
















Preview text:
REVIEW Chap 4: Accounting Cycle
1. Income Statement: Listed in order of size, beginning with the larger items, regardless of its amount 2. Balance Sheet - Assets:
+ Current Assets: used ≤ 1 year + A/R less formal than N/R
+ Property, Plant, and Equipment ≈ fixed/plant assets: used more than 1 year - Liabilities:
+ Current Liabilities: due ≤ 1 year
+ Long-term Liabilities (mortgage payable): renewed rather than paid 3. Closing entries
- Right after Financial Statements
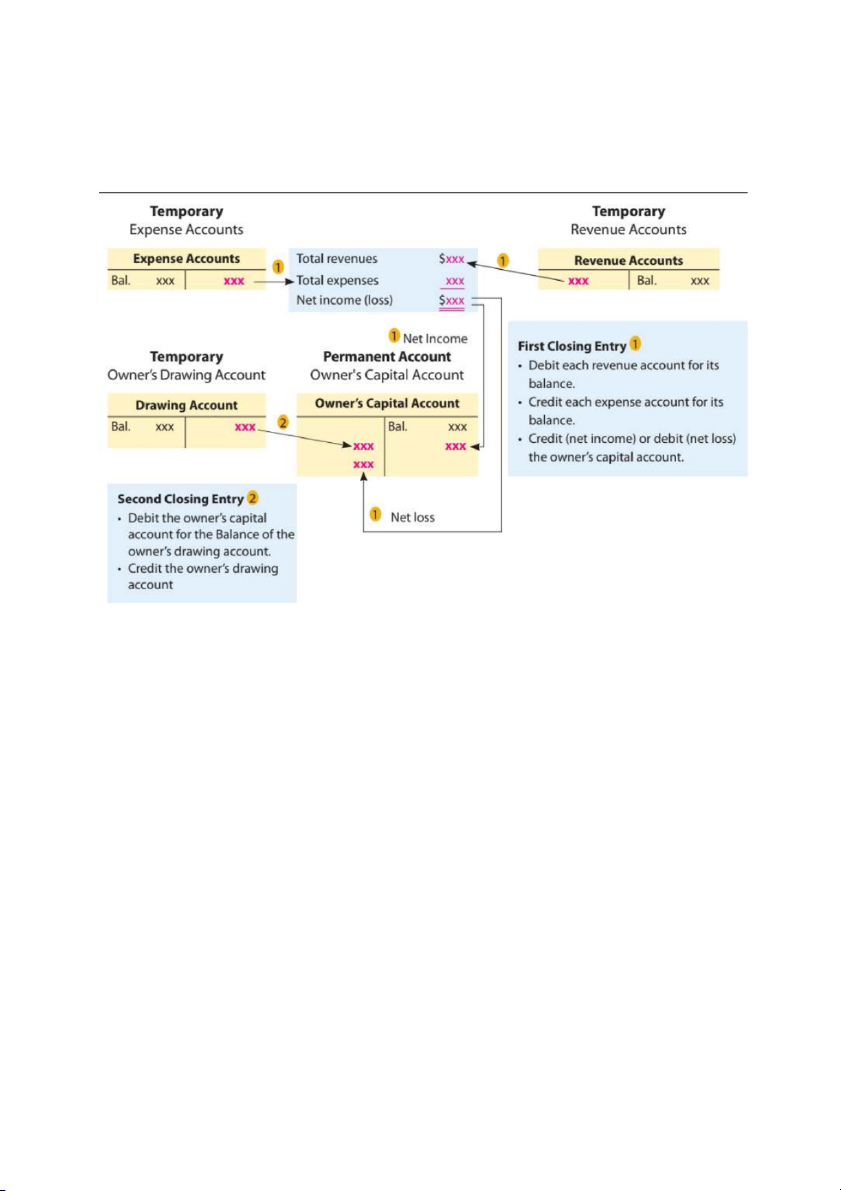
- Permanent / Real accounts: Cash, A/R, Equip, Accum.Dep., A/P, Capital
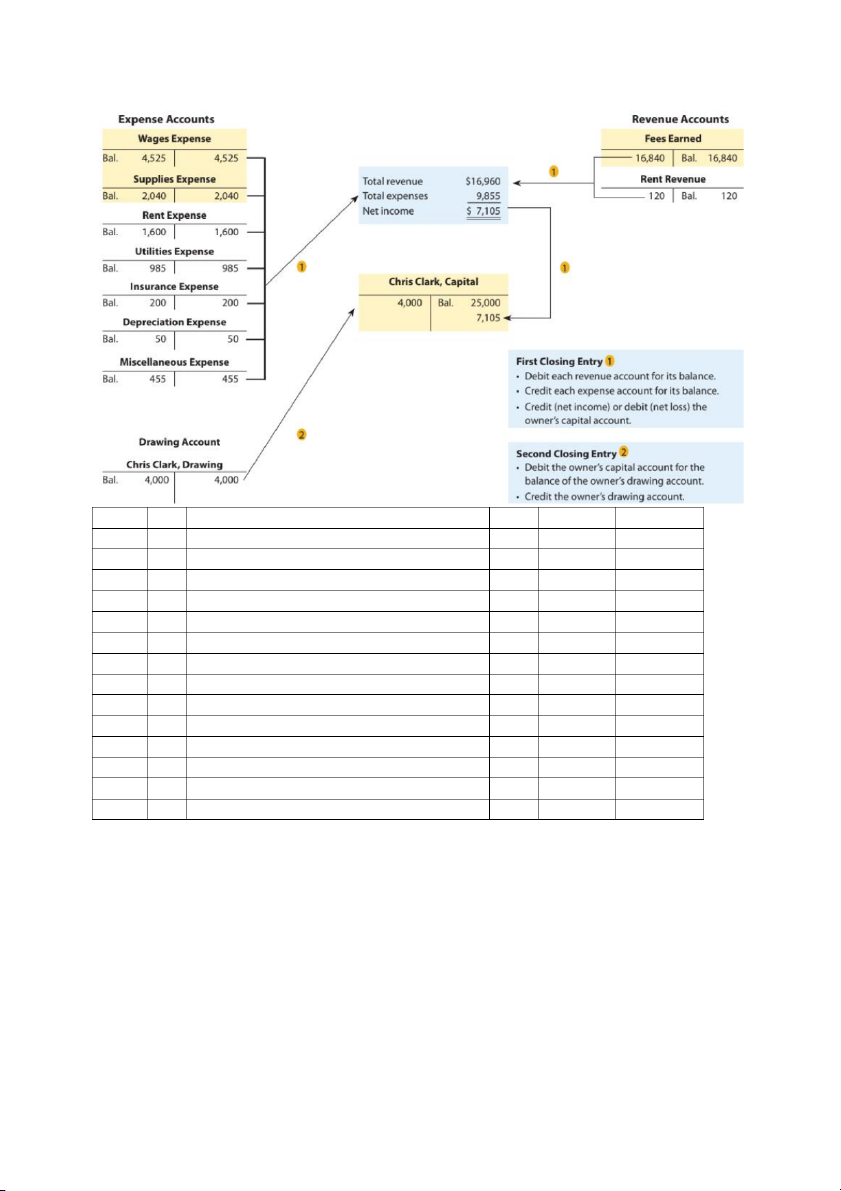
