













Preview text:
UNIT TIME VALUE OF MONEY Structure 2.0 Objectives 2.1 2.2 Future Value of a Cash Flow 2.3 Future of an Annuity 2.4 Present Value of a Single 2.5 Value of Series of Cash Flows 2.5.1 Present Value of an of Uneven Cash Flows 2.6 Let Us Up 2.7 Key Words 2.8 Answers to Your Progress 2.0
After studying this unit, you should be able to: explain value present value concepts;
explain compound interest and discount; value of a single and an annuity;
compute present value of a single amount and an annuity. INTRODUCTION You must heard that a rupee today is than a rupee tomorro
you imagine, why is so? Let me tell you by a n example. Anil's grandfath to gift him one
at the end of five years; and gave a
having Rs. 75,000 today. Had you been in Anil's place choice y
made? Would you have accepted Rs. after five years or Rs. 75,00
What do you say? Apparently, Rs. 75,000 today is attractive tha Rs.
after five years because present is than future. You cou Rs. 75,000 the inarket and this Rs. at the
years would have less purchasing power due to inflation, We you hav
that a rupee today is worth more a rupee But are so simple.
value of money concepts will unravel th of such choices all of us face in our daily life. We a of value of
constitute 90% of finance sense. decisions involve
flow occurring at different points Therefore, of value of money is ve ry In unit, you will learn about co interest discount concepts future value of a single and a and present of a single an annuity is start value of a single for a single period Time of Money one period. FUTURE VALUE CASH of let explain the meaning of value. By value
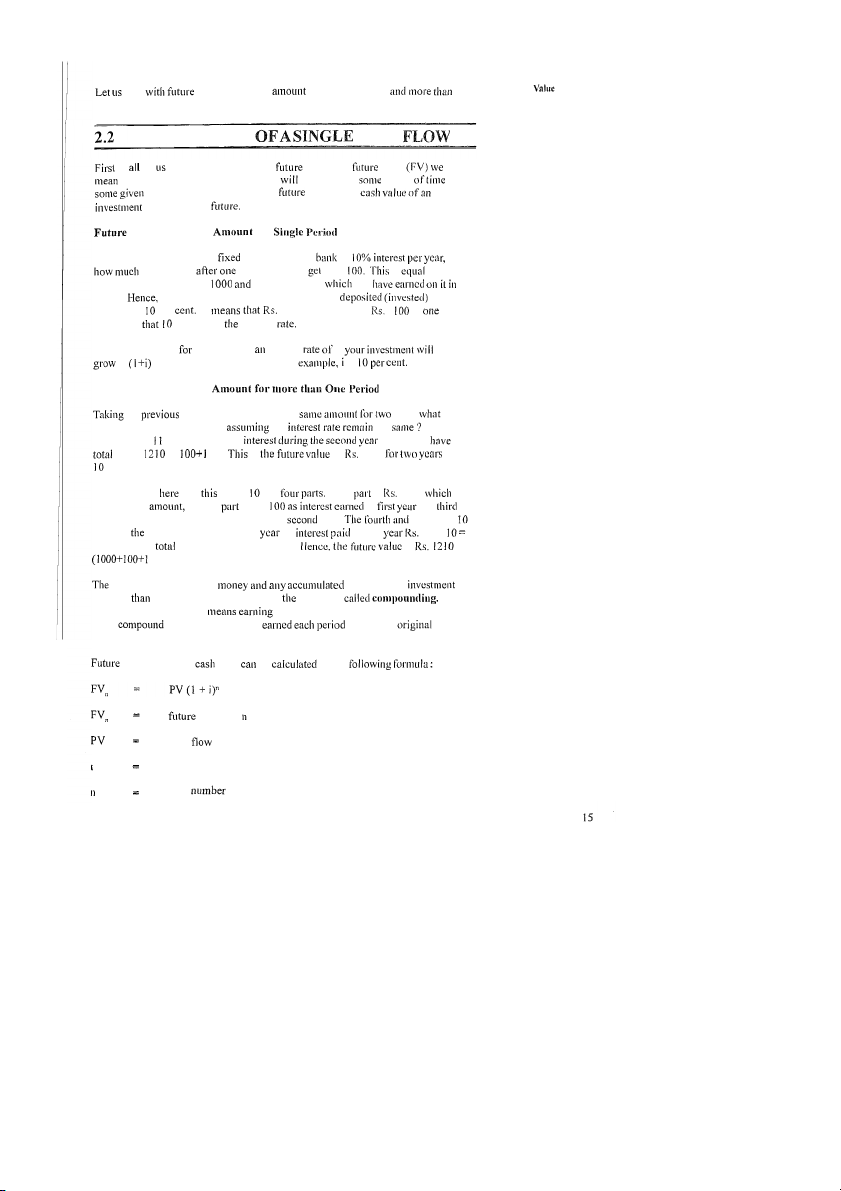
the amount of money an investment grow to over period at
interest rate. In other words, value is the at sometime in Value of a Single for If you deposit Rs. 1000 in a account of your at you will get year'? You will Rs. I is to your principal amount Rs. Rs. 100 interest you a year.
