

Preview text:
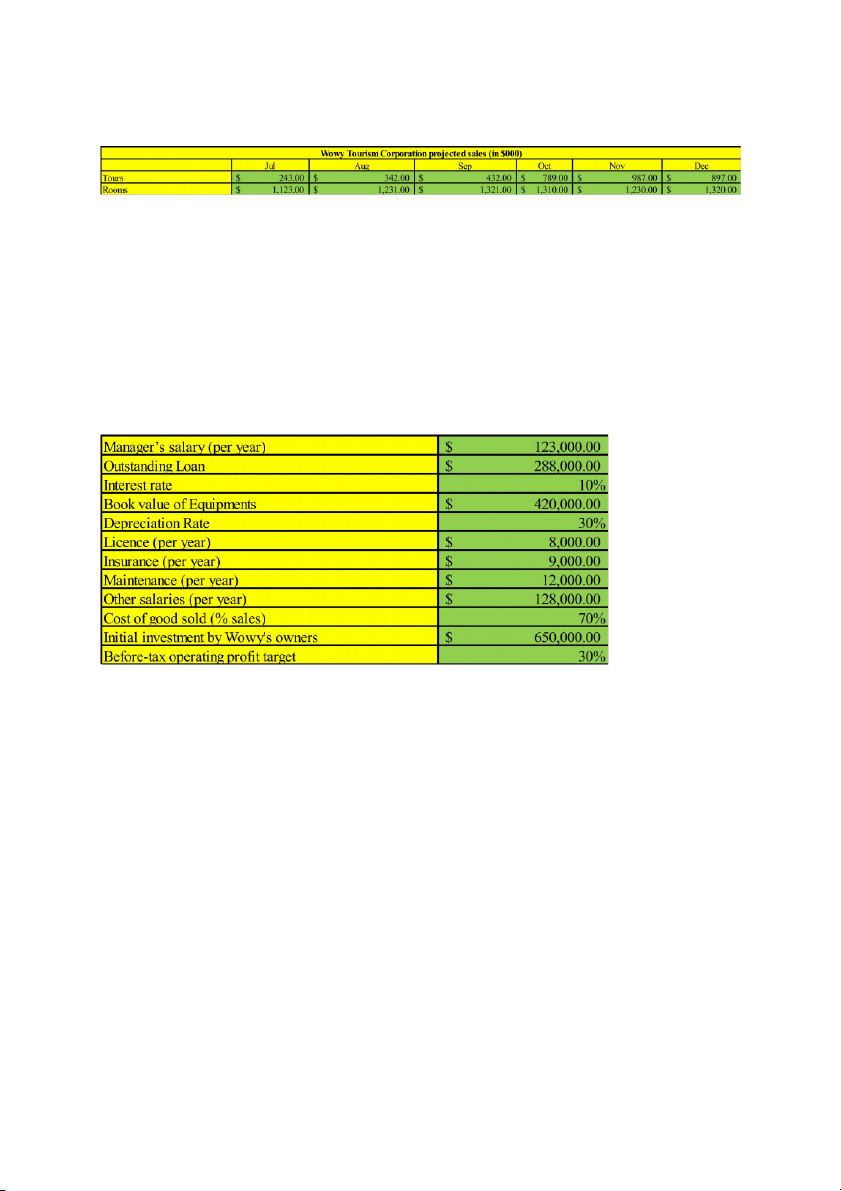
Question 01: The marketing department of Wowy Tourism Corporation has projected the following sales in
the last six months of the current financial year.
Most of Wowy Tourism Corporation’s sales are made to corporate clients. Past experience indicates that
25% of tour sales are for cash, 30% is collected in the month following the sale, 45% is collected two
months following the sale. In the past, 40% of room sales have been for cash, 50% is collected in the month
following the sale, 10% is collected two months following the sale. Prepare a schedule showing Wowy
Tourism Corporation’s projected cash receipts in September, October, November and December?
Question 02: TAK Tourism Services Corporation’s assets have a book value of $9,876,543 and the owners
believe the assets should generate a 66% return after tax. Assume tax is charged at the rate of 32%. The
corporation has several fixed costs which include 10% interest charged on a $6,543,210 bank loan, $543,210
of equipment and fittings depreciation and other fixed costs of $876,120 per year. The manager estimates
that operating expenses will be $1,999,999. Calculate TAK Tourism Services Corporation’ s sales?
