


Preview text:
NG ÂM V Ữ À ÂM V H Ị C TIẾẾNG ANH Ọ
1. How are pure vowels diffrent from ? diphthong
Pure vowels remain constract and do not glide from 1 vowel to another. By contrast, Diphthongs
consist a movenant or glide from 1 vowel to another.
2. On what criteria are classified? consants
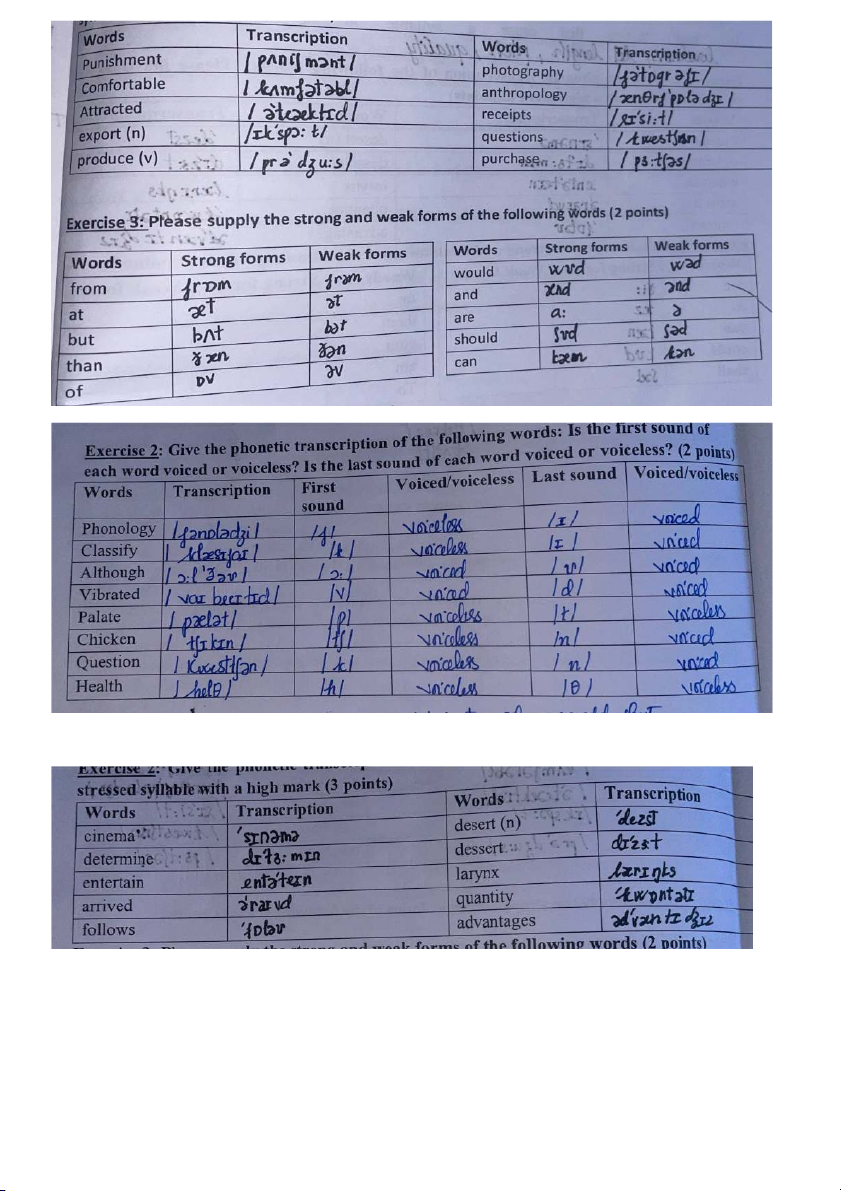
There are 4 criteria to . classify the consonants
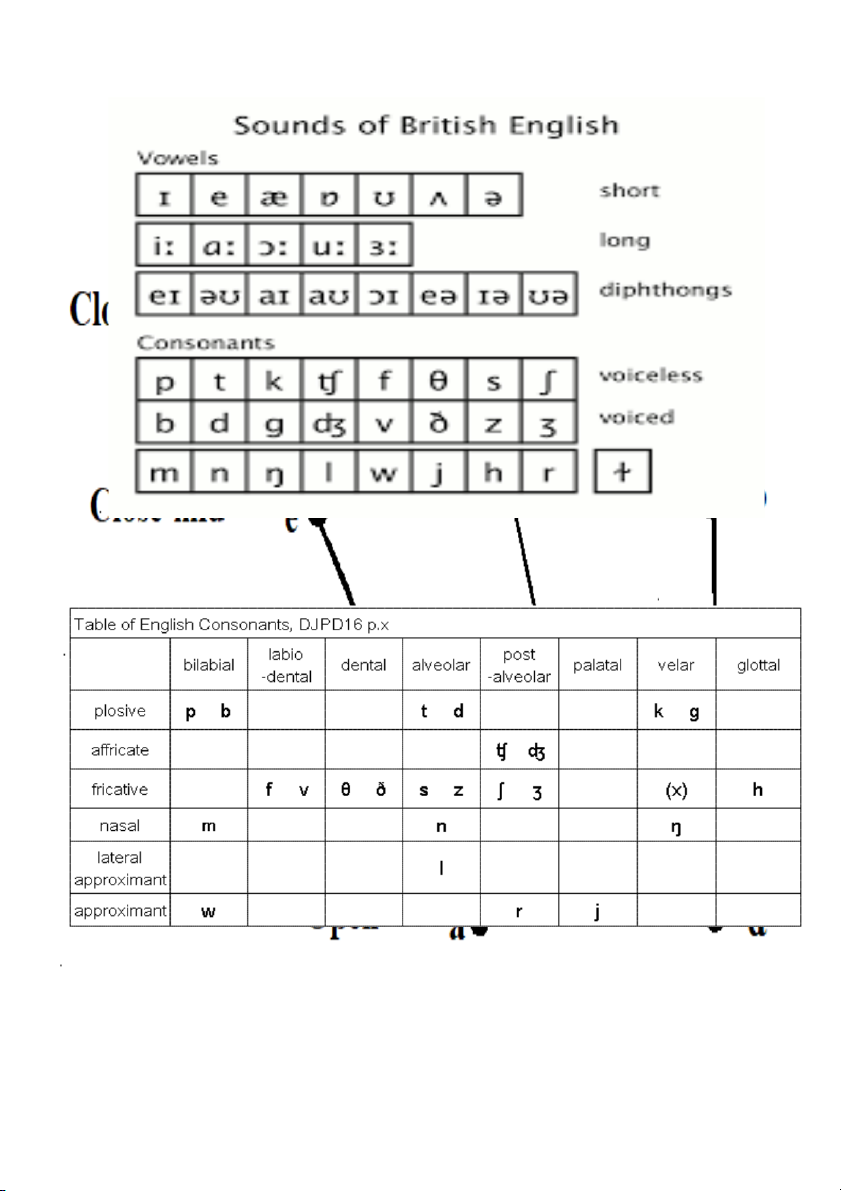
- Place of articulation (obstructions): 9 possibilities: Bilabial, Labio-dental, alveolar, post-alveolar,
dental, palate-alveolar, velar, glottal - : 6 possibilities: plos Manner of articulation
ive, fricative, affricate, nasal, lateral, gliding
- State of vocal cords (voicing):2 possibilities: voiced/voiceless
- Positions of soft palate: 2 possibilities: the soft palate is up/down (oral/nasal)
Example: /p/: bilabial, plosive, voiceless, ora.
3. What is a syllable? Present the nature of the syllable.
A syllable is a unit of pronunciation uttered without interruption, loosely, a single sound.
The nature of the syllable: Syllable may be defined both phonetically and phonological. Phonetically,
syables are usually describled as consiting of a centre which has little or no obstruction to airflow and
which sounds comparatively loud, before and after this centre, there will be greater obstruction to airflow or less loud sound.
