






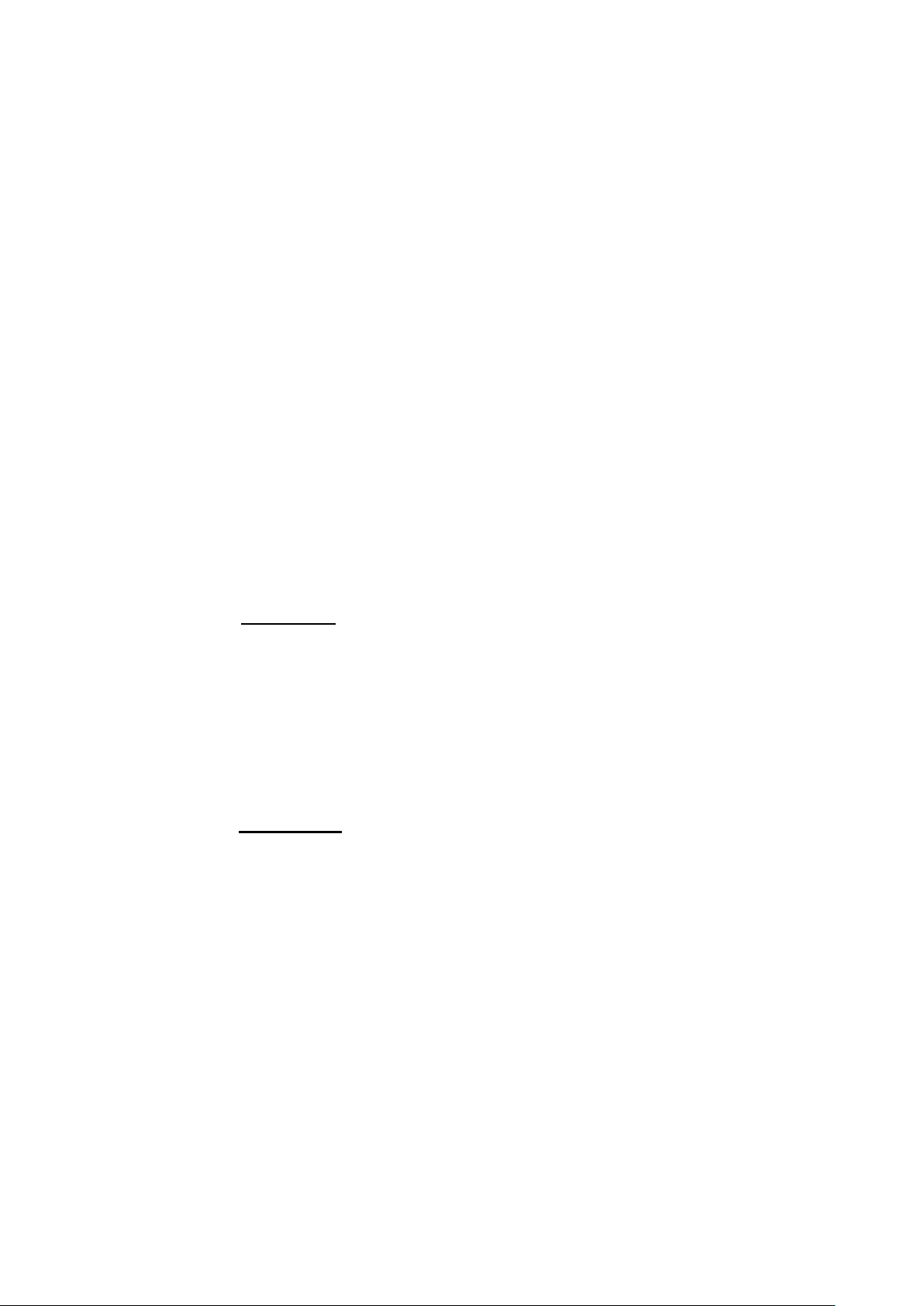






Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
TABLANGUAGE OF NEWSPAPER I. DEFINITION 1. Newspaper NEWSPAPER = NEWS + PAPER The word ‘news’ means
‘tidings, new information of recent
events’. original means the papers with
news about everything: Newspaper is a
paper that is printed usually daily or
weekly and that contains news, articles
of opinion, features, and advertising, etc.
