

Preview text:
Lesson 3: Elasticity (Độ co giãn)
According to the law of demand:
Side Effect: P increases Q decreases
Magnitude Effect: How many units does the quantity demanded decrease?
Example: when the price of vegetable (broconi) increases by 10% and the price of electricity
increases by 10%? The quantity demanded will change by the same amount? Ans: NO but HOW
Questions: what characteristics of goods/market can determine the response sensitivity of customers to changes in price?
Explain the notation: : how the percentage change in Y will cause Exy percentage change in X. Y is the determinant.
Definition: A measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good respond to a change in the
price of that good, computed as the percentage change. (Explanation:) Properties:
is a relative number (without unit)
always takes the negative value because of the law of demand (a negative association
between price and quantity demanded):
o is always positive because P>0; Q>0 The sign of depends on the . Because of the law demand () . How do we compute the ??? The mid-point method The poind method Condition
If you have two different point, such The change from A to B is very small, that A and B .
like one point on the demand curve.
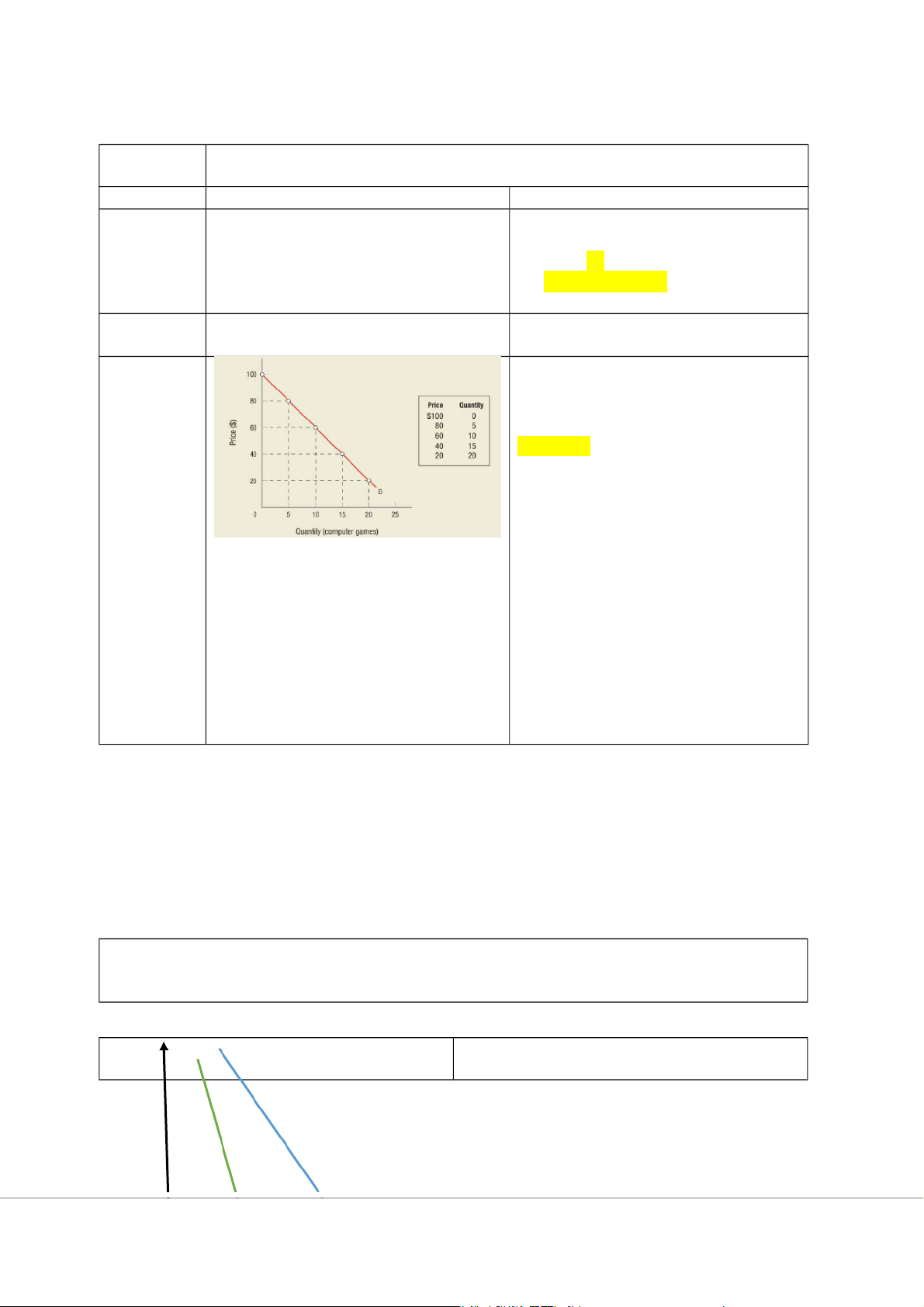
We have A and the information about the demand function. Formulatio n Example Demand function:70-0,02Q A
Intepretation: EDP=-0.75. means that at
price P=30, 1-percentage change in price
causes quantity demanded to change by 0.75%.
