

Preview text:
CHAPTER 5. INVENTORY COSTING I. MULTIPLE CHOICES
1. (LO 1) K Which of the following should not be included in a company’s physical inventory?
a. Goods held on consignment from another company
b. Goods shipped on consignment to another company
c. Goods in transit that were purchased from a supplier and shipped FOB shipping point
d. Goods in transit that were sold to a customer and shipped FOB destination.
2. (LO 1) AP As a result of a physical inventory count, Atlantic Company determined
that it had inventory worth $180,000 at December 31, 2021. This count did not take into
consideration the following: Rogers Consignment store currently has goods that cost
$35,000 on its sales floor that belong to Atlantic but are being sold on consignment by
Rogers. The selling price of these goods is $50,000. Atlantic purchased $13,000 of goods
that were shipped on December 27, FOB destination, and they were received by Atlantic
on January 3. Determine the correct amount of inventory that Atlantic should report. a. $230,000 b. $215,000 c. $228,000 d. $193,000
3. (LO 2) AP Peg City Brews uses a perpetual inventory system and has the following
beginning inventory, purchases, and sales of inventory in April: Unit Total Units cost cost Inventory, Apr. 1 6,000 $9 $ 54,000 Purchase, Apr. 9 18,000 10 180,000 Sale, Apr. 12 (20,000) Purchase, Apr. 18 16,000 11 176,000
What was the moving weighted average unit cost after the last purchase on April 18? a. $9.75 b. $10.75 c. $11.00 d. $10.00
4. (LO 2) AP Using the data in question 3, the cost of goods sold in a perpetual inventory system under FIFO is: a. $174,000. b. $180,000. c. $195,000. d. $194,000.
5. (LO 3) K Using FIFO, the current asset Merchandise Inventory will report:
a. the most recent cost of purchases.
b. the oldest cost of purchases.
c. the average cost of all purchases.
d. the exact amount of each inventory unit on hand.
6. (LO 4) C In Fran Company, ending inventory is overstated by $4,000. The effects of
this error on the current year’s cost of goods sold and profit, respectively, are: a. understated, overstated. b. overstated, understated. c. overstated, overstated. d. understated, understated.
7. (LO 5) C Rickety Company purchased 1,000 units of inventory at a cost of $15 each.
There are 200 units left in ending inventory. The net realizable value of these units is $12
each. The ending inventory under the lower of cost and net realizable value rule is: a. $2,400. b. $3,000. c. $600. d. $12,000.
8. (LO 5) K The inventory turnover ratio provides an indication of:
a. how much profi t the company has per dollar of sales.
b. whether the company consistently has too much or too little inventory.
c. the number of days inventory is held in stock.
d. the company’s cash flow position.
9. (LO 6) AP If a company’s cost of goods sold is $240,000, its beginning inventory is
$50,000, and its ending inventory is $30,000, what are its inventory turnover and days sales in inventory? a. 3 times and 122 days b. 6 times and 61 days c. 4.8 times and 76 days d. 8 times and 46 days
*10. (LO 7) AP Kam Company uses a periodic inventory system and has the following: Unit Units Cost Inventory, Jan. 1 8,000 $11 Purchase, June 19 13,000 12 Purchase, Nov. 8 5,000 13 26.000
If 9,000 units are on hand at December 31, what is the cost of the goods sold using weighted average? a. $106,962 b. $108,000 c. $180,000 d. $202,038
*11. (LO 7) AP Using the data in question 10, the ending inventory using a periodic inventory system and FIFO is: a. $100,000. b. $108,000. c. $113,000. d. $117,000.
*12. (LO 8) AP Filman Company has net sales of $200,000 and a cost of goods available
for sale of $156,000. If the gross profit margin is 30%, the estimated cost of the ending
inventory under the gross profit method is: a. $16,000. b. $60,000. c. $37,200. d. $76,000.
*13. (LO 8) AP Deko Company reports the following selected information: cost of goods
vailable for sale at cost, $60,000; at retail, $100,000; and net sales at retail, $70,000. What
is the estimated cost of Deko Company’s ending inventory under the retail method? a. $18,000 b. $21,000 c. $30,000 d. $42,000 II. EXERCISES
E6.4 (LO 2) AP On May 1, Black Bear Company had 400 units of inventory on hand, at a
cost of $4.00 each. The company uses a perpetual inventory system. All purchases and sales
are on account. A record of inventory transactions for the month of May for the company is as follows: Date Purchases Date Sales May 4 1,300 @ $4.10 May 3 300 @ $7.00 14 700 @ $4.40 16 1,000 @ $7.00 29 500 @ $4.75 18 400 @ $7.50 Instructions
a. Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using FIFO.
b. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions.
c. Calculate gross profit for May.