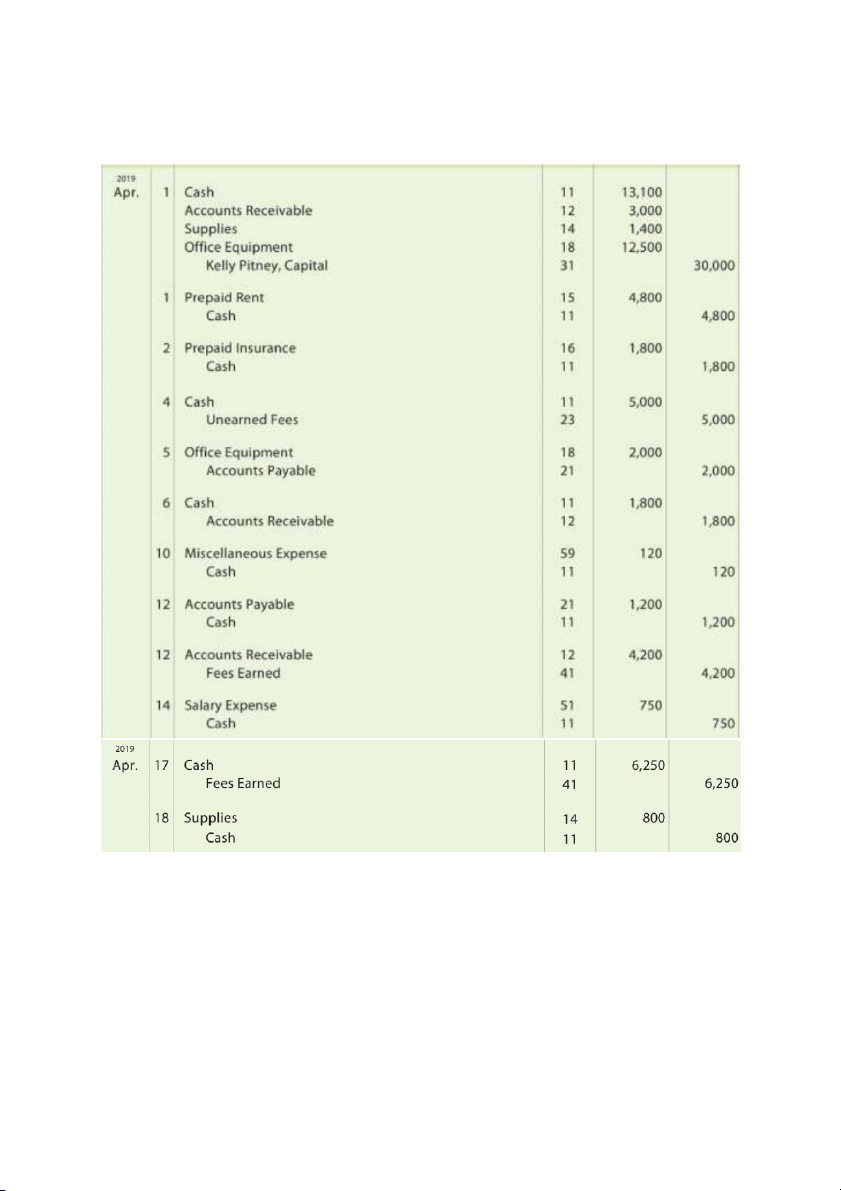
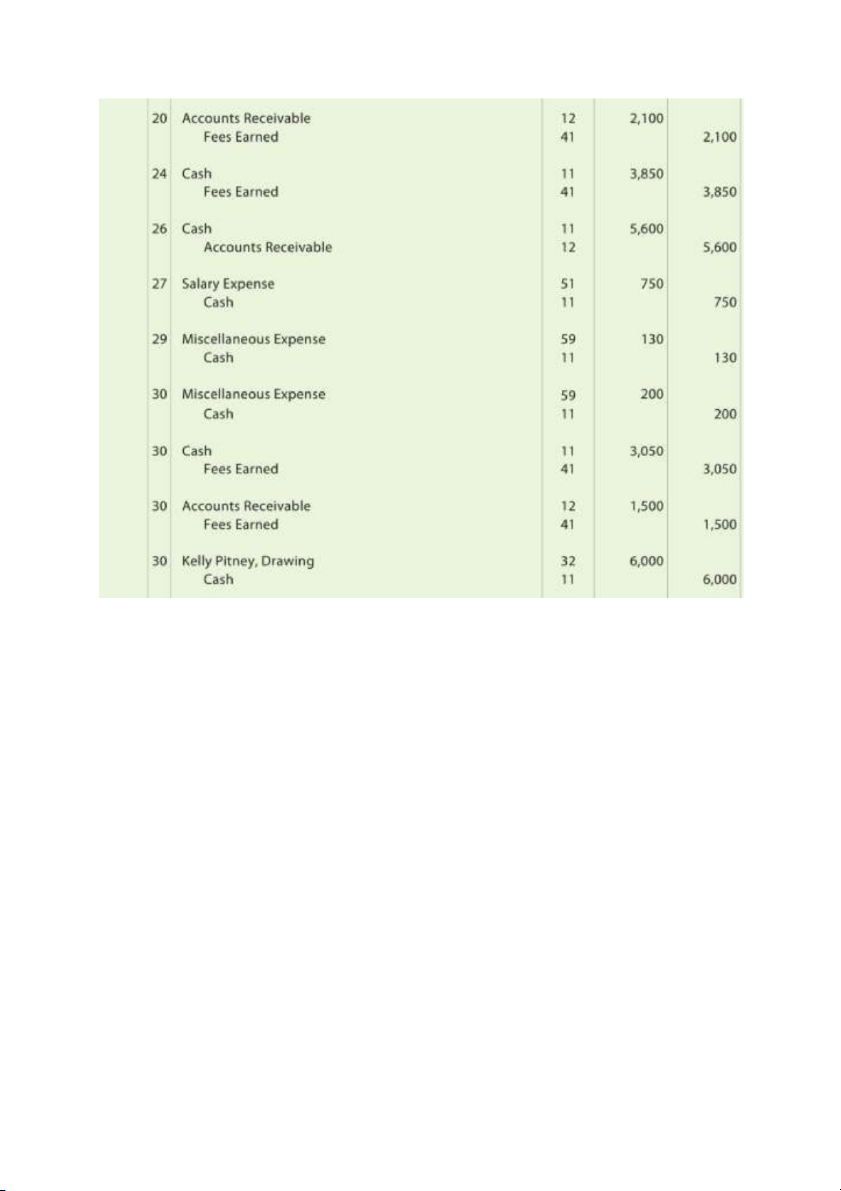
- Temporary / Nominal accounts: Rev., Exp., Drawing Dec. 31 Rent Revenues 120 Fees Earned 16,840 Income Summary 16,960 31 Income Summary 9,855 Wages Exp. 4,525 Supplies Exp. 2,040 Rent Exp. 1,600 Utilities Exp. 985 Insurance Exp. 200 Dep. Exp. 