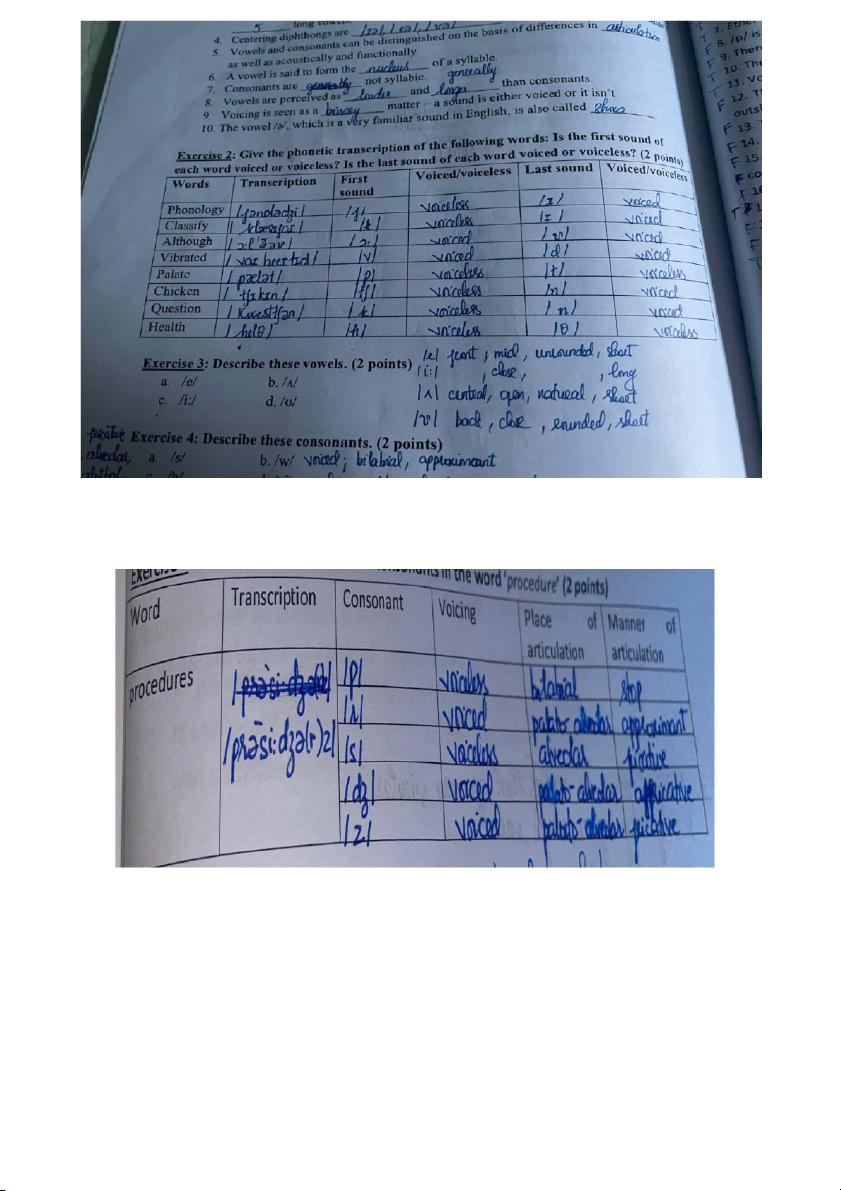
4. On what criteria are pure vowels (Monophthong) classified?
A pure vowel (monophthong) is an unchanging sound in the pronunciation of which the organs of
speech do not perceptibly change the position throughout the duration of the vowel in a syllable.
They are classified by criteria: 4
Shaped of lips: Spread, unrounded, rounded
Position of tongue: High, middle, low
Highest position of the tongue: Front, central, back
Length of sounds: Long, short
5. What are the major differences between vowels and consonants, in terms of articulation and distribution?
The most common view is that vowels are sounds in which there is no obstruction to the flow of air as it
passes from the larynx to the lips. Consonant sounds are made with a narrow or complete closure in the
vocal tract. Vowels are more sonorous than consonants. Distribution: English vowels are found in both
stressed and unstressed syllables. They can occur in the initial, medial, or final positions within words.
English consonants have more restrictions on their distribution compared to vowels. They can occur in all
positions within words but have specific patterns and constraints.
6. According to what principles are the E
diphthong classified? Illustrate your answer with examples?
According to the quality of the second element.
7. What is a minimal pair? Give your own examples
Minimal pair: are words that are very similar and only vary by a single sound.
8. What is a distinctive feature?
When a feature distinguishes one phoneme from another, it is a distinctive feature.
9. What are the functions of stress?
Stress is the pronounciation of a syllables word with more force and prominence than others nearby.The
prominence of a stressed syllable can be achieved in terms of production and perception. At least four
different factors: loudness, length, pitch, quality.)
Function: Proper use of stress enables you to clearly understand the difference between such pairs as the
noun 'present (gift) and the verb present (to introduce; to offer), or the noun and the adjective. Stress can
also change the meaning of a sentence.
10.Indicate the possibilities of elision? Give illustrations.
