





Preview text:
Web ngữ nghĩa
MỘT SỐ HƯỚNG NGHIÊN CỨU VÀ Mục tiêu: phát triển ỨNG DỤNG các chuẩn chung và ô c ng nghệ cho phép máy tính có thể hiểu được nhiều hơn thông tin trên Web, sao cho chúng có thể hỗ trợ tốt hơn việ n vi c khám phá c khám thông tin, tích hợp dữ liệu, và tự động hóa các công việc.
Hanoi University of Technology – Master 2006 2 Các loại ứng dụng
Những gì có thể làm được
Các dạng dữ liệu bán cấu trúc
Nếu dữ liệu đầu vào ở dạng RDF, các hàm sau Các ứng d g ụng m g ở: thêm các chức năng m g ới với có thể thực hiện
các loại dữ liệu cũ và mới
Tích hợp nhiều nguồn dữ liệu Ví dụ:
Suy diễn để sinh ra thông tin mới
Truy vấn để sinh ra kết quả mong muốn
Quản lý thông tin cá nhân (Chandler) Mạng xã hội (FOAF) Các hàm tổng quát
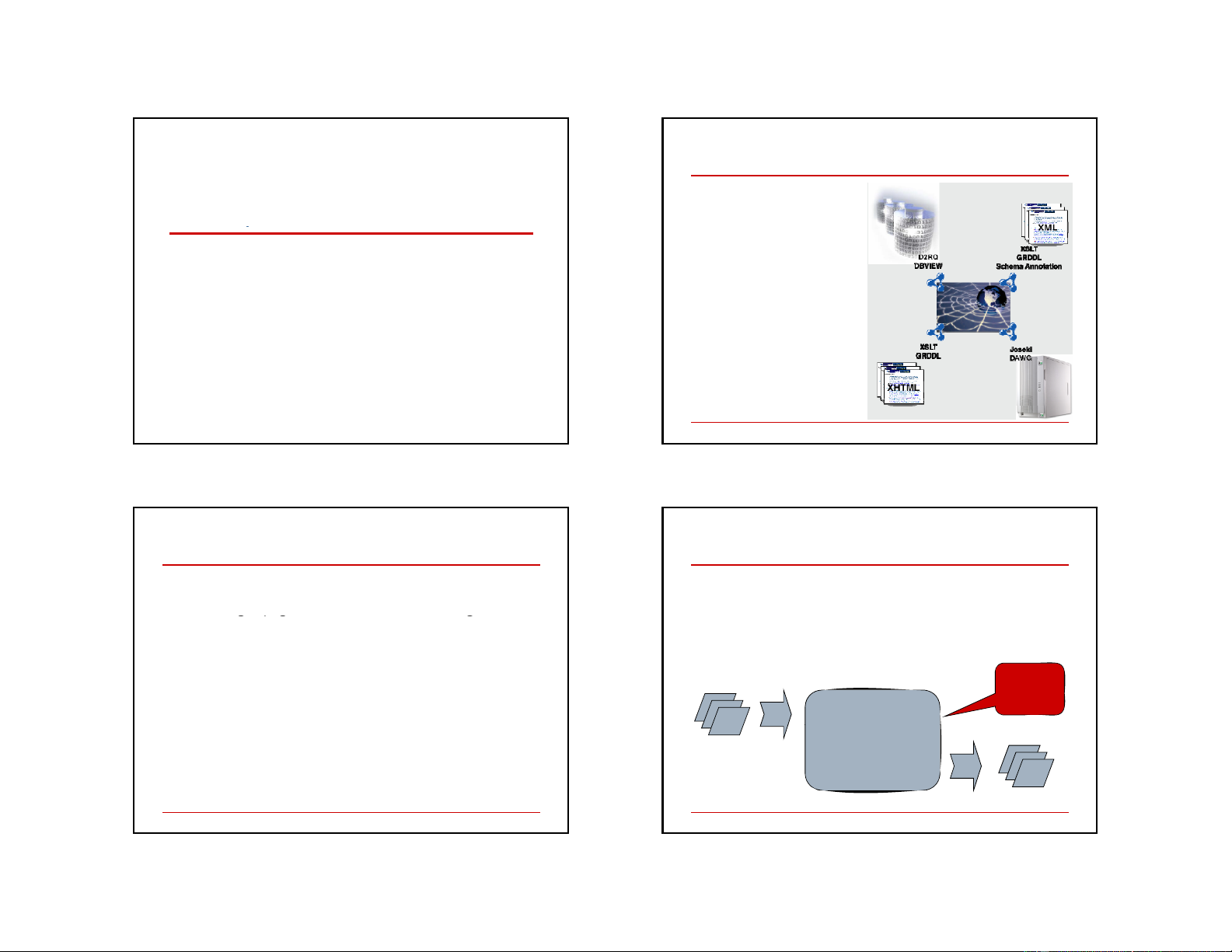
Tổ chức thông tin (RSS,PRISM) RDF Dữ D li ữ ệ li u th ệ ư u th vi ư ệ vi n/b ệ ả n/b o tàng (Dublin Core, A t ggrega i tion, Results Harmony) Inference, Query Input data RDF 3 4 1 Aggregation + Inference = New Knowledge
Aggregation + Inference: Example
Building on the success of XML
Consider three datasets, describing:
Common syntactic framework for data
vehicles’ passenger capacities
representation, supporting use of common tools the capacity of some roads
But, lacking semantics, provides no basis for
the effect of policy options on vehicle usage
automatic aggregation of diverse sources
Aggregation and inference may yield: RDF: a semantic framework
passenger transportation capacity of a given
Automatic aggregation (graph merging)
road in response to various policy options Inference from aggre gg gat g ed data sources
using existing open software building blocks generates new knowledge
Domain knowledge from ontologies and inference rules 5 6 What needs to be done? Benefits Information design
Greater use of off-the-shelf software Data-use strategie g s and inference rules
reduced development cost and risk
Mechanisms for acquisition of existing data Re-use of information designs sources
reduced application design costs; better
Mechanisms for presentation or utilization of
information sharing between applications the resulting information Flexibility
systems can adapt as requirements evolve Open access to informati inform o ati n making n maki possi ng bl possi e bl new applications 7 8 2
Lots of Tools (not an
Recommendation: Low risk approach exhaustive list!) Categories: Some names:
Focus on information requirements Triple Stores Jena, AllegroGraph, Mulgara,
this is unlikely to be wasted effort Inference engines Sesame, flickurl, … g
Start with a limited goal, progress by steps Converters TopBraid Suite, Virtuoso environment, Falcon, Drupal 7,
adapting to evolving requirements is an Search engines Redland, Pellet, …
advantage of SW technology; if it can do this Middleware Disco, Oracle 11g, RacerPro,
for large projects it certainly must be able to do CMS IODT, Ontobroker, OWLIM, Talis
so for early experimental projects
Semantic Web browsers Platform, …
Use existing open building blocks Development RDF Gateway, RDFLib, Open i env t ronmen s
Anzo, DartGrid, Zitgist, Ontotext, Semantic Wikis Protégé, … … Thetus publisher, SemanticWorks, SWI-Prolog, RDFStore… … 9 10 Application patterns
To “seed” a Web of Data...