Question 03: Wowy Tourism Corporation has presented the following information
Required: What sales revenue does the Wowy Tourism Corporation have to achieve in order to make its
before-tax operating profit target?
Giải: Interest=288,000x10%=28,800 (I)
Depreciation=420,000x30%=126,000
Sale=COGS(70% sale)+(Operating expenses+Depreciation+EBIT)(30% sale)
EBIT=EBT+I= 650,000x30%+28,800= 195,000+28,800= 223,800
Operating expenses= mana’s salary+licence+insurance+maintenance+other salaries= 123,000+8,000+9,000 +12,000+128,000=280,000
30% sale= 280,000+126,000+223,800= 629,800 => sale= 2099,333
Question 04: Prepare the balance sheet using the following WOWY's financial data:
1. Owner contributes $2,992,000 cash to commence business. Cash: 2,992,000; contributed capital: 2,992,000
2. Purchased a car for $311,000, paying $211,000 in cash and obtaining a long-term debt for the balance.
Long-term assets: 311,000; Cash: -211,000; Long-term debt: 100,000
3. Purchased inventory on credit for $2,800. inventory: 2,800; account payable: 2,800
4. Billed clients $6,130 for use of game facilities. sales: 6,130; account receivable: 6,130
5. Received $2,000 from customers billed in (4) above. Cash: 2,000; account receivable: -2,000
6. Paid $500 to trade creditors to reduce amount owing for inventory stock purchased. Cash: -500; account payable: -500
7. Owners withdrew $881,500 from the business. Cash: -881,500; contributed capital: -881,500
8. The accountant has determined that $900 of inventory stock has been used. inventory: -900; expense: 900
9. Paid $4,200 for miscellaneous expenses (telephone, electricity, etc.). cash -4,200; expense: 4,200
10. Repaid $80,000 of the long-term debt. Cash: -80,000; long-term debt: -80,000
Giải: Cash = 2,992,000 - 211,000 + 2,000 - 500 - 881,500 - 4,200 - 80,000 = 1,816,800
Inventory = 2,800 - 900 = 1,900
Account receivable = 6,130 - 2,000 = 4,130
-> current assets = 1,816,800 + 1,900 + 4,130 = 1,822,830 Long-term assets = 311,000
=> TOTAL ASSETS = current + long-term assets = 1,822,830 + 311,000 = 2,133,830
Account payable = 2,800 - 500 = 2,300 (current liability)
Long-term liability = 100,000 - 80,000 = 20,000
-> total liability: 2,300 + 20,000 = 22,300
Shareholder’s enquity = 2,992,000 - 881,500 = 2,110,500
Gain/Loss = Sale - Expenses = 6,130 - 900 - 4,200 = 1,030
-> total enquity: 2,110,500 + 1,030 = 2,111,530
=> TOTAL L&E = 22,300 + 2,111,530 = 2,133,830
Question 5: The conference department of the HNH Tourism Corporation has fixed costs of $558 per day. A
university is seeking a quote in connection with a conference it is planning to hold next year. The university
would like HNH to provide morning coffee, lunch, afternoon tea and to prepare conference materials to be
distributed to all conference attendees. The corporation’s cost of providing food and drink during the day is
$5.8 per attendee. In addition, preparing the conference materials would cost the corporation $3 per
attendee. The university has estimated that the conference will be attended by between 150 and 180 people. Required:
(a) What is the total average cost per attendee if the conference has an attendance of 150 people?
(b) What is the total average cost per attendee if the conference has an attendance of 180 people?
(c) Explain why the cost per attendee is affected by the number of people that attend the conference?
