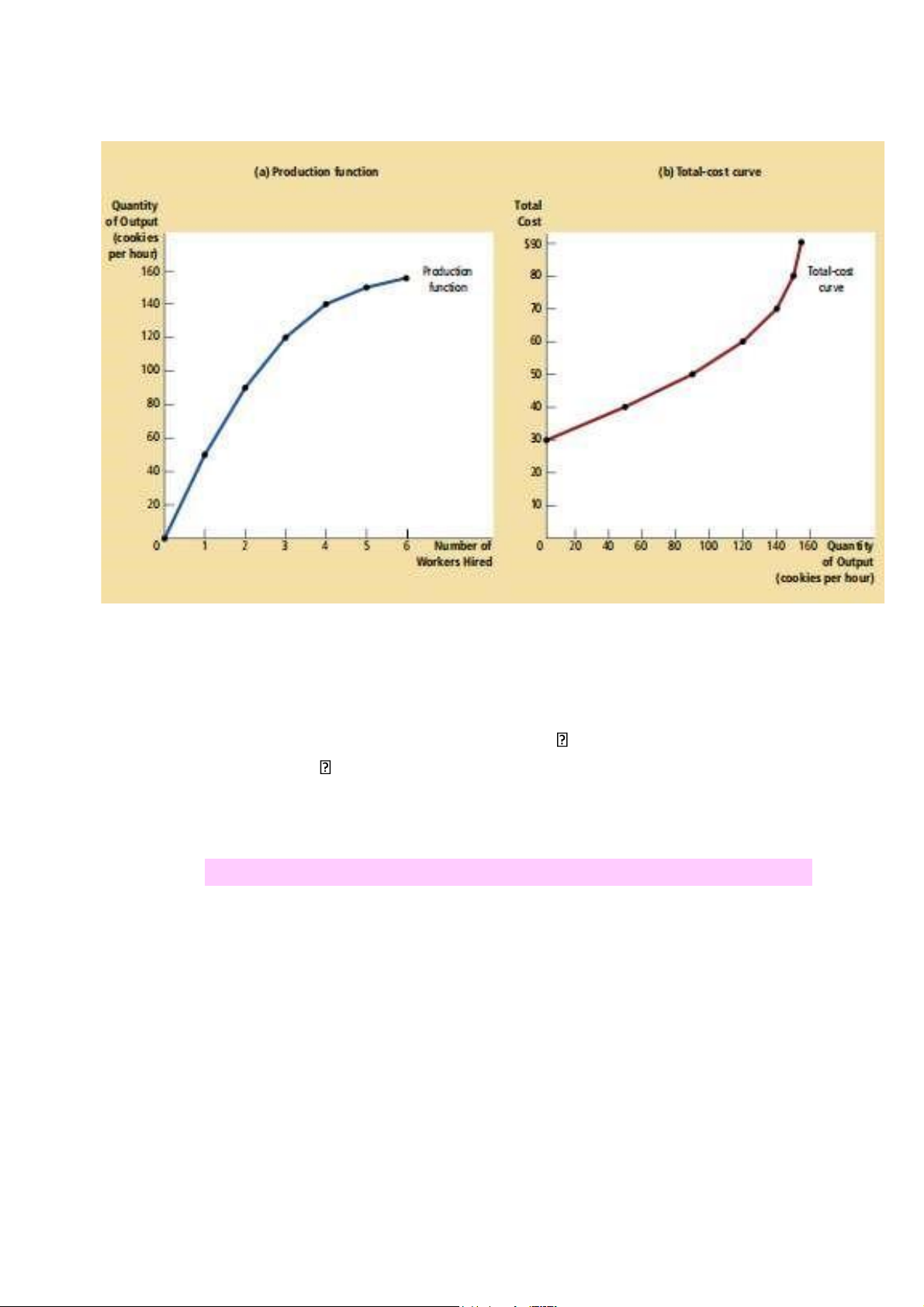
- Production Function : relationship between quantity of inputs used
to make a good n the quantity of output of that good.
- Recall: Rational pple think at the margin .
- Marginal product of an input in the production process is the increase
in output obtained form an additional account.
- Table1 : no. Of worker increase 1-2-3-4 marginal product decrease
50-40-30-20 called Diminishing marginal product
- Diminishing marginal product is whereby the marginal prodcut od an
input declines as the quantity of the input increase.
