

Preview text:
Seminar 6: Question By Le Thanh Ha
Type I: True/False question (give a brief explanation)
1. For a firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry, total revenue, marginal
revenue, and average revenue are all equal.
Một doanh nghiệp Cạnh tranh hoàn hảo có tổng doanh thu, doanh thu cận biên và
doanh thu trung bình bằng nhau.
2. In competitive markets, firms that raise their prices are typically rewarded with larger profits.
Trong thị trường cạnh tranh, doanh nghiệp tăng giá và thu được lợi nhuận lớn hơn.
3. A firm operating in a perfectly competitive industry will continue to operate in the
short run but earn losses if the market price is less than that firm’s average total cost
but greater than the firm’s average variable cost.
Một doanh nghiệp trên thị trường CTHH sẽ thua lỗ những vấn sản xuất nếu mức giá đặt bán
thấp hơn tổn chi phí bình quân nhưng lớn hơn chi phí biến đổi bình quân.
4. A firm will shut down in the short run if revenue is not sufficient to cover all of its fixed costs of production.
Doanh nghiệp sẽ đóng cửa nếu phần doanh thu không đủ bủ đắp chi phí cố định trong sản xuất.
5. Đường cầu của hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo nằm ngang, đây là một đường cầu hoàn toàn không co giãn.
6. Người bán trong thị trường cạnh tranh hoàn hảo là người thiết lập giá bán trên thị trường.
7. Vì có nhiều hãng trên thị trường cạnh tranh hoàn hảo nên không ai có thể tác động
gây ra sự thay đổi giá bán trên thị trường.
8. Doanh nghiệp cạnh tranh hoàn hảo sẽ tối đa hóa lợi nhuận nếu mức giá bán sản
phẩm bằng với chi phí cận biên sản xuất sản phẩm.
9. Đường cung của hãng CTHH là đường chi phí cận biên tại thời điểm mức giá bán
lớn hơn tổng chi phí bình quân (ATC) Type II: Discussion questions
1. List and describe the characteristics of a perfectly competitive market.
2. Why would a firm in a perfectly competitive market always choose to set its
price equal to the current market price? If a firm set its price below the current
market price, what effect would this have on the market?
Tại sao hãng CTHH thường chọn mức giá bằng với mức giá thị trường? Nếu doanh nghiệp
đặt giá thấp hơn giá thị trường thì điều gì xảy ra?
3. Use a graph to demonstrate the circumstances that would prevail in a
competitive market where firms are earning economic profits. Can this scenario
be maintained in the long run? Explain your answer.
4. Một hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo có hàm tổng chi phí , và hàm chi phí cận biên
MC = 2Q + 180. Mức giá sản phẩm đang bán trên thị trường là 1200.
a. Tìm mức giá và sản lượng mà doanh nghiệp đặt ra để tối đa hóa lợi nhuận và
tính mức lợi nhuận này.
b. Tìm mức giá và sản lượng mà doanh nghiệp hòa vốn.
c. Tìm mức giá và sản lượng mà doanh nghiệp sẽ đóng cửa sản xuất.
d. Thiết lập và mô tả đường cung của hãng cạnh tranh hoàn hảo. Type III: Multiple Choice
1. Đặc điểm nào sau đây không phải của thị trường cạnh tranh hoàn hảo?
a. Người bán là người chấp nhận giá
b. Mỗi hãng bán những sản phẩm đồng nhất.
c. Việc tự do gia nhập bị hạn chế.
d. Mỗi doanh nghiệp sẽ chọn mức sản lượng để tối đa hóa lợi nhuận.
2. Hành vi chấp nhận giá được mô tả là:
a. Nếu doanh nghiệp đặt giá cao hơn thì họ sẽ mất toàn bộ thị phần của mình
b. Doanh nghiệp có động cơ đặt giá thấp hơn và thu lợi.
c. Doanh nghiệp có thể bán một số lượng hạn chế sản lượng ở mức giá thị trường
trước khi giá thị trường giảm.
d. Hãng chấp nhận giá sẽ tối đa hóa lợi nhuận khi đặt giá cao hơn chi phí cận biên.
3. For a firm operating in a competitive industry, which of the following statements is not correct?
a. Price equals average revenue.
b. Price equals marginal revenue. c. Total revenue is constant.
d. Marginal revenue is constant.
4. If a competitive firm is currently producing a level of output at which marginal
revenue exceeds marginal cost, then
a. a one-unit increase in output will increase the firm's profit.
b. a one-unit decrease in output will increase the firm's profit.
c. total revenue exceeds total cost.
d. total cost exceeds total revenue.
5. Hung is a gourmet chef who runs a small catering business in a competitive
industry. Hung specializes in making wedding cakes. Hung sells 20 wedding cakes
per month. His monthly total revenue is $5,000. The marginal cost of making a
wedding cake is $200. In order to maximize profits, he should
a. make more than 20 wedding cakes per month.
b. make fewer than 20 wedding cakes per month.
c. continue to make 20 wedding cakes per month.
d. We do not have enough information with which to answer the question.
6. A competitive firm has been selling its output for $20 per unit and has been
maximizing its profit, which is positive. Then, the price rises to $25, and the firm
makes whatever adjustments are necessary to maximize its profit at the now-higher
price. Once the firm has adjusted, which of the following statements is correct?
a. The firm's quantity of output is higher than it was previously.
b. The firm's average total cost is higher than it was previously.
c. The firm's marginal revenue is higher than it was previously.
d. All of the above are correct.