(d) If 150 people attend the conference and the corporation wants to earn a profit of 30% on revenue, what
price per person should be charged? Giải:
(a) Cost per attendee if 150 peo = 3 + 5.8 + 558/150 = 12.52
(b) Cost per attendee if 180 peo = 3 + 5.8 + 558/180 = 11.9
(c) Because the fixed cost of corporation wouldn’t change in spite of the attendees
(d) Price charged due to profit = 130%[150x(3+5.8) + 558] = 2,441.4
Price per person = 2,441.4/150 = 16.276
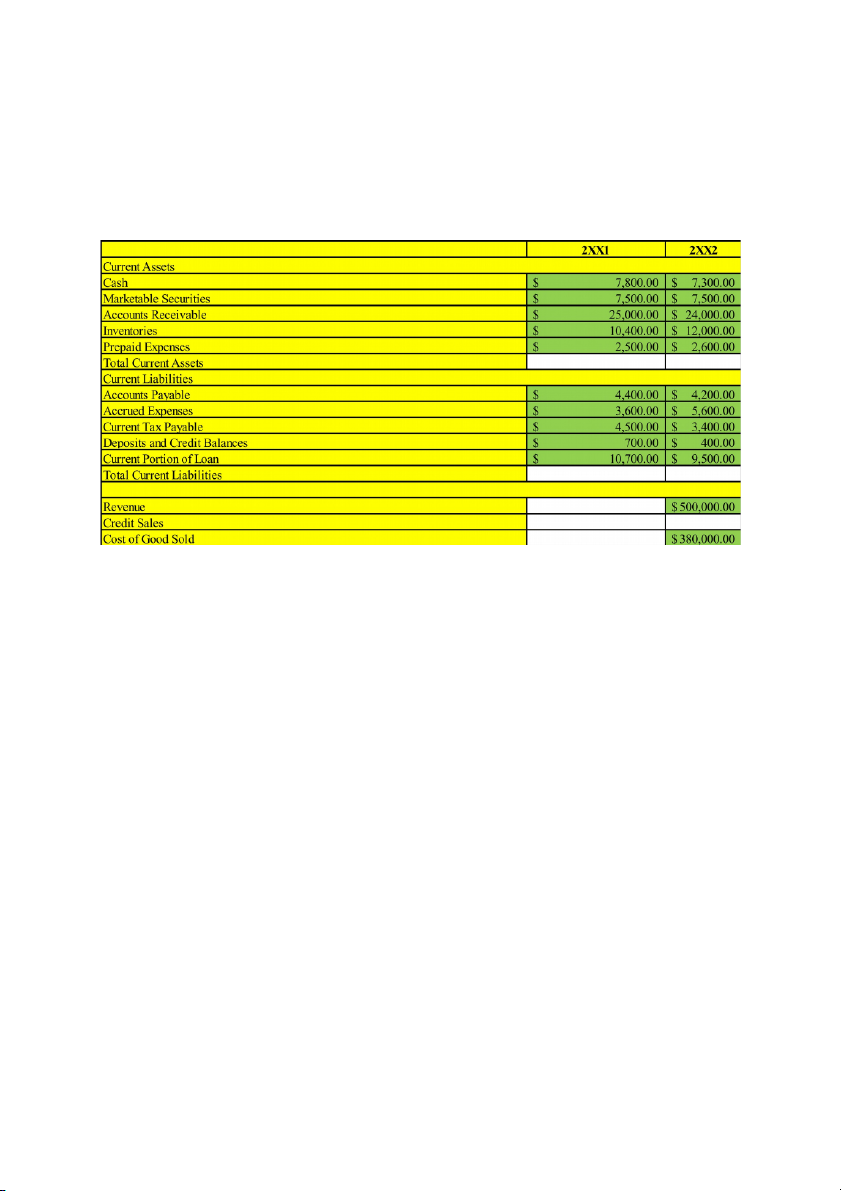
Question 6: Wowy Tourism Corporation has presented the following information
Revenue for the year 2XX2 was $500,000 (38% of this was credit sales) and the cost of good sold was $380,000. Required:
a/ For both years calculate the working capital?
b/ For both years calculate the current asset ratio?
c/ Calculate the account receivable turnover for Wowy? Calculate the account receivable collection period for Wowy?