50 Misc. Exp. 455 31 Income Summary 7,105 Chris Clark, Capital 7,105 31 Chris Clark, Capital 4,000 Chris Clark, Drawing 4,000
Note: Income Summary account does not appear on the financial statements EXAMPLE ACCOUNTING CYCLE
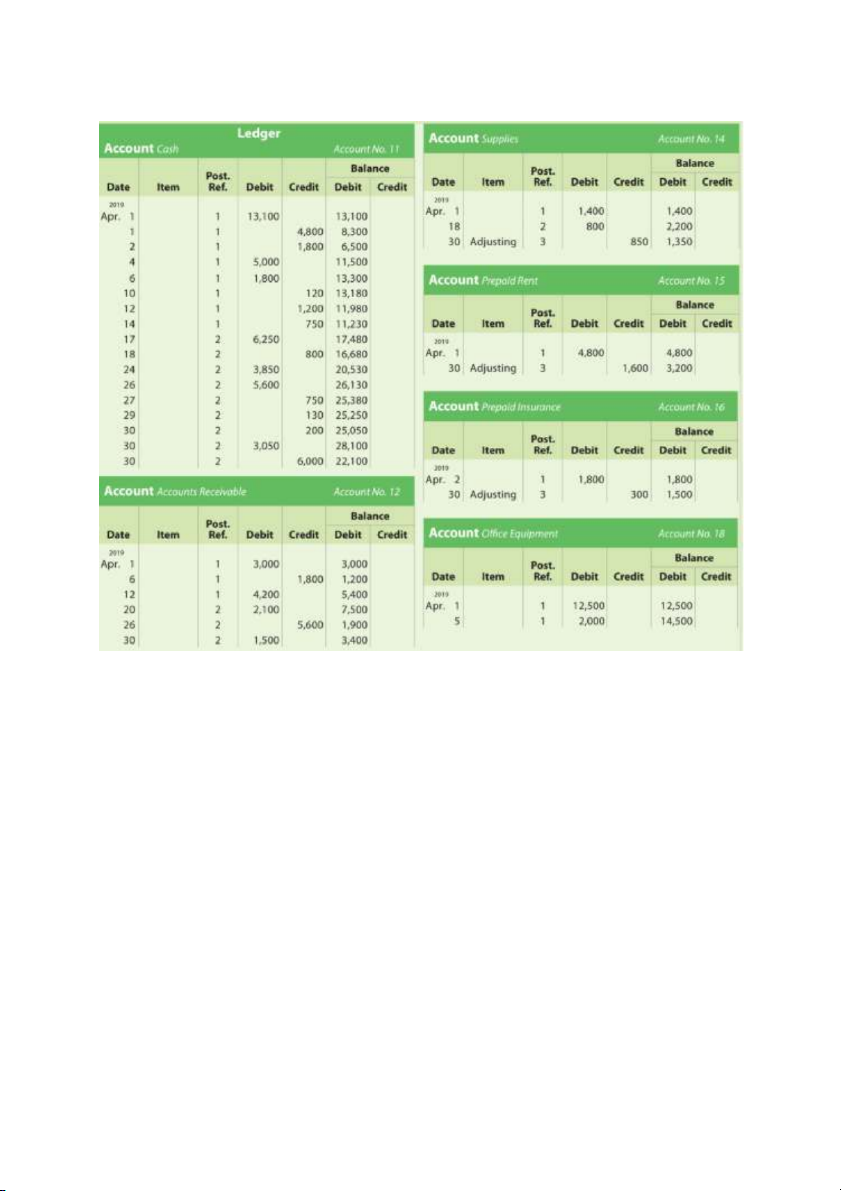
Step 1: Journalizing transactions Step 2: Posting
