



























Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING Lecture PLANNI NG AND COORDI NATI ON 5 I N THE SUPPLY CHAI N lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING AGGREGATE lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING PLANNING IN A SUPPLY CHAIN 8Introduction lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
• Why is it interesting to look from lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
asupply chain perspective to the planning?
• What solutions do organisations
haveto upscale (or down scale) capacity?
• What is the role of ICT related to theplanning issue? lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING Example
• Paper is seasonal product, in spring
more paper is consumed because of
printing the annual year reports.
Running a mill is costly. To optimize
revenues the industry uses aggregate
planning to determine production and inventory levels. lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING Introduction
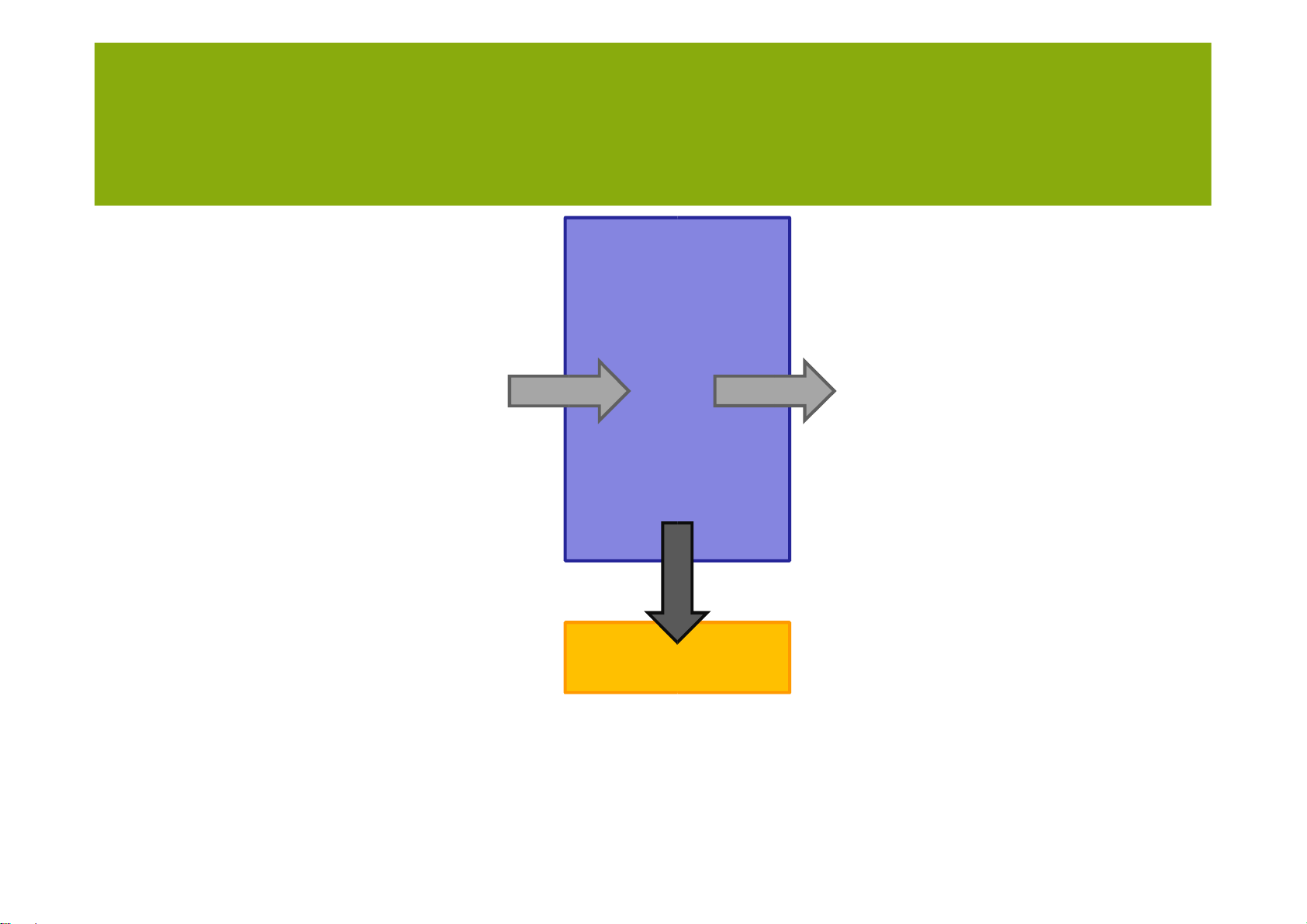
• Aggregate planning is the process where a company determines planned levels of: – Capacity – Production – Sub-contraction lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING – Inventory – Stock-outs – Pricing Objectives
