





Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD|46958826 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC KHOA HỌC TỰ NHIÊN, ĐHQG-HCM KHOA HÓA HỌC
BÀI TẬP HÓA ĐẠI CƯƠNG 2 (CHE0002) (Lưu hành nội bộ)
Biên soạn: THẦY CÔ
GIẢNG DẠY HÓA ĐẠI CƯƠNG 2
Tp. Hồ Chí Minh – năm 2020 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
CHAPTER 1. THERMOCHEMISTRY / Chương 1. NHIỆT HÓA HỌC
(EX7-1A) How much heat, in kilojoules (kJ), is required to raise the temperature of 237
g of cold water from 4.0 to 37.0 °C (body temperature)? (ClH20 = 4,18 J/g oC)
Hãy tính lượng nhiệt bằng kilojoules (kJ) cần để tăng nhiệt độ của 237 g
nước lạnh từ 4,0 oC lên 37,0 oC (ClH20 = 4,18 J/g oC).
23 (EX7-1B) How much heat, in kilojoules (kJ), is required to raise the temperature of 2.50
kg Hg(l) from –20.0 oC to –6.0 oC? Assume a density of 13.6 g/mL and a
molar heat capacity of 28.0 Jmol-1 °C–1 for Hg(l).
Hãy tính lượng nhiệt bằng kilojoules (kJ) cần để tăng nhiệt độ của 2,5 kg
Hg(l) từ –20,0 oC lên –6,0 oC. Cho biết tỷ trọng và nhiệt dung mol của Hg (l)
lần lượt là 13,6 g/mL và 28,0 J mol–1 oC–1.
23 (EX7-2A) When 1.00 kg lead (specific heat = 0.13 J g–1 oC–1) at 100.0 oC is added to a
quantity of water at 28.5 oC, the final temperature of the lead-water mixture is 35.2 oC.
What is the mass of water present?
Khi 1,00 kg chì ( nhiệt dung riêng = 0,13 J g–1 oC–1) tại 100,0 oC được nhúng
vào nước có nhiệt độ 28,5 oC, nhiệt độ sau cùng của hỗn hợp chì-nước là
35,2 oC. Hỏi khối lượng nước là bao nhiêu?
23 (EX7-2B) A 100.0g copper sample (specific heat = 0.385 Jg–1 °C–1) at 100.0 oC is added
to 50.0 g water at 26.5 °C. What is the final temperature of the copper-water mixture? 100 g
đồng (nhiệt dung riêng = 0.385 J g–1 oC–1) tại 100,0 oC được nhúng vào 50.0 g nước
có nhiệt độ 26.5 oC. Hỏi nhiệt độ sau cùng của hỗn hợp đồng–nước là bao nhiêu?
23 (EX7-3A) Vanillin is a natural constituent of vanilla. It is also manufactured
for use in artificial vanilla flavoring. The combustion of 1.013 g of vanillin,
C8H8O3, in a bomb calorimeter causes the temperature to rise from 24.89 to
30.09 oC. What is the heat of combustion of vanillin, expressed in kilojoules
per mole? (the heat capacity of the calorimeter assembly is 4.90 kJ/oC).
Vanillin là một thành phần tự nhiên trong vanilla. Nó cũng được sản xuất làm
hương nhân tạo mùi vanilla. Đốt cháy 1,013 g vanillin, C8H8O 3, làm nhiệt độ
trong nhiệt lượng kế tăng từ 24,89 lên 30,09 oC. Hỏi nhiệt đốt cháy của vanillin
là bao nhiêu kJ/mol? (biết nhiệt lượng kế có nhiệt dung là 4,90 kJ/ oC).
23 (EX7-3B) The heat of combustion of benzoic acid is –26.42 kJ/g. The combustion of a
1.176 g sample of benzoic acid causes a temperature increase of 4.96 oC in a bomb
calorimeter assembly. What is the heat capacity of the assembly?
Nhiệt đốt cháy của acid benzoic là –26,42 kJ/g. Đốt cháy 1,176 g acid benzoic làm nhiệt
độ trong một nhiệt lượng kế tăng 4,96 oC. Tìm nhiệt dung của nhiệt lượng kế này.
23 (EX7-4A) Two solutions, 100.0 mL of 1.00 M AgNO3(aq) and 100.0 mL of 1.00
M NaCl(aq), both initially at 22.4 oC, are added to a Styrofoam-cup
calorimeter and allowed to react. The temperature rises to 30.2 oC.
Determine qrxn per mole of in the reaction. 1 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
Hai dung dịch 100,0 mL AgNO3(aq) 1,00 M và 100,0 mL NaCl(aq) 1,00 M đều ở
nhiệt độ 22,4 oC được thêm vào một nhiệt lượng kế cốc Styrofoam và để
cho phản ứng xảy ra trong nhiệt lượng kế này. Nhiệt độ sau đó tăng lên
đến 30,2 oC. Hãy tìm nhiệt phản ứng (kJ/mol) của phản ứng sau: Ag+ (aq) + Cl (aq) → AgCl(s)
23 (EX7-4B) Two solutions, 100.0mL of 1.020 M HCl and 50.0 mL of 1.988 M NaOH, both
initially at 24.52 oC, are mixed in a Styrofoam-cup calorimeter and allowed to react.
What will be the final temperature of the mixture? The heat of neutralization reaction is –56 kJ/mol H2O.
Hai dung dịch 100,0 mL HCl 1,020 M và 50,0 mL NaOH 1,988 M đều ở nhiệt độ
24,52 oC được trộn lẫn trong một nhiệt lượng kế cốc Styrofoam và để cho
phản ứng xảy ra trong nhiệt lượng kế này. Hỏi nhiệt độ sau cùng của hệ
thống? Cho biết nhiệt phản ứng trung hòa là –56 kJ/mol H2O tạo thành.
23 (EX7-5A) How much work, in joules, is involved when 0,225 mol N2 at a
constant temperature of 23 oC is allowed to expand by 1.50 L in volume
against an external pressure of 0.750 atm?
Cho biết lượng công liên quan trong quá trình 0,225 mol N2 tại nhiệt độ không
đổi 23 oC giãn nở thêm 1,50 L chống lại áp suất ngoài 0,750 atm là bao nhiêu?
23 (EX7-5B) How much work is done, in joules, when an external pressure of 2.50 atm is
applied, at a constant temperature of to 20.0 °C, to 50.0 g N2(g) in a 75.0 L cylinder? Cho
biết lượng công sinh ra tính bằng joules chống lại áp suất ngoài 2,25 atm tại nhiệt độ
không đổi 20,0 oC của 50,0 g N2(g) trong xylanh thể tích 75,0 L chống lại áp
suất ngoài 0,750 atm là bao nhiêu? (Xylanh tuơng tự hình 7-8)
23 (EX7-6A) In compressing a gas, 355 J of work is done on the system. At the
same time, 185 J of heat escapes from the system. What is ΔU for the system?
Khi nén một khí, lượng công 355 J được đưa vào hệ thống cùng lúc với 185
J nhiệt thoát ra từ hệ thống. Hỏi ΔU của hệ thống la bao nhiêu?
23 (EX7-6B) If the internal energy of a system decreases by 125 J at the same
time that the system absorbs 54 J of heat, does the system do work or have work done on it? How much?
Nếu nôi năng của một hệ thống giảm đi 125 J cùng lúc với việc hấp thu 54 J nhiệt
lượng. Hỏi hệ thống này nhận công hay sinh công? Lượng công là bao nhiêu?
23 (EX7-7A) What mass of sucrose must be burned to produce 1.00 ×103 kJ of heat? The
heat of combustion of sucrose is –5,65 ×103 kJ/mol sucrose.
Hãy tính lượng sucrose cần đốt cháy để tạo ra 1,00 ×103 kJ nhiệt lượng. Cho
biết nhiệt đốt cháy của sucrose là –5,65 ×103 kJ/mol sucrose.
23 (EX7-7B) A 25.0 mL sample of 0.1045 M HCl(aq) was neutralized by
NaOH(aq). Determine the heat evolved in this neutralization. The heat of
neutralization reaction is –56 kJ/mol H2O. 2 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
25,0 mL HCl(aq) 0,1045 M được trung hòa bằng NaOH(aq). Hãy tính lượng
nhiệt tỏa ra của quá trình trung hòa này. Biết nhiệt phản ứng trung hòa là –
56 kJ/mol H2O tạo thành.
23 (EX7-8A) What is the enthalpy change when a cube of ice 2.00 cm on edge is brought
from –10.0 °C to a final temperature of 23.2 °C? For ice, use a density of 0.917 g/cm3 a
specific heat of 2,01 J/g–1 oC–1, and an enthalpy of fusion of 6,01 kJ/mol.