Rs. 1 100 is the future value o f Rs. 1000 for one year at per It 1000 today is worth I in year given per cent is interest Thus, if you invest one period at interest i, to
per rupee invested. In tlic above is
Future Value of a Single the example, if you invest the years
will you have after two years, tlic the You will earn Rs. 00 + 10 + Rs. 100 so you will of Rs. (1 10). is of 1000 at per cent. You can notice that Rs. 12 has First is 1000 is the principal second is Its. in and
part is another Rs. 100 earned as interest in year. last is Rs. which is interest earnecl in second on in first 100 x Rs. 10. So tlie interest earned is Its. 2 10. is oo+ 10). process of putting your interest on an for more a period, thereby reinvesting interest is Compounding tlie interest
interest on interest. We can call tlie result interest. The interest only on tlie principal is c
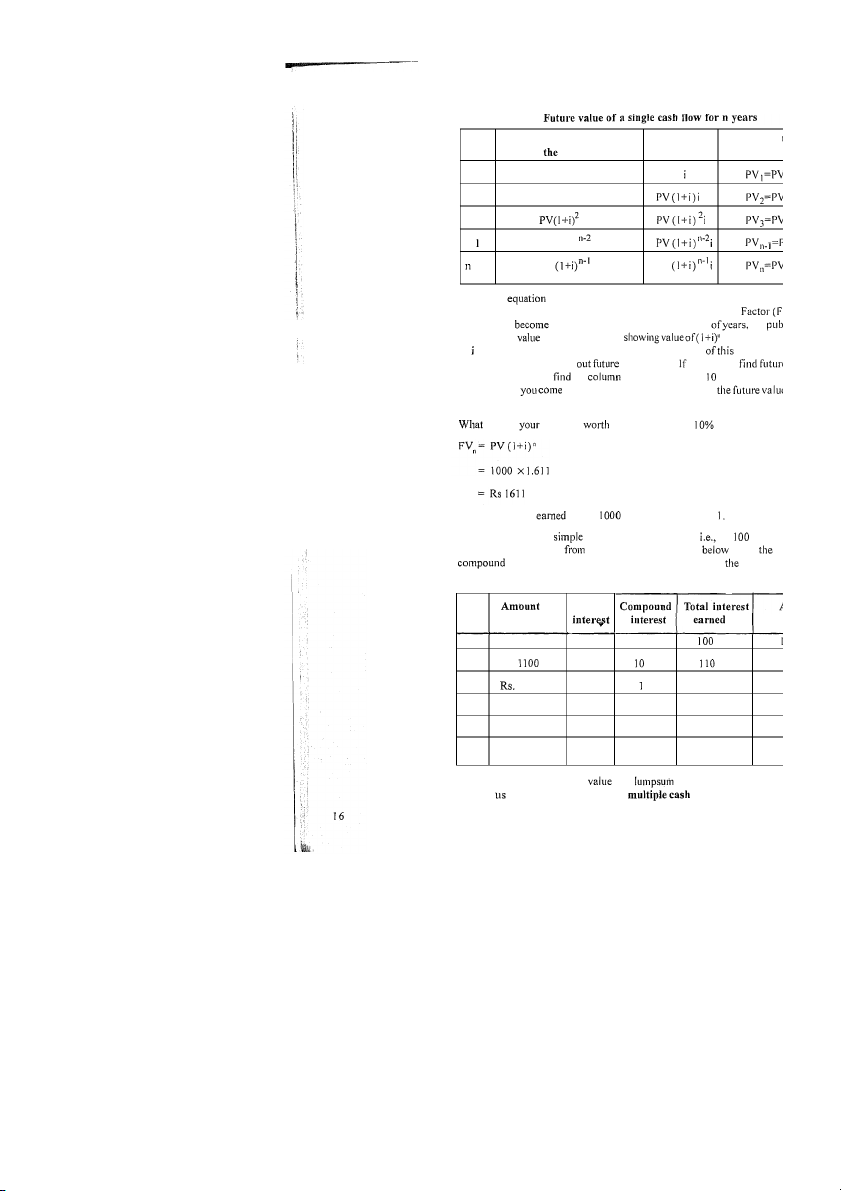
alled simple interest. value of a single flow be by tlie value for years cash rate of interest per year total of years , Foundation of Finance Year
Amount in the beginning of Interest Amount at period the 1 PV PV X 2 PV(1 +i) 3 n- PV (1 +i) PV PV The above
in the table is a basic equation in compounding analysis
factor is called the compounding factor or Future Value Interest calculations
very difficult with increasing number the called Future tables are available with different c