d/ Calculate the inventory turnover for Wowy? Calculate days in inventory for Wowy? Giải:
a/ 2xx1 total current assets = 7,800 + 7,500 + 25,000 + 10,400 + 2,500 = 53,200
2xx1 total current liabilities = 4,400 + 3,600 + 4,500 + 700 + 10,700 = 23,900
2XX1 NWC = 2xx1 total current assets - 2xx1 total current liabilities = 53,200 - 23,900 = 29,300
2xx2 total current assets = 7,300 + 7,500 + 24,000 +12,000 + 2,600 = 53,400
2xx2 total current liabilities = 4,200 + 5,600 + 3,400 + 400 + 9,500 = 23,100
2XX2 NWC = 2xx2 total current assets - 2xx2 total current liabilities = 53,400 - 23,100 = 30,300
b/ 2xx1 current asset ratio = 2xx1 current assets/2xx2 current liabilities = 53,200/23,900 = 2.226
2xx2 current asset ratio = 2xx2 current assets/2xx2 current liabilities = 53,400/23,100 = 2.312
c/ receivable turnover = sales/average receivable = 500,000/[(24,000+25,000)/2] = 20.408
Receivable period = 365/receivable turnover = 365/20,408 = 17.885
d/ inventory turnover = COGS/average inventories = 380,000/[(10,400+12,000)/2] = 8.482
Inventories holding period = 365/inventory turnover = 365/8.482 = 43.032
Question 7: DVH Tourism Corporation has annual fixed costs of $2,645,088. The corporation is open for
360 nights in the year and charges an average room rate of $223. The variable costs associated with room