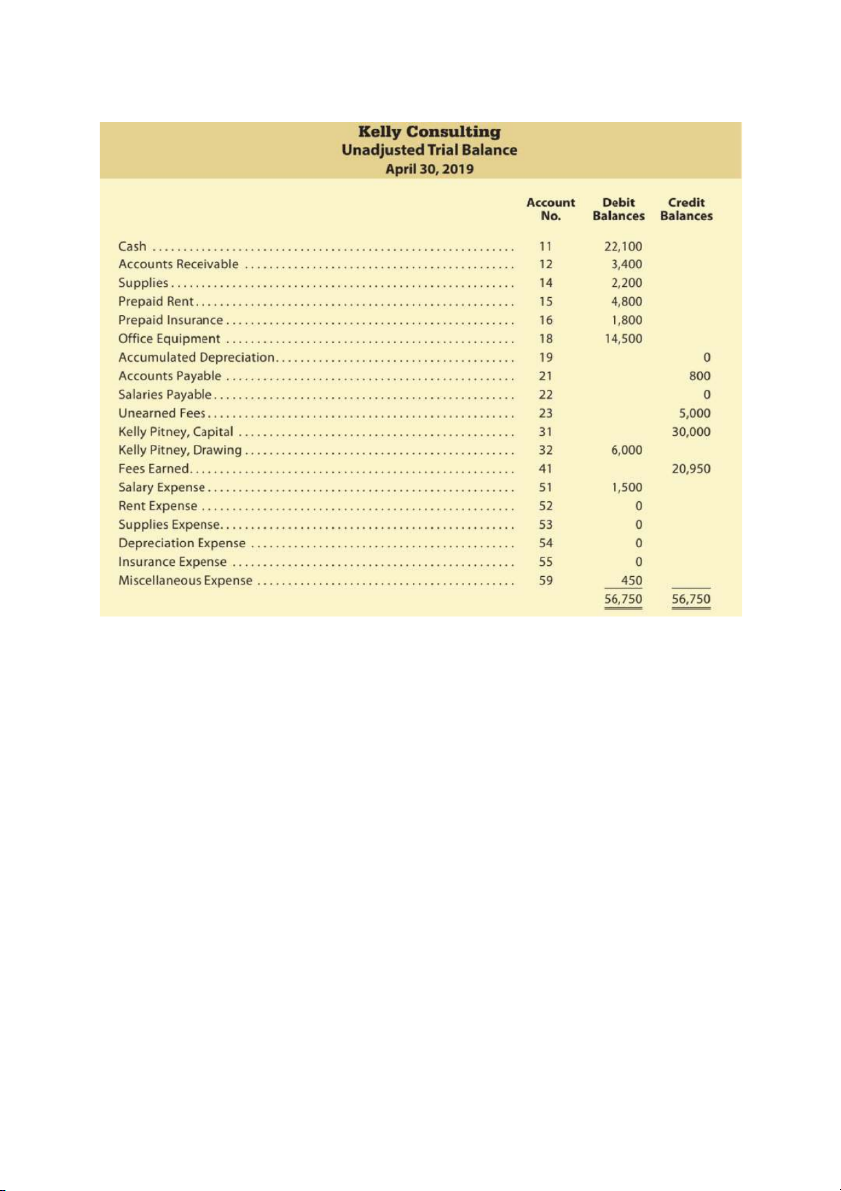
Step 3: Unadjusted trial balance
Step 4: Gathering & Analyzing adjustment data
Step 5: End-o -period spreadsheet f (OPTIONAL)
Step 6: Journalizing & Posting adjusting entries
Step 7: Adjusted trial balance
Step 8: Financial Statements
Step 9: Journalizing & Posting closing entries