A printed publication (usually issued daily or weekly) consisting of folded
unstapled sheets and containing news, feature articles, advertisements, and
correspondence. (Definitions from Oxford Languages)
A document consisting of news reports, articles, and photographs that is
published every day or every week (Cambridge Business English Dictionary) 2. Online newspaper
An online newspaper (or electronic news or electronic news publication) is
the online version of a newspaper, either as a stand-alone publication or as the
online version of a printed periodical
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Online_newspaper)
A newspaper is a regularly printed document consisting of large sheets of
paper that are folded together, or a website, containing news reports, articles,
photographs, and advertisements.
(https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/newspaper) lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
They offer several advantages over traditional newspapers, such as:
● Timeliness: Online newspapers can provide breaking news in realtime,
which is not possible with print media.
● Accessibility: Online newspapers can be accessed from anywhere in the
world with an internet connection. ● Interactivity: Online newspapers allow readers to interact with the content by commenting on articles, sharing them on social media, and more.
● Cost-effectiveness: Online newspapers are often cheaper than print media
because they do not require printing and distribution costs.
However, online newspapers also have some disadvantages. For example,
they may not be accessible to people who do not have access to the internet or
who prefer reading print media. Additionally, online newspapers may be less
reliable than traditional newspapers because anyone can publish content online
without proper fact-checking or editorial oversight.
II. COMPARE ARTICLE AND NEWSPAPER 1. FORM
Newspapers and articles are both written forms of communication, but they
have some key differences in terms of form and purpose: Newspaper Article Format
have a standardized format that Articles are more flexible in
includes sections like the front page, format and can vary widely. local news, national
and They can be found in various international news, business, publications, including lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 sports, entertainment, and magazines, websites, and
classifieds. The front page typically academic journals. The
features headlines and images. format can include long
narratives, images, charts, and graphics, depending on the type of article. Publicatio
Newspapers are typically published Articles can be published on n
daily, although some local or different schedules,
smaller newspapers may be depending on the publication. Frequency published weekly. Magazines may be monthly or quarterly, while online
articles can be published daily or as often as needed. Objective
Newspapers aim to provide Articles cover a wide variety Reporting
objective reporting of current of subjects, such as health,
events. They follow established science, lifestyle, culture, and
journalistic standards and are opinion pieces. They often
expected to present the news in a explore a topic in-depth. neutral and balanced manner. Length
News articles in newspapers are The length of articles can vary
generally concise and to the point, significantly, from short op-
often consisting of around 300 to eds of a few hundred words to 800 words. They
prioritize in-depth investigative pieces delivering the most
critical or longform features that may information quickly. run several thousand words. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
Authorship Articles in newspapers are usually Articles can be written by a
written by journalists or reporters. wide range of authors,
The byline provides the name of the including journalists, experts, author or contributor. academics, and contributors. Authorship is clearly stated. 2. ELEMENTS
Newspapers and articles share some common elements but also have
differences in terms of their structure and content. Here's a comparison of the
elements of newspapers and articles:
Common Elements:
Headlines: Both newspapers and articles use headlines to grab readers'
attention and provide a brief summary of the main topic or story.
Byline/Authorship: Both include the name of the author or contributor responsible for the content. This helps readers identify the writer. Text: Both contain written text, which forms the body of the
content. This text provides the main information, details, and context for the topic.
Images: Newspapers and articles often include visuals like photographs,
illustrations, charts, and graphics to complement the written content and make it more engaging.
Subheadings: Both may use subheadings to divide the content into sections
or to provide additional context and organization within the text.
Differences in Elements: lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 Newspaper:
Sections: Newspapers are typically divided into various sections, such as local
news, national/international news, business, sports, entertainment, and more.
Each section contains articles specific to that category.
Layout: Newspapers follow a standardized layout with columns of text, which
can vary in length, and often have a traditional, formal appearance.
