




Preview text:
lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
Macro Tut 6: The Money Growth & Inflation
Multiple Choice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
1. The price level rises if either
a. money demand shifts rightward or money supply shifts leftward; this rise in the price level is associated
with a rise in the value of money.
b. money demand shifts rightward or money supply shifts leftward; this rise in the price level is associated
with a fall in the value of money.
c. money demand shifts leftward or money supply shifts rightward; this rise in the price level is associated
with a rise in the value of money.
d. money demand shifts leftward or money supply shifts rightward; this rise in the price level is associated
with a fall in the value of money.
2. If velocity = 5, the price level = 1.5, and the real value of output is 2,500, then the quantity of money is a. 333.33. b. 750.00. c. 1,050.00. d. 8,333.33. M x V = Y x P ⇨ M = (2,500 x 1.5) / 5
3. When the money market is drawn with the value of money on the vertical axis, an increase in the money
supply causes the equilibrium value of money
a. and equilibrium quantity of money to increase.
b. and equilibrium quantity of money to decrease.
c. to increase, while the equilibrium quantity of money decreases.
d. to decrease, while the equilibrium quantity of money increases.
4. When the money market is drawn with the value of money on the vertical axis, an increase in the money
supply creates an excess
a. supply of money, causing people to spend more.
b. supply of money, causing people to spend less.
c. demand for money, causing people to spend more.
d. demand for money, causing people to spend less.
This cause price level to rise => people need to spend more to buy G and S
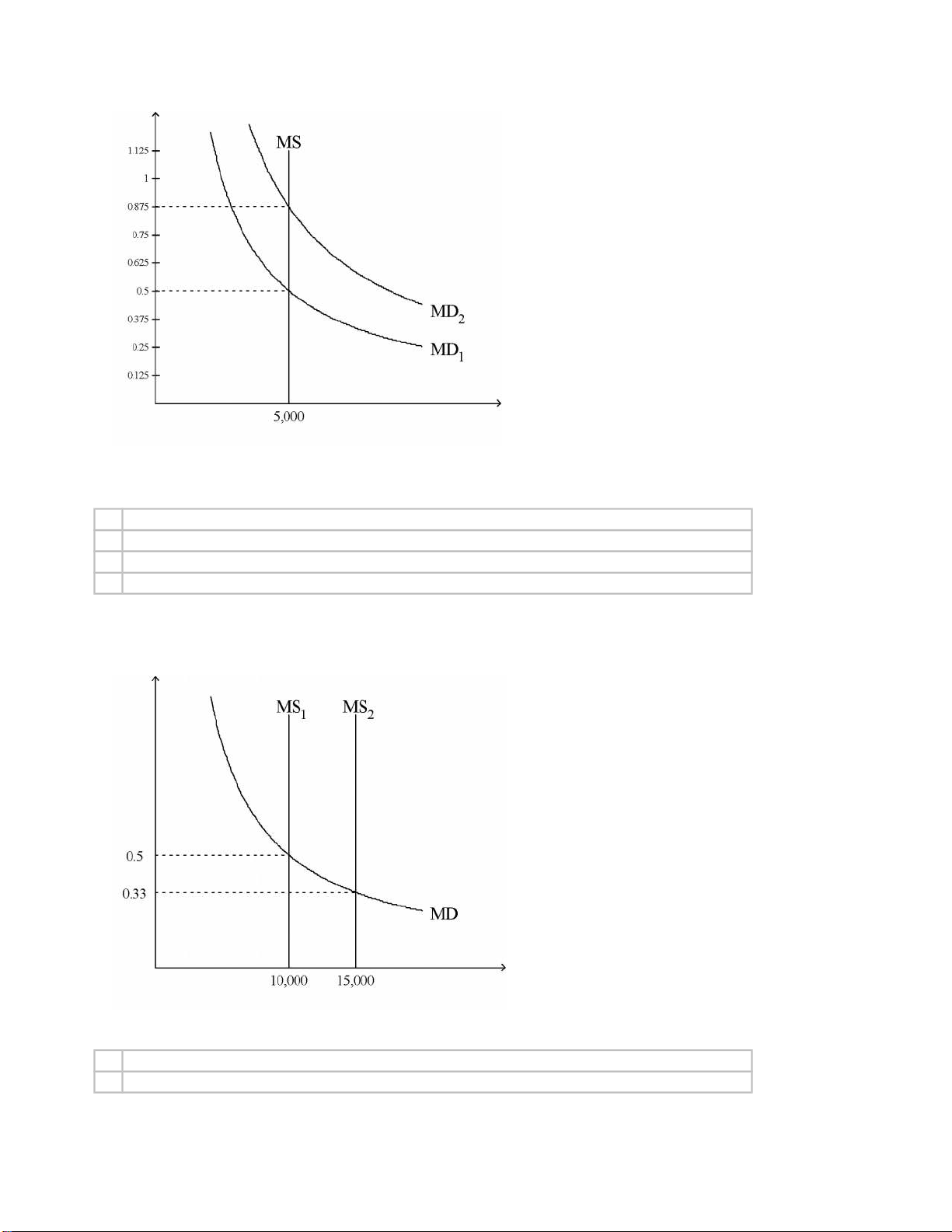
Figure 30-2. On the graph, MS represents the money supply and MD represents money demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes. lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
5. Refer to Figure 30-2. If the relevant money-demand curve is the one labeled MD1, then the equilibrium value of money is
a. 0.5 and the equilibrium price level is 2.
