







































Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 Lecture I NFORMATI ON TECHNOLOGY AND 9 SUSTAI NABI LI TY lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 17 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN A SUPPLY CHAIN Introduction lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 • What is importance of
information inthe supply chain? • How can availability of informationbe improved? What examples?
• What are the risks related to theimplementation and use of information technology? lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY The role of IT
• Information is a key driver in the supply chain
andcrucial to supply chain performance.
• Information must have following characteristics:
– Must be accurate: true picture of the situation
– Must be accessible in a timely manner: easy & direct
– Must be of right kind: not data but information lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
– Must be shared: shareholders should share commonview
Supply chain drivers and information
• Supply chain drivers and information: Facility
Determining location, capacity, schedules, and
trade offs: efficiency, flexibility, demand, exchange rates, taxes and so on. Inventory
Demand patterns, costs of carrying inventory, costs
of stocking out, costs of ordering Transportation
Deciding on transportation networks, routings, modes, lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Sourcing
Information on product margins, prices, quality,
delivery lead-times, and so on. Pricing &
Information on demand (volume and segment), revenue
product margin, lead time and availability. management
The supply chain IT framework (global)
• The supply chain IT framework is a help tounderstand
the role of IT within a supply chain: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Supplier Internal Customer Relationship Supply Chain Relationship Management Management Management ( SRM ) ( ISCM ) ( CRM )
TransactionManagement Foundation ( TMF )
• The model will be explained in the next slides: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Customer Relationship Management
• Customer Relationship Management (CRM)focus on
downstream interactions between the enterprises and customers. • Processes included: – Marketing – Sell – Order management – Call/service center lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Internal Supply Chain Management
• Internal Supply Chain Management (ISCM)focusses
on the interns operations within the enterprise. • Processes included: – Strategic planning – Demand planning – Supply planning – Fulfillment – Field service lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Supplier Relationship Management
• Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)focusses on
upstream interactions between the enterprise and its suppliers. • Processes included: – Design collaboration – Source – Negotiate – By lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY – Supply collaboration lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
The supply chain IT framework (detail) lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SRM ISCM CRM Design Strategic Collaboration Market Planning Source Demand Planning Sell Negotiate Supply Planning Call Center Buy Order Fulfilment Management Supply Field Collaboration Service (TMF ) lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
The transaction management foundation
• The transaction management foundation is the historical
home of the largest enterprise software players: SAP,
Oracle, Sage Group, Infor Global Solutions and Microsoft. lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Supply chain visibility, coordinated planning,
forecasting, and replenishment, collaborative product
development, coordinated logistics, coordinated promotions SRM ISCM CRM Supplier Our Company Customer
The future of IT in the supply chain
• The following three important trends will impact IT inthe supply chain:
– The growth of software as SaaS lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
– Increased availability of real-time data
– Increased use of mobile technology
• Saasis software owned, delivered and managed remotely.
• Mobile technology offers many new ways of doingbusiness Risk management in IT
• Several risks are associated with IT: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
– Installing new IT systems: forced to transition from an old
process to a new process. Troubles can be :
• In business process: difficulty in (re)learning even resistance • Technical issue
– The risk of relying on IT systems: In case systems fail operations can come to a stop • Solutions:
– Incremental- or big-bang implementation – Running duplicate systems
– Only implement the level of complexity needed lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Supply chain IT in practice
• Some general advices to making decisions regarding supply chain IT:
– Select an IT system that addresses the company’s keysuccess factors
– Take incremental steps and measure value
– Align the level of sophistication with the need forsophistication lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
– Use IT systems to support decision making, not tomanage decisions – Think about the future lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SAP ERP modules
mySAP Supply Chain Management Strategic Planning
Strategic Supply Chain Design Strategic Sourcing
Forecasting & Lifecle Demand Planning Planning Promotion Planning
Consensus Demand Planing Safety Stock Supply Network Distribution Customer Supplier Supply Planning Planning Planning & Planning Collaboration Collaboration Outsourcing Procurement
Purchase Order Processing Receipt Confirmation I nvoice Verification Manufacturing
Production Planning & Detailed Scheduling
Manufacturing execution I nbound Outbound Warehouse & Physical Warehousing Processing Processing Crossdocking Storage I nventory Order fulfilment Sales Order Processing Logistics Coordination Billing Transportation
Transportation Planning
Transportation Execution Freight Costing lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Procurement Manufacturing Fulfilment Transportation Supply Chain Visibility Visibility Visibility Visibility Visibility Analytics Source: SAP website Operations 254 Management, a strategic SAP ERP implementation • Industry solutions are best-practice
templatesdesigned to maximize efficiency and minimize customisation.