occupancy are $46 per room night. Required:
(a) How many room nights would the corporation sell to break even?
(b) If the corporation pays 34% tax, how many rooms must be sold in order to make an after-tax profit of $1,399,036.32? Giải:
(a) assume n as the room nights would be sold to break even
Revenue = fixed costs + variable costs <=> n x 223 = 2,654,088 + (n x 46) <=> n x (223-46) = 2,645,088 <=> n = 14994 (rooms)
(b) assume N as the room nights to make an after-tax of 1,399,036
EBT = NI+T<=>EBT=NI+34%EBT<=>68%EBT=NI<=>EBT=NI/68%=1,399,036.32/0.66= 2,119,752
Meanwhile EBT = sales - cost = sales - (fixed costs + N x variable costs) = N x 223 - (2,645,088 + N x 46)
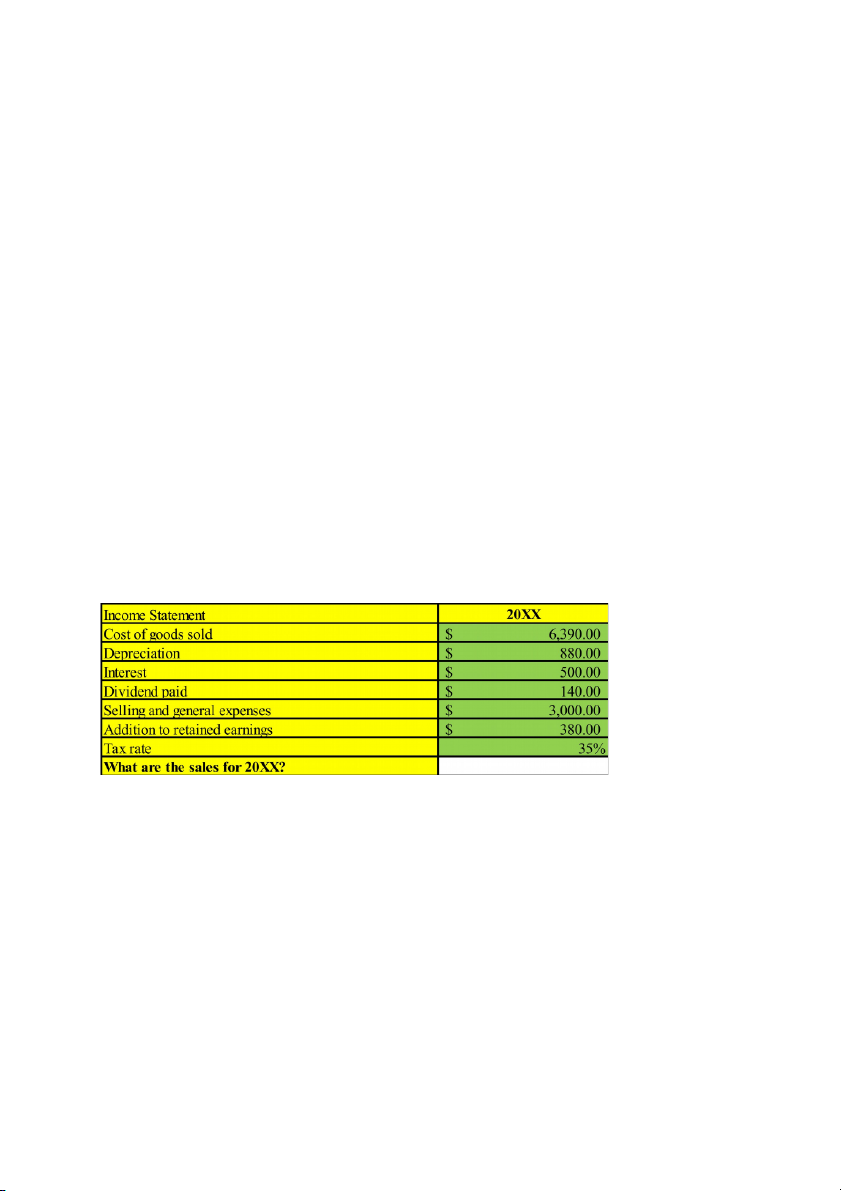
<=> 2,119,752 = 177N - 2,645,088 <=> N = 26970 (rooms) Question 8:
Giải: NI = retained earnings + dividend paid = 380 + 140 = 520
EBT = NI/(100% - tax rate) = NI/0.65 = 520/0.65 = 800
EBIT = EBT + I = 800 + 500 = 1,300
Sales = COGS + Operating expenses + Depreciation + EBIT = 6,390 + 3,000 + 880 + 1,300 = 11,570
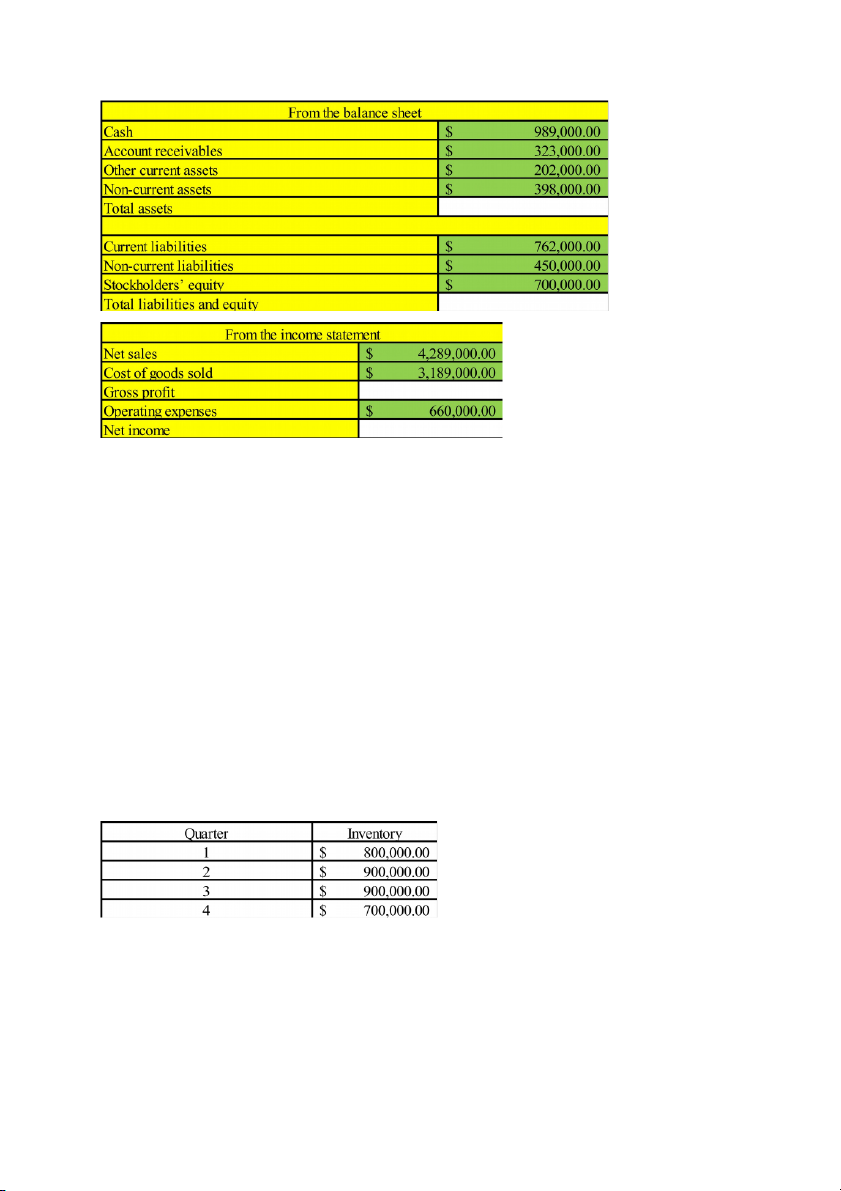
Question 9: Wowy Tourism Corporation has presented the following information
Fill in the blank and compute the following ratios: (a) current ratio, (b) debt ratio, (c) receivable turnover, (d)
asset turnover, (e) return on equity, (g) return on assets?