b. 2 and the equilibrium price level is 0.5.
c. 0.5 and the equilibrium price level cannot be determined from the graph.
d. 2 and the equilibrium price level cannot be determined from the graph.
Price level = 1/value of money => 1/0.5 = 2
Figure 30-3. On the graph, MS represents the money supply and MD represents money demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes.
6 . Refer to Figure 30-3. What quantity is measured along the vertical axis? a. the price level b. the velocity of money lOMoARcPSD| 39099223 c. the value of money d. the quantity of money
7 . According to the classical dichotomy, which of the following is influenced by monetary factors? a. real GDP b. unemployment c. nominal interest rates
d. All of the above are correct.
8 . According to the classical dichotomy, which of the following is not influenced by monetary factors?
a. nominal GDP and nominal interest rates b. real wages and real GDP
c. the price level and nominal GDP
d. None of the above is correct
Classical dichotomy NOT affected by REAL wages and GDP but AFFECTED by Nominal GDP, Interest Rate
9 . Velocity is computed as
a. ( P x Y ) / M .
b. ( P x M ) / Y .
c. ( Y x M )/ P .
d. ( Y x M ) / V . M x V = P x Y ⇨ V = (P x Y)/M
10. If Y and M are constant, and V doubles, the quantity equation implies that the price level
a. falls to half it’s original level. b. doubles. c. more than doubles. d. does not change. M x 2V = P x Y ⇨ P = (M x 2V)/Y
11. Suppose over some period of time the money supply tripled, velocity fell by half, and real GDP doubled.
According to the quantity equation the price level is now a. 6 times its old value. b. 3 times its old value. c. 1.5 times its old value. d. 0.75 times its old value. 3 M x 1/2V = 2Y x P
⇨ P = 3/4 (Áp dụng cthuc giống hệt câu 10)
12. Suppose that when the money supply changes, real output and velocity do not change. Then a 2 percent
increase in the money supply
a. decreases the price level by 2 percent.
b. decreases the price level by less than 2 percent.
c. increases the price level by less than 2 percent. lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
d. increases the price level by 2 percent.
102%M x V = P x Y ( 2 vế positive relationship) => 2% tăng bên trái dẫn đến 2% tăng bên phải
13. If money is neutral and velocity is stable, an increase in the money supply creates a proportional increase in a. real output only. b. nominal output only. c. the price level only.
d. both the price level and nominal output.
14. In the U.S., people are required to pay taxes on
a. nominal interest earnings, irrespective of their real interest earnings.
b. real interest earnings, irrespective of their nominal interest earnings.
c. real capital gains, irrespective of their nominal capital gains.
d. All of the above are correct.
15. You bought some shares of stock and, over the next year, the price per share increased by 5 percent, as did
the price level. Before taxes, you experienced
a. both a nominal gain and a real gain, and you paid taxes on the nominal gain.
b. both a nominal gain and a real gain, and you paid taxes only on the real gain.
c. a nominal gain, but no real gain, and you paid taxes on the nominal gain.
d. a nominal gain, but no real gain, and you paid no taxes on the transaction.
16. You put money into an account and earn an after-tax real interest rate of 2.5 percent. If the nominal
interest rate on the account is 8 percent and the inflation rate is 2 percent, then what is the tax rate? a. 28.00 percent b. 36.25 percent c. 43.75 percent d. 67.50 percent
Tax rate = (Nominal interest rate – Inflation rate – After tax real IR) / Nominal IR
17. For a given real interest rate, a decrease in the inflation rate would
a. decrease the after-tax real interest rate and so decrease saving.
b. decrease the after-tax real interest rate and so increase saving.
c. increase the after-tax real interest rate and so decrease saving.
d. increase the after-tax real interest rate and so increase saving.