It is fairly difficult to “categorize” applications
Data has to be published, ready for integration Some of the applica pp tion patter p ns: And this is now happeni pp ng! g data integration Linked Open Data project
intelligent (specialized) Web sites (portals) with
eGovernmental initiatives in, eg, UK, USA, improved local search France,...
content and knowledge organization
Various institutions publishing their data
knowledge representation, decision support data registries, repositories
collaboration tools (eg, social network applications) 11 12 3
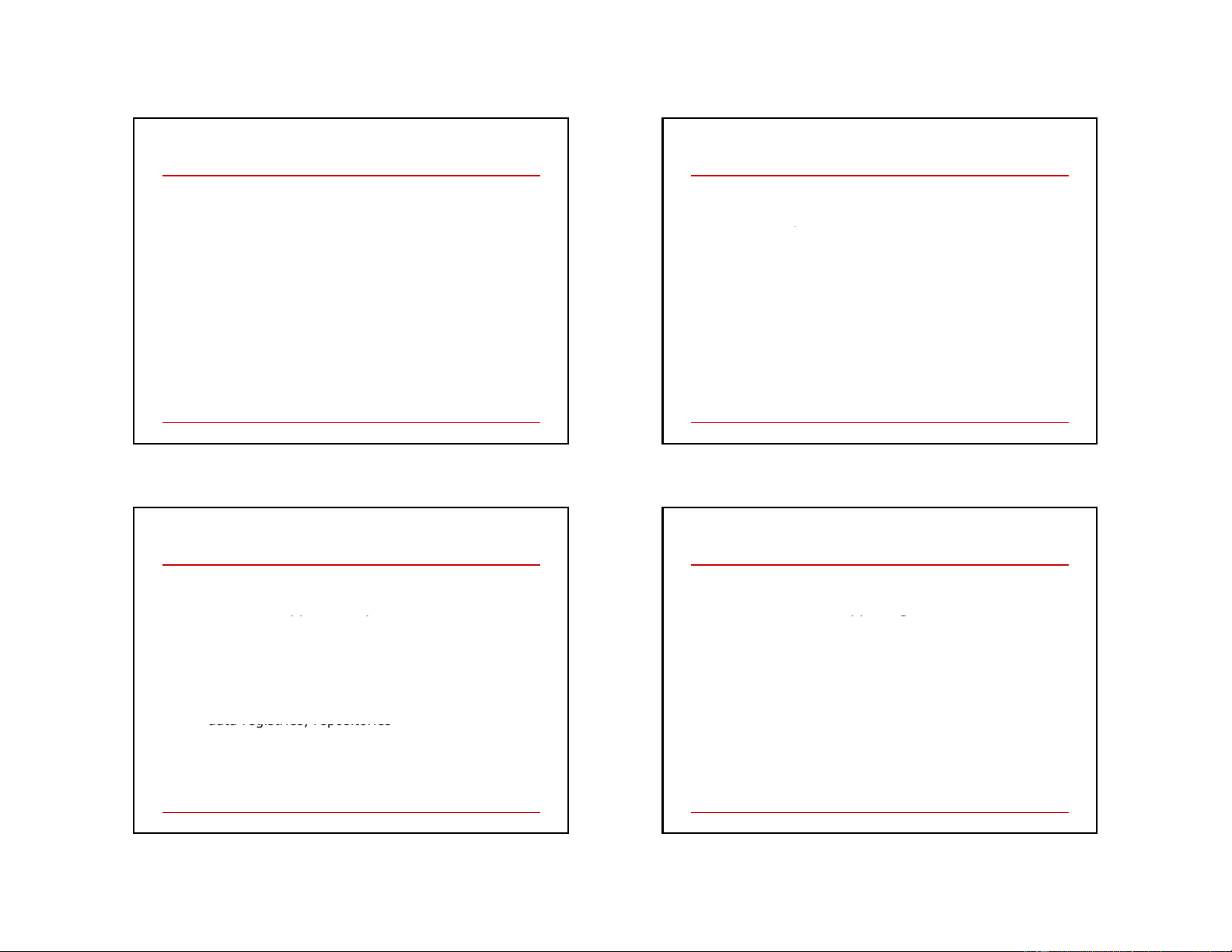
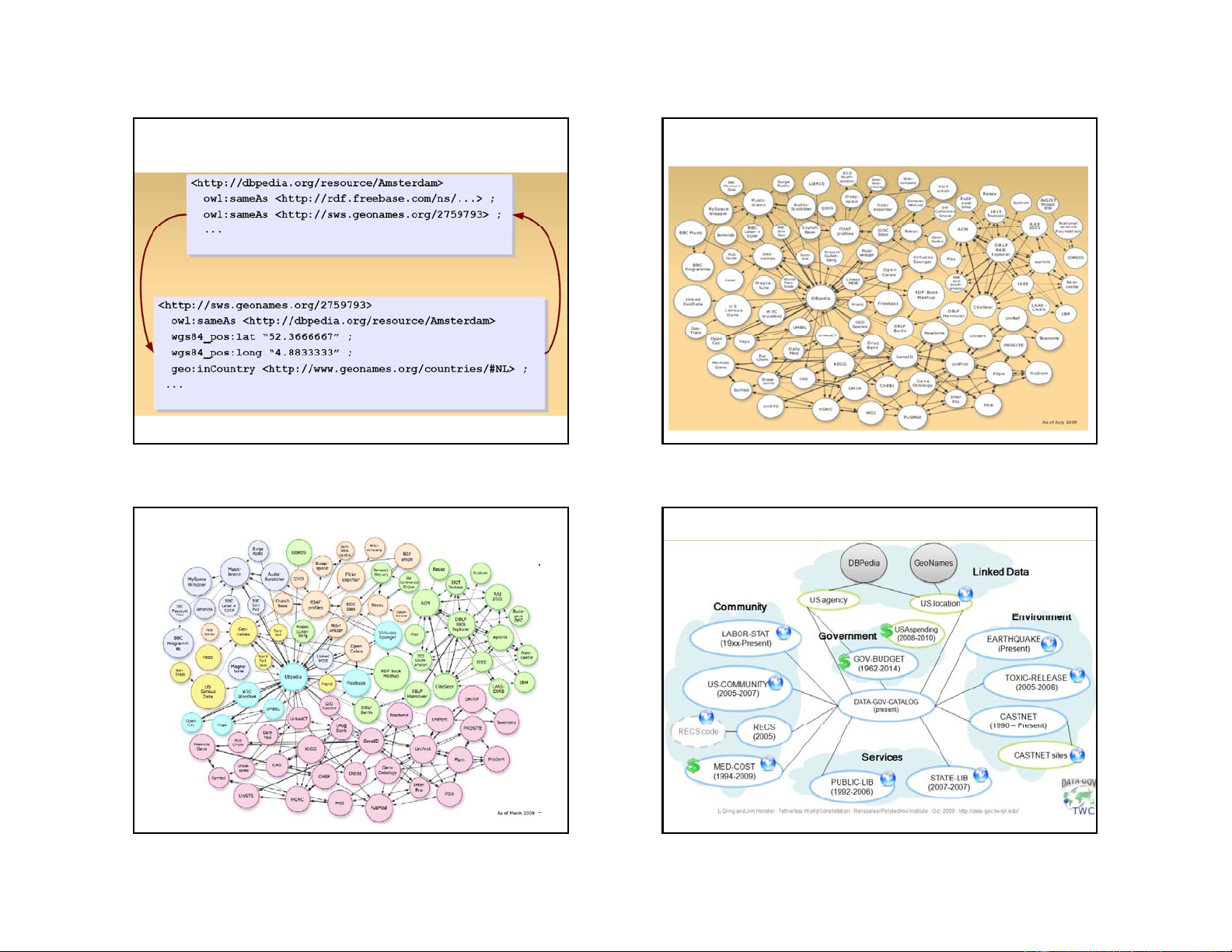
Linking Open Data Project
Goal: “expose” open datasets in RDF Set RDF links among the g data items from different datasets Set up SPARQL Endpoints
Billions triples, millions of “links” 13 14
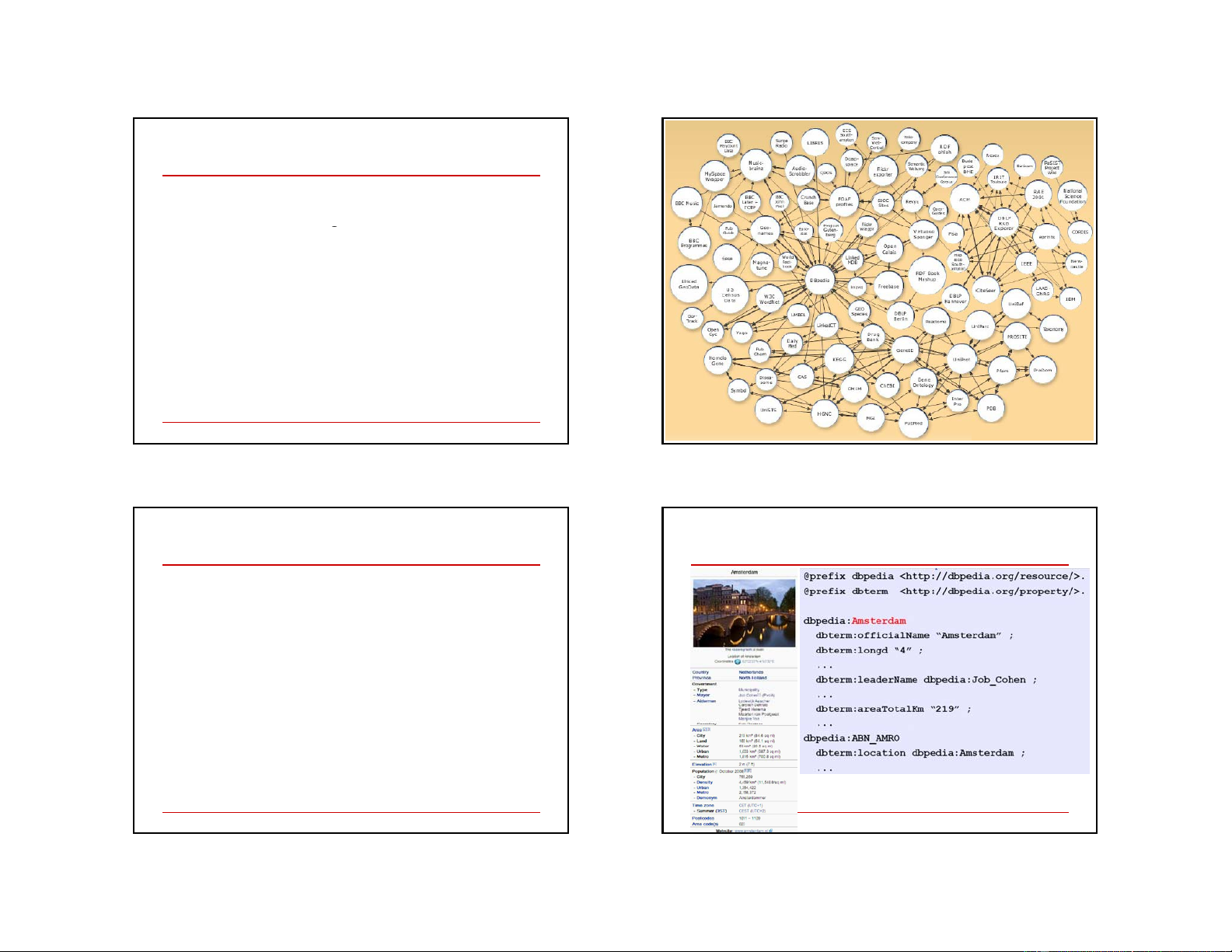
Extracting structured data from
Example data source: DBpedia Wikipedia
DBpedia is a community effort to extract