Inverted Pyramid Style: News articles in newspapers follow the inverted pyramid style, where the most important information is
presented at the beginning, and the details are provided in descending order of importance. Quotes: Newspapers
frequently include quotes from sources, experts, or people involved in the
news story to provide direct insights and perspectives.
Short and Concise: News articles in newspapers are typically concise and to
the point, focusing on delivering the most crucial information efficiently. Article:
Flexibility in Structure: Articles have a more flexible structure. They can be
found in various publications and may have varying formats, including long
narratives, op-eds, interviews, or in-depth features.
Topic Diversity: Articles cover a wide range of topics, from health, science,
and lifestyle to culture, opinions, and analysis. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
Length Variation: Articles can vary in length significantly, from short pieces
of a few hundred words to lengthy, in-depth articles that may run several thousand words.
Style: Articles can have a more personal or opinionated style, depending on
the nature of the content and the publication.
Content Depth: Articles often provide more extensive coverage and
exploration of a topic, allowing for in-depth analysis and discussions.
III. FUNCTIONS OF NEWSPAPER 1. To inform people
● This function plays an important role in a newspaper to inform its readership.
● Newspapers provide facts that readers must have in order to be informed
citizens and to make decisions. => Referential function Example: When reading The New York Times (New York, Thursday, April 23, 1970),
readers can get information about the event of millions of people joining Earth Day observances Across the nation.
2. To promote certain political views
● Through this function, newspapers help to ensure and maintain the duties
and ways that the government or the state to the people, from the people to
the state wants to offer, and faithfully reflect thoughts and prayers. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
● The desire of the government or the state toward the people in order to raise
their political awareness and self-awareness is a means of contributing to
the perception of society today. => Influential function Example:
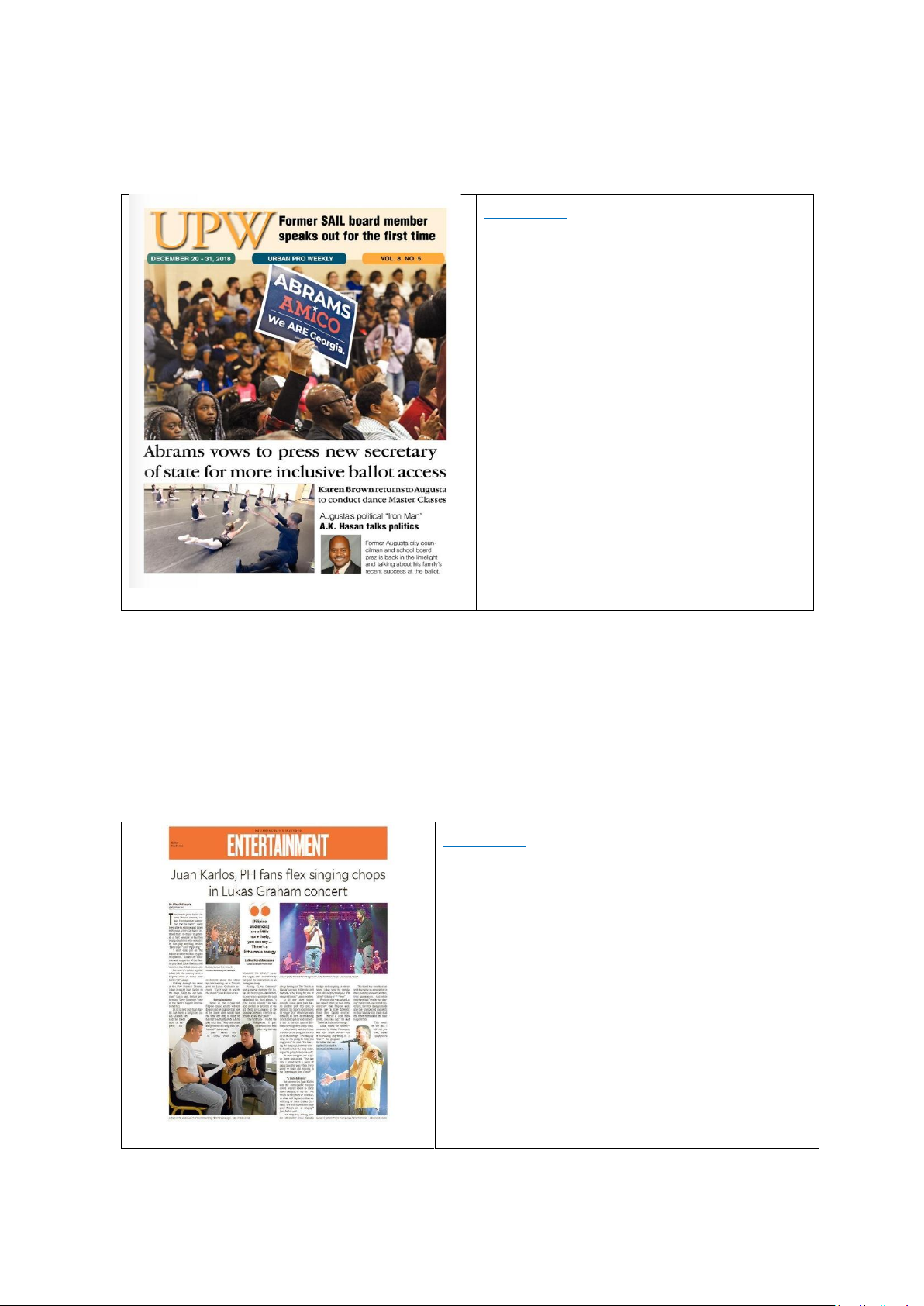
In the paper entitled “Abrams vows
to press new secretary of state for
more inclusive ballot access” on
UPW (December 20-31, 2018), the state shows the duty that the
government promises to press for a
new secretary of state for more inclusive ballot access. 3. To entertain people
● Newspapers also seek to offer a diversion and simply entertain.
Nowadays, many newspapers will publish crosswords, games and
puzzles. Many feature cartoon strips and humorous writings.
