








Preview text:
Cloud Computing Lecture
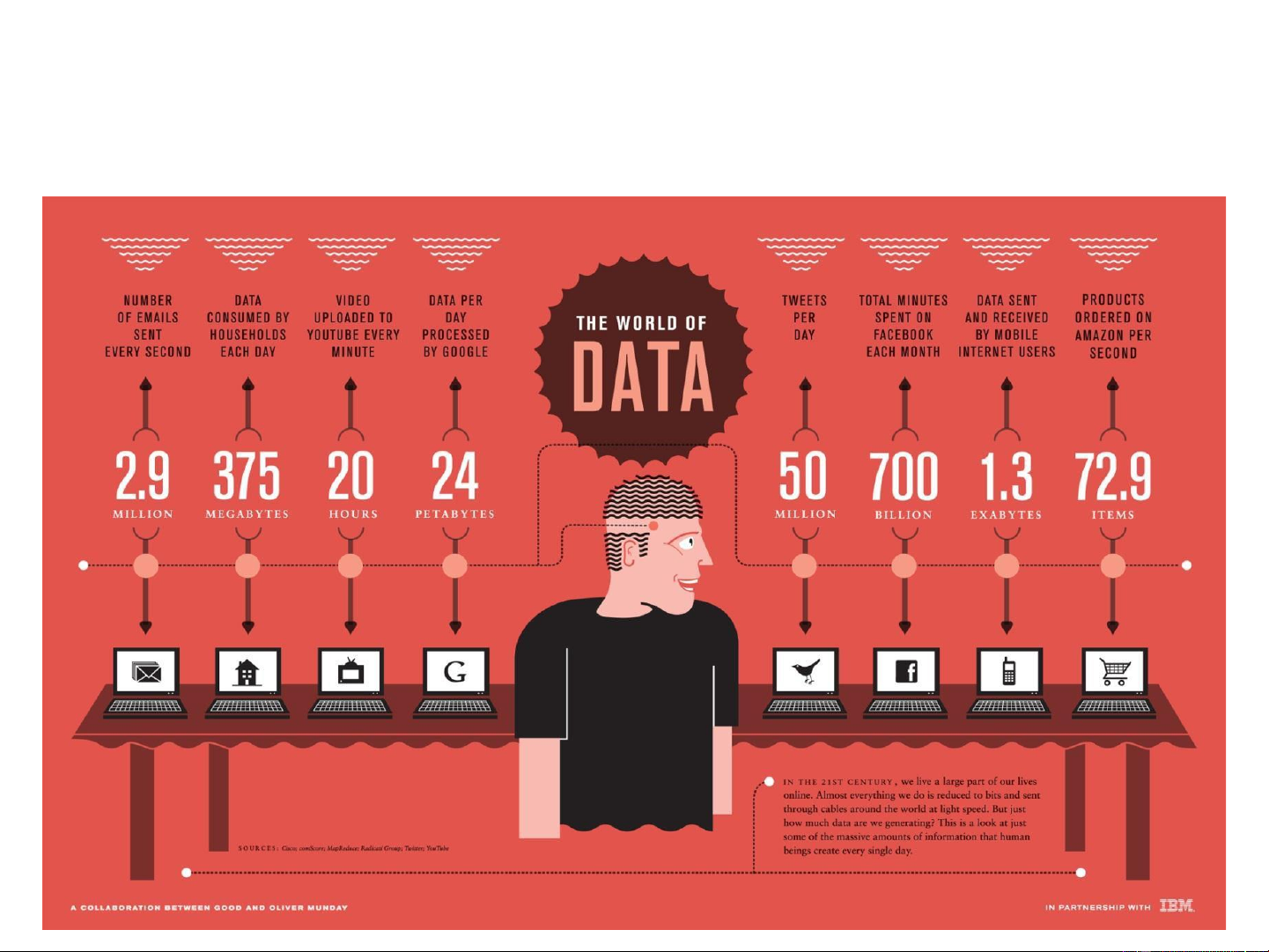
Introduction to Cloud Computing Our story… 2 Our Data Now… Personal Data Emails, Calendars, Contacts, Documents and Media Location Information, etc… 3 We Live in a World of Data… 4 The World of Data 5 Big Data
• Big data is defined as large pools of data that can be captured,
communicated, aggregated, stored, and analyzed. • Data continues to grow:
▪ In mid-2010, the information universe carried 1.2 zettabytes and 2020
predictions expect nearly 44 times more at 35 zettabytes coming our way.