Giải: total assets = cash + account receivables + other current assets + non-current assets = 1,912,000
Total L&E = current L + non-current L + stockholder’s E = 1,912,000
Gross profit = sales - COGS = 1,100,000
NI = 1,100,000 - 660,000 = 450,000
(a) Current ratio = current assets/current liabilities = 1.2(4917)
(b) Debt ratio = total L/total assets = 0.634
(c) Receivable turnover = sales/average receivables = 13.279
(d) Assets turnover = sales/average total assets = 2.243
(e) ROE = NI/total equity = 0.643
(f) ROA = NI/total assets = 0.235
Question 10: In the last financial year AAA Tourism Corporation achieved a revenue of $49.12million and a
gross profit margin of 40%. Its end-of-quarter inventory balance were as follows: Required:
a/ Calculate the corporation’s inventory turnover and the average day of inventory?
b/ Comment on AAA Tourism Corporation’s liquidity, assuming most of its competitors (BBB Corp) record an inventory turnover of 60?
Giải: a/ COGS = sale x (100% - gross profit margin) = 49,120,000 x 0.6 = 29,472,000
Inventory turnover = COGS/average inventories = 35.724
Inventories holding period = 365/inventories turnover = 10.217
b/ dựa vào mặt bằng chung, ta thấy hiệu suất sử dụng hàng tồn kho của công ty thấp hơn. Điều này cho thấy
khả năng thanh khoản của công ty là kém hơn so với công ty đối thủ
Based on the general level, we see that the company's inventory utilization efficiency is lower. This shows
that the company's liquidity is worse than that of its competitors
Question 11: Wowy Tourism Corporation uses 58,580,000 tons of rice per year. The carrying costs are
$990/ton. The cost per order is $1580.
a/ Calculate the economic order quantity per order?
b/ Calculate the optimal number of orders per year?
c/ Calculate the total costs of optimal inventory? Giải: a/ EOQ = = 13674.15907
b/ optimal number of orders per year = sales/EOQ = 4283.993
c/ total cost = (EOQ/2 x carrying cost) + (sales/EOQ x cost per order) = 6836395.793
Question 12: The laundry department of the Ears Tourism Services Corporation orders concentrated laundry
detergent in 10-kilogram boxes. Each box costs $98. It costs $46 to place, process and receive a laundry
detergent order and Ears has estimated that it would cost $15 to hold a box of detergent in inventory for a
year. The corporation uses 25 boxes of detergent per quarter.
a/ Calculate the economic order quantity per order? Explain the result?
b/ Calculate the optimal number of orders per year? Giải:
Question 13: DVH Tourism Corporation has annual fixed costs of $9,696,000. The corporation is open for
365 nights in the year and charges an average room rate of $196. The variable costs associated with room
occupancy are $58 per room night. Required:
(a) How many room nights would the corporation sell to break even?
(b) How many rooms must be sold in order to make an before-tax profit of $4,868,000?