Indicate the possibilities of elision. Give illustrations. Here are some possibilities of elision, along with
illustrations: Contraction of sounds: "I am" -> "I'm"; Elision of unstressed syllables: "Probably" ->
"Prob'ly"; Deletion of word-final sounds: "Going to" -> "Gonna", Elision of word boundaries: "Let us™
-> "Let's"; Reduction of function words: "I have" -> "I've"; Contraction of verb+not:"Cannot"-> "Can't!
11.What is meant by “assimilation of voice”. Give illustrations.
This may refer to assimilation involving the feature [+/- voice]. In a certain environment we can
consequently observe. The voicing or devoicing of a segment.
EX: "Pigs eat" -> /pigz it/ (original: /piks it/).
The voiceless /k/ sound assimilates to the voiced /g/ sound of "pigs."
12.What is regressive assimilation? Give 2 examples to illustrate.
Regressive assimilation where a sound is influenced by the sound which follow it.
Ex: The /n/ sound is influenced by the following sound and changes to an /m/ sound, /ɪnf me ə n/ (information) ɪʃə / → ɪmf me ə n/ (imformation). ɪʃə
FILL IN THE MISSING INFORMATION.
1. Phonetics describes the sounds in a language.
2. Phonology studies the ways in which speech sounds form system and patterns in human language.
Phonology is also concerned with how sound patterns are affected by the combination of words.
3. There is a big diference between the ay sounds are ư
spelled in English (letters) and how they are
pronounced (sounds). For example, the same letter “a” is used to respresent different sounds in the
words “cake, any, sofa, call, mat”. In the words “two, to, too”, different letters may represent the same
sound. Or letters may represent no sounds. Take the words “comb, honest,” for instance.
4. In the English language, there are 26 letter and 44 sounds (20 vowels and consonants).
5. IPA stands for International Phonetic Alphabet. It consists of a set of symbols in which one symbol
always represents one sound.
6. English spelling patterns are and ar inconsitent
e not always a reliable guide to pronounciation.
7. In many languages the word for ‘language’ is also the word for tounge.
8. The Interanational Phonetic Alphabet consists of a set of symbol, each of which always represents one sound.
9. In producing a lateral, the center of the tongue is in close contact with the roof of the mouth, but the
sides of the tongue are lowered so that the air can escape along the sides of the tongue.
10.The most familiar and common sound in English is schwa.
11.A voiced sound is a sound pronounced with the vibration of the vocal cords.
12.The 5 long vowels are different from the 7 short vowels not only in length but also in quality.
13.If we close our vocal cords close enough for them to be slightly touching each other, the air passage
between them causes them to vibrate.
14.Pure vowels or monophthongs remain
and don’t glide from one v constant owel to another.
15. Can be described as central, mid, neutral, short vowel.
16.Vowels and consonants can be distinguished on the basis of differences in articulation, as well as
acoustically and functionally.
17.The most important thing to remember about all the diphthongs is that the second part is much
shorted and weak than the first part.
18.If the tongue touches the teeth, the place is dental.
19.An affricative is a consonant which starts as a plosive, but instead of ending with plosion, ends with
africative made in the same place.
20. the four bilabial sounds in english are p,b,m,w.
21.Some word pairs, such as peat /pit/, sheep /ship/, cannot be distinguished if it were not for vowel length.
22.Vowels are produced with little obstruction in the vocal tract and are voiced.
23.English spelling patterns are inconsistent and are not always a reliable guide to pronunciation.
24.In producing vowels, the tongue does not make a great deal of contract with the soft palate, which is
the upper surface of the mouth.
25.A vowel is said to form the nucleus of a syllable.
26.When the back of the tongue is in contact with the soft palate, the place is velar.
27.Consonant sounds are speech sounds produced with a narrow or complete closure/obstruction in the vocal tract.
28.A nasal consonant involves a complete closure in the oral cavity, but air is allowed to escape through
the nose, since the velum is lowed.
29.Pure vowels can also be called single vowel/monophthongs. 30.There are pure vowels 12
in English: short vowels and 7 long v 5 owels.
31.Vowels and consonants can be distinguished on the basis of differences in articulation as well as
acoustically and functionally.
32.A vowels perceived as louder and longer than consonants.
33.Voicing is seen as a binary matter – a sound is either voiced or it isn’t.
34.In counting the syllables in words, we are in fact counting the vowels.
35.Experimental work has shown that 4 factors that cause a syllable to be made prominent are not equally improtant.
36.Words generally stressed in sentences are content words including nouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, and question words.
37.Certain words can be pronounced in 2 different ways, which are called strong form weak form. and
38.The word “that” has a weak form when used in a relative clause.