Khi một khối băng lập phương cạnh dài 2,00 cm được đưa từ –10,0 oC lên 23,2 oC, biến
thiên enthalpy của quá trình la bao nhiêu? Cho biết tỷ khối của băng là 0,917 g/cm3,
nhiệt dung riêng của băng là 2,01 J.g–1 oC–1 và nhiệt nóng chảy của băng là 6,01 kJ/mol.
23 (EX7-8B) What is the maximum mass of ice at –15,0 oC that can be completely
converted to water vapor at 25 oC if the available heat for this transition is 5,00×103
kJ,? (heat of water evaporization at 25oC is 44 x 103 J/mol).
Hỏi khối lượng tối đa băng tại nhiệt độ –15,0 oC có thể chuyển thành hơi nước tại 25 oC
khi dùng lượng nhiệt 5,00 ×103 kJ? (nhiệt hóa hơi của nước ở 25oC là 44 x 103 J/mol).
23 (EX7-9A) The standard heat of combustion of propene, C3H6(g), is –2058 kJ/mol, and
C3H8(g), is -2219 kJ/mol . Use this value and the standard enthalpy of formation of
CO2(g) and water(l) to determine ΔHo for the hydrogenation of propene to propane.
Nhiệt đốt cháy chuẩn của propene, C3H6(g), là –2058 kJ/mol C3H6(g), của
propane C3H8(g), là -2219 kJ/mol C3H8(g) Hãy sử dụng dữ liệu này và tra
cứu thêm các dữ liệu nhiệt hình thành chuẩn của CO2(g) và nước(l) để xác
định ΔHo của quá trình hydrogen hóa của propene thành propane.
23 (EX7-9B) From the data in Practice Example 17 and the following equation, determine
the standard enthalpy of combustion of one mole of 2-propanol, CH3CH(O)CH3(l).
Sử dụng các kết quả tính toán của bài tập 17 kết hợp với dữ liệu dưới đây để
xác định nhiệt đốt cháy chuẩn của một mole 2-propanol CH3CH(OH)CH 3(l)
CH3CH=CH2(g) + H2O(l) → CH3CH(OH)CH3(l)ΔHo = –52,3 kJ
23 (EX7-10A) The standard enthalpy of formation for the amino acid leucine is –637,3
kJ/mol C6H13O2N(s). Write the chemical equation to which this value applie
Nhiệt hình thành chuẩn của amino acid leucine là –637,3 kJ/mol C6H13O2N(s).
Hãy viết phương trình hóa học tương ứng với giá trị này.
23 (EX7-10B) How is ΔHo for the following reaction related to the standard enthalpy of
formation of NH3(g) listed in Appendix? What is the value of ΔHo = ?
Giá trị ΔHo của phản ứng dưới đây liên hệ như thế nào với nhiệt hình thành chuẩn của
NH3(g) trong bảng phụ lục? Giá trị của ΔHo là bao nhiêu? 2NH3(g) → N2(g) + 3 H2(g)
23 (EX7-11A) Use data from Appendix to calculate the standard enthalpy of combustion of
ethanol, CH3CH2OH(l), at 298.15 K.
Sử dụng dữ liệu trong bảng phụ lục để tính nhiệt đốt cháy chuẩn của
ethanol, CH3CH2OH(l), tại 298,15 K. 3 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
23 (EX7-11B) Calculate the standard enthalpy of combustion at 298.15 K per mole of a
gaseous fuel that contains C3H8 and C4H10 in the mole fractions 0.62 and 0.38, respectively.
Hãy tính nhiệt đốt cháy chuẩn tại 298,15 K cho 1 mol của một nhiên liệu khí
chứa C3H8 và C4H10 với tỷ lệ phân mol tương ứng là 0,62 va 0,38.
23 (EX7-12A) The overall reaction that occurs in photosynthesis in plants is:
6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) → C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) ΔHo = 2803 kJ
Use this value and the standard enthalpy of formation of CO2(g) and water(l)
from Appendix to determine the standard enthalpy of formation of glucose, C6H12O6(s) at 298 K
Phản ứng chung xảy ra trong quá trình quang hợp của thực vật là:
6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l) → C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) ΔHo = 2803 kJ
Hãy sử dụng dữ liệu này và tra cứu thêm các dữ liệu nhiệt hình thành mol
chuẩn của CO2(g) và H2O(l) cần thiết trong bảng phụ lục để xác định nhiệt
hình thành chuẩn của glucose, C6H12O6(s) tại 298 K.
23 (EX7-12B) A handbook lists the standard enthalpy of combustion of gaseous dimethyl
ether at 298 K as –31,70 kJ/g(CH3)2O (g). What is the standard molar enthalpy of
formation of dimethyl ether at 298 K? Use this value and the standard enthalpy of
formation of CO2(g) and water (l) from Appendix.
Một handbook liệt kê nhiệt đốt cháy chuẩn của dimethyl ether tại 298 K là –
31,70 kJ/g(CH3)2O (g). Hãy sử dụng dữ liệu này và tra cứu thêm các dữ liệu
nhiệt hình thành mol chuẩn của CO2(g) và H2O(l) cần thiết trong appendix
để xác định nhiệt hình thành mol chuẩn của khí dimethyl ether tại 298 K.
23 (E9) A 74.8 g sample of copper at 143,2 oC is added to an insulated vessel containing
165 mLof glycerol, (C3H8O3, d=1,26 g/mL), at 24,8 oC. The final temperature is 31,1 oC.
The specific heat of copper is 0,385 J.g−1.oC−1. What is the heat capacity of glycerol in J.g−1.oC−1?
Một mẫu đồng có khối lượng 74,8 g ở nhiệt độ 143,2 oC được cho vào bình cách
nhiệt có chứa sẵn 165 mL glycerol (C3H8O3, d=1,26 g/mL) tại nhiệt độ 24,8 oC.
Nhiệt độ cuối cùng thu được là 31,1 oC. Biết nhiệt dung riêng của đồng là 0,385
J.g−1.oC−1. Hỏi nhiệt dung của glycerol tính theo đơn vị J.g−1.oC−1 là bao nhiêu?
23 (E22) The heat of solution of KI(s) in water is 20,3 kJ/mol KI. If a quantity of
KI is added to sufficient water at 23,5 oC in a Styrofoam cup to produce
150.0 mLof 2.50 M KI, what will be the final temperature? (Assume a density
of 1.30 g/mL and a specific heat of 2,7 J.g−1.oC−1 for 2.50 M KI.)
Nhiệt hòa tan KI rắn trong nước là 20,3 kJ/mol KI. Nếu một lượng KI cho vào lượng
nước vừa đủ ở 23,5 oC trong cốc Styrofoam để tạo thành 150,0 mL dung dịch KI
có nồng độ 2,5 M. Tính nhiệt độ sau cùng của hệ biết rằng dung dịch có d= 1,30
g/mL và nhiệt dung riêng của dung dịch KI 2,5 M là 2,7 J.g−1.oC−1. 4 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
23 (E26) The heat of neutralization of HCl(aq) by NaOH(aq) is 55,84 kJ/mol H2O produced.
If 50,00 mL of 1.05 M NaOH is added to 25.00 mLof 1.86 M HCl, with both solutions
originally at 24.72 oC what will be the final solution temperature? (Assume that no heat
is lost to the surrounding air and that the solution produced in the neutralization
reaction has a density of 1.02 g/mL and a specific heat of 3.98 Jg−1oC−1)
Nhiệt trung hòa của dung dịch HCl và NaOH là 55,84 kJ/mol H2O tạo thành.
Nếu cho 50,00 mL dung dịch NaOH nồng độ 1,05 M vào 25,00 mL dung dịch
HCl nồng độ 1,86 M có cùng nhiệt độ là 24,72 oC, thì nhiệt độ sau cùng của
hệ là bao nhiêu? Xem rằng không có sự thất thoát nhiệt ra bên ngoài và
dung dịch sau trung hòa có d= 1,02 g/mL và nhiệt dung riêng là 3,98 J.g−1.oC−1.
28. (E33) The enthalpy of sublimation for dry ice (i.e., CO2) is ΔHo= 571 kJ/kg at
−78,5 oC and 1 atm. If 125.0 J of heat is transferred to a block of dry ice that
is −78,5 oC, what volume of CO2 gas (d = 1.98 g/L) will∆ be generated?
Nhiệt thăng hoa của đá khô CO2 = 571 kJ/kg ở nhiệt độ −78,5 oC và 1 atm.