• Applications are becoming data-intensive. 6 What Do We Do With Data? Store Share Access Process …. and Encrypt more!
We want to do these seamlessly... 7
Using Diverse Interfaces & Devices Desktops Mobile Devices …and even appliances Consumer Electronics
We also want to access, share and process our data
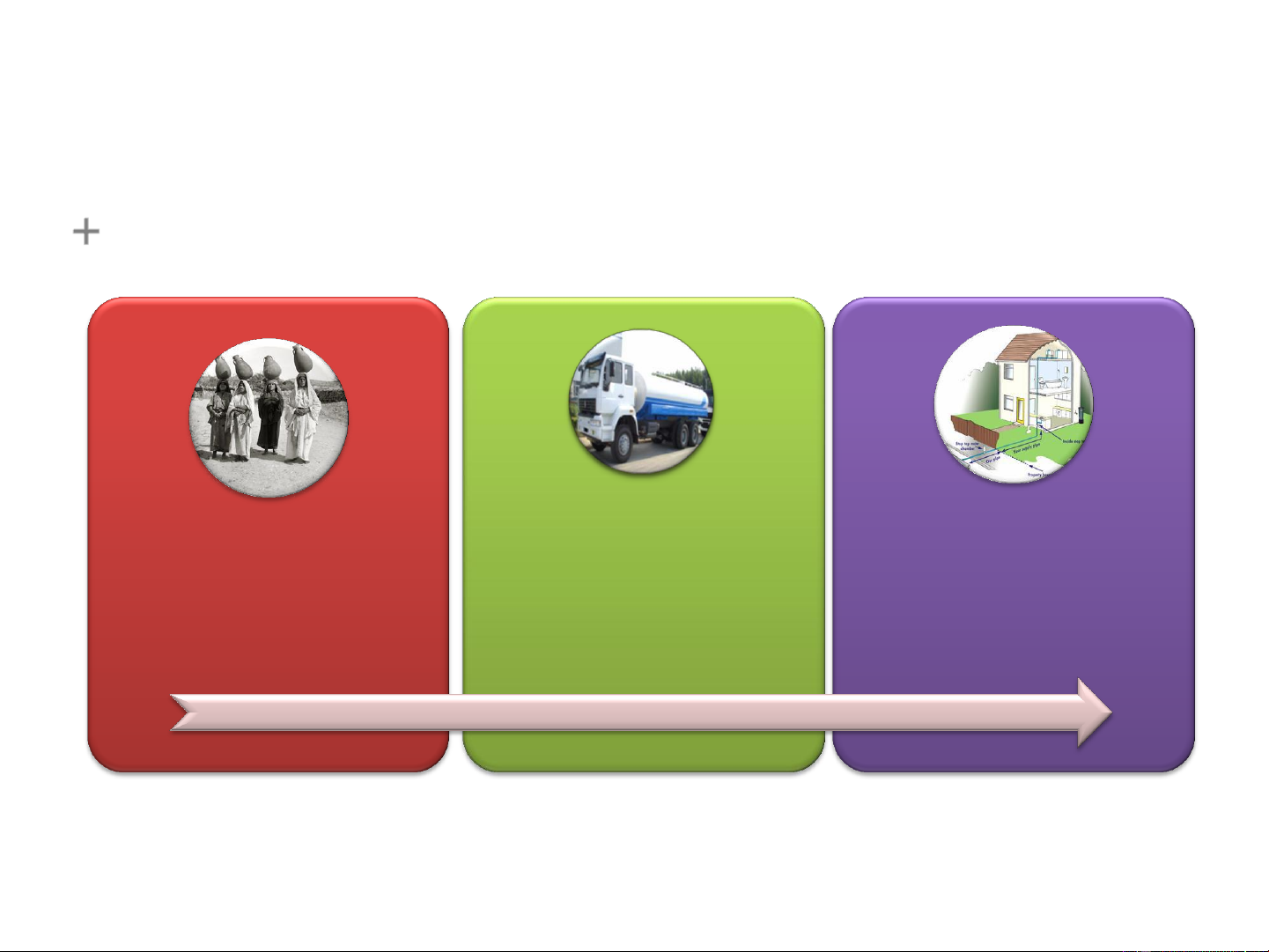
from all of our devices, anytime, anywhere! 8 What About the Future? How will you… …work on documents? …get your news & info? …create, access, store and share media? …navigate? …communicate with …live in an intelligent friends and family? home? 9 … 10 Has this Happened Before? Innovation Product Service 11 Think of it this Way … Evolution of water Utility Get a continuous Generate your own Buy it as a product supply of the utility utility through a dedicated connection 12 …and Banking? Evolution of Banking Traditional Banking No Banks Banking Instruments Internet Banking (Take care of your (Give your money (Cheques / Credit (…more services) own money ) to the bank) Cards) 14 So What is Cloud Computing? 15 Can We Define Cloud Computing?