39.The word “squeak” has an initial three-consonants cluster.
40.The word “twelfths” has a final cluster 4 .
41.In the production of fricative, we will feel the air coming out of our mouth and producing noise
because of the friction.
42.A constriction between the vocal cords, inside the larynx, has a
place of articulation. glottal
43.In some words, the type of stress that is weaker than the primary stress but stronger than that of the
first syllable of “around” is . secondary stress
44.Syllables consist of a centre which has vowels to airflow and which sounds comparatively loud.
45.When a feature distinguishes one phoneme from another, it is a distinctive feature.
46.There is a possibility of up to 4 consonants at the end of a word.
47.What we might call a minimal syllable would be a single vowel in isolation.
48.A voiceless sound is a sound pronounced without the vibration of the vocal cords.
49.In the word “eat” ( when it is not followed by a vowel ), the realization of /t/ is aspiration.
50.If we close our vocal cords close enough for them to slightly touching each other, the air passage
between them causes to vibrate.
51.Four factors that cause a syllable to be made prominent are loudness, length, pitch, quality.
52.Words generally stressed in sentences are content words which are important in a sentence which convey meaning.
53.When studying initial consonant cluster, we can find the possibility of up to three-consonants at the beginning of a word.
54.When two different forms are in ever idential
y way except for one sound segment that occurs in the
same place in the string, the two words are called a minimal pair.
55.An affricative is a consonant which starts as a plosive, but instead of ending with plosion, ends with a
fricative made in the same place.
56.Words generally unstressed in sentences are function words which include articles, prepositions,
pronouns, conjunctions, and helping verbs.
57. Assimilation is of two sorts: we have regressive assimilation where a sound is influenced by the
sound which follows it; progressive assimilation where a sound is influenced by the sound that precedes it.
58. Elision refers to the disappearance of one or more sounds in connected speech which would be
present in a word pronounced in isolation.
59.When a word ends with an /u:/, / /or /a ǝʊ /
ʊ sound, the next word starts with a vowel sound, we
often link them with a /w/ sound.
60.When a sound ends with an /з:/, //, /:/ or /e / sound and the n ǝ
ext word starts with a vowel sound,
we often link them with a /r/ sound.
61.In the sentence "Walk down the path to end of the canal', there are r 5 hythm units. TRUE – FALSE
F 1. The only difference between pen and when is due only to the difference in voicing.
T 2. There are only 9 voiceless sounds in English.
F . /e/ is a front mid neutr 3 al short vowel.
T 4. /l/ is a close, front and unrounded short vowel.
F 5. /r/ is a voiced, palatal, approximant consonant.
T 6. /I/ is voiced, alveolar, lateral consonant.
T 7. Ether - Either is a minimal pair.
F . /p/ is pronounc 8
ed exactly the same in PEAK as in SPEAK.
F 9. There are 26 phonemes in the English language.
T 10. The first sound of the word 'chocolate' is voiceless, palate-alveolar, affricative. T V
11. oicing is seen as a binary matter - a sound is either voiced or it isn't.
F 12. The vocal tract is the passage way through which air passes from the tongue out into the air outside our bodies.
F 13. The consonant /j/ can be described as voiced, approximant, palato-alveolar. F . There ar 14
e 5 alveolar sounds in English.
F 15. Syllables consist of a centre which has great obstruction to airflow and which sounds
comparatively loud, before and after this centre, there will be greater obstruction to the airflow.
F 16. When a feature distinguishes one word from another, it is a distinctive feature.
T 17.There are 3 neutral pure vowels in English.
F 18. There are 6 closing diphthongs.
F 19. In terms of place of articulation, consonants are classified into 6 categories.
T . There are 20
4 front pure vowels in english.
F 21. The closing diphthong glides towards the closing vowel /i:/ or /u/
F 22. All voiced sounds of English have similar voiceless sounds.
T 23. /e/ is a front mid unrounded short vowel.
F 24. The word 'helped' has a four-consonant final cluster.
F 25. The word 'sphere' has an initial three Consonant cluster.
F 26. Cause - Course is not a minimal pair.
T 27. Jokes- Chokes is a minimal pair.
F 28. /t/ is pronounced exactly the same in TEA as in EAT.
F 29. When a diphthong is pronounced, the first part is shorter and quieter than the second part.
T 30. The first sound of the word 'tea' is voiceless, alveolar, plosive.