Nếu truyền một lượng nhiệt 125,0 J vào đá khô ở −78,5 oC, lượng thể tích
khí CO2 tạo thành là bao nhiêu? (d = 1,98 g/L).
23 (E46) We can determine the purity of solid materials by using calorimetry. A gold ring
(for pure gold, specific heat = 0.1291 J.g−1.K−1) with mass of 10.5 g is heated to 78,3 °C
and immersed in 50.0 g of 23,7 °C water in a constant-pressure calorimeter. The final
temperature of the water is 31,0 °C. Is this a pure sample of gold?
Phương pháp lượng nhiệt kế có thể sử dụng để xác định độ tinh khiết của kim loại. Một
nhẫn vàng (vàng nguyên chất, nhiệt dung riêng là 0,1291 J.g−1.K−1) có khối lượng 10,5
g được gia nhiệt đến 78,3 °C và cho vào 50,0 g nước ở 23,7 °C trong nhiệt lượng kế
đẳng áp. Nhiệt độ cuối cùng của nước là 31,0 °C. Đây có phải là vàng nguyên chất.
23 (E51) In each of the following processes, is any work done when the reaction is carried out
at constant pressure in a vessel open to the atmosphere? If so, is work done by the
reacting system or on it? (a) Neutralization of Ba(OH)2 by HCl(aq); (b) conversion of
gaseous nitrogen dioxide to gaseous dinitrogen tetroxide; (c) decomposition of calcium
carbonate to calcium oxide and carbon dioxide gas.
Hãy xác định quá trình nào sau đây sinh công, nhận công hay công bằng
không ở điều kiện áp suất không đổi và hệ thống mở (a) Sự trung hòa dung
dịch Ba(OH)2 bằng dung dịch acid HCl; (b) khí NO2 chuyển thành khí N2O4;
(c) phân huỷ của canxi cacbonat thành oxit canxi và khí carbonic.
23 (E137) Write the balanced chemical equations for reactions that have the following as
their standard enthalpy changes.
Hãy viết∆ các phương trình phản ứng hóa học tương ứng cho các nhiệt
tiêu chuẩn sau a. ∆ = 82,05 kJ/mol N2O (k)
b. ∆ = −394,1 kJ/mol SO2Cl2 (l) c.
= −1527 kJ/mol CH3CH2COOH (l) 5 lOMoARcPSD|46958826 ∆ NH = −292.3 kJ
3 (k) + O2 (k)→ NO (k) + H2O (l) ∆
32. (E70) Given the following information:
H2 (k) + O2 (k)→H2O (l) = −285.8 kJ
N2 (k) + H2 (k)→ NH3(k) = −46.2 kJ Hãy xác ∆ ∆ ∆ 2 2 → reaction: N
(k) + O (k) →2 NO (k), expressed in Determine ∆ for the following ∆ 2 2 term of ∆H, and . định
của phản ứng sau: N (k) + O (k) 2 NO (k)
23 (E77) One glucose molecule, C6H12O6 (s) is converted to two lactic acid molecules,
CH3CH(OH)COOH (r) during glycolysis. Given the combustion reactions of
glucose and lactic acid, determine the standard enthalpy for glycolysis.
Trong quá trình lên men, một phân tử glucose, C6H12O6 (r) sẽ chuyển hóa thành hai phân tử
acid lactic, CH3CH(OH)COOH (r). Cho biết nhiệt phản ứng đốt cháy của glucose và
acid lactic, hãy xác định enthalpy tiêu chuẩn của quá trình chuyển hóa trên. ∆
C6H12O6 (r) + 6 O2 (k) → 6 CO2 (k) + 6 H2O (l) = 2808 kJ + 3 H O (l) =
CH3CH(OH)COOH (r) + 3 O2 (k) → 3 CO2 (k) ∆ 2 1344 kJ
23 (E81) Use the information given here, data from Appendix D, and equation (7.21) to
calculate the standard enthalpy of formation per mole of ZnS(s).
Tra cứu bảng số liệu nhiệt tạo thành tiêu chuẩn, hãy tính nhiệt tạo thành
mol∆ tiêu chuẩn của ZnS rắn theo phản ứng sau: 2 ZnS (r) + 3 O2 (k) →2
ZnO (r) + 2 SO2 (k) = 878,2 kJ
23 (E91) The decomposition of limestone, CaCO3 (s), into quicklime, CaO(s), and CO2 (g) is
carried out in a gas-fired kiln. Use data from Appendix D to determine how much heat is
required to decompose 1,35×103 kg CaCO3(s). (Assume that heats of reaction are the same as at and 1 bar.)
Nhiệt phân CaCO3 (r) cho ra CaO (r) và CO2 (k). Từ bảng số liệu nhiệt tạo
thành tiêu chuẩn, hãy tính cần cung cấp bao nhiêu nhiệt lượng để nhiệt
phân 1,35×103 kg CaCO3 rắn ở điều kiện chuẩn.
23 (E95) A British thermal unit (Btu) is defined as the quantity of heat required to change
the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1 oF. Assume the specific heat of water to be
independent of temperature. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of
the water in a 40 gal water heater from 48 to 145 °F in (a) Btu; (b) kcal; (c) kJ?
Btu hay BTU (viết tắt của British thermal unit, tức là đơn vị nhiệt Anh) là một đơn vị năng
lượng được định nghĩa là lượng nhiệt cần thiết để thay đổi nhiệt độ của 1 lb (pound) nước
là 1 oF. Xem nhiệt dung riêng không phụ thuộc vào nhiệt độ, hãy cho biết nhiệt lượng cần
thiết để tăng nhiệt độ 40 gallon nước từ 48 đến 145 °F theo đơn vị (a) Btu, (b) kcal và (c) kJ. 0
(E130) The temperature increase of 225 mLof water at 25 oC contained in a Styrofoam
cup is noted when a 125 g ample of a metal at 75 oC is added. With reference to 6 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
Appendix, the greatest temperature increase will be noted if the metal is (a)
lead; (b) aluminum; (c) iron; (d) copper.
Cho một mẫu kim loại có khối lượng là 125 g ở 75 oC vào 225 mL nước ở 25 oC
trong cốc Styrofoam. Dựa vào bảng số liệu nhiệt dung riêng của một số chất, hãy
cho biết nhiệt độ hệ sẽ tăng cao nhất khi là kim loại nào: chì, nhôm, sắt hay đồng?
(E101) A particular natural gas consists, in mole percents, of 83.0% CH4, 11.2% C2H6 and 5.8%
C3H8. A 385 L sample of this gas, measured at 22.6 oC and 739 mmHg, is burned at
constant pressure in an excess of oxygen gas. How much heat, in kilojoules, is evolved
in the combustion reaction?
Một hỗn hợp khí gồm 83,0 % CH4, 11,2% C2H6 và 5,8 % C3H8 theo số mol. Một thể tích 385 L
hỗn hợp khí có nhiệt độ 22,6 oC và áp suất là 739 mmHg được đốt cháy với oxy dư ở điều
kiện đẳng áp. Vậy có bao nhiêu nhiệt (kJ) tỏa ra khi đốt lượng hỗn hợp khí trên?
0 (E104) A calorimeter that measures an exothermic heat of reaction by the
quantity of ice that can be melted is called an ice calorimeter. Now consider
that 0.100 L of ∆Hpressure in air. The heat
liberated is captured and used to melt 9.53 g ice at 0 oC (of ice is 6,01
methanegas,atand744mmHgisburnedatconstant kJ/mol).
Write an equation for the complete combustion of and show that
combustion is incomplete in this case.
Khí metan có thể tích 0,1 L tại 25 oC và 744 mmHg được đốt cháy ở áp suất không đổi trong
∆không khí. Lượng nhiệt giải phóng được sử dụng để làm nóng chảy 9,53 g băng ở
0 oC ( ó ả của băng là 6,01 kJ/mol). Vậy quá trình đốt cháy CH4 trong trường
hợp này là hoàn toàn hay không? Viết phương trình phản ứng thích hợp
của phản ứng đốt cháy khí metan ở điều kiện trên.
23 (E138) The standard molar heats of combustion of C(graphite) and CO(g) are −393.5
and −283.0 kJ/mol respec vely.∆HUse those data and that for the following reac on
CO (k) + Cl2 (k) → COCl2 (k) có= −108 kJ to calculate the standard molar enthalpy of formation of COCl2(g).
