











Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 Lecture MANAGI NG 7a I NVENTORI ES I NTHE SUPPLY CHAI N (i) lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 12 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 Introduction lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 • What is maybe the biggest hinder inmanaging the supply chain?
• What are the risks if you do notmanage the supply chain well?
• How can you cover for this risk? lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY Safety inventory
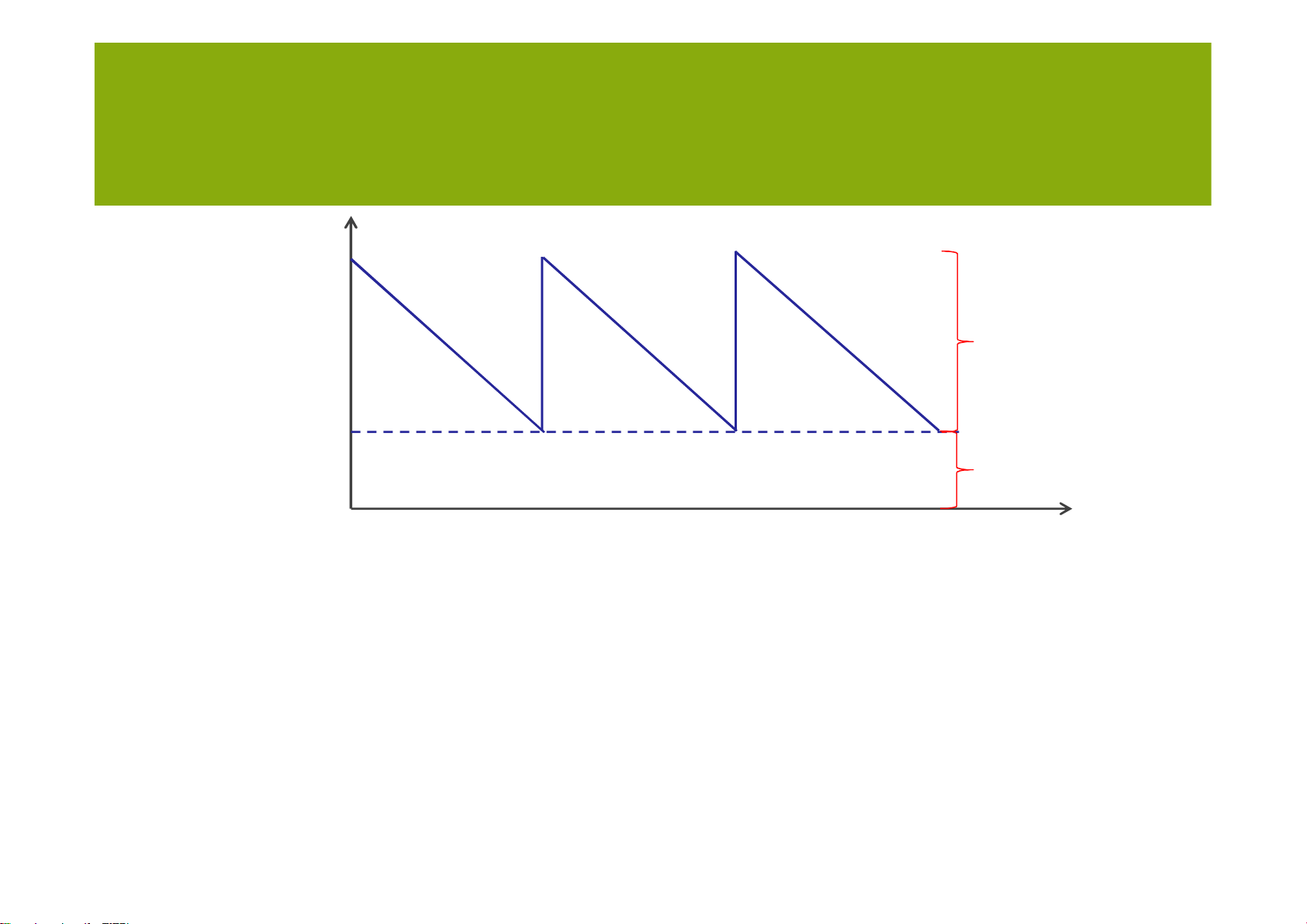
• Safety inventory is inventory carried to satisfy
demand that exceeds the amount forecasted for a given period. lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY Inventory Cycle inventory Safety inventory Time lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
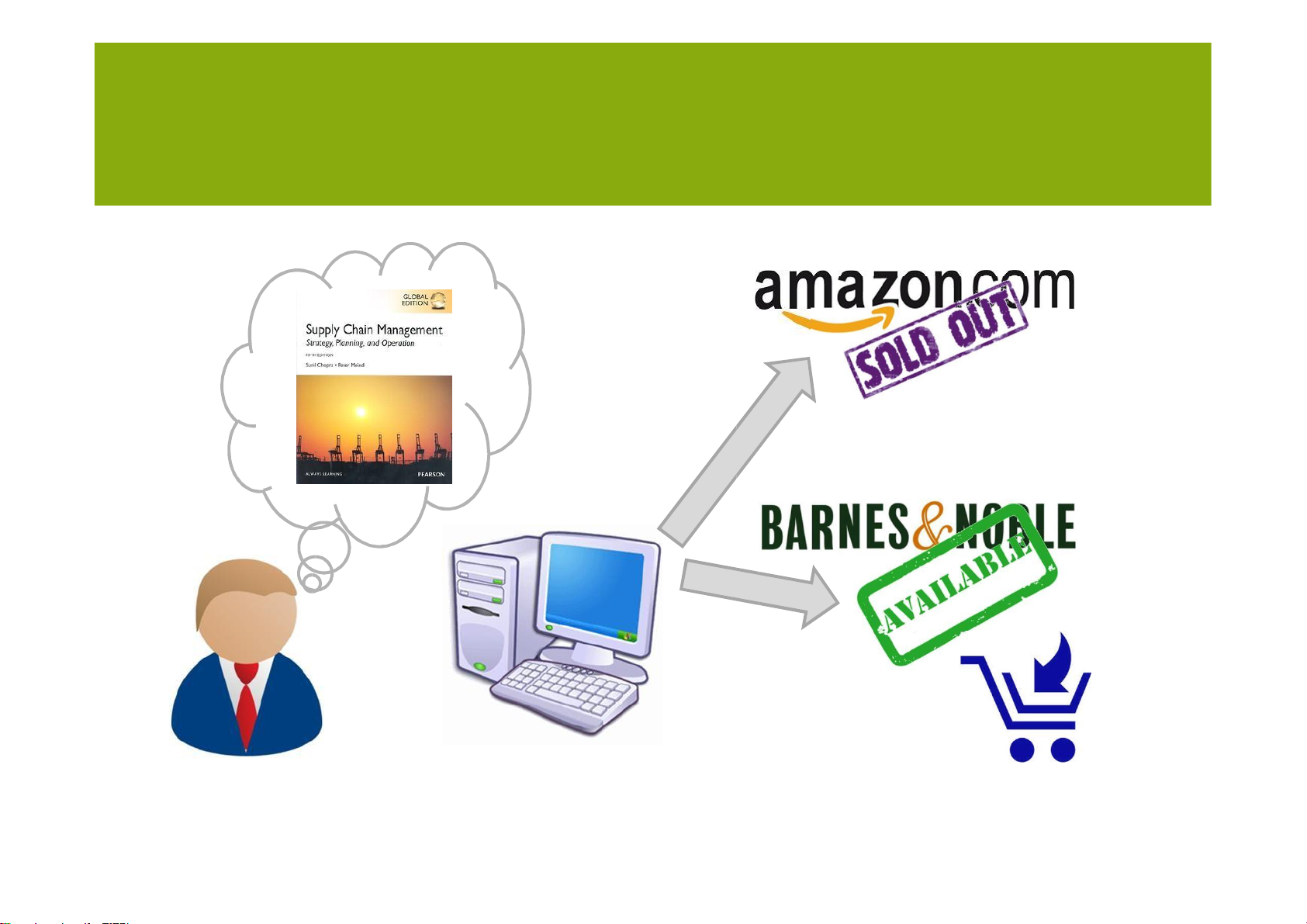
Example importance of availability lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY Trade-off of safety stock
• A supply chain manager has to balance:
– Pro: Increase of product availability
– Con: cost of holding (safety) inventory
• Higher pressure on product availability, because:
– Internet increases the ease of searching
– Increased variability and customization
– Shorter product life cycle lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
• High pressure on reduced inventory because: – Need to reduce costs
Safety inventory and demand uncertainty
• Key questions for planning safety stock:
– What is the appropriate level of product availability
– How much safety inventory is needed – What actions can be taken to improve
productavailability while reducing safety inventory?
• Demand has a systematic and a random component lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
• Goal is of forecasting is:
– Predict the systematic component
– Estimate the random component
Measuring product availability
• Product availability can be measured by:
– Product fill rate (fr): is the fraction of product
demandthat is satisfied from product in inventory
– Order fill rate: is the fraction of orders that are
filledfrom available inventory lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
– Cycle service level (CSL): is the fraction ofreplenishment
cycles that end with all the customer demand being met. Replenishment policies • Replenishment policies is the process of
regardingwhen to order and how much to order. • Two main approaches: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
– Continuous review: Inventory is continuously
checkedand when at Reorder point (ROP) a lot size Q is ordered.
– Periodic review: Inventory is checked at a
regularinterval and the order is placed to raise the
inventory to a certain threshold.