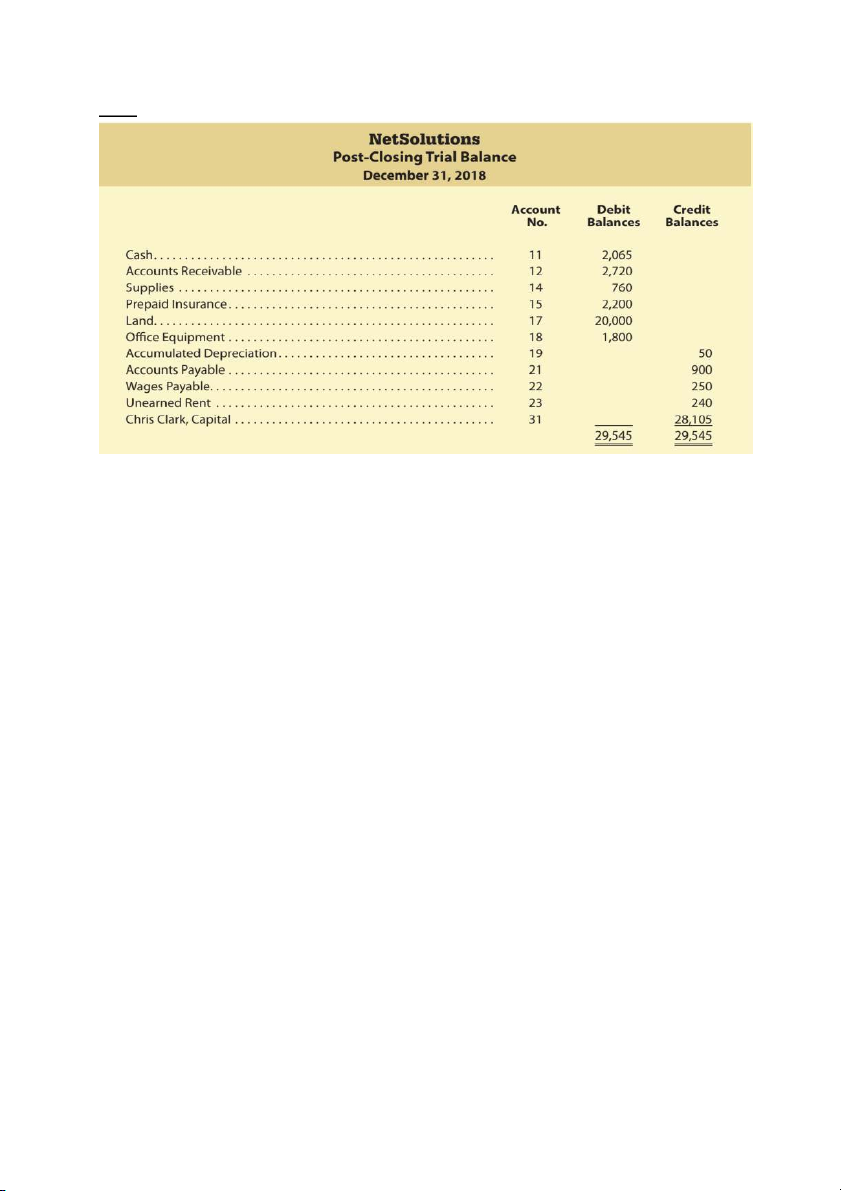
Step 10: Post-closing trial balance
Chap 6: Merchandising Business Service Business Merchandising Business Provide service to customer
Buy → Sell merchandise (goods) - Rev. → Fees earned - Rev. → Sales - Exp. → Exp
- Exp. → Cost of goods sold (COGS)
→ Sales – COGS = Gross profit
→ Net income = Rev. – Exp.