o f and n. You would see such tables attached at the end block of th can use these tables to find value factor. you have to at 10% for five years, the that corresponds to percent and the the rows until
to five years. That is how we found for the example given below. will be Rs. 1000 after five years at ? The total interest on Rs. in five years is Rs. 61 In five years the total interest earned is Rs. 500, Rs. per year Rs. 111 (Rs. 61 1-500) is compounding. Table given shows sim
interest and total amount earned each year and at end of fiv Table 2.1 Year in Simple the beginning at the 1 Rs. 1000 100 0 2 Rs. 100 1 3 1210 100 2 121 1 4 Rs. 1331 100 33.1 133.1 1 5 Rs. 1464.1 100 46.4 146.4 1 500 110.5 610.5 We have discussed the future of a (single) amount for num Now let
calculate future value of flows. Let
with same example. Suppose you deposit Rs. 1000 today in a bank at 10%. of one you again deposit 1000. How now you two years? At of will have Rs. 21 00. 1 + deposit 1000). you have
this deposit for another year at at the end of year you will Rs. 2 100 x .10 Rs. 23 0.00 Let illustrate it of also called line I 1000 2) Future value 0 2 This is one way of out value two deposits 1000. is another
The first Rs. 1000 is deposited two years at I its value is Rs. 1000 x x 1.2 100 Rs. 12 10 The second is deposited for so its value is Rs. total value is 0 1 23 1 0