=> Entertainment function Example: When reading Philippine Daily InquirerEntertainment, readers can
entertain with Juan Karlos, PH fans
through the flexing singing chops in Lukas Gram concert. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
4. To provide a service to readers
● Local newspaper act as community bulletins, providing information about local events and issues Example: Newspaper Thừa Thiên Huế
published on September 25, 2019
provided information about the role
of lagoon economy in building new
rural areas in Thua Thien Hue.
5. To raise people’s awareness
● Newspapers can be so influential that they can affect the way we
think about international events and British politics by presenting issues in a certain way.
● The choice of words, the decisions about which facts to include and
which to exclude, the ranking of events on the front page all
influence the reader. The editor of a newspaper will seek to present
the world in a certain way so that the intended audience identifies with the paper’s viewpoint. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 Example:
The edit of the Thừa Thiên Huế
news was published on October
18, 2023 seeks to present events
and information to focus on the message of preserving and promoting heritage values so that the intended audience identify with the paper’s viewpoint.
Conclusion: The function of newspaper language is to inform and entertain
people, and to present them with a particular ideology and an interpretation of events.
IV. FEATURES OF NEWSPAPER 1. Headline language
a. There are three headlines:
● The main HEADLINE will be larger than the others and may
occasionally be in colour to draw attention.
● The STRAPLINE or OVERLINE is the secondary headline
that appears above the main one. It is used to provide extra
information or to clarify the main headline.
● The SUB-HEADLINE follows the main headline, and qualifies or elaborates it. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
⇨ Headlines need to be simple, easily readable and appropriate to the
kind of newspaper in which they are printed.
⇨ Headlines have been affected by ideas to be expressed, kind of
reader, paper’s house style. b. The lexis
● The lexis chosen indicate simple, easily readable as
something about the political persuasion of the newspaper
and about the intended audience.
● Analyzed connotation of the words and the point of view conveyed
● Headlines in broadsheets: factual, interpretation
● Headlines in tabloids: sensation c. The Style
● The style of headlines is important: they need to be simple, but
must also create impact.
● There are two style of newspaper: tabloid and broadsheet TABLOID: lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 ✔
Being common and headlines will often disrupt collocations.