2. From the Production Function to the Total-Cost Curve
- These changes in slope occur for the same reasons. lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765
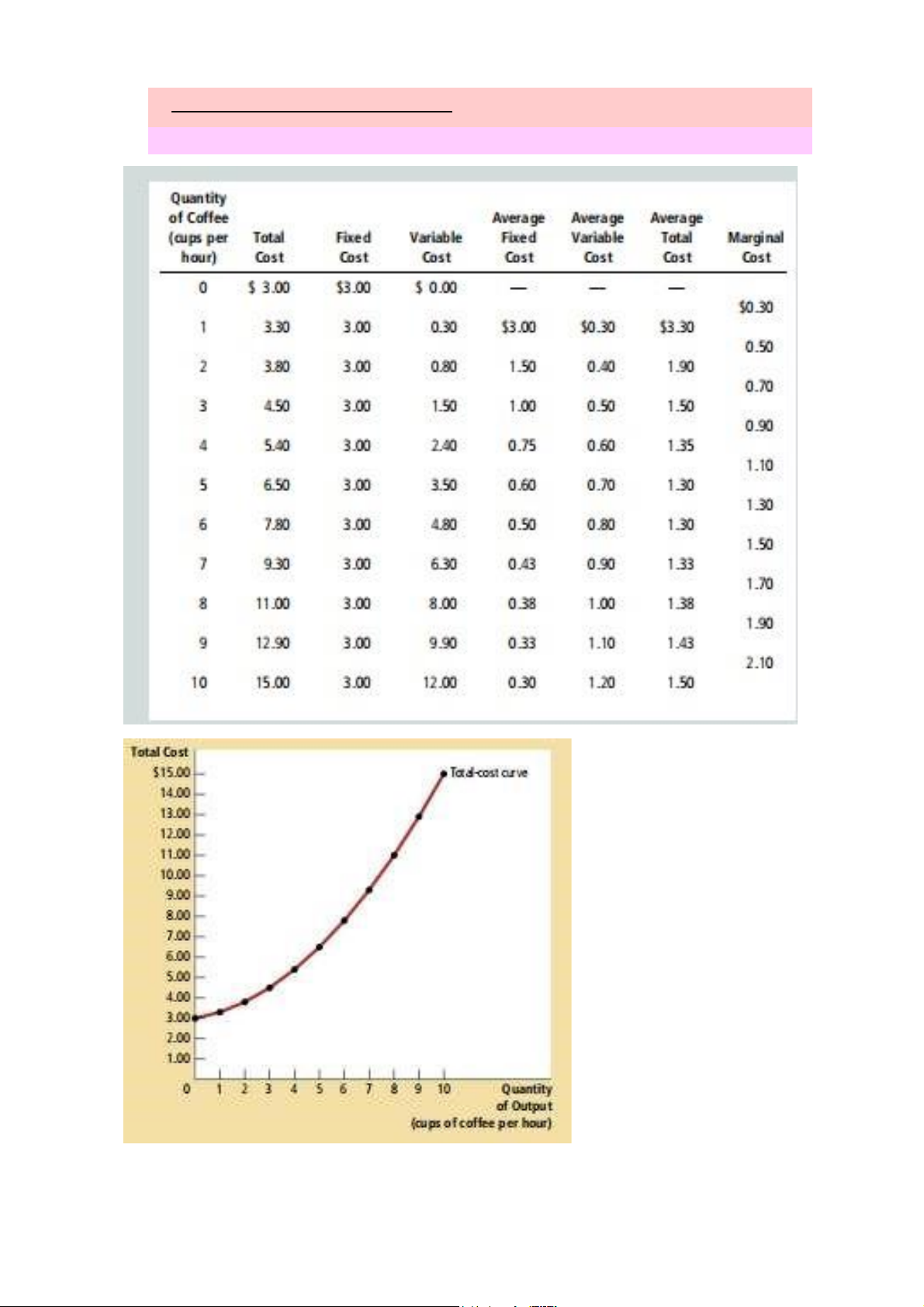
D. The various Measures of Cost 1. Fixed and Variable Cost lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765 2. Average an Marginal Cost
- Average total cost : Total Cost / Quantity of output ( quantity of
output : 2 cups of coffee/ total cost : $3.8 ATC= $3.8/2= $1.9/
quantity of output : 3 cups : total cost: $4.5 ATC: $4.5/3= $1,5)
- Average Variable Cost = Variable Cost / Quantity of output
( Quantity ( ouput) : 2 cups , total variable cost: $0.8 )