So there are two ways to calculate value for the balance forward one year at a 2) Calculate tlie value of each and add methods will give you same answer. Effect of
You may remember tlie example of in beginning. Suppose his great father had Rs. 100 for 60 years ago 10% rate. it would
grown till today? Let us find out value Factor. FVIF ( 1 of In this case is Rs. 600 as Rs. 29,848 compounding. Therefore, effect of is great over to short periods 2.3 FUTURE OF AN ANNUITY
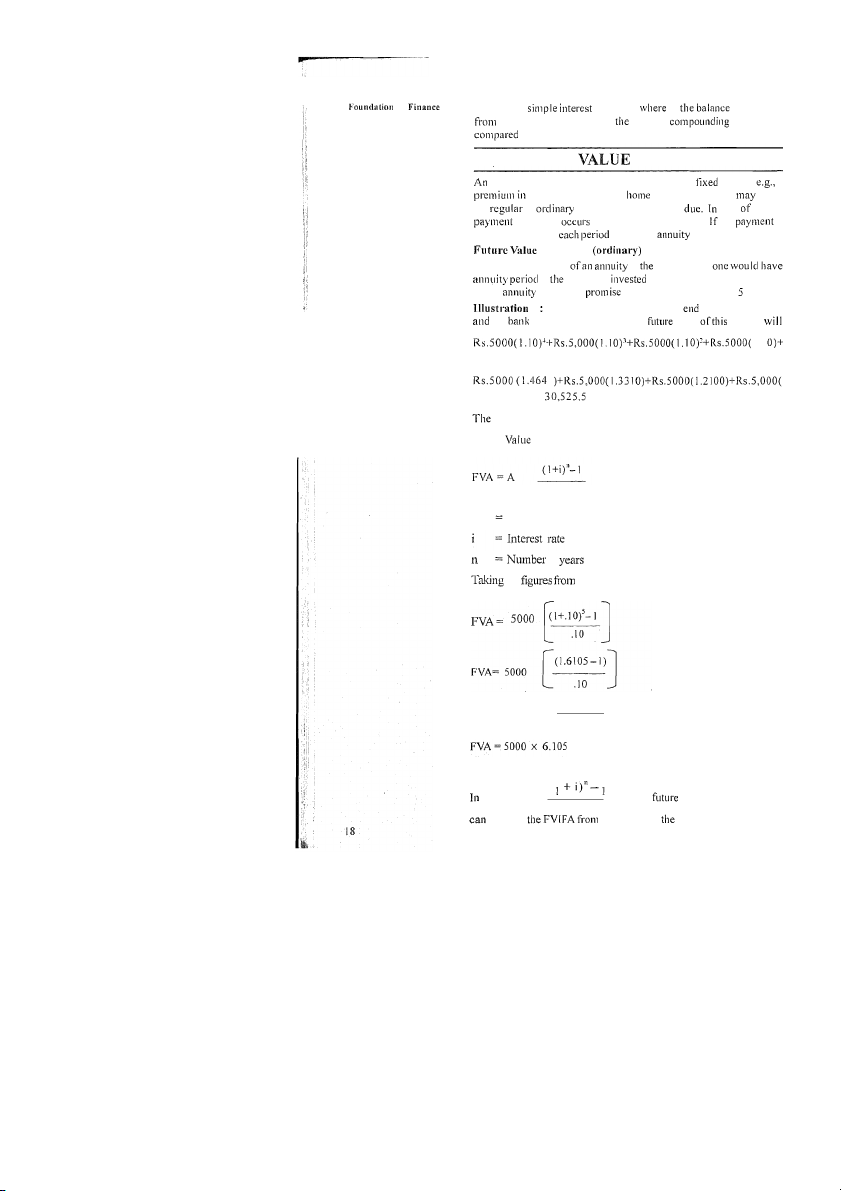
annuity is a series of payments (or receipts) of amount p case of life policy and loans etc. Annuity be of t ( n ) or annuity, and (b) annuity case regular or receipt at the end of each period. the or at the beginning o f it is called due. of Regular Annuity The compound value is total amount if amount is
at a certain rate of interest and i o f the period. A
to pay Rs. 1000 a year for years is 1
if you deposit Rs. 5000 at tlie of every year in a the is paying 10% interest, the value annuity 1 . 1 O r 1 = Rs. I
above procedure can be expressed as given below : I Future of An Annuity A Periodic cash flow of the illustration 1 0.6105 FVA = 5000 x 0 . 1 0 FVA = Rs. 30,525 the formula is called value interest factor o f i find out the table, see table for 10% for 5 years 5000 by 6.105 get 30525 of Money
2: A person plans to contribute Rs. 2,000 retirement account is paying 8% interest.