Nhiệt đốt cháy mol tiêu chuẩn của carbon graphite là −393,5 kJ/mol và của khí carbon
monoxide là −283,0 kJ/mol. Hãy tính nhiệt tạo thành∆mol tiêu chuẩn của khí phosgene
(COCl2), biết phản ứng: CO (k) + Cl2 (k) → COCl2 (k) có = −108 kJ
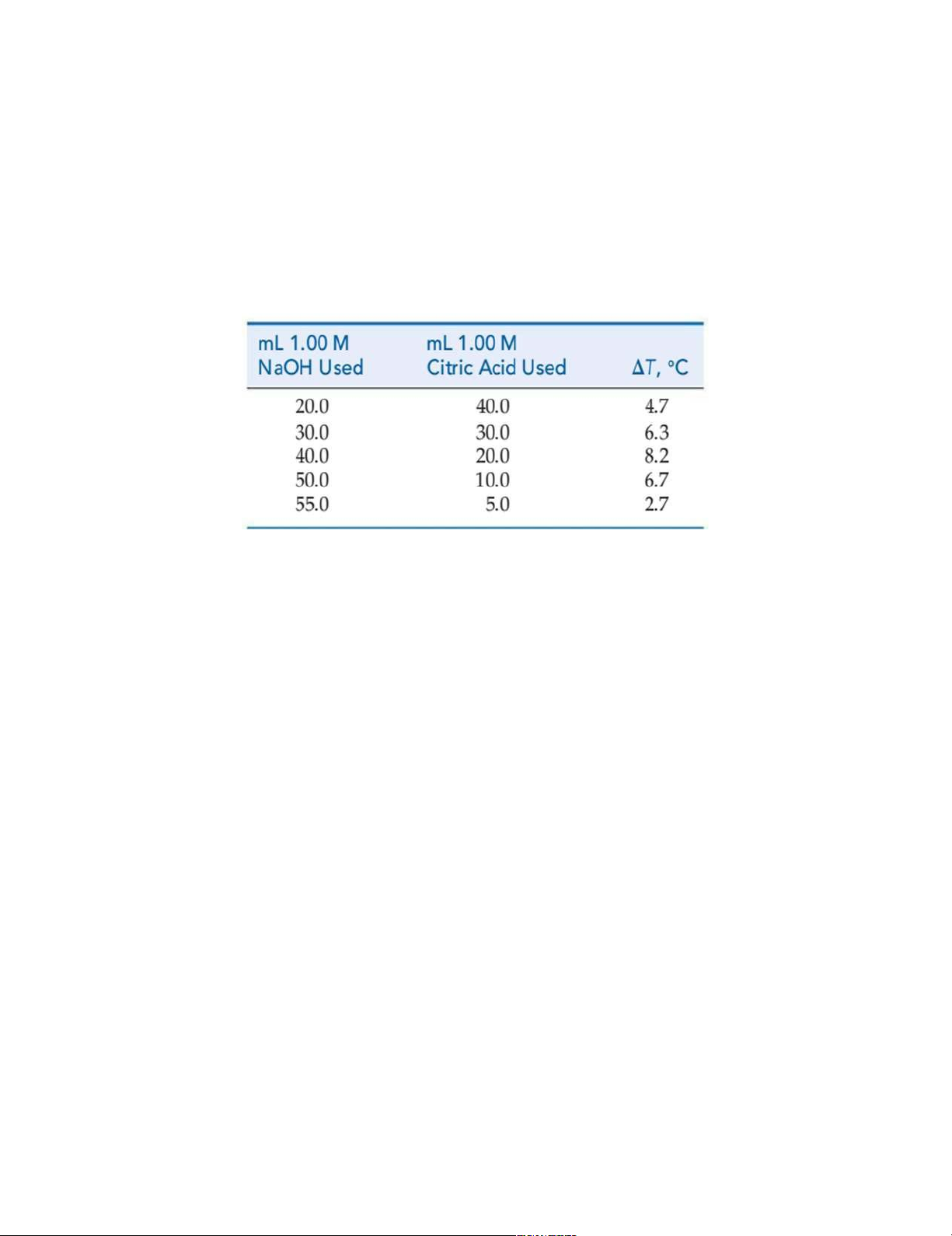
23 (E122) We can use the heat liberated by a neutralization reaction as a
means of establishing the stoichiometry of the reaction. The data in the
appendix are for the reaction of 1.00 M NaOH with 1.00 M citric acid,
C6H8O7, in a total solution volume of 60.0 mL.
23 Why is the temperature change in the neutralization greatest when the
reactants are in their exact stoichiometric proportions? That is, why not
use an excess of one of the reactants to ensure that the neutralization
has gone to completion to achieve the maximum temperature increase. 7 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
23 Rewrite the formula of citric acid to reflect more precisely its acidic properties.
Then write a balanced net ionic equation for the neutralization reaction.
Phản ứng trung hòa giữa các lượng thể tích khác nhau của NaOH nồng độ 1,00
M với acid citric C6H8O7 nồng độ 1,00 M được ghi nhận ở bảng bên dưới.
23 Tại sao nhiệt độ của phản ứng thay đổi nhiều nhất khi phản ứng trung
hòa xảy ra hoàn toàn.
24 Hãy viết công thức cấu tạo thể hiện tính acid của acid citric. Từ đó viết
phương trình phản ứng trung hòa trên. 8
CHAPTER 2. THERMODYNAMIC CHEMISTRY: ENTROPY–GIBBS ENERGY / CHƯƠNG 2.
NHIỆT ĐỘNG HỌC: ENTROPY – NĂNG LƯỢNG TỰ DO 23 (EX 19.1)
A. Predict whether entropy increases or decreases in each of the following reactions.
(a) The Claus process for removing H2S from natural gas: 2 H2S (g) + SO2(g) → 3 S(s) + 2 H2O(g)
(b) the decomposition of mercury(II) oxide: 2 HgO (s) → 2 Hg(l) + O2(k)
B. Predict whether entropy increases or decreases or whether the outcome
is uncertain ineach of the following reactions.
23 Zn(s) + Ag2O(s) → ZnO(s) + 2 Ag(s)
24 the chlor-alkali process, 2 Cl–(aq) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 OH–(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
Dự đoán entropy tăng, giảm hay không thể dự đoán (kèm giải thích) cho các phản ứng sau:
a. 2 H2S (k) + SO2(k) → 3 S(r) + 2 H2O(k)
b. 2 HgO(r) → 2 Hg(l) + O2(k)
c. Zn(r) + Ag2O(r) → ZnO(r) + 2 Ag(r)
d. 2 Cl–(dd) + 2 H2O(l) → 2 OH–(dd) + Cl2(k) + H2(k)
5888 (EX 19.2) A. What is the standard molar entropy of vaporization, for a
chlorofluorocarbon that once was heavily used in refrigeration systems? Its
normal boiling point is −29,79 oC and ∆H°vap = 20.2 kJ.mol–1.
Hãy tính entropy mol chuẩn ∆Sovap cho quá trình bay hơi của CCl2F2, cho biết
nhiệt độ sôi của CCl2F2 là −29,79 oC và nhiệt hóa hơi ∆Hovap = 20,2 kJ.mol−1.
23 (EX 19.2) B. The entropy change for the transition from solid rhombic sulfur to solid
monoclinic sulfur at What is the standard molar enthalpy change, ∆Hotr, for this transition
Sự thay đổi entropy mol chuẩn cho quá trình chuyển trạng thái thù hình từ rhombic
sulfur rắn sang monoclinic sulfur rắn ở 95,5 oC là ∆Sotr = 1,09 J.mol−1K−1. Hãy tính
enthalpy mol chuẩn ∆Hotr cho quá trình chuyển trạng thái trên.
23 (EX 19.3) A. Use data from Appendix D to calculate the standard molar entropy change
for the synthesis of ammonia from its elements. N2(k) + 3 H2(k) → 2 NH3(k) ∆So298K = ?
Sử dụng các số liệu entropy mol chuẩn của các chất (tra cứu trong Handbook) để tính
biến thiên entropy mol chuẩn cho phản ứng tổng hợp ammonia ở 25 oC: N2(k) + 3 H2(k) → 2 NH3(k)
23 (EX 19.3) B. N2O3 is an unstable oxide that readily decomposes. The decomposition of
1.00 mol of to nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide at is accompanied by the
entropy change ∆S° = 138.5 J K-1. What is the standard molar entropy of at 25 °C?