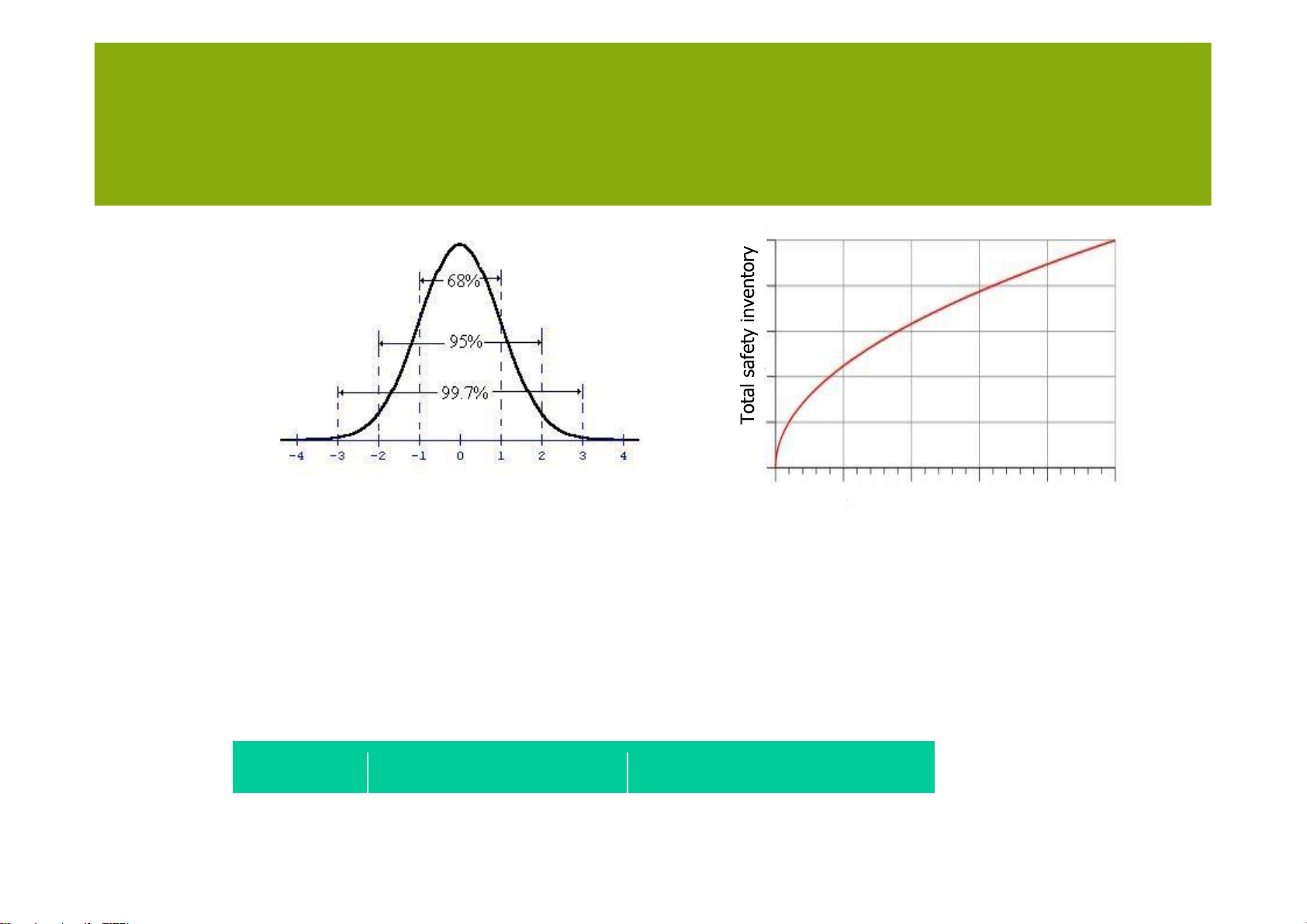
Impact uncertainty on safety stock
• The safety stock level is influenced by:
– Uncertainty in lead-time (of supplier, production) – Uncertainty in demand
– Number of independent stocking locations lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY Number of independent Stocking locations
Impact uncertainty on safety stock • This could lead to the following mathematicaloutcomes: Fill rate Safety inventory Costs lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY 97.5% 67 + 98.0% 183 ++ 98.5% 321 ++++ 99.0% 499 +++++++++ 99.5% 767 +++++++++++++++
• How to balance or to improve?
Impact uncertainty on safety stock
• The impact on safety stock can be improved by: – Reducing the lead-time
– Reducing the uncertainty in demand lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
– Reducing the number of independent stockinglocations
The role of IT in inventory management
• IT can support inventory management by: – Improved visibility:
• To see how much is available
• To see where this is available (store, warehouse, other stores)–
Better coordination of the supply chain: • Using RFID systems
• Integrating different stages (collaborative planning, etc) lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 MANAGING UNCERTAINTY
• It is important to recognize that
informationaccuracy important (garbage in -> garbage out!)