structured (“infobox”) information from Wikipedia
provide a SPARQL endpoint to the dataset
interlink the DBpedia dataset with other datasets on the Web 15 16 4
Automatic links among open
Linking Open Data Project datasets (cont)
Processors can switch automatically from one to the other… 17 18
Linking Open Data Project (cont) Linked Open eGov Data 19 20 5
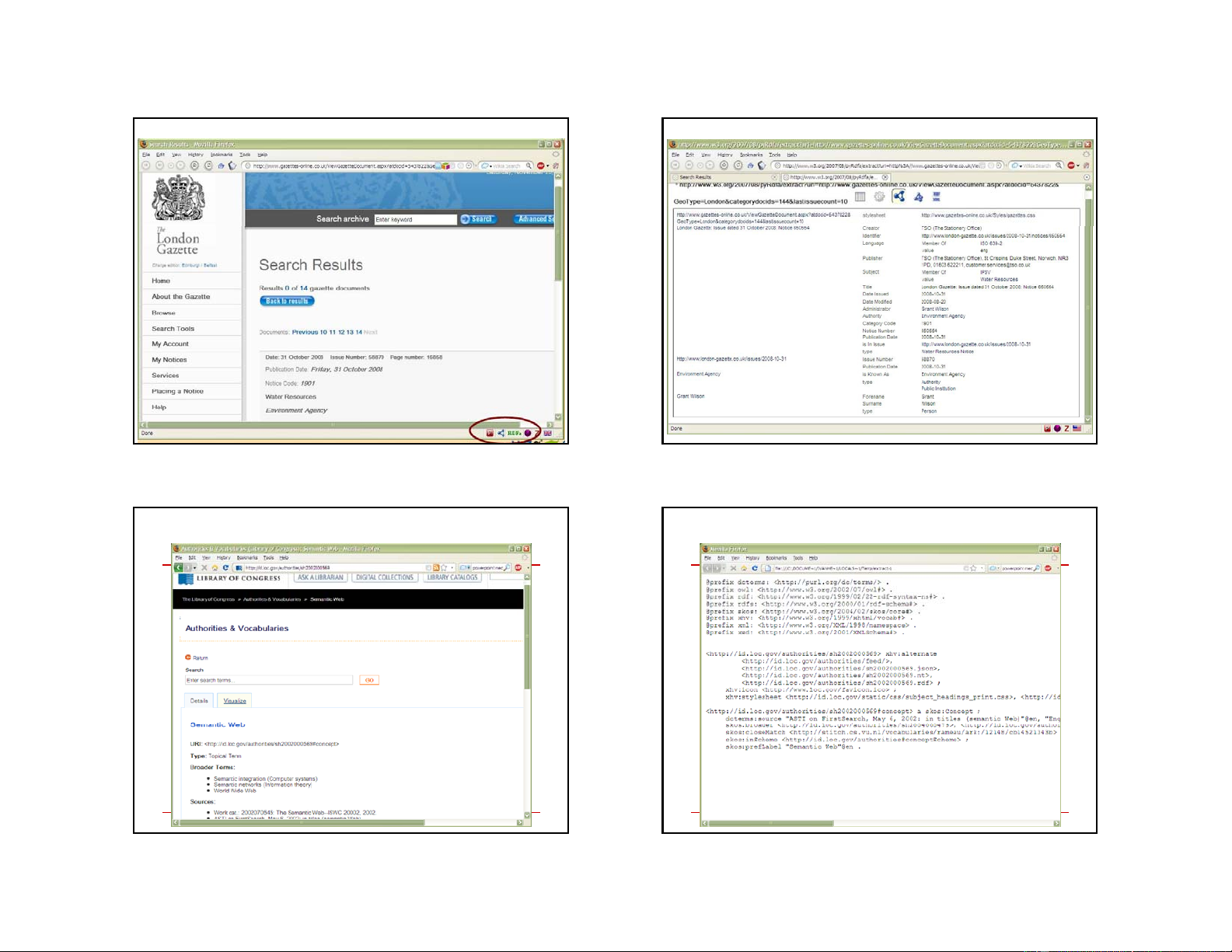
Publication of data (with RDFa): London Gazette
Publication of data (with RDFa): London Gazette 21 22
Publication of data (with RDFa & SKOS): Library of
Publication of data (with RDFa & SKOS): Library of
Congress Subject Headings
Congress Subject Headings 23 24 6
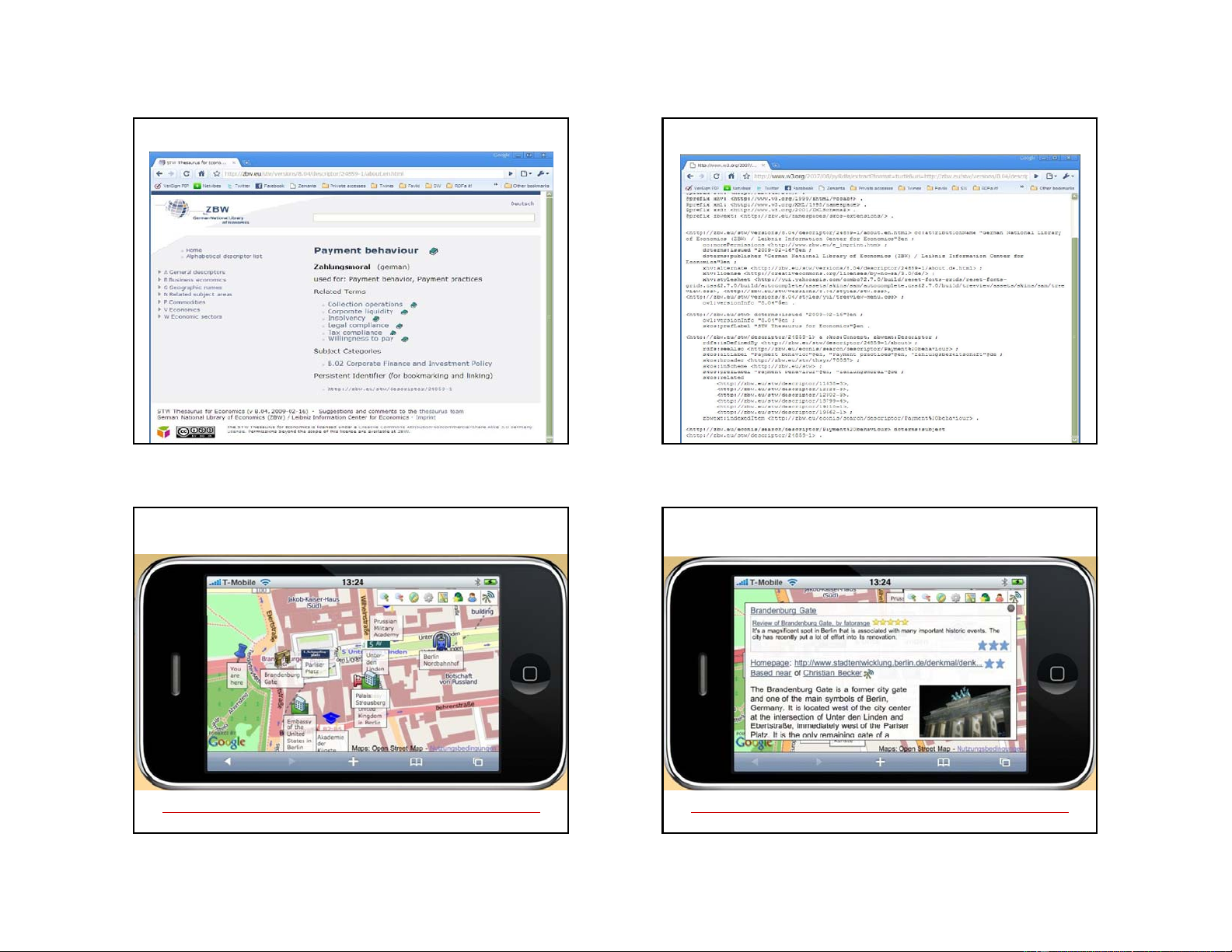
Publication of data (with RDFa & SKOS):Economics
Publication of data (with RDFa & SKOS):Economics Thesaurus Thesaurus 25 26
Using the LOD cloud on an iPhone
Using the LOD cloud on an iPhone 27 28 7
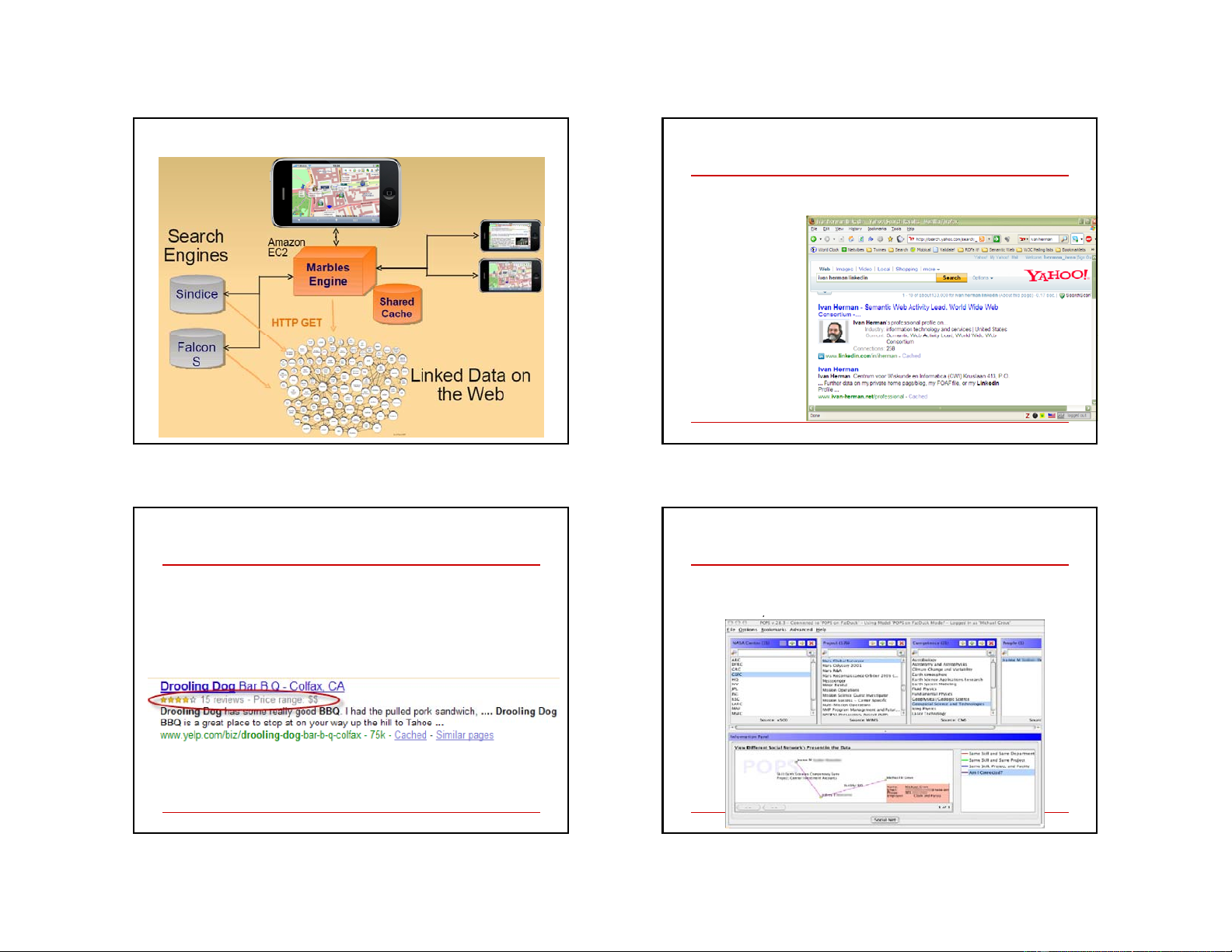
You publish the raw data, W3C