10-percentage change in price causes
quantity demanded to change by 7.5%. E.g., A and B . Change in quantity demanded is smaller the change in price. Intepretation: When the price The level of response response
increases (decreases) by 1%, 10% the less to the change in price quantity demanded decreases
(increases) by 1%, 10%, holing other factors constant. Types of Elasticity: Perfect Elasticity: Perfect Inelasticity: Unit Elasticity: Elasticity: (co gian nhiều) Inelasticity: (co giãn ít)
Tồn tại mối quan hệ giữa hệ số co giãn và độ dốc của đương cầu
Càng co giãn đường cầu càng thoải
Càng ít co giãn đường cầu càng dốc Inelastic Elastic
A significant change in price only cause a A small change in price cause a significant
small change in quantity demanded. change in quantity demanded.
Determinants of level: (Important)
Availability of Close Substitutes:
oMore close substitutes the market is more competitive Customers is more
sensitive to any change in price (Customers have many options) increases
oE.g.,: Electricity versus Broconi:
Electricity has no close substitutes Customers have no option rather
than the electricity The market for electricity is less eslastic.
Broconi: there are many types of vegtable in the market The market for broconi is more eslastic Proportion of Income spent on:
oA large proportion (e.g., travelling package, diamond rings…) more elastic.
oA small proportion (e.g., salt, toothbrush…) more inelastic.
5M/month, a package of salt (price 5k/unit) Definition of Market
oE.g., Food (the general market, including drinking, eating, meat,…) Inelastic
oChicken meat (a specific meat in the food market face the competition from other
meat like beef, porlk…) Elastic
oFood (have no option) Meat Chicken meat (other substituted goods: beef,
pork,...) Chicken leg: Following this way to define the food market, the elasticity increase
oConclusion: The more specific market is, the higher level of elasticity is
The time frame: the time duration after the price change: 1 day, 1 month, 10 months, 1 year
oThe longer time after the price change, the more elastic demand is.
E.g., the price of gasoline: 20k/1litere of gasoline--> 40k/litre of gasoline.
After one day, you still aceept to use your motorcycle to go to school.
After one month, you can make the change to use the public transportation--> sensitive
Why is important??? It can help us determine the price strategy ( when we raise/reduce the price of goods in the market).
Consider the situation that the firm want to raise the price (P), there are two effects in the market:
Price Effects (Hiệu ứng giá) lên doanh thu (TR): P increases TR increases
Quantity Effects (Hiệu ứng sản lượng) lên doanh thu (TR): P increases Q decreases TR decreases
Việc tăng giá làm tổng doanh thu tăng hay giảm??? Câu trả lời phụ thuộc vào hiệu
ứng giá và sản lượng, cái nào lớn hơn. Price Strategy:
Nếu thị trường mà khách hàng rất nhạy cảm trước giá cả (co giãn nhiều), doanh
nghiệp nên giảm giá vì nó sẽ làm thị phần của doanh nghiệp mở rộng--> có tác động tới TR
Nếu thị trường mà khách hàng ít nhạy cảm trước giá cả (co giãn ít), doanh nghiệp nên
tăng giá vì tôi tăng giá thì phần lớn khách hàng sẽ tiếp tục tiêu dùng và doanh nghiệp
được phép bán sản phẩm ở mức giá cao hơn.