E6.5 (LO 2) AP Top Light Company uses a perpetual inventory system. The company began
2021 with 1,000 lamps in inventory at a cost of $12 per unit. During 2021, Top Light had the
following purchases and sales of lamps: February 15 Purchased 2,000 units @ $18 per unit April 24 Sold 2,500 units @ $30 per unit June 6 Purchased 3,500 units @ $23 per unit October 18 Sold 2,000 units @ $33 per unit December 4 Purchased 1,400 units @ $26 per unit
All purchases and sales are on account. Instructions
a. Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory using weighted average. ( Round the
weighted average cost per unit to two decimal places.)
b. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions.
c. Calculate gross profit for the year.
E6.6 (LO 2, 3) AP Dene Company uses a perpetual inventory system and reports the following inventory
transactions for the month of July: Units Unit Cost Total Cost July 1 Inventory 150 $5 $ 750 12 Purchases 230 6.75 1,552.5 20 Sale (250) 28 Purchases 490 7 3,430 Instructions
a. Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under (1) FIFO and (2) weighted
average. (Round the weighted average cost per unit to two decimal places.)
b. Which cost formula gives the higher ending inventory? Why?
c. Which cost formula results in the higher cost of goods sold? Why?
*E6.13 (LO 7) AP Lombart Company uses a periodic inventory system. Its records show the
following for the month of April, with 25 units on hand at April 30: Unit Total Units Cost Cost April 1 Inventory 30 $ 8 $240 45 11 495 12 Purchases 15 12 180 16 Purchases Total 90 $915 Instructions
a. Calculate the ending inventory and cost of goods sold at April 30 using the FIFO and
weighted average cost formulas.
b. Prove the cost of goods sold calculations.
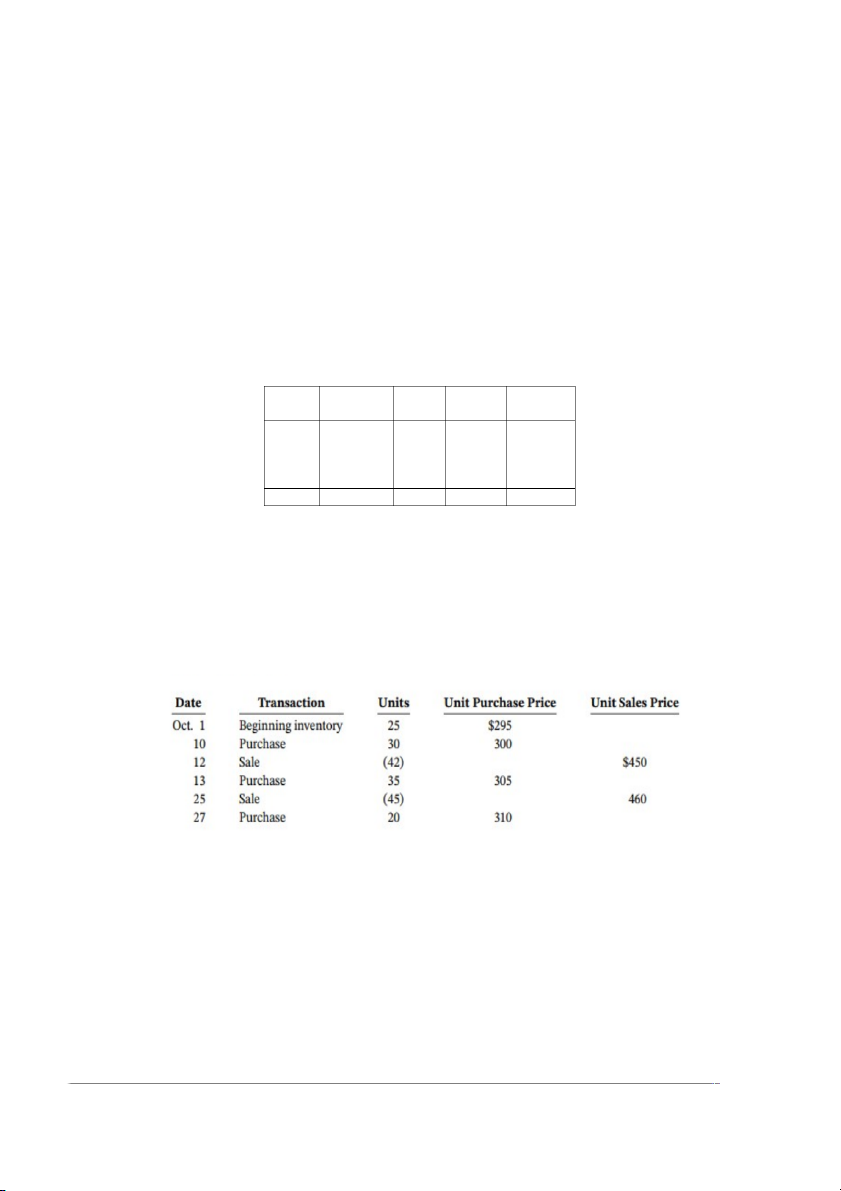
*E6.15 (LO 2, 7) AP Xpert Snowboards sells an ultra-lightweight snowboard that is
considered to be one of the best on the market. Information follows for Xpert’s purchases and
sales of the ultra-lightweight snowboard in October: Instructions
a. Calculate the cost of goods sold and the ending inventory using FIFO and weighted
average, assuming Xpert uses a perpetual inventory system. (Round the weighted average
cost per unit to two decimal places.)