• Main objectives of aggregate planning are to identify
following operational parameters: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
– Production rate –units to produce per time unit – Workforce – Overtime – Machine capacity level – Sub contracting – Backlog – Inventory on hand lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANIING The planning challenge • Forecast • Production costs
• LabourProduction quantities • Subcontractingfrom:
• Changing capacity• Regular time • Labor/machine hours•
Overtime required per unit• Subcontracting
• Inventory holding costsInventory held
• Stock-out costsBacklog/Stock-outs
• ConstraintsWorkforce hired/laid off
• Limits on overtimeMachine capacity
• Limits on layoffsincrease/decrease • Limits on capital lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING • Limits on stock- outs • Constraints from suppliers Aggregate • Planning • • • • Profitability lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING Aggregate strategies
• Aggregate planning is focusing on three costs:
– Capacity (regular, overtime, subcontracting) – Inventory – Backlog • Three strategies:
– Chase strategy – using capacity as the lever lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
– Flexibility strategy – using utilization as the lever
– Level strategy – using inventory as the lever
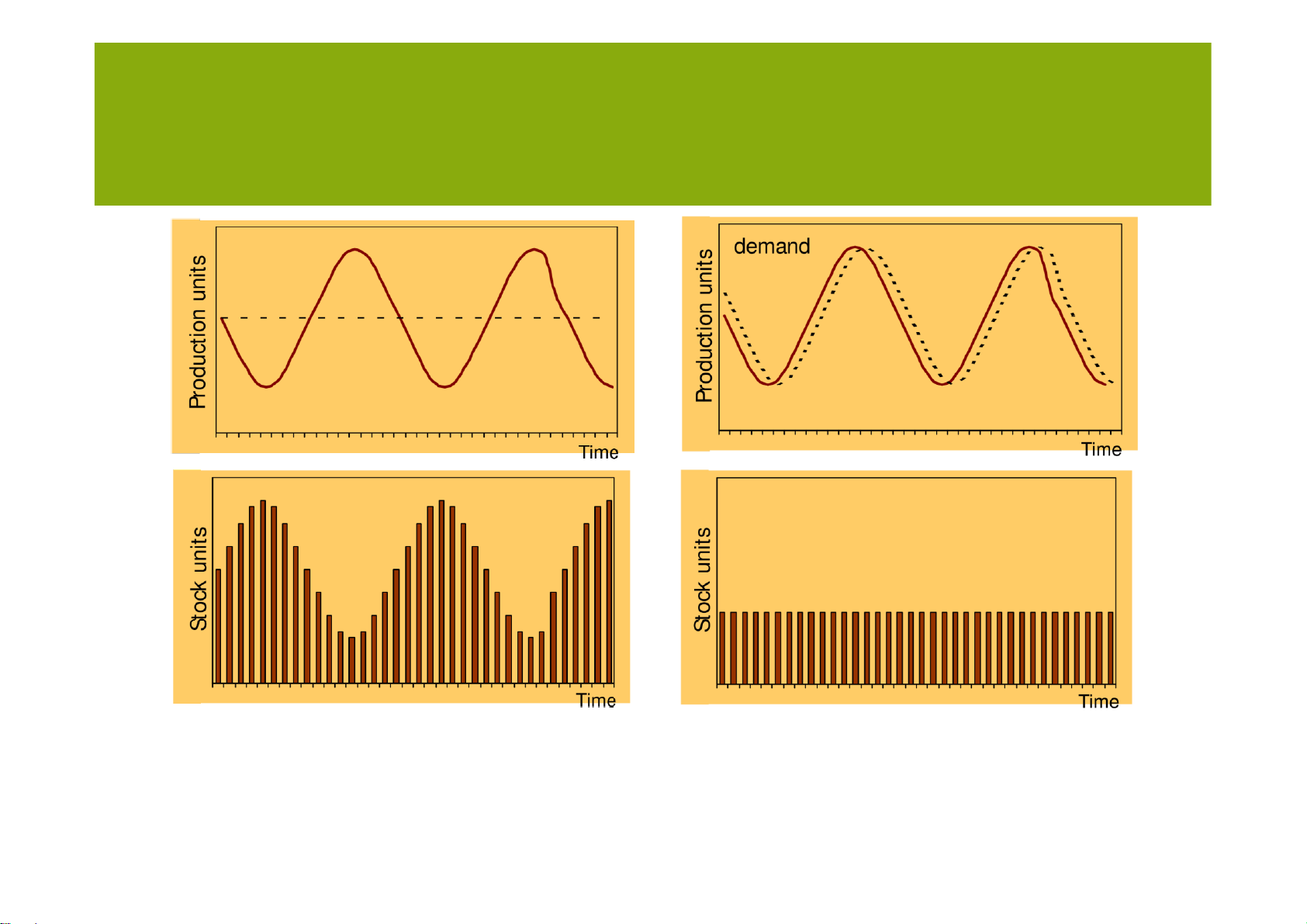
Leveling and chasing demand Level
production Chase demand lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING Constraints
• Workforce, hiring and layoff constraints • Capacity constraints
• Inventory balance constraints
• Overtime limit constraints lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
Building a master production schedule
• Master Production Schedule (MPS) identifies
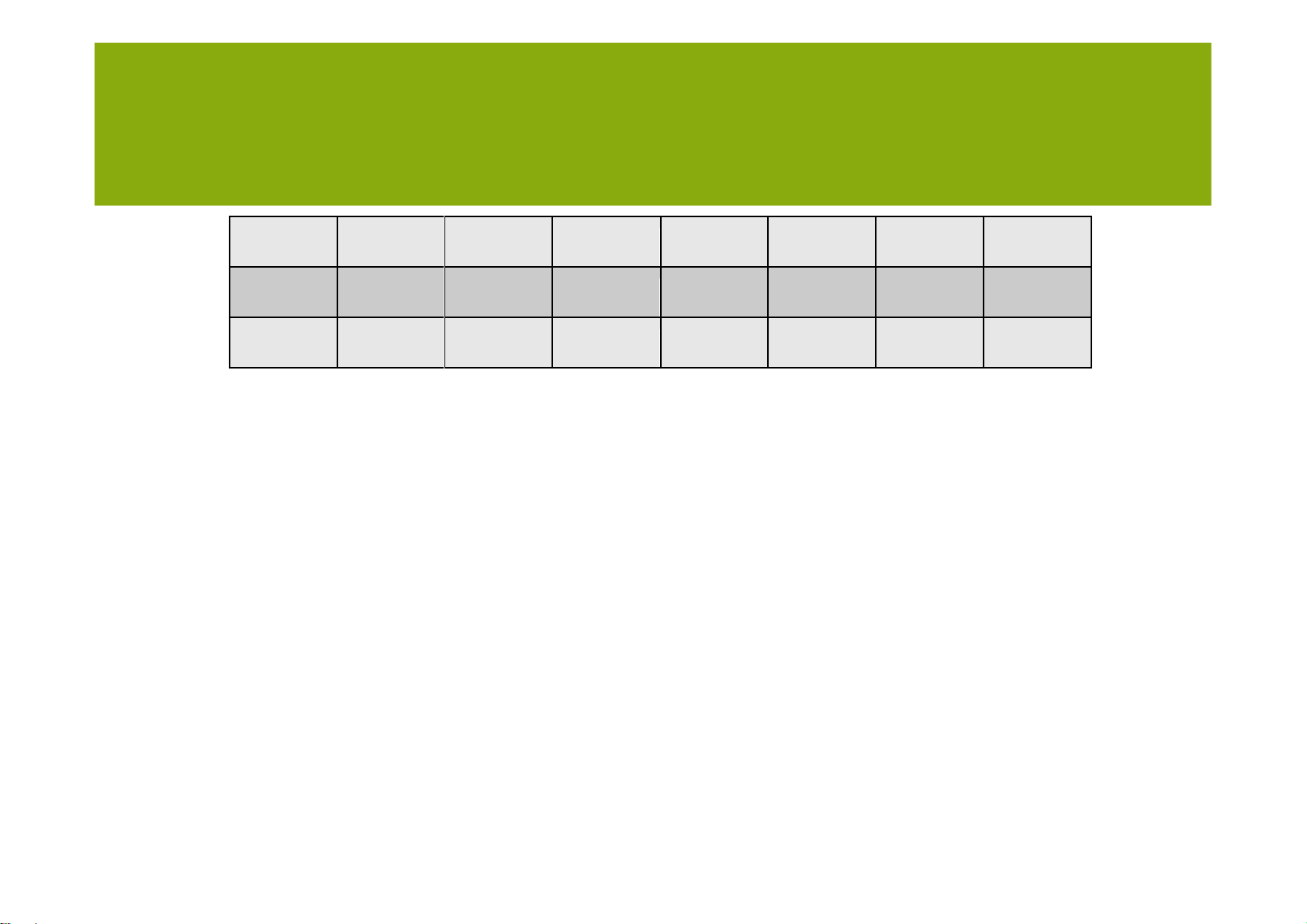
allbatches which needs to be produced in each period. • Example: Family Set-up Batch Prod. Prod. Numb. Set-up Prod. time size time quant. set-ups time time A 8 50 5.60 256 5 40 1,433.6 B 6 150 3.00 640 4 24 1,920.0 C 8 100 3.80 512 5 40 1,945.6 lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING D 10 50 4.80 256 5 50 1,228.8 E 6 100 3.60 512 5 30 1.843.2 F 5 75 4.30 384 5 25 1,651,2 The role of IT
• The most early IT supply chain products
wereaggregate planning modules • Advantages of using IT:
– Can go beyond linear programming to solve theproblem lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
– Possibility to combine with production planning andinventory planning
Implementing aggregate planning
• Today aggregate planning modules are part of ERPpackages.
• Important aspects related to implementation:
– Think beyond the enterprise, focus on supply chain lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 AGGREGATE PLANNING
– Make plans flexible, forecasts are never accurate
– Rerun planning when new data emerges
– Use aggregate planning as capacity increases lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING 9 lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING Introduction lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING •
What can you tell about demand anddemand patterns? • How does demand connect
sales tooperations and the supply chain? •
What solutions do organizations
haveto influence the capacity and/or demand? lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING Example
• Red Tomato Tools is selling
gardenproducts which is seasonal, concentrated in spring.
• Two strategies for managinginventory: – Producing only during season,leaving plant capacity unused lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING
– Producing flat during year
absorbingsales fluctuation via stock Predictable variability
• Predictable variability is change in demand that canbe forecasted.