✔Having/being a less formal tone and not being serious about the issue.
✔Focusing on human – interest stories BROADSHEET: ● Informative ● Straightforward d. Structure
● The structure of headline are noun phrases (noun strings)
● Using omission and passive voice to focus the attention of the reader. e. Ambiguity ⮚ Having two meanings: ✔Depending on word class lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 ✔
✔Different connotations of a word alter the meaning
✔Word order is altered to make the headline concise ⮚ Kinds of ambiguity:
✔Kinds of vocabulary will give readers some senses about news
The way in which participants and location are named
are another means of distinguishing between the two different kinds of reportage.
✔The connotation of word are used very interesting in reports.
✔Both broadsheet and tabloids use modifiers to help journalist to provide detail.
✔Abbreviates are used to add extra detail.
⮚ Some kinds of adverbials: time, place, manner,
reason, method… are added by answering
question like now: When, Why, Where, What for, How long?
⮚ In broadsheet or compacts they provide accurate information lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 ✔
⮚ In tabloids they develop a sense of narrative.
✔Selective perception means that although report might
cover the same event, the information included may not the same. 2. Report a. Lexis
● Using informal/formal lexis ● Modifier
The noun phrases contain modifier, that dramatise the central characters
✔They used pre-modification prepositional phrase postmodifiers
● The naming of participants and places ✔Participants ✔Places b. Grammar Tabloids:
● Simple and compound sentences
● Short paragraph: 1-3 sentences lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 ✔
● Developing a chatty approach
Broadsheets/ compacts: ● Wider variety of sentence
● Avoid cramming too many ideas into one sentence: a sentence
should communicate no more than one idea or two connected ideas
and should not exceed a maximum of thirty words. c. Style
● Marked themes bring clause elements other than the
subject to the front of the sentence and give them prominence.
● Use of passive voice rather than the active also has this effect. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
● Use both direct and indirect speech – they may directly quote the exact words
spoken by an individual or they may report those words indirectly.
● Chronological structure: d. Sources
●Are important in newspaper articles and provide another way to
distinguish between tabloids and broadsheets
●Informative and Straightforward
✔ Broadsheets: cite official sources
✔Tabloids: cite ordinary people who have no particular authority.
Conclusion: All the features discussed above help to indicate the point of view
or ideology of a newspaper. By contrasting the approach of two or more reports,
a linguist can come to continuous about the intended audience and the house style of a paper. Example: lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 1. HEADLINE
- 1.2. The lexis simple, 1.1. Headline: - easily readable Headlines
- Main headline “Texas Officials Had in broadsheets:
Few Rules For Power Grid”: larger
factual and interpretation: “few
than the others and may occasionally
- rules”, “weak points”
be in colour (black, italicized and
Using of present tense verbs and bold) to draw attention. passive voice “raised” to
emphasize the impact that Texas
- The Strapline “Weak Points in System
had few rules for power grid. =>
Raised Blackout Risk” provide extra Government power policies
information and to clarify the main
happened in the past (“had few
headline in which the paper focuses
rules”) but their effects still last
on analyzing the weaknesses in the to the present.
government's responsibility for
increasing the risk of power outages in this region. 1.3. The Style: 1.4. Structure: - simple, and create impact.
- The structure of headline “Texas
Officials Had Few Rules For lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 - Informative and straightforwa rd
Power Grid” is a simple sentence
related to the subject that Texas
and affirmative sentence => to
officials had few rules for the power grid. increase emphasis on the
government's responsibility for
the electric energy management situation in Texas.
- The Strapline “Weak Points in
System Raised Blackout Risk” is a noun phrase (noun strings).