“Cloud Computing is the transformation of
IT from a product to a service” Innovation Product Service 16 Cloud Computing
Transformation of IT from a Product to a Service Innovation of IT IT Products Cloud Computing New Disruptive Buy and Maintain On-Demand IT Technology the Technology services on a Pay-as You-Go basis 17
So… how would you transform
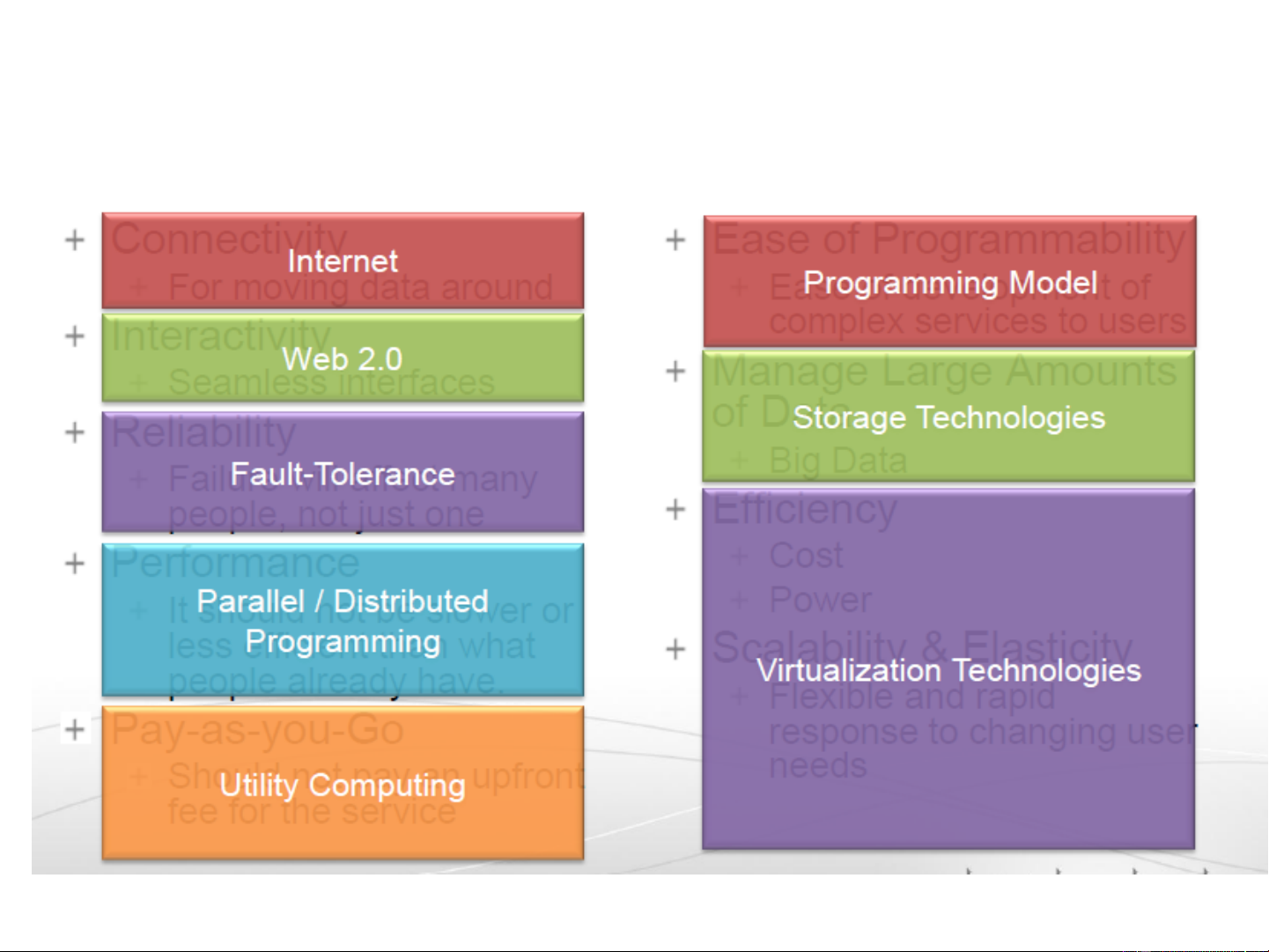
information technology into a Service? 18 Requirements to Transform IT to a Service • Connectivity • Ease of Programmability • For moving data around