• Objective: balance supply with demand maximizingprofitability by: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING
– Manage supply using capacity, inventory,subcontracting
– Manage demand using short-term price discounts andpromotions Managing supply
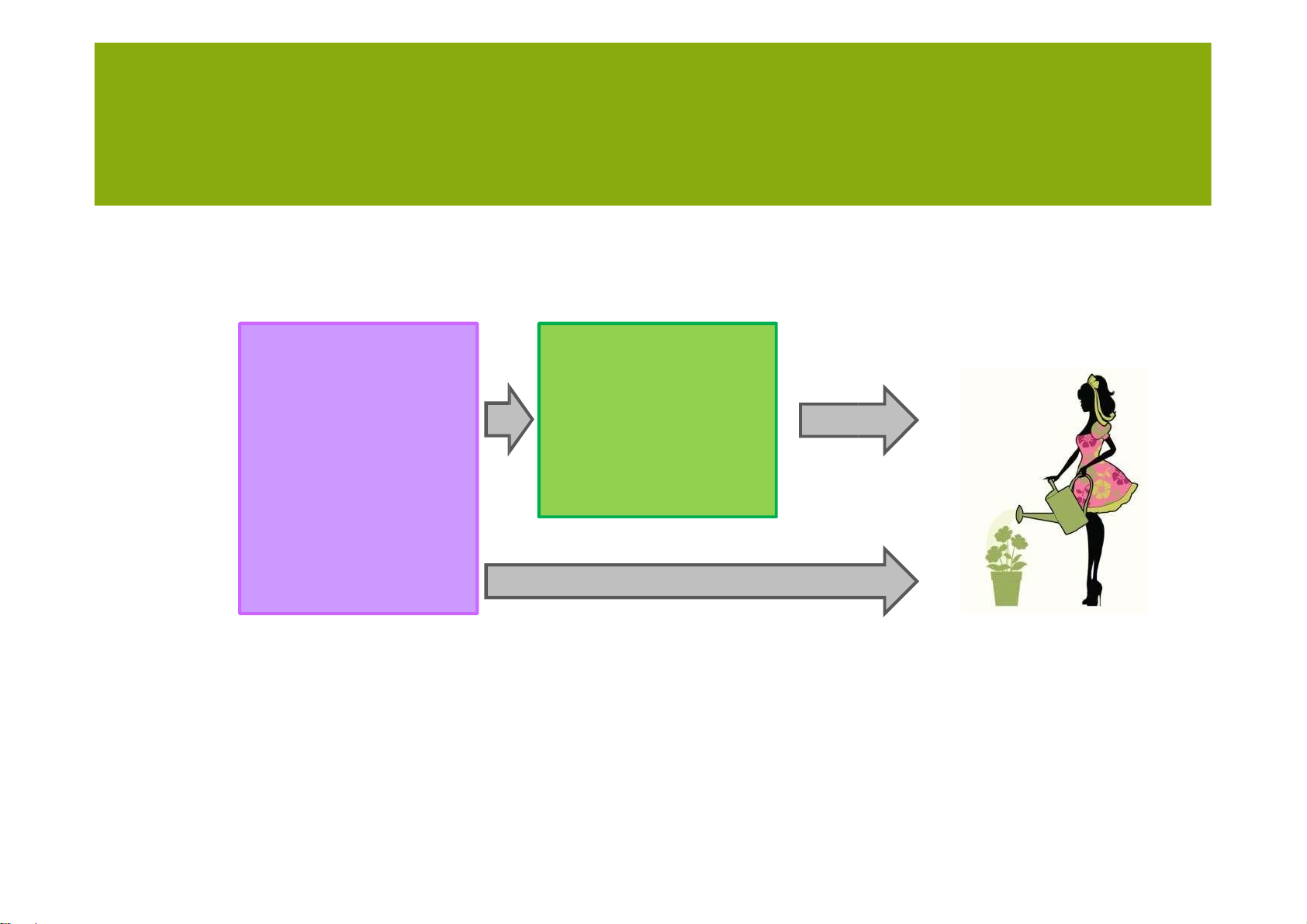
• A firm can manage supply by following factors: – Production capacity lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING –Inventory Customer Inventory Capacity lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING Managing capacity
• Firms can manage capacity by using a combination of:
– Time flexibility from workforce – Use of seasonal workforce – Use of subcontracting – Use of dual facilities
– Design product flexibility in the process lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING Managing inventory
• Firms can manage capacity by using a combination of:
– Using common components across multiple products
– Build inventory of high-demand or predictable- demandproducts lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING Managing demand
• Supply chains can manage demand by using acombination of: – Pricing – Promotion lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING
• Note: Promotion decisions are mostly made byretailers
without taking into account the impact on the rest of the supply chain.
Factors influencing timing of promotion
• Four key factors influencing promotion:
– Impact of the promotion on demand – Cost of holding inventory
– Cost of changing the capacity level – Product margins lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING
• The increase in demand comes from: – Market growth – Stealing share – Forward buying
Implementing sales & operations planning
• Important aspects related to implementation:
– Coordinate planning across enterprises in the supplychain
– Take predictable variability into account when makingstrategic decisions lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SALES AND OPERATIONS PLANNING
– Design S&OP to understand and manage the drivers ofdemand usage
– Ensure that S&OP process modifies plans as the realityof forecasts changes