b. Calculate gross profit for the year.
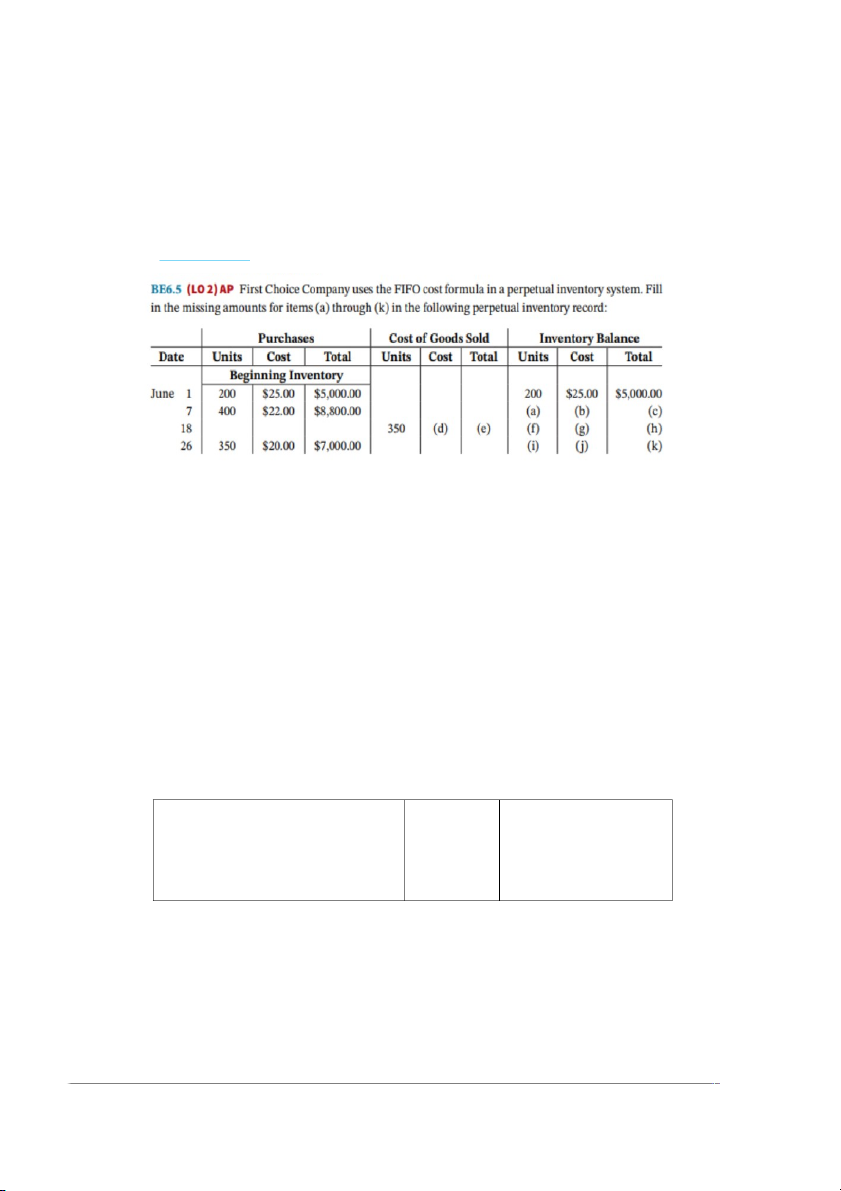
BE6.6 (LO 2) AP Average Joe Company uses the FIFO method; weighted average cost; and
cumulative weighted average cost formula in a perpetual inventory system. Fill in the missing
amounts for items (a) through (k) in the following perpetual inventory record (round the
weighted average cost to two decimal places):
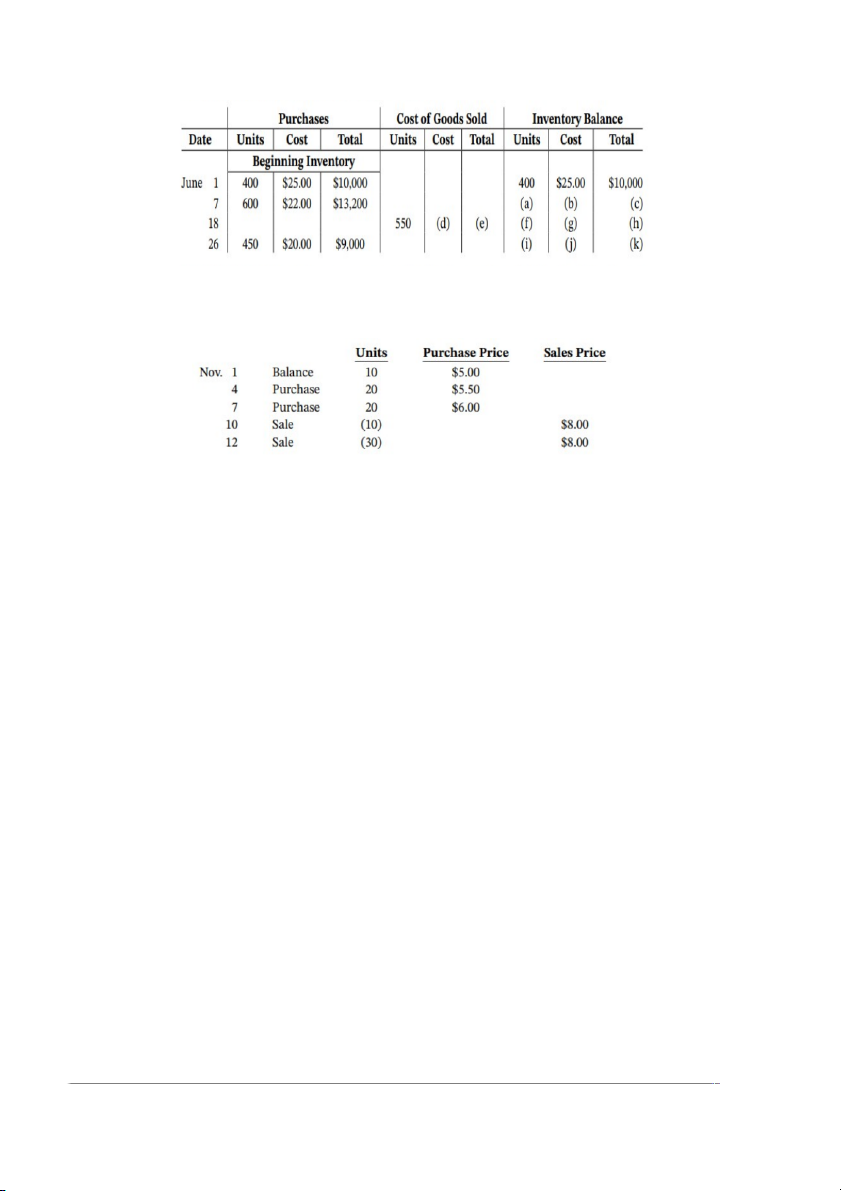
BE6.7 (LO 2) AP Jordy & Company uses a perpetual inventory system. The following
information is available for November:
Calculate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory under (a) FIFO and (b) weighted
average cost formula; and (c) cumulative weighted average cost formula. (Round the
weighted average cost per unit to two decimal places.)
(d) Prepare journal entries to record the transactions using the FIFO method. Assume all sales and purchases are on credit.
(e) Which formula will result in a higher ending inventory?
(f) Which formula will result in a higher cost of goods sold?
BE6.11 (LO 4) AN Collie Company incorrectly included $23,000 of goods held on
consignment for Retriever Company in Collie’s beginning inventory for the year ended
December 31, 2020. The ending inventory for 2020 and 2021 was correctly counted.
(a) What is the impact on the 2020 financial statements?
(b) What is the impact on the 2021 financial statements?
BE6.12 (LO 4) AN Firstin Company reported profit of $90,000 in 2020. When counting its
inventory on December 31, 2020, the company forgot to include items stored in a separate
room in the warehouse. As a result, ending inventory was understated by $7,000.
a. What is the correct profit for 2020?
b. What effect, if any, will this error have on total assets and owner’s equity reported on the
balance sheet at December 31, 2020?
c. Assuming the inventory is correctly counted on December 31, 2021, what effect, if any,
will this error have on the 2021 financial statements?.