Using the LOD cloud on an iPhone use it… Yahoo’s SearchMonkey
Search based results may be customized via small applications Metadata e embedded in pages (in RDFa, eRDF, etc) are reused Publishers can export extra (RDF) data via other formats 29 30 Google’s rich sniplet Find experts at NASA
Expertise locater for nearly 70,000 NASA civil servants
Embedded metadata (in microformat or RDFa)
is used to improve search result page
over 6 or 7 geographically distributed databases, data sources, and , web services…
at the moment only a few vocabularies are
recognized, but that will evolve over the years 31 32 8
Public health surveillance A frequent paradigm: (Sapphire) intelligent portals
Integrated biosurveillance system (biohazards,
bioterrorism, disease control, etc)
“Portals” collecting data and presenting them
Integrates multiple data sources to users new data can be added easily
They can be public or behind corporate firewalls
Portal’s internal organization makes use of semantic data, ontologies
integration with external and internal data better queries, often better based on controlled vocabularies or ontologies… 33 34
Help in choosing the right drug regimen
Portal to aquatic resources
Help in finding the best drug regimen for a specific case, per patient Integr Inte ate gr ate data fr om data fr var om i var ous sour ous ce sour s ce (patie s nts (patie ,
physicians, Pharma, researchers, ontologies, etc)
Data (eg, regulation, drugs) change often, but the tool is
much more resistant against change 35 36 9
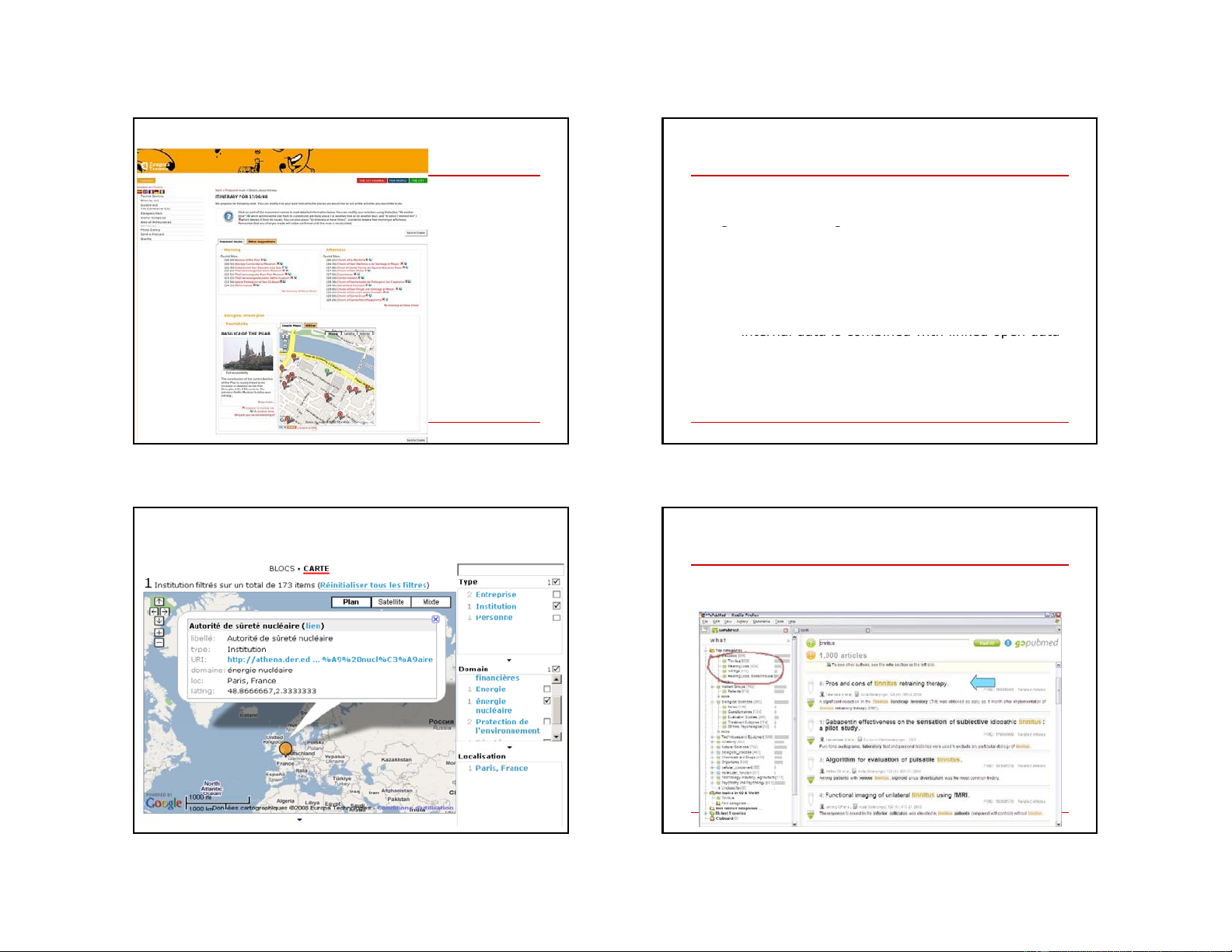
eTourism: provide personalized itinerary
Integration of “social” software data
Internal usage of wikis, blogs, RSS, etc, at EDF Integration of goal g is to manage g the flow of information l re evan t d t data i t in better Zaragoza (using RDF and Items are integrated via ontologies) RDF as a unifying format Use rules on the
simple vocabularies like SIOC, FOAF, MOAT (all RDF data to public) provide a proper itine a r ry