person retires in 30 years, what is the value of amount? A
You can also directly find out value interest for an annuity at 8% for 30 years from tlie value annuity table, is 13.28
value of annuity is 2,000 x 1 13.28 Rs. 2,26560 Finding interest rate
Illustration 3 : Suppose you receive a of Rs. 94,000 at of 8 years after paying
Rs. 8,000 for 8 years. What is the implicit (i) in this First of all find 96,000 = at tlie value annuity table and row corresponding years until we find
close to 12, it is 12.300 and is below the column of 12%. rate is below 12 per cent. Annuity Now, take an
where the total annuity
(received or paid), rate of interest and tlie is known. You are to find tlie amount of annuity. you deposit in a annually so you get Rs. at of at rate Annual x 1 = Rs. x 15.937 = Rs. 9,412.05
So you should deposit Rs. 9,412.05 in a every year for years in order to get Rs. at the end of years. Note: The called a denominator. Illustration 4: How a save to accumulate Rs. for
by tlie end of 10 years, at the rate 8%. 1 Annual Annuity = x Annual x Rs. 6,903
A person should save Rs. 6,903 annually years to get Rs. Future Value of Due An annuity for flows occur at of each per annuity due. Lease installment are tlie of annuity due. To
annuity due. tlie methods used in calculating annu wi I I be applied. Let us
calculation for tlie future value of a Rs. 1,000 ordin
for 3 years at 8 percent and compare it that of future value of annuity due 3 at 8 per
Note that the casli flows for the o
annuity occur at the end of periods and 3, those annu at beginning 2, 3 and 4. difference value of an ordinary annuity annuity is point at which
(FV) is calculated. For an ordinary annuity. FV is calculated as of the l
flow. while for an annuity due, FV is calculated as of period t flow. T i e value of 3 year annuity due is equal to Future 3 year ordinary annuity for one more pe riod. v annuity is as future value x of Year Ordinary annuity I 1,000 Rs. 1,000 Rs. 1,000
Future value of an ordinary annuity at 8% for 3 years, is Rs. 3246 Annuity due Rs. 1,000 Rs. 1,000 Rs. 1,000 (Rs. 1,000) (FVIFA (Rs. 1.08) (Rs. 3,246) (1.08) Rs.
Future value of an annuity due of 8% for 3 years (FVAD,). = Rs. 3,506 Progress A 1 ) What do you by value?
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... 2) What is compounding?
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... 3) What is difference between annuity and annuity due? 4)