- Marginal Cost ( MC): the increase in total cost that arises from an extra unit of prodution
- Marginal cost = change in total cost/ change in quantity
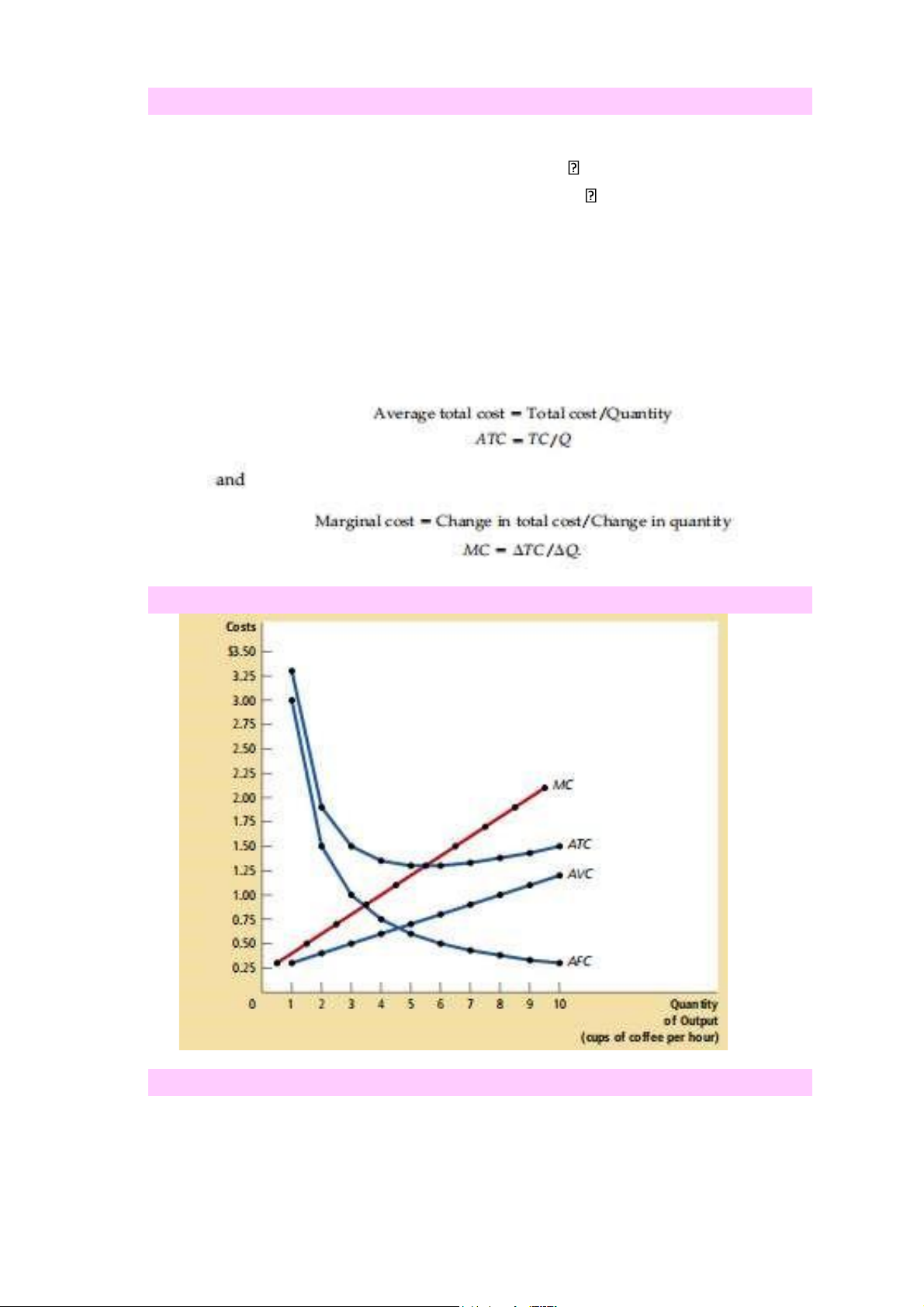
3. Cost Curves and their shape 4. Typical Cost Curves
- Cost curve share 3 most important properties to remember
+ Marginal cost eventually rises lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765
+ The average total cost curve is U-Shaped
+ The marginal-cost curve crosses the average-total-cost curve at the minimum of average total cost
E. Costs in the Short Run an in the Long Run
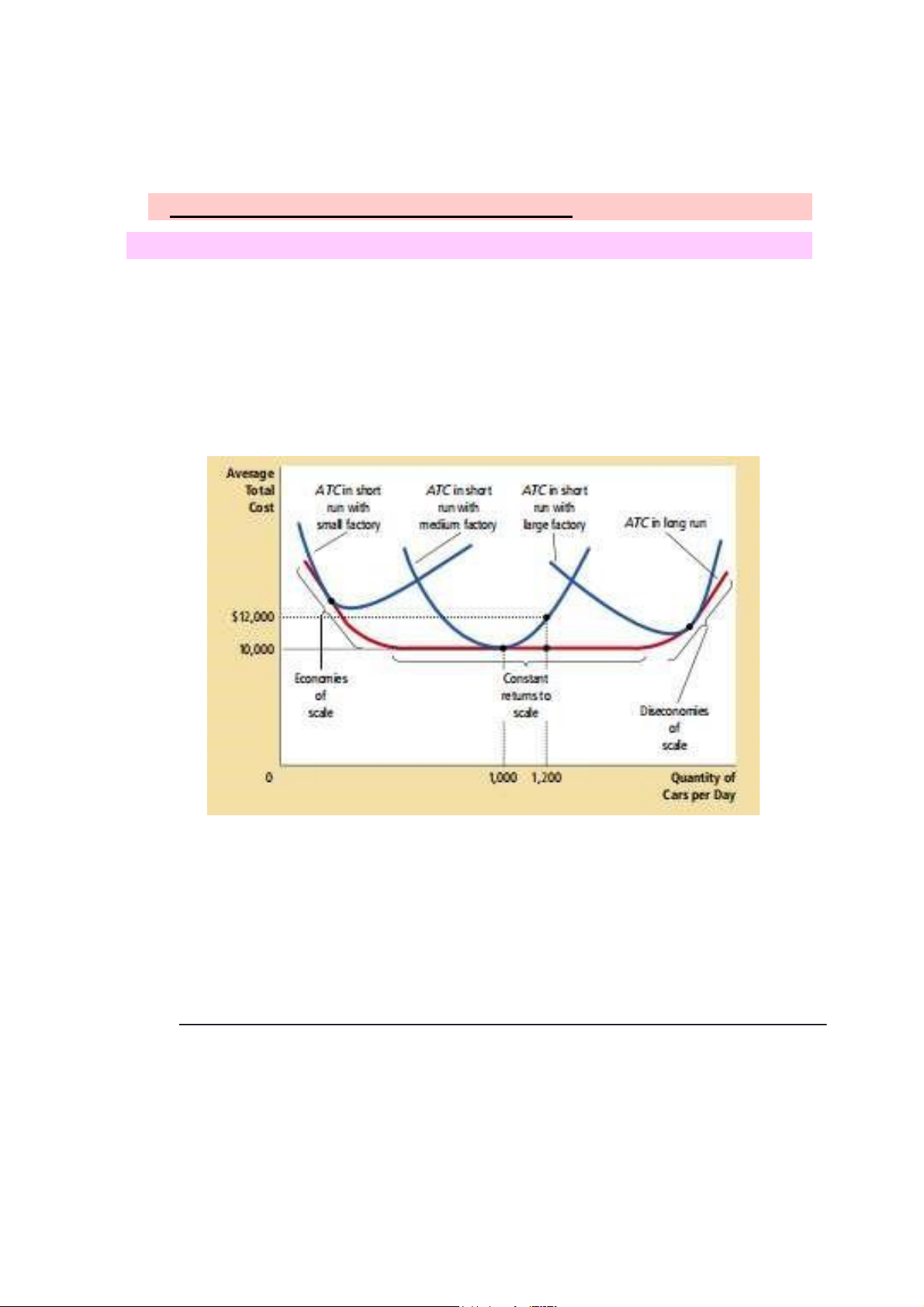
1. The relationship between shortrun n Long-run average total cost
- When long-run average total cost fall as the quantity of output
increase, firms said to be have ecoomies of scale
- When long-run average total cost rises as the quantity of output
increase , firm said to have diseconomies of scale
- When long-run avaerage cost stay the same as the quantity of output
changes, firms said to have constant return to scale.
+ Economies of scale often rise bcs higher production level allow
specialiazation among workers ( Specialization: each worker does a specific task)
- Diseconomies od scale may be caused by coordination problem
inherent in extremely large organization. ( Ex: the more cars ford produce ) EXERCISE 2. lOMoAR cPSD| 59114765 Answer 3.