N2O3 là một oxid không bền, dễ bị phân hủy theo phương trình phản ứng sau:
N2O3(k) → NO(k) + NO2(k)có ∆So298K = 138,5 J.K−1 Hãy
tính entropy mol tiêu chuẩn của N2O3(k) ở 25 oC. 9 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
23 (EX 19.4) A. Which of the four cases in Table 19.1would apply to each of the following reactions:
(a) N2(g) + 3 H2(g) → 2 NH3(g) ∆Ho298K = −92,22 kJ
(b) 2 C(graphite) + 2 H2(g) → C2H4(g) ∆Ho298K = 52,26 Kj
Dự đoán các phản ứng sau có xảy ra tự nhiên ở nhiệt độ thường hay không?
23 N2(k) + 3 H2(k) → 2 NH3(k) ∆Ho298K = −92,22 kJ
b. 2 C(graphite) + 2 H2(k) → C2H4(k) ∆Ho298K = 52,26 kJ
5888 (EX 19.4) B. Under what temperature conditions would the following
reactions occur spontaneously? (a) The decomposition of calcium
carbonate into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. (b) The roasting of zinc
sulfide in oxygen to form zinc oxide and sulfur dioxide. This exothermic
reaction releases 439.1 kJ for every mole of zinc sulfide that reacts. 5888
điều kiện nhiệt độ nào để các phản ứng sau xảy ra tự nhiên?
23 CaCO3(r) → CaO(r) +CO2(k)
b. ZnS(r) + 3/2 O2(k) → ZnO(r) + SO2(k) ∆Ho298K = −439,1 kJ
8. (EX 19.5) A. Determine ∆Go at 298.15 K for the reaction 4 Fe(r) + 3 O2(k) → 2 Fe2O3(r)
∆Ho298K = −1648 kJ and ∆So298K = −549,3 J K−1
Tính ∆Go ở 298 K cho phản ứng sau: 4 Fe(r) + 3 O2(k) → 2 Fe2O3(r) ∆Go298K = ?
Cho biết ∆Ho298K = −1648 kJ và ∆So298K = −549,3 J K−1
5888 (EX 19.5) B. Determine for the reaction in Example 19–5 by using data
from Appendix D. Compare the two results.
Tính ∆Go ở 298 K cho phản ứng sau bằng cách sử dụng năng lượng tự do mol
chuẩn của các chất (tra trong Handbook) 2 NO (k) + O2 (k) → 2 NO2 (k)∆Go298K = ? 0 (EX 19.7)
0 Use the data in Appendix D to decide whether the following reaction is
spontaneous under standard conditions at 298.15 K. N2O4(g) → 2 NO2(g)
1 If a gaseous mixture of and both at a pressure of 0.5 bar, is introduced into a
previously evacuated vessel, which of the two gases will spontaneously convert into the other at 298.15 K.
a. Sử dụng các số liệu nhiệt động cần thiết của các chất (tra cứu trong
Handbook), cho biết phản ứng sau có xảy ra tự nhiên ở nhiệt độ 298K
không? N2O4(k) → 2 NO2(k)
0 Nếu ban đầu trong bình có hỗn hợp hai khí N2O4 và NO2 với áp suất mỗi khí
là 0,5 bar thì phản ứng trên sẽ xảy ra tự nhiên theo chiều nào? Giải thích.
ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀȀĀĀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀԀ0 (EX 19.8) A. Determine
the equilibrium constant at 298.15 K for AgI(s)Ag+(aq) +
I−(aq) Compare your answer to the for AgI in Appendix D.
Sử dụng các số liệu nhiệt động cần thiết của các chất (tra cứu trong Handbook)
tính hằng số cân bằng cho quá trình sau ở 298K: AgI(r) Ag+(dd) + I−(dd)
So sánh với trị số Ksp của AgI tra trong bảng. 10 lOMoARcPSD|46958826 0
(EX 19.8) B. At 298.15 K, should manganese dioxide react to an appreciable extent with
1 M HCl(aq), producing manganese(II) ion in solution and chlorine gas?
Tại 25 oC, mangan dioxit có phản ứng với một mức độ đáng kể với dung dịch
HCl 1 M để tạo ra ion mangan (II) trong dung dịch và khí chlorine không? 0
(EX 19.9) A. At what temperature will the formation of NOCl (g) from NO(g) and Cl2(g)
have Kp = 1.50×102? For the reaction 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) 2 NOCl(g) at 25 oC, ∆Ho =
−114,1 kJ.mol−1 và ∆So = −146,5 J.mol−1.K−1.
Tại 25 oC phản ứng: 2 NO(k) + Cl2(k) 2 NOCl (k) có ∆Ho = −114,1 kJ.mol−1 và
∆So = −146,5 J.mol−1.K−1. Hãy xác định nhiệt độ mà tại đó cân bằng trên có Kp = 1,5×102
14. (EX 19.9) B. For the reaction 2 NO(g) + Cl2(g) 2 NOCl(g), what is the value of
K at (a) 25 oC (b) 75 oC Use data from Example 19–9. [Hint: The solution to
part (a)can be done somewhat more simply than that for (b)].
Xét cân bằng sau ở 25 oC: 2 NO(k) + Cl2(k) 2 NOCl(k) có ∆Ho = −114,1
kJ.mol−1 và ∆So = −146,5 J.mol−1.K−1. Tính hằng số cân bằng KP cho phản
ứng trên ở 25 oC và ở 75 oC. (EX 19.10)
0 Estimate the temperature at which for the reaction in Example 19-10. Use
data from Appendix and Figure 19-12.
1 What is the value of for the reaction 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) 2 SO3(g) at 235 oC. Use data
from Appendix, Figure 19-12 and the van’t Hoff equation (19.15) Cho
phản ứng: 2 SO2(k) + O2(k) 2 SO 3(k)có ∆Ho = −1,8×102 kJ.mol−1
a. Tại 900K phản ứng trên có Kp = 42. Hãy xác định nhiệt độ mà tại đó phản ứng có Kp = 5,8×10−2
b.. Tính Kp cho phản ứng trên ở nhiệt độ 235 oC?
0 (E.2) Arrange the entropy changes of the following processes, all at 25 oC, in
the expected order of→increasing ∆S and explain your reasoning:
H2O (l, 1 atm) → H2O (k, 1 atm)
CO2 (s, 1 atm) → CO2 (k, 10 mmHg)
H2O (l, 1 atm) H2O (k, 10 mmHg)
Sắp xếp sự biến đổi entropy (∆S) của các quá trình (tại 25 oC) sau đây theo thứ tự tăng dần:
a. H2O (l, 1 atm) → H2O (k, 1 atm)
b. CO2 (s, 1 atm) → CO2 (k, 10 mmHg)
c. H O (l, 1 atm) →H O (k, 10 mmHg) 0
(E.10) Pentane is one of the most volatile of the hydrocarbons∆ in gasoline. At 298.15 K,
the∆ following enthalpies of formation are given for pentaneC5H12 (l): -173,5 kJ mol- 1;C5H12 (k) = –146,9 kJ22
(a) Estimate the normal boiling point of pentane.
(b) Estimate for the vaporization of pentane at∆298 K.
(c) Comment on the significance of the sign of at 298 K. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
(k) = –146,9 kJ mol–1. ∆ 5 12 ∆ 5 12
Pentane là một trong những hydrocarbon dễ bay hơi trong xăng. Tại 298.15 K, các giá trị
enthalpy tạo thành của pentane có giá trị sau:
C H (l) = –173,5 kJ mol–1; C H ∆ c. Rút ra nhận xét từ
a. Ước lượng nhiệt độ sôi của pentane.
b. Ước lượng giá trị cho quá trình hóa hơi của pentane tại 298 K. 18. giá trị
tại 298 K thu được. of the reaction N H (k) + 2 OF (k) N F (k) + 2 H O (k) by
(E.31) Assess the feasibility ∆ 2 4 2 2 4 2 25 oC →
determining each of the following quantities for this reaction at
(a) ∆So (The standard molar entropy of N2F4 (g) is 301.2 J K–1)
(b) ∆Ho (Use data from Appendix and F O and N F bond energies of 222 and respectively) (c) ∆G° →
Cho phản ứng: N2H4 (k) + 2 OF2 (k)
N2F4 (k) + 2 H2O (k). Xác định các giá trị sau và nhận
xét chiều phản ứng tại 25 oC.
a. ∆So (biết So298 N2F4 (k) = 301,2 J.K–1).
b. ∆Ho (sử dụng số liệu trong bảng phụ lục và năng lượng liên kết của F–O và N–F tương
ứng là 222 và 301 kJ mol–1. c. ∆Go.
