




Preview text:
To understand human resources management, we should first review what managers do.
Managers: People who are responsible for accomplishing the organization’s
goals through directing the efforts of people within an organization.
Organization: An entity that consists of people with formally assigned roles
who work together to achieve organizational goals.
Managers help organizations achieve its goals through performing the five
basic functions of management:
Planning: Establishing goals and standards; developing rules and procedures;
developing plans and forecasts.
Organizing: Giving each subordinate a specific task; establishing departments;
delegating authority to subordinates; establishing channels of authority and
communication; coordinating the work of subordinates.
Staffing: Determining what types of people should be hired; recruiting
prospective employees; selecting employees; setting performance standards;
compensating employees; evaluating performance; counseling employees;
training and developing employees.
Leading: Getting others to get the job done; maintaining morale; motivating subordinates.
Controlling: Setting standards such as sales quotas, quality standards, or
production levels; checking to see how actual performance compares with these
standards; taking corrective action as needed.
Human Resources Management:
The process of acquiring, training, appraising, and compensating employees,
and of attending to their labor relations, health and safety, and fairness concerns.
1. Distinguish between Job Description & Job specification. Provide examples of JD &
JS for positions such as: a secretary, a receptionist, a sales representative, a waiter,
Job Descrption is the list of a job’s duties, responsibilities, reporting relationships,
working conditions, and supervisory responsibilities.
Job Specifications is the list of a job’s “human requirements”, that is the personality,
education, skills, experience, and so on - another product of job analysis.
Ex: Teacher - JD: Teaching - JS: Having experience of teaching. Secretary:
JD: Manage office tasks, answer calls, schedule appointments, and assist in organizing meetings.
JS: Proficient in MS Office, excellent communication skills, strong organizational abilities. Receptionist:
JD: Greet visitors, manage incoming calls, handle inquiries, and maintain a tidy reception area.
JS: Customer service experience, pleasant demeanor, multitasking abilities. Sales Representative:
JD: Identify and pursue new sales opportunities, build client relationships, and meet sales targets.
JS: Sales experience, persuasive communication, target-driven mindset. Waiter:
JD: Take orders, serve food and beverages, ensure guest satisfaction, and handle payments.
JS: Customer service orientation, ability to work in a fast-paced environment, attention to detail.
2. What is Job Analysis? Explain how information gathered through a job analysis can be used in different ways.
Job Analysis is a procedure of determining duties & skill requirements of a job and
the kind of person who should be hired for it.
In general, to recruit right people, we need to know what the job need and what
people need to do, so we use JA to recruit.
In general, to train employees, we need to know the traning needs including what the
job needs, what the people need to do, so we need to use JA to traning
3. What are sources of candidate (recruitment tools)? Describe them.
Inside candidates: current employees or “hiring from within”
job posting (intranet, mail,…) is publicizing an open job to employees and listing its
and listing its attributes, like qualifications, supervisor, working schedule, and pay rate Outside candidates:
Internet: Social networking provides recruiting assitance.
Social media: Recuiting is shifting from online job boards to social networking sites.
Advertising: The best medium should be selected based on the positions for which you are recruiting.
Employment Agencies: There are three main types of employment agencies.
Public agencies are operated by federal, state, or local governments.
Agencies associated with non-profit organizations.
Private agencies charge fees for each applicant they place.
Temporary Workers/Alternative Staffing: The benefits of contingency staffing
include increases in overall productivity, and time and expenses saved by not having
to recruit, train, and document new employees.
Outsourcing: having an outside vendor supply services that the company’s own
employees previously did in-house.
Offshoring: having outside vendors or employees abroad supply services that the
company’s own employees previously did in-house.
Executive recruiters: Also called headhunters, are special employment agencies
retained by employers to seek out top-management talent for their clients.
Telecommuters:Telecommuters do all or most of their work remotely, often from
home, using information technology
Military Personnel: Returning and discharged military personnel can provide a great source of trained recruits.
College Recruiting: Involves sending employers’ representatives to college
campuses to prescreen applicants and create an applicant pool of management
trainees, promotable candidates, and professional and technical employees.
Referrals and walk-ins: are alternatives for identifying potential candidates.
4. Which recruitment tools/ methods that are low-cost?
Social media: Recuiting is shifting from online job boards to social networking sites.
Public Agencies: operated by federal, organization, Government
Referrals and walk-ins: are alternatives for identifying potential candidates.
Internal Recruitment: transferring/ promoting current employees or “hiring from within”. Int
5. How many basic types of question that can be used in an interview?
What are they? Provide at least 02 examples for each type.
Situation questions:
focus on the candidate’s ability to explain what his/her behavior
would be in given situation. Example:
1. What would you do if you made a mistake no one noticed?
2. What would you do if a manager asked you to perform a task you've never done before?
Behavioral questions:
focus on the candidate behaved under certain situations &
usually start with “Tell me of a time when…” Example:
1. Give me an example of a time you had a conflict with a team member. How did you handle it?
2. Tell me about a time you made a mistake at work. How did you resolve the
problem, and what did you learn from your mistake?
Knowledge & Background questions:
probe candidates’ job related knowledge and experience. Example:
1. What are your strengths and weaknesses?
2. What is your greatest strength/weakness?
6. What is employee orientation? Why do we need to provide orientation for employees?
Orientation/Onboarding: Provides new employees w basic background ith the
information they need to do the jobs.