You have deposited Rs. 10,000 in a fixed deposit in a bank at 6% rate of
interest. How much will you get after 5 years? much Rakesh will get 12 years if lie deposits in a fixed disposit at 1 O%? Foundation of
2.4 PRESENT VALUE OF A SINGLE CASH have seen that tlie
value of Re. 1 for one year at 10% is Rs.
put a question in a different way. How have to invest today
Re. I in one year? You know tlie value here is Re. but is t of Re.
You need Re. 1 at the end of the year, the present value that PV + I Present value of 1 is Re. 909. Let us see factor = FV, (1 + 1 In -
is the present value interest factor or discou Suppose you want to
Rs. 1500 in three years at 7% rate interest should you
today to get Rs. 1,500 in three years? Present value is just opposite of value. In future value we do
of money. In present value concept we discount back to present. Tl reducing
to their present value is called discou value today of the received in the is c alled its present value. know PV of Rs. 500 in year at 8%, then: PV x 1.08 = 500 1 PV = Rs. 462.5 1.08
You need not do much calculations. Value Tables help you in fin
present value of cash flow. These tables are given at end of this blo multiply
present value interest factor by amount. So, x 0 Rs. 462.5. (See
factor at 8% for one year i n present value table, i of M o n e y 2.5
PRESENT VALUE OF SERIES OF FLOWS
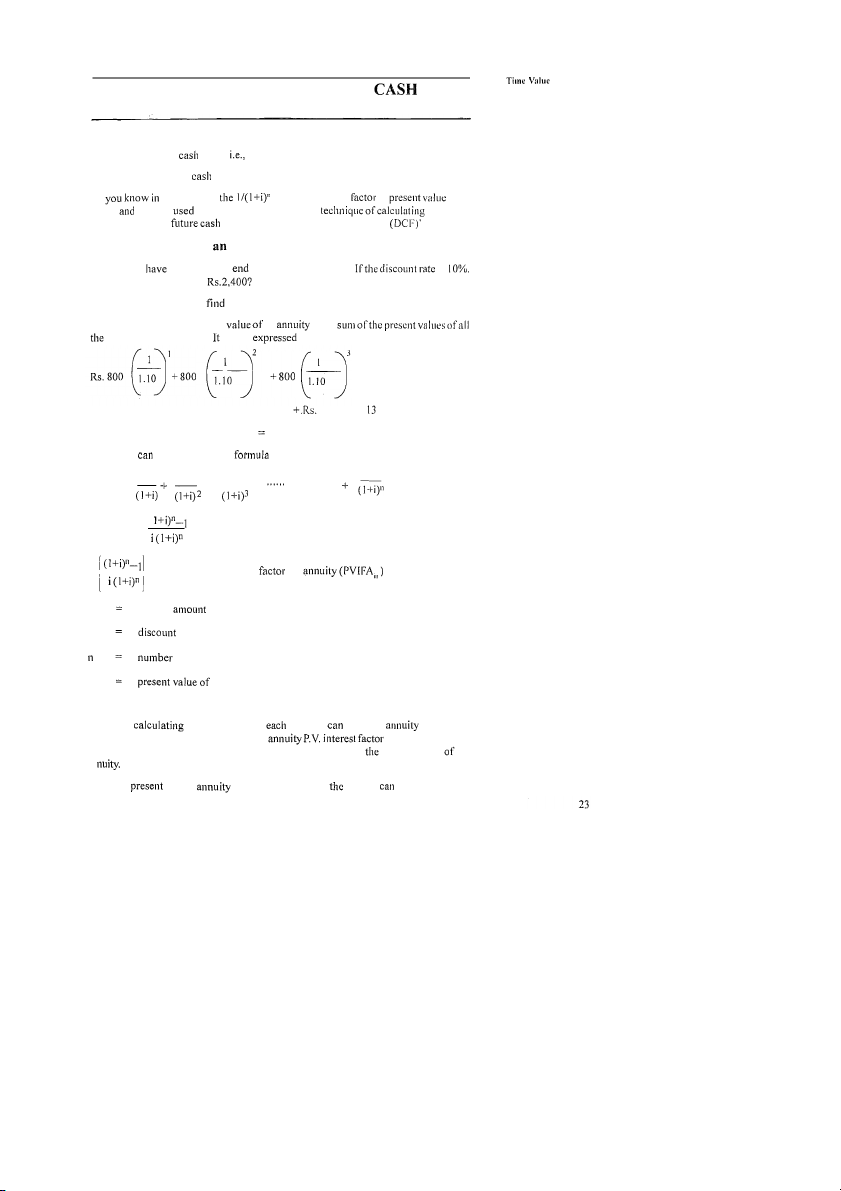
Tlie series of cash flows may be a) Even series of flows annuity b) Uneven series of flows As tlie equation is called discount or factor tlie rate is called discount rate. Tlie the present value of a flow is c alled 'Discounted Cash Flow valuation. 2.5.1 Present Value of Annuity You want to Rs. 800 at tlie of each of three years. is What tlie present value of There are two methods to out present value.
Under first method the present an is tlie inflows of this annuity. can be as follows:
= Rs. 800 x 0.9091 + Rs. 800 x 0.8264 800 x 0.75 =
Rs. 727.28 + 66 1.12 + 60 1.04 Rs. 1989.44 Tlie above be arrived by tlie A A A A A or PVA = + - + + - (1 +;)I)- I ( PVA = A I-I is present value interest for A annuity I rate of years PVA annuity Alternate Method Instead of present value for year we multiply amount by
annuity present value interest factor. See table, it is 2.48685
at 10% for 3 years. So Rs. 800 x 2.48685 = Rs. 1989.44 is present value an an Note: If value table is not available PVIFA be calculated as follows:-