• Fast track implementation by standardised
approach,for example AccelaratedSAP solution: lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
– Phase 1: Project preparation
– Phase 2: Business Blueprint – Phase 3: Realisation
– Phase 4: Final preparation
– Phase 5: Go Live & support Operations 255 Management, a strategic lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY 18 SUSTAINABILITY IN THE SUPPLY CHAIN lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Introduction • How are supply chain managementand sustainability connected? • Can you give examples of
howsustainability can be improved along the supply chain? lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 The role of sustainability
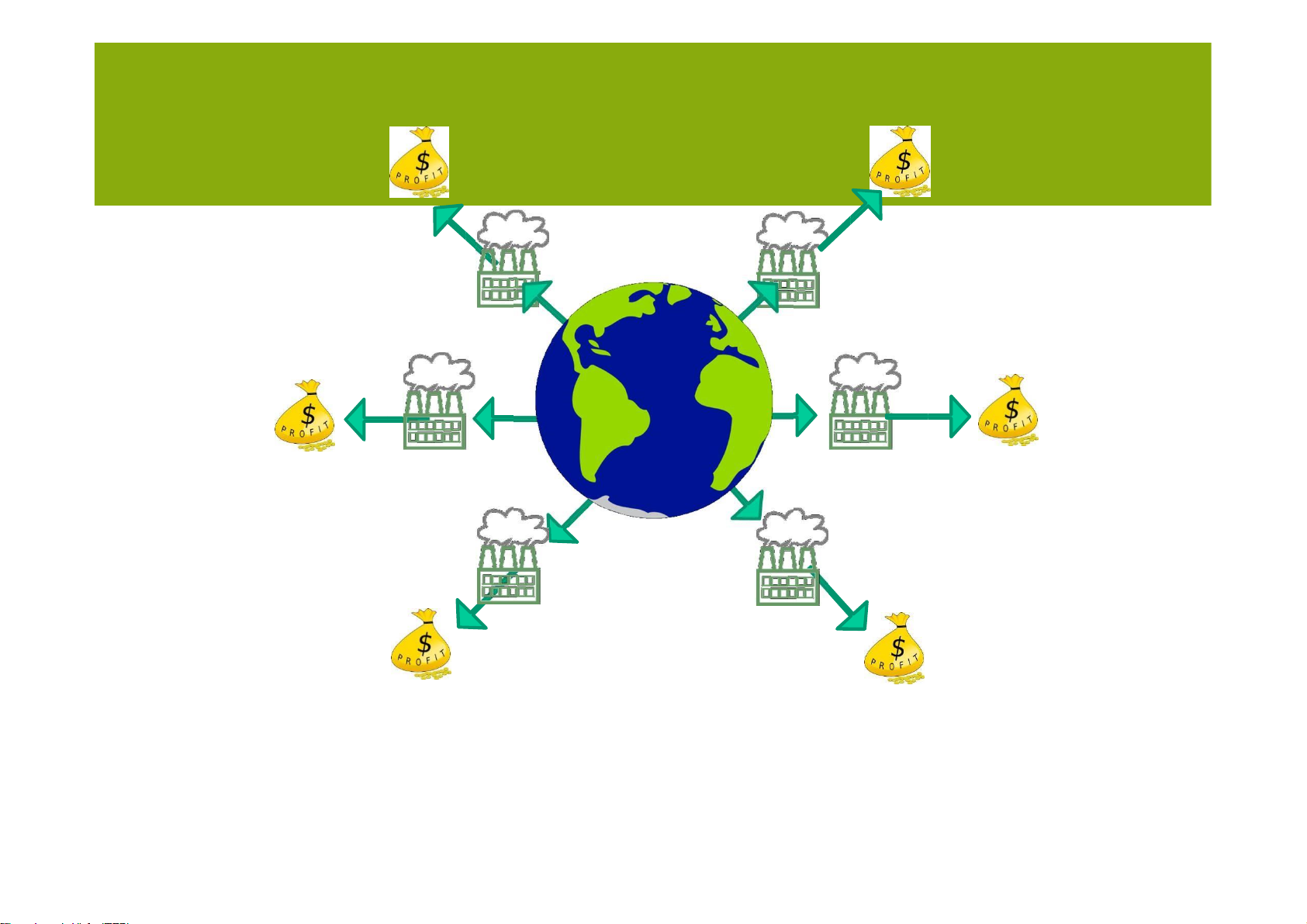
• The health and survival of a supply chain and
everyindividual depends on the health of the surrounding world.