In other word, if firms want to raise the price:
Elastic: Price Effect< Quantity Effect TR decreases
Inelastic: Price Effect> Quantity Effect TR increases EDP P increase P decrease EDP > 1 TR decrease TR increase EDP = 1 TR not change TR not change EDP < 1 TR increase TR decrease
The relationship between the elasticity level and the slope of demand curve:
More elastic the flatter demand curve is
More inelastic the steeper demand curve is
The Slope and Elasticity are two different concepts: Slope Elasticity Demand Function (D): P= a-bQ Slope of demand function= -b Elasticity: Slope is constant
Thus, is conditional on the point on
the demand curve (Depend on the
value of ).Elasticity change along the demand curve
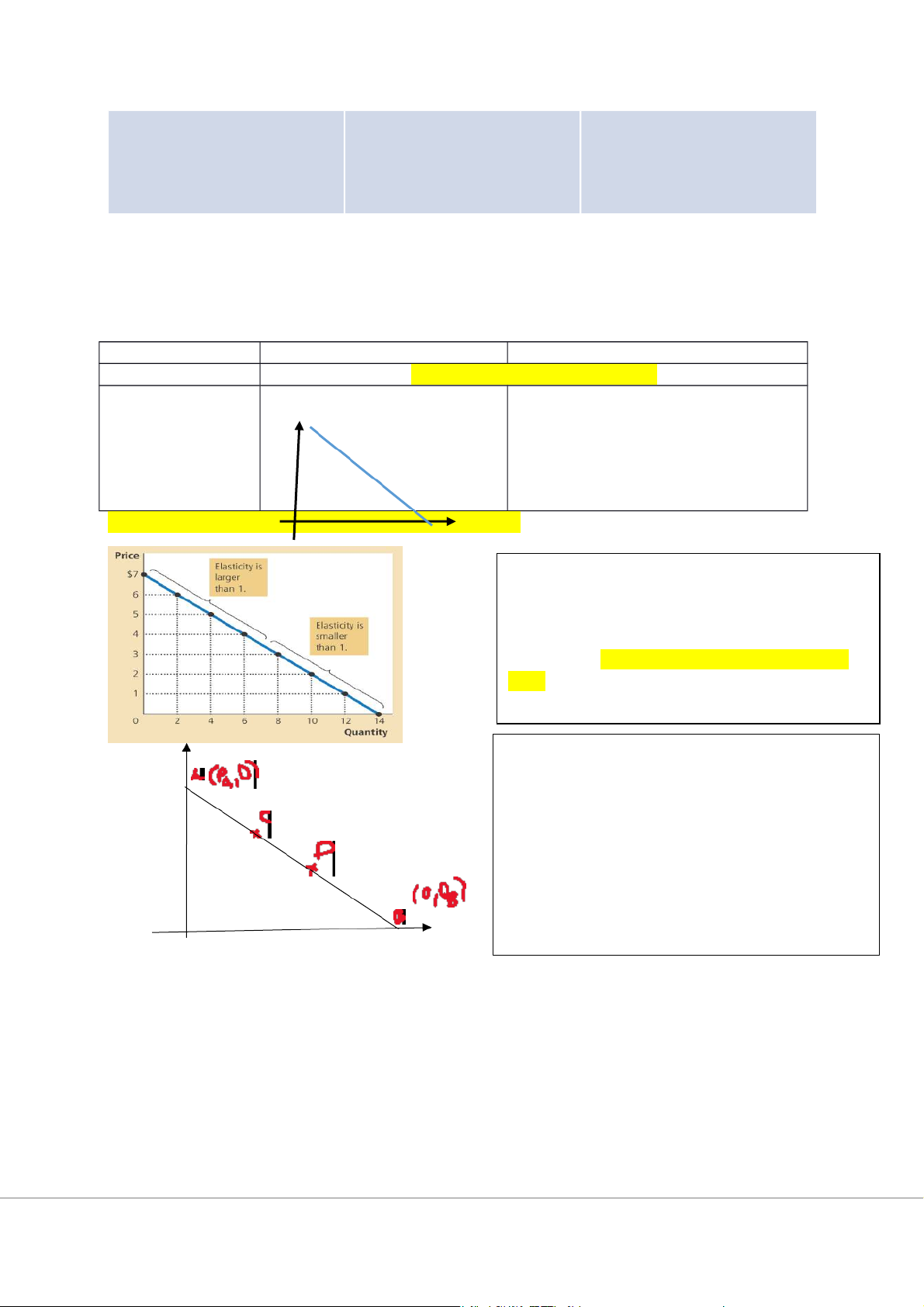
How does the elasticity change along the demand curve?
The slope of linear demand curve is constant.
The price elasticity of demand decreases from the
left hand side to the right hand side.
Alternatively, the demand is more elastic at a high price. At point A: At point B: Similarly, w can prove that: gi m dầần t ả ừ A đếến B. T i m ạ c giá cao ứ , s n ph ả m seẽ co giãn h ẩ ơ n. Price elastic of demand:
Cross-price elasticity of demand:
How to calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand: mid-point method and point method. Example:
When the price of orange is 16k/kg and the price of tangerine is 14k/kg, the quantity demanded
of tangerine is 30 kg. When the price of orange decreases to 12k/kg, then the quantity demanded
of tangerine is 22 kg. What is the cross-price elasticity of demand for tangerine? Solution:
The sign of depends on the association between X and Y. X and Y are substitued: o o X and Y and complemetary: o
3. The income elasticity of demand:
The sign of depends on the type of goods.
The normal goods:: Higher income make people to consume more. oNecessities: oLuxuries:
The inferior: : Higher income make people to consume less.