We need to provide orientation for employees because:
Make the new employee feel welcome
Make sure the new employee has the basic information
Help the new employee understand the organization in a broad sense
Start socializing the person into the firm’s culture and ways of doing things
7. What are 3 training methods that we can use to train sales employees at a fashion store? On-the-Job
Training (OJT): Training a person to learn a job while working on it
Apprenticeship Training:
OJT + Classroom instruction Informal
Learning: Learning through day-to-day unplanned interactions
between the new worker and his/her colleagues
Informal learning: Internal Recruitment: transferring/ promoting current employees or “hiring from within”.
Job Instruction training: Teaching a new employee the logical sequence of steps in a job
Listing each job’s basic tasks, along with key points, to provide step-by-step training for employees.
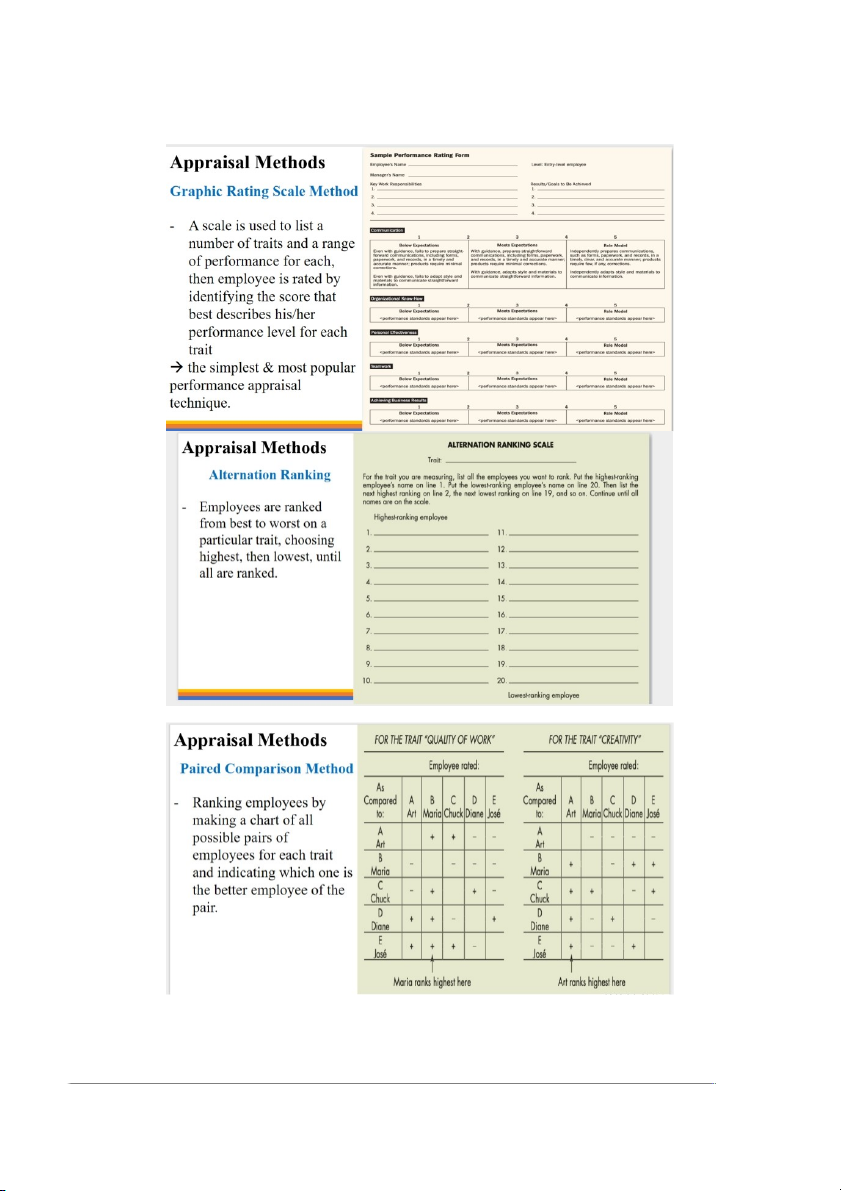
8. What is performance appraisal? Describe performance appraisal process.
Performance appraisal means evaluating an employee’s current and/or past
performance relative to his/her performance standards.
Performance appraisal is the process of 3 steps, including: 1. Setting work standard
2. Accessing the employee’s actual performance relative standards
3. Providing feedback to the employee.
9. Why do we need to conduct performance appraisal? Who should do the appraising?
We need to conduct performance appraisal to
Identify training and development needs
Decide pay/promotion/retention decisions
Performance management process
Let employees know what is expected of them
Who = Peer Appraisal + Rating Committees + Self Ratings + Appraisal by
Subordinates + 360 Degree Feedback + Crowd appraisals + Supervisor
10. Practise using appraisal methods to appraise your HRM-teammembers
performance (graphic rating scale, alternation ranking, paired comparison,
forced distribution, behaviorally anchored rating scale).
11. What is employee compensation? Compare direct financial payment and
indirect financial payment, examples?
Employee compensation: All forms of pay or rewards given to employees arising from the employment
Direct financial payment
is paying directly by money. Ex: wages, salaries,
incentives, commissions & bonuses.
Indirect financial payment
is using money to buy other benefits and then pay
the benefits to employees. Ex: insurance, vaction.
12. How many types of equity in determining pay rate? What are they? How to
establish pay rates while ensuring equity.
There are 4 types of equity in determining pay rate: External equity:
one company vs. other companies. => Salary surveys Internal equity:
a job vs other jobs within the same company => Job evaluation Individual equity:
individual’s pay vs coworkers (same jobs) within the company,
based on performance. => Performance appraisal & incentive pay Procedural equity:
the “perceived fairness of the processes and procedures used to
make decisions regarding the allocation of pay” => Communications, grievance
mechanisms, employee participation.