• Ease of development of complex • Interactivity services to users • Manage Large Amounts • Seamless interfaces of Data • Reliability • Big Data
• Failure will affect many people, • not just one Efficiency • • Performance Cost Power • •
It should not be slower or less Scalability & Elasticity
efficient than what people already
• Flexible and rapid response to have changing user needs • Pay-as-you-Go
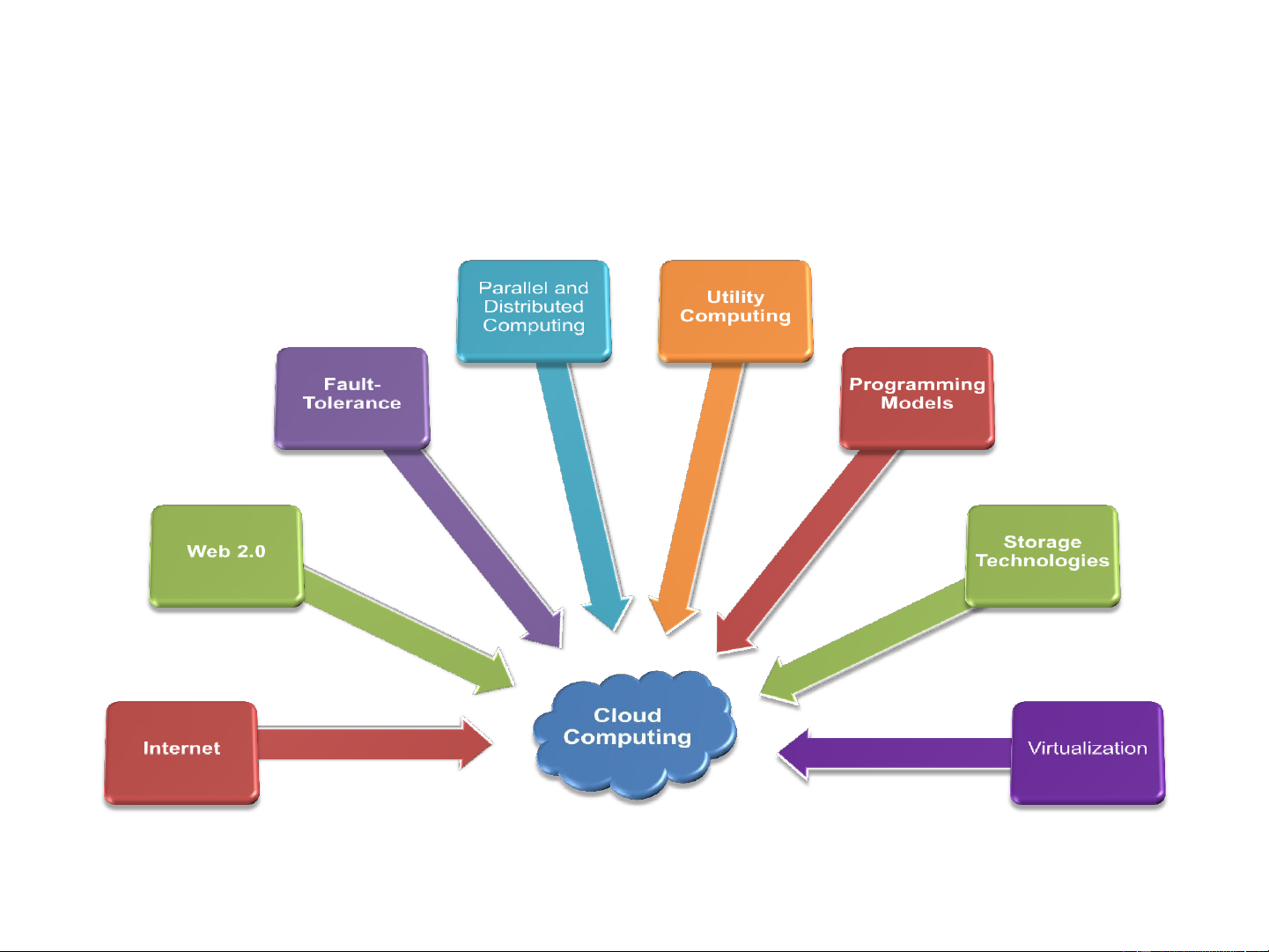
• Should not pay an upfront fee for the service 19 Requirements to Transform IT to a Service Combine the Enabling Technologies… 21