→ Gross profit Operating Exp. = Net income –
- Merchandise Inventory: goods on hand at the end of an accounting period → Current Assets 1. Buyer a) Purchase Transactions Perpetual Periodic
- Detailed cost of goods purchase & sale
- Not detailed inventory on hand
- Record continously: COGS & on hand
- Count → on hand (physical inventory) → COGS
- Record at the end of accounting period
- Record each time a sale occurs
→ Perpetual: + used with high unit values + better control
+ but require additional work, cost
Ex: Purchase inventory by cash
Purchase inventory on account
On account → Invoice (seller to buyer)
- The term called credit terms
- Buyer is allowed an amount of time to pay → called credit period
Ex: n/30 : net 30 days → due within 30 days
n/eom → due by the end of month b) Purchase Discounts
- Buyers normally take all purchase discounts
Ex: 2/10, n/30 : 2% discount if paid within 10 days, net amount due within 30 days Jan. 5 Merchandise Inventory 3,000 A/P Alpha Technologies – 3,000
If the invoice is paid within the discount period: Jan. 15 A/P Alpha Technologies – 3,000 Merchandise Inventory 60 Cash 2,940
If the invoice is not paid within the discount period: Feb. 4 A/P Alpha Technologies – 3,000 Cash 3,000
c) Purchase Returns and Allowances
- Allowances ≈ Deduction in price
→ Debit Memo (buyer send to seller to notify the reasons → debit A/P of buyer) Journal:
Ex: May 2. Purchased $5,000 of merchandise on account from Delta Data Link, terms 2/10, n/30
4. Returned $1,000 of the merchandise purchased on May 2
12. Paid for the purchase of May 2 less the return and discount May 2 Merchandise Inventory 5,000 A/P Delta Data Link – 5,000 4 A/P Delta Data Link – 1,000 Merchandise Inventory 1,000 12 A/P Delta Data Link – 4,000 Cash 3,920 Merchandise Inventory 80 2) Seller
Rev. → Sales ≈ Sales of Merchandise a) Cash Sales
Ex: Mar. 3 Sold merchandise for $1,800 and COGS was $1,200 Mar. 3 Cash 1,800 Sales 1,800 COGS 1,200 Merchandise Inventory 1,200
- Customers using MasterCard or VISA → recorded as Cash Sales BUT
- By the end of period, an exp. appears → called Credit Card Exp.
Ex: Mar. 31 Paid credit card processing fees of $4,150 Mar. 31 Credit Card Exp. 4,150 Cash 4,150 b) Sale on Account
Ex: Sold on account of $18,000 and COGS was $10,800 c) Sale Discounts → contra-revenue account → Debit Account
Ex: Sold $18,000 of merchandise to Digital Technologies on Mar. 10t h with credit terms 2/10, n/30. The COGS was $10,800. Mar.
10 A/R – Digital Technologies 18,000 Sales 18,000 10 COGS 10,800 Merchandise Inventory 10,800
If paid within the discount period: Mar. 19 Cash 17,640 Sales Discounts 360 A/R – Digital Technologies 18,000
If not paid within the discount period: Apr. 19 Cash 18,000 A/R – Digital Technologies 18,000
d) Sale Returns and Allowances → contra-revenue account → Debit Account
Ex: June 13 Digital Technologies returned the merchandise of $150, cost of merchandise returned was $110 June
13 Sales Returns and Allowances 150 A/R – Digital Technologies 150 Merchandise Inventory 110 COGS 110 3) Freight (FOB ≈ Free On Board)
Ex: June 10. Purchased merchandise from Magna Data $900, terms FOB shipping point
10. Paid freight of $50 on June 10 purchase from Magna Data
Ex: June 20. NetSolutions sold merchandise to Planter Company on account, $800, terms FOB
shipping point. NetSolutions paid freight of $45, which was added to the invoice. The cost of
the merchandise sold was $360. i) Seller ii) Buyer June 20 Merchandise Inventory 845 A/P NetSolutions – 845
Purchased merchandise, terms FOB shipping point
Ex: June 15. Sold merchandise to Kranz Co. on account $700, terms FOB destination. The COGS was $480
15. Paid freight of $40 on the sale of June 15 Summary EXAMPLE
4) Financial Statements a) Income Statement
i) Multiple-step income statement
ii) Single-step income statement
b) Statement of Owner’s Equity c) Balance Sheet i) Account form ii) Report form 5) Adjusting Entry
- Under perpetual system, invetory recorded continously
→ Merchandise Inventory balance = inventory on hand HOWEVER
- There is some loss of inventory due to shoplifting, employee theft, or errors
→ Merchandise Inventory balance > physical inventory on hand
→ This difference called inventory shrinkage (inventory shortage) Ex: 6) Closing Entry