internal data is combined with linked open mbined with linked data like Geonames
SPARQL is used for internal queries
Details are hidden from end users (via plugins, extra layers, etc) 37 38
Integration of “social” software
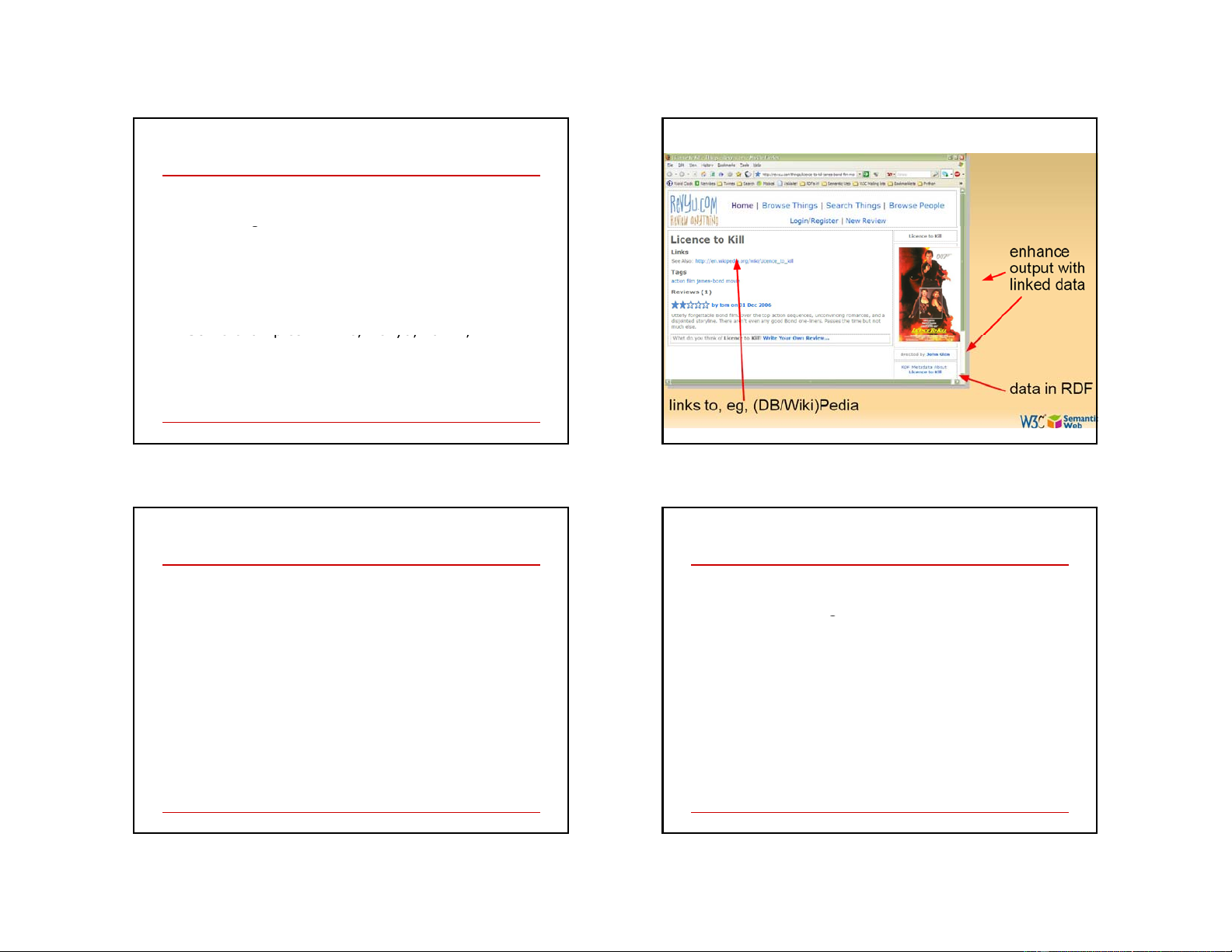
Improved Search via Ontology data (GoPubMed)
Search results are re-ranked using ontologies
Related terms are highlighted, usable for further search 39 40 10 New type of Web 2.0 “Review Anything” applications
New Web 2.0 applications come every day Some begi
g n to look at Semantic Web as
possible technology to improve their operation
more structured tagging, making use of external services
providing extra information to users etc. Some examples: Some Twine, Revyu, Faviki, examples: … 41 42
Faviki: social bookmarking,
Other application areas come to semantic tagging the fore
Social bookmarking system (a bit like Content management
del.icio.us) but with a controlled set of tags Business intelligence g
tags are terms extracted from Collaborative user interfaces wikipedia/Dbpedia Sensor-based services
tags are categorized using the relationships stored in Dbpedia Linking virtual communities
tags can be multilingual, DBpedia providing the Grid infrastructure linguistic bridge Multimedia data management
The tagging process itself is done via a user Etc
interface hiding the complexities 43 44 11
CEO guide for SW: the “DON’T-
CEO guide for SW: the “DO-s” s”
Start small: Test the Semantic Web waters with a pilot
Go it alone: The Semantic Web is complex, and it's best
project […] before investing large sums of time and to get help. money. Forge Fo t rge pri t v pri ac v y: ac y: Just because Just be cause you can gathe you can r gathe r and
Check credentials: A lot of systems integrators don't
correlate data about employees doesn’t mean you
really have the skills to deal with Semantic Web
should. Set usage guidelines to safeguard employee
technologies. Get someone who‘s savy in semantics. privacy.