• The 2005 World Summit of the United
Nationsintroduced the three pillar framework of
sustainable development: economic, environmental and Social sustainability. lOMoARcPSD| 36782889
SUSTAINABILITY Factors driving focus on sustainability
• The factors driving increased focus on sustainability are:
– Reducing risk and improving the financial performanceof the supply chain
– Attracting customers who value sustainability
– Making the world more sustainable lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 The tragedy of the commons lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABLE Key metrics for sustainability
• Key metrics for sustainability are: – Energy consumption – Water consumption – Greenhouse gas emissions – Waste generation lOMoARcPSD| 36782889
Sustainability and the supply chain drivers
• Discussion per supply chain driver how this can contribute to sustainability: – Facilities – Inventory – Transportation – Sourcing – Information – Pricing lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Facilities lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY
• Facilities: can be significant usersof
water and energy and emitters of waste and green house gasses. • Opportunities: – Reuse energy • Examples: – Leveling energy use – Reduction of energy use lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Inventory lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY • Inventory: besides raw materials,work in process and
finished products also inventory in landfill. • Opportunity: – Cradle-to-cradle approach • Examples: – Less harmful materials – Use materials for new lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Transportation lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY
• Transportation is also closelyrelated,
think about CO2 emission but also waste generated. • Opportunity: – Reduce transportation
– Improve efficiency– Cleaner energy sources • Examples:
– Cleaner/more efficient engines lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Sourcing lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY • Majority of energy, waterconsumption, waste and
emission occur in the extended supply chain. • Opportunities:
– Include the extended supply chain
– Work with sustainable suppliers • Example: – Put a price premium lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Information lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY
• Good information is one of thebiggest challenges. • Opportunities:
– Improve information exchange–
Include sustainability in metrics • Examples:
– Align sustainability efforts acrossthe extended supply chain lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Pricing lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY • Visibility and pricing can stimulatesustainability. • Opportunities: – Motivating customers to emphasizeon sustainable products/services – Use incentives • Examples: – Tax reduction lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Closed loop supply chains lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY
• Closed loop supply chains are
thebiggest challenge to improve sustainability. • Opportunities – Reduce – Reuse – Recycle – Revitalize – Recovery (recover energy) – Landfill (disposal) lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY Some examples lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY
• Heathrow consolidates the deliveries for
the different retailers. Using grouped (bulk)
transportation reduces the impact.
• Deutsche Post has reduced the amount of
paper necessary for airway bills reducing the consumption of paper.
• Maersk ordered new ships (Triple-E class)
being more energy efficient reducing carbon
emission per container with 50%. lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY More examples lOMoARcPSD| 36782889 SUSTAINABILITY
• IKEA reduce package for one product with 1
centimeter and can now load 4 extra sofas in a truck.
• Imported containers are not always fully
loaded, could be emptying in the harbor and
continue with bulk transportation.
• The usage of electronic logistic markets the
efficiency of combined transportation can be improved.