19. (E.68) Following are some standard Gibbs energies of formation, per mole of metal
oxide at 1000 K: NiO –115 kJ; MnO, –280 kJ; TiO2, –630 kJ. The standard Gibbs energy
of formation of CO at 1000 K is –250 kJ per mol CO. Use the method of coupled
reactions (page 851) to determine which of these metal oxides can be reduced to the
metal by a spontaneous reaction with carbon at 1000 K and with all reactants and
Cho giá trị ∆ của các oxit kim loại tại 1000 K là: NiO, –115kJ; MnO, –280 kJ; TiO2, –630 kJ. Năng lượng tự do Gibb tạo thành của CO là –250 kJ/mol. Xác
định oxit kim loại nào sẽ bị khử bởi C tại 1000 K. (Các chất đều ở trạng thái chuẩn).
products in their standard states. 0
(E.68) Consider the vaporization of water: at with in its standard state, but with the
partial pressure of at 2.0 atm. Which of the following statements about this
vaporization at are true? (a) ∆Go = 0; (b)→∆G = 0; (c) ∆Go > 0; (d) ∆G > 0. Explain
Xem xét quá trình hóa hơi nước: H2O(l) H2O (k) tại 100 oC, với H2O(l) trong
trạng thái chuẩn, H2O (k) có áp suất riêng phần là 2,0 atm. Phát biểu nào
sau đây về quá trình trên là đúng? (a) ∆Go = 0; (b) ∆G = 0; (c) ∆Go > 0; (d) ∆G > 0. Giải thích. 0
(E.6) Which substance in each of the following pairs would have the greater
entropy? Explain. (a) at and 1 atm: 1 mol H2O (l) or 1 mol H2O (g) Ȁ Ā
⸀ ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀ ᜀ ĀȀ Ā
⸀ ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀ0 at and 1
atm: 50.0 g Fe(s) or 0.80 mol Fe(s) Ȁ Ā
⸀ ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀ ᜀ ĀȀ Ā
⸀ ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀ1 1 mol Br2 (l,
1 atm, 8 oC) or 1 mol Br2 (s, 1 atm, –8 oC) Ȁ Ā
⸀ ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀ ᜀ ĀȀ Ā
⸀ ᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀᜀĀ2 0.312 mol
SO2 (g, 0.110 atm, 32.5 oC) or O2 0.284 mol (g, 15.0 atm, 22.3 oC)
So sánh giá trị entropy trong mỗi cặp chất sau: 12 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
Tại 75 oC và 1 atm: 1 mol H2O(l) và 1 mol H2O (k)
Tại 5 oC và 1 atm: 50,0 g Fe(r) và 0.80 mol Fe(r)
1 mol Br2 (l, 1 atm, 8 oC) và 1 mol Br2 (s, 1 atm, –8 oC)
0,312 mol SO2 (k, 0,110 atm, 32,5 oC) hay 0,284 mol O2 (k, 15,0 atm, 22,3 oC). 0
(E.8) By analogy to and how would you define entropy of formation? Which would
have the largest entropy of formation: CH4 (g), CH3CH2OH (l), or CS2(l)? First make a
qualitative prediction; then test your prediction with data from Appendix D.
Dự đoán chất nào trong các chất sau có entropy tạo thành lớn nhất: CH4 (k),
CH3CH2OH (l), hay CS2(l). Sau đó kiểm tra bằng các số liệu tra trong phụ lục D.
23. (E.36) →Calculate the equilibrium constant and Gibbs energy for the reaction CO (k) + 2
H2 (k) CH3OH (k) tại 483 K by using the data tables from Appendix D. Are the values
determined here different from or the same as those in exercise →35? Explain.
Tính năng lượng tự do Gibbs của phản ứng sau CO (k) + 2 H2 (k) CH3OH (k) tại 483 K.
(Tra các số liệu trong phụ lục D).
5888 (E.41) Use thermodynamic⇌ data at 298 K to decide in which direction the reaction 2
SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2 SO3 (g) is spontaneous when the partial pressures of SO2, O2 and
SO3 are 1,0×10–4, 0.20, and 0.10 atm, respectively.
Dùng các số liệu⇌ nhiệt động tại 298 K xác định chiều tự diễn ra của phản ứng sau: 2 SO2
(k) + O2 (k) 2 SO3 (k) tại áp suất riêng phần của SO2, O2 và SO3 lần lượt là 1,0×10–4; 0,20 và 0,10 atm. →
25. (E.55) Use data from Appendix D to establish at 298 K for the reaction: 2
NaHCO3(s) Na2CO3(s) + H2O(l) + CO2 (g)→(a) ∆So (b) ∆Ho (c) ∆Go (d) K.
Cho phản ứng: 2 NaHCO3(r) Na2CO3(r) + H2O(l) + CO2 (k). Tính các giá trị ∆So, ∆Ho, ∆Go, K. 0
(E.86) The decomposition⇌ of the poisonous gas phosgene is represented by the
equation COCl2 (k) CO (k) + Cl2. Values of for this reaction are Kp = 6.7×10–9 at 99.8 oC
and 4.44×10–2 at 395 oC. At what temperature is 15% dissociated when the total gas pressure is maintained at 1.00 atm?
Sự phân hủy của khí độc phosgene được minh họa qua phương trình: COCl2 (k) CO (k) –9 o –2 395 oC. Khi
+ Cl2 (k). Giá trị KP của phương trình là 6,7×10
tại 99,8 C và 4,44×10 tại ⇌
áp suất tổng được duy trì là 1 atm, xác định nhiệt độ tại đó 15% COCl2 bị phân hủy. a. Estimate ∆ ∆
27. (E.109) A handbook lists the following standard enthalpies of formation at 298 K for cyclopentane
C5H10 (l) = –105.9 kJ mol–1, and
C5H10 (k) = –77.2 kJ mol–1 c. Comment∆
the normal boiling point of cyclopentane. (k) = –77,2 kJ mol–1 Cho các số liệu
C5H10 (l) = –105,9 kJ mol–1; ∆ C5H10 b. Estimate
for the vaporization of cyclopentane at 298 K a. Ước lượng ∆ ∆
on the significance of the sign of at 298 K
nhiệt độ sôi của cyclopentane.
b. Ước lượng ∆Go cho quá trình hóa hơi của cyclopentane tại 298 K. 13 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
c. Nhận xét về dấu của ∆Go tại 298 K.⇌
28. (E.110) Consider the reaction: NH4NO3 (s)
N2O (g) + 2 H2O(l) at 298 K.
(a) Is the forward reaction endothermic or exothermic?
(b) What is the value of ∆Go at 298 K?
(c) What is the value of K at 298 K?
(d) Does the reaction tend to occur spontaneously at temperatures above 298 K, below 298 K, both, or neither
Xét phản ứng NH4NO3(r) ⇌ N2O (k) + 2 H2O(l) tại 298 K.
a. Phản ứng thuận thu nhiệt hay tỏa nhiệt?
b. Tính giá trị ∆Go tại 298 K. c. Tính K tại 298 K.