- Using omission (relative clause),
and passive voice (“Weak Points
in System Raised Blackout Risk”) to focus the attention of the
reader. By choosing the passive
voice, the journalist was able to
foreground the object of active
sentence (“weak points”) 1.5.Ambiguity: - Word class: + common nouns (“rules”,
“officials”, “risk”, “power”, “grid”
+ concrete nouns: “Texas”,
- Participants: Texas officials, the
government of “Republic of Texas” and Texans
- Location: Texas in US. lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 2. REPORT 2.2. Grammar 2.1. Lexis
Broadsheets/ compacts:
- The report is a broadsheet-> influence Wider variety of sentence the reader
Ex: “Texas, the nation’s leading energy-
- Using formal lexis =>The formal tone producing state, seemed like the last
of the popular paper’s reader headline place on Earth that could run out of
helps to create a different kind of energy.” (simple sentence)
relationship with readers: the report is
factual (“Texas has been built on the The dominance of the energy industry
oil-and-gas business for the last 120 and the “Republic of Texas” ethos
became a devastating liability when
years, ever since the discovery of oil energy stopped flowing to millions of
on Spindletop Hill near Beaumont in Texans who shivered and struggled
through a snowstorm that paralyzed 1901”.
much of the state” (complex sentence)
- The proper noun: “Spindletop Hill”,
“Mr. Bush”, “Beaumont”, “Texans”,
“University of Houston”, “Ed Hirs”,
- They used pre-modification and
prepositional phrase post-modifiers
- The naming of participants and places
✔ the location: “Beaumont in
1901”; “Houston”, “across the plains of West Texas” ✔ Participants: Mr. Bush, lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847 2.3. Style 2.4. Sources
Marked themes: Across the plains of West
Broadsheets: cite official sources.
Texas, the pump jacks that resemble giant
“Deregulation was something akin
bobbing hammers define not just the
landscape but the state itself: Texas has been
to abolishing the speed limit on an
built on the oil-and-gas business for the last
interstate highway,” said
120 years, ever since the discovery of oil on
EdHirs, an energy fellow at the
Spindletop Hill near Beaumont in University of Houston.
1901=> brings clause element other than the “Competition in the electric industry
subject to the front of the sentence and give will benefit Texans by reducing monthly
rates and offering consumers more them prominence.
choices about the power they use,” Use of passive voice: George W. Bush,
Use both direct and indirect speech:
+ “Competition in the electric industry will
benefit Texans by reducing monthly rates and
offering consumers more
choices about the power they use,” George
W. Bush… (direct speech)
+ Across the plains of West Texas, the pump
jacks that resemble giant bobbing hammers
define not just the landscape… (indirect speech) V. TYPES OF NEWSPAPER
A. Depending on publication policy
, there are two types of newspaper:
popular newspaper and quality newspaper.
The popular newspaper's policy is primarily to report on soft news- readily
interpreted by all types of audiences, regardless of their level of education.
Readers may not require any prior experience or advanced knowledge to lOMoAR cPSD| 58794847
comprehend the news. Soft news covers news on violence, major accidents,
homicide, rape, entertainment, and disasters. People are more likely to pay
attention to bad news than good news, so soft news is the news that more people
would pay attention to. Furthermore, popular newspapers prefer to use
eyecatching vocabulary and eye-catching phrases, as well as pictures in
bright colors such as green, orange, and pink, to distract readers. In order to
capture people's interest, popular newspapers prefer to publish in a
straightforward and entertaining manner.
A quality newspaper is not the same as a popular newspaper. Although popular
newspapers focus on soft news, quality newspapers focus on hard news. Political
news, economic news, social news, environmental news, and so on are examples
of hard news. For those with no background knowledge, hard news is complicated
and challenging to grasp. Furthermore, difficult, informative, and indirect
language is used to report hard news. As a result, readers must be able to comprehend it.
Reah and Richardson, using somewhat different terminology, classify newspapers
into three types. Reah (2002) makes a distinction among 'broadsheets', 'middle
ranged' tabloids and 'tabloids'. ‘Broadsheets’ and ‘quality’ newspapers are taken
as similar and ‘tabloids’ and ‘popular’ newspapers are considered as synonyms.
Tabloid papers focus more on celebrity issues and tend to sensationalise.
Broadsheets tend to be more informative, covering more political and international news.
B. Depending on type of story : classify into 3 types 1.
Action stories( factual statement)
- Create stories from incidents: the naming of participants and places are real
- Introductory headline: capture the reader’s attention. Concentrate on exactly
what was happened, short, no more than 20 words