Nominal interest rate – Inflation rate – After tax real IR = Nominal IR x Taxt rate (Biến đổi từ cthuc câu 16)
⇨ After tax real IR = Nominal IR – Inflation rate – (Nominal IR x Tax rate)
⇨ Inflation rate giảm thì vế bên phải trở nên lớn hơn => After tax real IR tăng
EXERCISES AND PROBLEMS Exercise 1: Fill in the blank with NO MORE THAN 4 WORDS
1. ……Inflation………..is an increase in the overall level of prices
2. Deflation is a ……decrease……….in the overall level of prices
3. Hyperinflation is ……extraordinary high rate of…………inflation lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
4. Inflation is more about the value of …money…..than about the value of …goods and services…..
5. Demand-Pull Inflation occurs when ……aggregate demand……grows up quickly and runs ahead of
…aggregate supply………….for goods and services
6. Cost-push Inflation occurs when there is a rise in …production costs…………….
7. ………Value of money…….is a number of goods and services bought by each dollar
8. Money Supply (MS) determined by the …Central Bank………and the …Banking system……..
9. According to The Quantity Theory of Money, the primary cause of inflation is the …growth in the
quantity of money………………………
10. …Monetary equilibrium……………. is the point at which the quantity of money demanded balances
the quantity of money supplied
Excercise 2: Find the underlined parts that are incorrect in these statements and correct them:
11. The quantity theory of money suggests that an increase in the money supply increases A B
real output proportionately. Price level C
12. In the long run, an increase in the money supply tends to have an effect on real A B
variables but no effect on nominal variables. Doesn’t tend C D
13. Inflation tends to stimulate saving (people hold more money for their consumption) because it A
raises the after-tax real return to saving. reduces B C
14. If inflation turns out to be higher than people expected, wealth is redistributed to A B lenders from borrowers. C
15. Monetary neutrality means that a change in the money supply doesn't cause a change A B C
in anything at all. Real variables D
Problem 1: (Chưa xong)
If the tax rate is 40 percent, compute the before tax real interest rate and the after-tax real interest rate in each of the
following cases. (đề bài cho rate mà k có chữ ‘’after’’ thì assume là ‘’before tax’’) a. The nominal interest rate is 10
percent, and the inflation rate is 5 percent.
b. The nominal interest rate is 6 percent, and the inflation rate is 2 percent.
c. The nominal interest rate is 4 percent, and the inflation is 1 percent. Tax rate= 40% = 0.4
Nominal IR before tax = 0.1/ 0.06/ 0.4
Nominal IR after tax = 0.06/ 0.024/ 0,016 ( after tax thì áp 40% tax rate vào nominal IR seẽ ra after tax)
Inflation rate= 0.05/ 0.02 / 0.01 lOMoARcPSD| 39099223
a, Real interest rate = nominal – inflation = 10-5 = 5
Nominal interest rate after tax= nominal interest rate - tax rate x nominal interest rate = 10% - 40% x 10%= 0.06 (a) (số liệu của
before tax) 6 - 0.4 x 6= 3.6 (b) 4 - 0.4 x4= 6.4 (c)
Real interest rate after tax= nominal IR after tax - inflation rate= 0.06- 0.05= 0.01 (a)
0.036 – 0.02 = 0.034 (b) 0.064- 0.01= 0.054 (c) R: before tax nominal rate I: inflation rate T: tax rate
Before tax real interest rate = r – i
After tax rea interest rate = r(1-t) – i
a, Before Real IR = before tax nominal – inflation = 10 – 5 = 5%
b, 6 – 2 = 4% c, 4 – 1 = 3% Problem 2:
Assume that the quantity theory of money holds and that velocity is constant at 5. Output is fixed at its fullemployment
value of 10,000, and the price level is 2.
a- Determine the real demand for money and the nominal demand for money.
M = (PxY)/V = 4,000 = nominal demand
Real demand of money = M/P = 2,000
b- In this same economy the government fixes the nominal money supply at 5000. With output fixed at its
fullemployment level and with the assumption that prices are flexible, what will be the new price level?
What happens to the price level if the nominal money supply rises to 6000?
P = (M x V)/Y = (5,000 x 5)/10,000 = 2.5
If MS rises => P = (6,000 x 5)/10,000 = 3