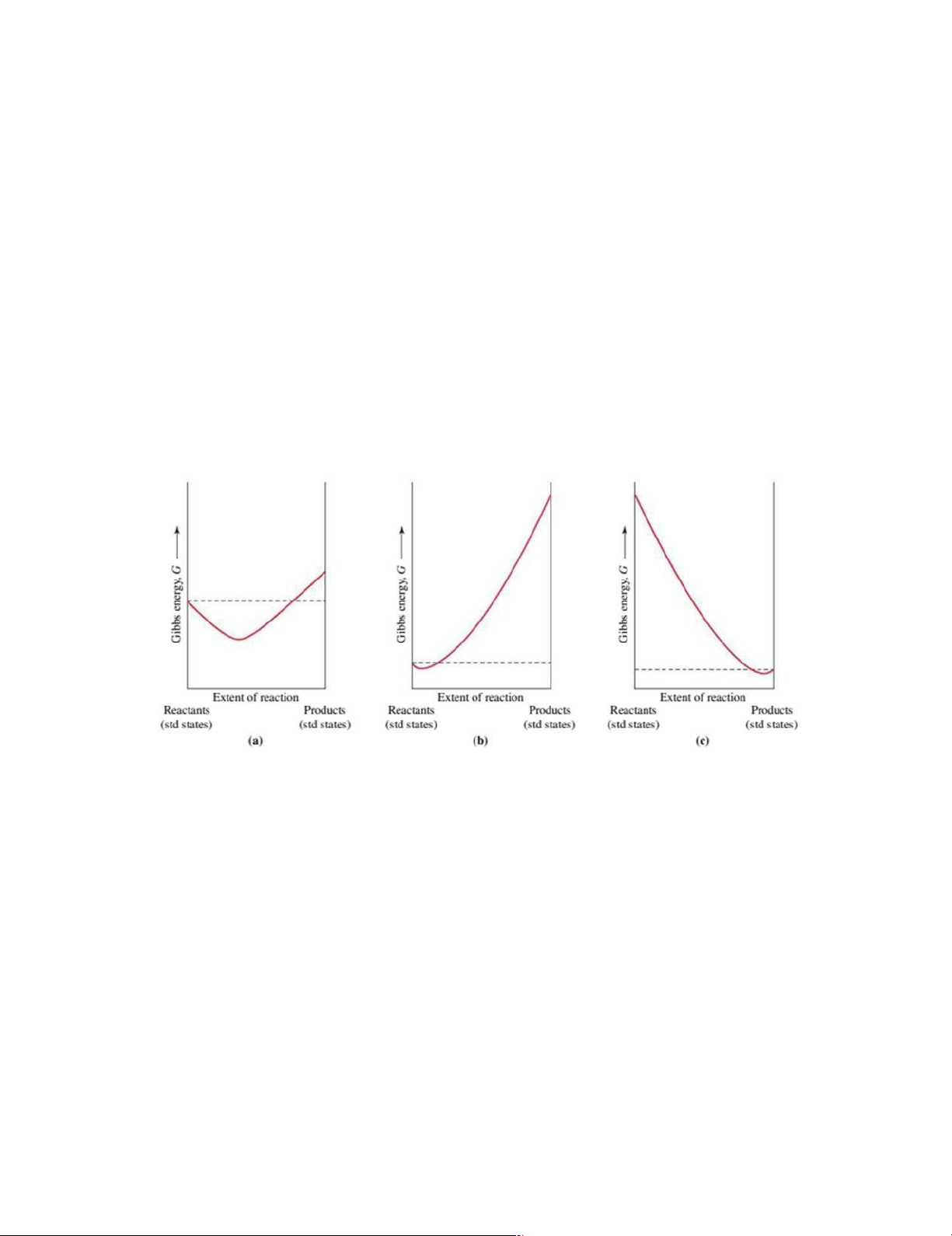
23 (E.111) Which of the following diagrams represents an equilibrium constant closest to 1?
Đồ thị nào trong các đồ thị sau minh họa hằng số cân bằng có giá trị gần 1?
(E.112) At room temperature and normal atmospheric pressure, is the entropy of the
universe positive, negative, or zero for the transition of carbon dioxide solid to liquid?
Tại nhiệt độ phòng và áp suất thường, entropy của vũ trụ âm, dương hay bằng không
cho sự chuyển pha của CO2 rắn thành lỏng? 4 lOMoARcPSD|46958826
CHAPTER 3. CHEMICAL KINETICS / Chương 3. ĐỘNG HÓA HỌC
0 (EX-14-1A) At some point in the reaction 2 A + B → C + D, [A] = 0.3629 M. At
a time 8.25 min later [A] = 0.3187. What is the average rate of reaction
during this time interval, expressed in M s–1?
Xét phản ứng 2 A + B C + D ở tại thời điểm [A] = 0,3629 M. Sau 8,25 phút [A] =
0,3187 M. Tính tốc độ trung bình của phản ứng (theo đơn vị M/s) trong khoản thời gian trên.
23 (EX–14-1B) In the reaction 2 A → 3 B, [A] drops from 0.5684 M to 0.5522 M in 2.50 min.
What is the average rate of formation of B during this time interval, expressed in M s–1?
Trong phản ứng 2 A → 3 B, [A] giảm từ 0,5684 M đến 0,5522 M trong 2,50 phút. Tính tốc
độ trung bình của sự hình thành B (theo đơn vị M/s) trong khoản thời gian trên.
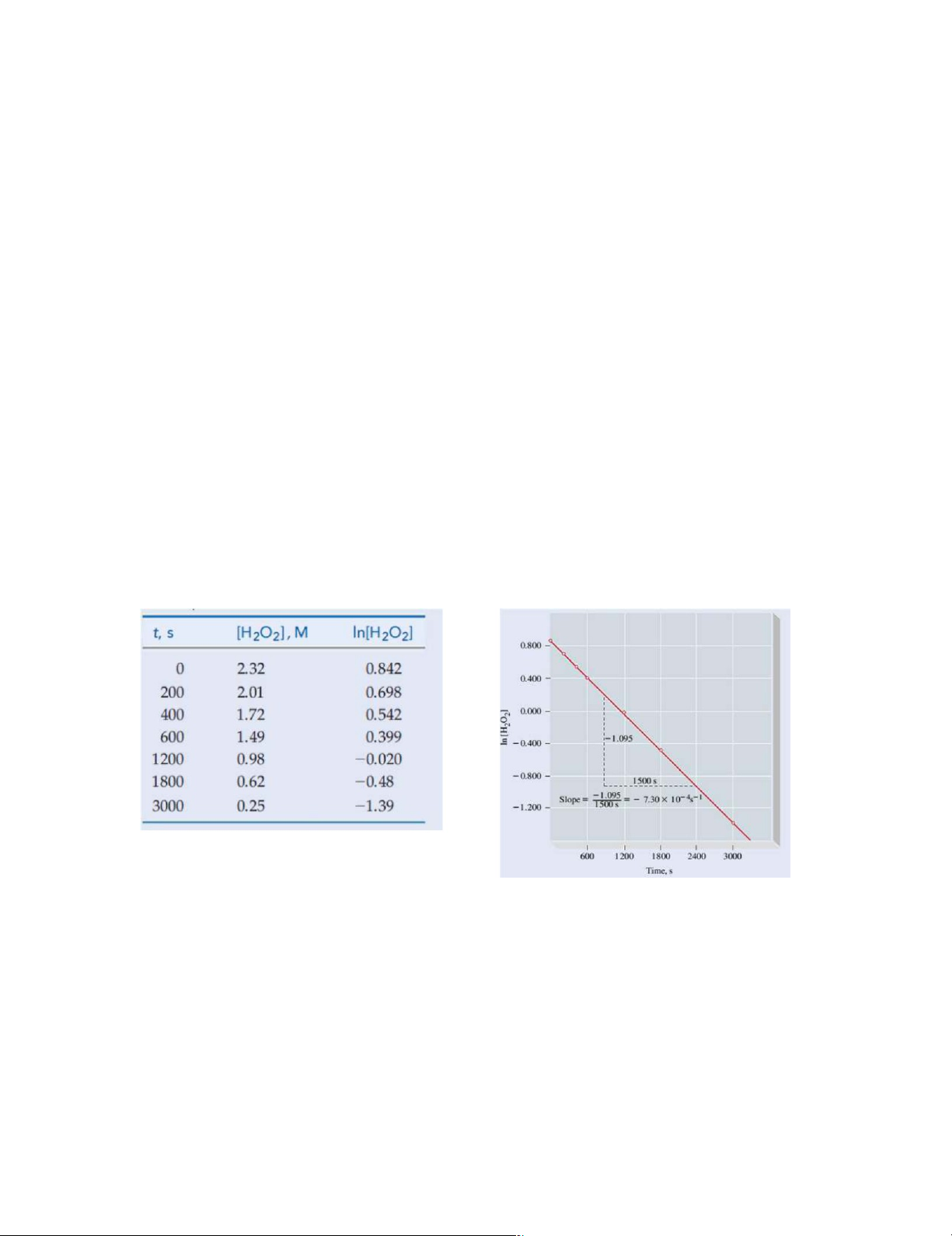
23 (EX-14-2A) For reaction H2O2(aq) → H2O(l) + ½ O2(g), determine (a) the instantaneous
rate of reaction at 2400 s and (b) [H2O2] at 2450 s. [Hint: Assume that the
instantaneous rate of reaction at 2400 s holds constant for the next 50 s.]
Xét phản ứng: H2O2(aq) → H2O(l) + ½ O2(g) và số liệu trong bảng bên dưới. Xác định:
23 Tốc độ tức thời của phản ứng ở 2400 s
24 Nồng độ [H2O2] ở 2450 s (Giả sử tốc độ tức thời của phản ứng ở 2400 s giữ không
đổi trong vòng 50 s kế tiếp). Time, s [H2O2], M 5888 2.32 2002.01 4001.72 6001.49 12000.98 18000.62 3000 0.25 0
(EX-14-2B) Use data only from the following table to determine [H2O2] at t = 100 s.
Compare this value with the one calculated in Example 14-2(b). Explain the reason for the difference?