7. When profit-maximizing firms in competitive markets are earning profits,
a. market demand must exceed market supply at the market equilibrium price.
b. market supply must exceed market demand at the market equilibrium price.
c. new firms will enter the market.
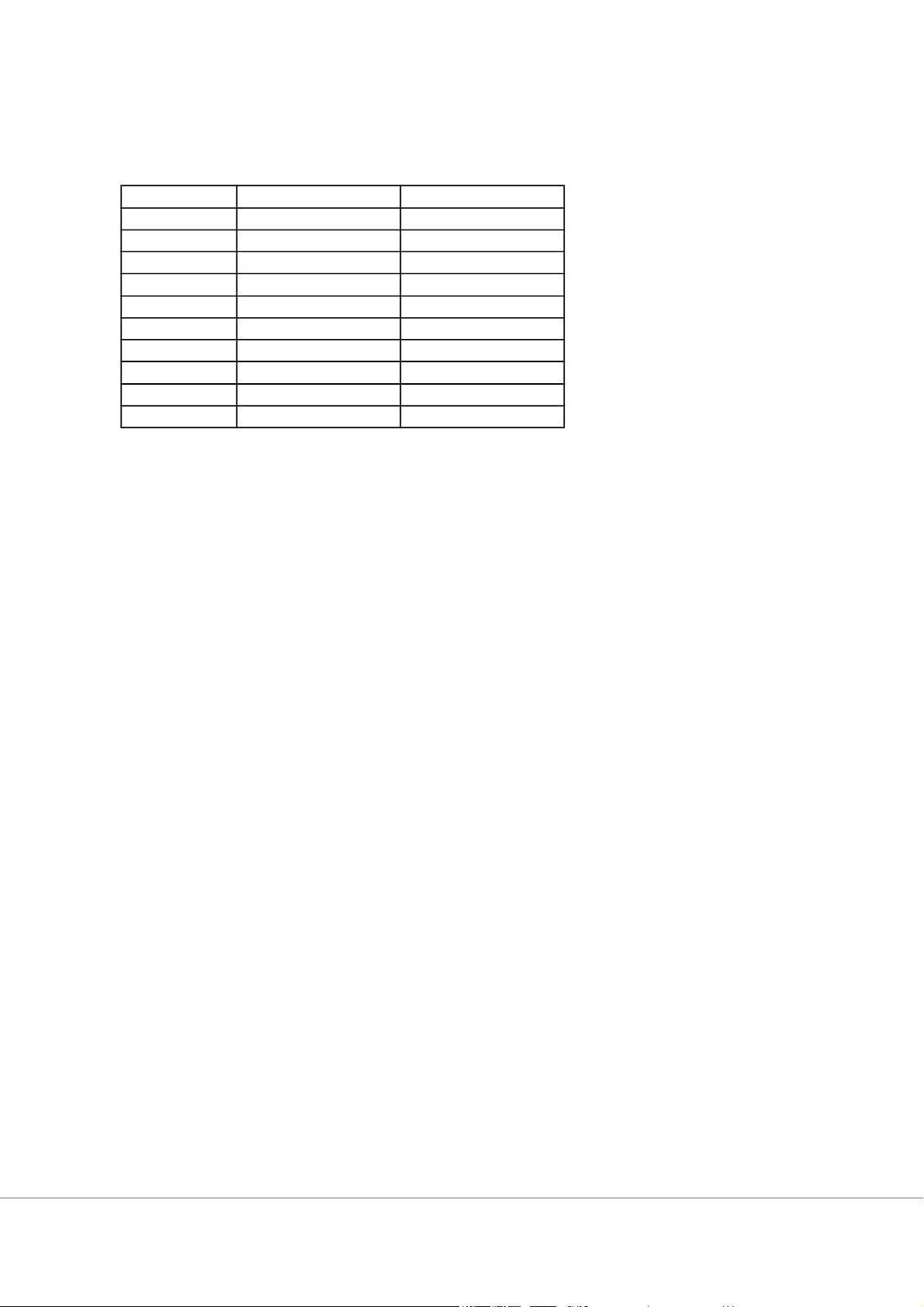
d. the most inefficient firms will be encouraged to leave the market. Table 6-1 Quantity Total Revenue Total Cost 0 $0 $10 1 $9 $14 2 $18 $19 3 $27 $25 4 $36 $32 5 $45 $40 6 $54 $49 7 $63 $59 8 $72 $70 9 $81 $82
8. Refer to Table 6-1. In order to maximize profit, the firm will produce a level of output
where marginal cost is equal to a. 3 b. 6 c. 8 d. 9
9. Refer to Table 6-1. If the firm finds that its marginal cost is $11, it should
a. increase production to maximize profit.
b. increase the price of the product to maximize profit.
c. advertise to attract additional buyers to maximize profit.
d. reduce production to increase profit.
10. Refer to Table 6-1. If the firm finds that its marginal cost is $5, it should
a. reduce fixed costs by lowering production.
b. increase production to maximize profit.
c. decrease production to maximize profit.
d. maintain its current level of production to maximize profit.