Xét phản ứng phân hủy H2O2. Sử dụng bảng dữ liệu sau xác định [H2O2] ở t = 100 s. Time (s) t (s) [H2O2] (M)
[H2O2] (M) [H2O2]/ t (M s 1) 15 lOMoARcPSD|46958826 0 400 2.32 0.60 15.0 ×10 4 400 400 1.72 0.42 10.5 ×10 4 800 400 1.30 0.32 8.0 ×10 4 1200 400 0.98 0.25 6.3 ×10 4 1600 400 0.73 0.19 4.8 ×10 4 2000 400 0.54 0.15 3.8 ×10 4 2400 400 0.39 0.11 2.8×10 4 2800 400 0.28
23 (EX-14-3A) The decomposition of N2O5 is given by the following equation: 23
N2O5 → 4 NO2 + O2. At an initial [N2O5]0 = 3.15 M, the initial rate of reaction = 23
45×10–5 M s–1 and when [N2O5]0 = 0.78 M, the initial rate of reaction = 1.35×10–5 M s–
1. Determine the order of this decomposition reaction.
Xét phản ứng phân hủy N2O5 theo phương trình sau: 2 N2O5 → 4 NO2 + O2
Khi nồng độ đầu của [N2O5]0 = 3,15 M tốc độ đầu của phản ứng = 5,45×10–5
Ms–1 và khi [N2O5]0 = 0,78 M tốc độ đầu của phản ứng = 1,35×10–5 Ms–1. Xác
định bậc của phản ứng phân hủy này.
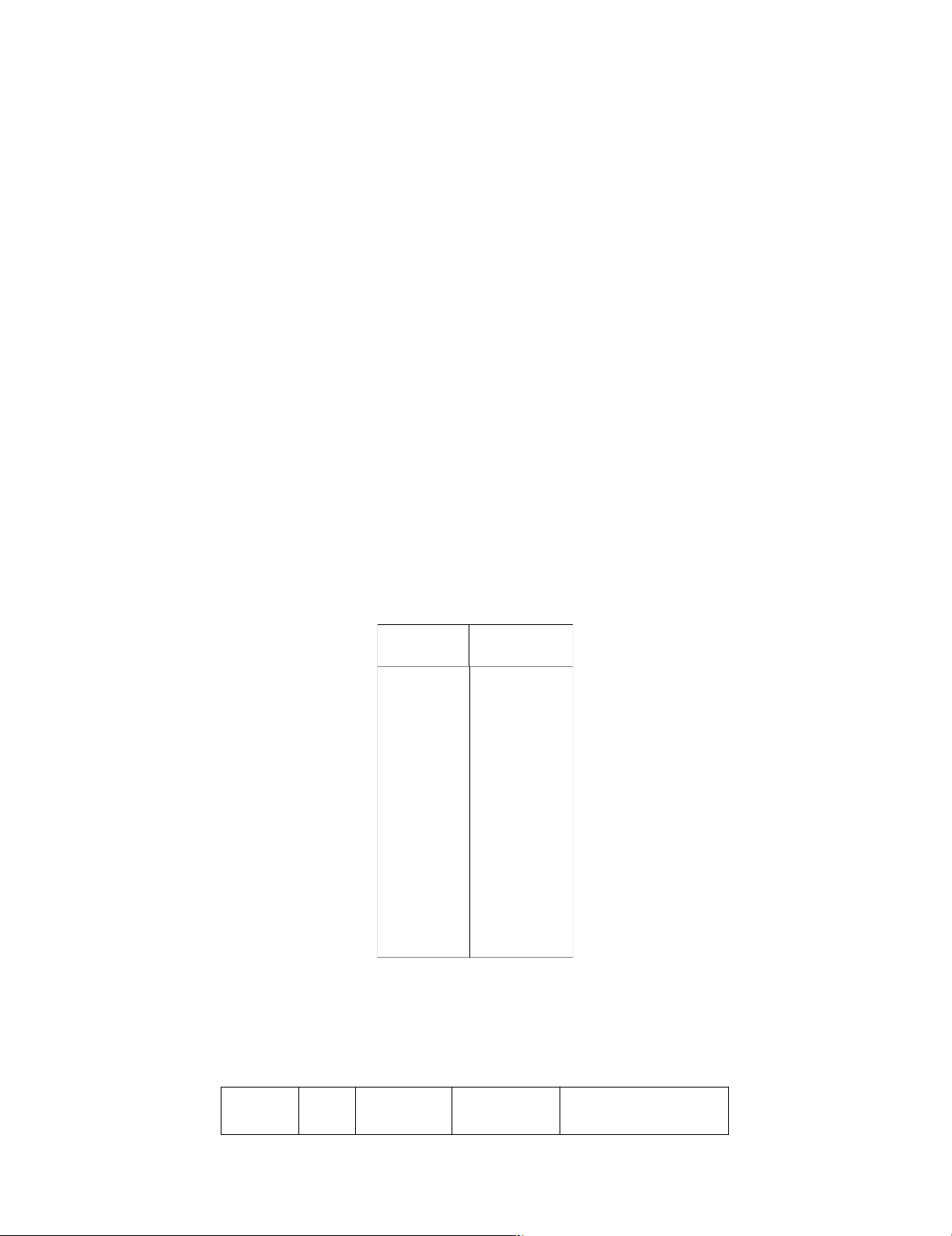
23 (EX-14-3B) Consider a hypothetical Experiment 4 in Table 14.3, in which the initial conditions are [HgCl 2–
2]0 = 0.025 M and [C2O4 ]0 = 0.045, v = k [HgCl2]2 [C 2–
2O4 ]2. Predict the initial rate of reaction.
Dự đoán tốc độ đầu của phản ứng: 2 HgCl 2–
2 + C2O4 2Cl– + 2CO2 + Hg 2–
2Cl2 Biết nồng độ đầu của [HgCl2]0 = 0,025 M và [C2O4 ]0 = 0,045.
23 (EX-14-4A) A reaction has the rate law: v = k [A]2[B]. When [A] = 1.12 M and [B] = 0.87
M and the rate of reaction = 4.78×10–2 M s–1. What is the value of the rate
constant, k? Một phản ứng có phương trình động học v = k [A]2[B]. Khi
nồng độ [A] = 1,12 M và [B] = 0,87 M, tốc độ của phản ứng = 4,78×10–2 Ms–1.
Xác định hằng số tốc độ k của phản ứng. lOMoARcPSD|46958826
23 (EX-14-4B) What is the rate of reaction 2 HgCl 2–
2 + C2O4 2 Cl– + 2 CO2 + Hg2Cl2, v = k [HgCl 2– 2–
2]2 [C2O4 ]2, at the point where [HgCl2] = 0.050 M and [C2O4 ]0 = 0.025 M. Phản ứng 2HgCl 2–
2 + C2O4 2Cl– + 2CO2 + Hg2Cl2. Có phương trình động học là: v = k [HgCl 2–
2]2 [C2O4 ]2. Xác định tốc độ của phản ứng khi [HgCl2] = 0,050 M và [C 2– 2O4 ]0 = 0,025 M.
5888 (EX-14-5A) The reaction A 2 B + C is first order. If the initial [A] = 2.80 M and k =
3.02×10–3 s–1, what is the value of [A] after 325 s?
Phản ứng A 2B + C là phản ứng bậc 1. Nếu nồng độ đầu của [A] = 2,80 M và k =
3,02×10–3 s–1. Xác định [A] sau 325 s.
10. (EX[-14]-=5B)−Use+ dataln[ ] in the following Figure and Table, together
with equation , to show that the decomposition of H2O2 is a first-order
reaction. [Hint: Use a pair of data points for H2O2 0 and H2O2 t and their
corresponding times to solve for k. Repeat this calculation using other sets
of data. How should the results compare?]
Chứng tỏ phản ứng phân hủy H2O2 là phản ứng bậc 1, H2O2 (aq) H2O (l) + ½
O2 (k). Sử dụng đồ thị và bảng dữ liệu động học sau.
5888 (EX-14-6A) Consider the first-order reaction A P with k = 2.95×10–3 s–1.
What percent of A remains after 150 s?
Xét phản ứng bậc 1: A
P với k = 2,95×10–3 s–1. Sau 150 s, % còn lại của A bao nhiêu? 0
(EX-14-6B) At what time after the start of the reaction is a sample of [H2O2] two–thirds decomposed?
Mất bao lâu để lượng mẫu [H2O2] bị phân hủy 2/3 so với thời điểm bắt đầu phản ứng.
Biết phản ứng phân hủy H2O2 tuân theo động học bậc 1. H2O2(aq) H2O(l) + 1/2O2(k)
0 (EX-14-7A) Di-t-butyl peroxide (DTBP) is used as a catalyst in the
manufacture of polymers. In the gaseous state, DTBP decomposes into
acetone and ethane by a first-order reaction. 17