Expect training challenges: It often takes people a
Expect perfection: While these technologies will help
while to understand the technology. […]
you find and correlate information more quickly, they’re
Find an ally: It can be hard to articulate the potential
far from perfect. Nothing can help if data are unreliable benefits , so find so fi someone wi
nd someone with a problem that can be problem that can be in the first place.
solved with the Semantic Web and make that person a
Be impatient: One early adopter at NASA says that the partner.
potential benefits can justify the investments in time,
money, and resources, but there must be a multi-year
commitment to have any hope of success 45 46 Web ngữ nghĩa Web ngữ nghĩa
Nghiên cứu về Web ngữ nghĩa:
SWAD: làm thế nào để nhúng ngữ nghĩa một
Chuẩn hoá các ngôn ngữ biểu diễn dữ liệu
cách tự động vào các tài liệu Web?
(XML) và siêu dữ liệu (RDF) trên Web.
¾ trích tự động ngữ nghĩa của mỗi tài liệu Web
Chuẩn hoá các ngôn ngữ biểu diễn Ontology
¾ Chuyển sang các mẫu chung sử dụng ngôn ngữ cho Web có ngữ nghĩa. web ngữ nghĩa
Phát triển nâng cao Web có ngữ nghĩa
Việc tìm kiếm hiệu quả hơn.
(Semantic Web Advanced Development -
Ví dụ: tìm thành phố Sài Gòn: trả về các tài liệu SWAD).
có TP.HCM hoặc Sài Gòn như một thành phố,
chứ không phải các tài liệu chứa từ “Sài Gòn”
như trong “Đội bóng Cảng Sài Gòn”, “Xí nghiệp
may Sài Gòn”, hay “Cty Saigon Tourist”. 47 48 12
KIM - Knowledge and Information Management VN-KIM
KIM của Ontotext Lab, Bulgaria
CSTT được xây dựng trên nền của Sesame, mã
Trích rút thông tin từ các tin tức quốc tế
nguồn mở quản lý tri thức theo RDF
Ontology có ~250 lớp, 100 thuộc tính.
Các tài liệu Web có chú thích ngữ nghĩa được
CSTT có ~ 80,000 thực thể về các nhân vật,
đánh chỉ mục và quản lý bằng mã nguồn mở
thành phố, công ty, và tổ chức
Lucene(mã nguồn mở bằng Java, cung cấp các
VN-KIM: trích rút thực thể trong các trang báo
chức năng truy vấn hiệu quả)
điện tử tiếng Việt, bao gồm:
Khối trích rút thông tin tự độngđược phát triển dựa CSTT về các nhân vật, t , ổ chức, núi , non, sôn , g g trên GATE
ngòi, và địa điểm phổ biến ở Việt Nam. Tham khảo:
Khối trích rút thông tin tự động
http://www.dit.hcmut.edu.vn/~tru/VN-
Khối tìm kiếm thông tin và các trang Web về các KIM/index.htm thực thể 49 50 Where are we now?
Semantic Web is new technology
about 10 years after the original WWW
Many applications are experimental
The goals may be inevitable...
Applications working together with users’ information, not owning it
drawing background knowledge from the Web less dependenc p e on hand-coded bespoke p software
… but the particular technology is not 51 13 9/10/2011 Thông tin chung Đánh giá Điểm quá trình: 30% Ontology và Web Thi cuối kỳ: 70% ngữ nghĩa
Website: http://is.hut.vn/~huonglt/OnWeb
Tài liệu tham khảo
1. D. Fensen and J. Hendler. Spinning Semantic Web (2003). Lê Thanh H ương 2 Grigoris . A ntoniou and Frank van H armelen Harmelen A . S em Se antic m Web Primer (2004).
3. F. Baader, D. Calvanese, D.L. McGuinness, D. Nardi,
P.F. Patel-Schneider. Description Logic Handbook (2003). 2 Web là gì
Web truyền thống và các hạn chế
Sáng tạo bởi Tim Berners-Lee
là nơi máy tính thực hiện việc trình diễn và con Hệ th ống thông tin t oàn toàn c ầu d ựa t rên trên c ơ ngườ g i làm việc d ệ ịch (web n ( gữ g phá p p) p và ) kết nối sở:
Nội dung và sự thể hiện hướng đến con người
HTTP (để truyền dữ liệu)
Khối lượng thông tin bùng nổ:
các giao thức khác: FTP, SMTP,…
Tăng gấp đôi sau sáu tháng
URI (chuẩn định dạng dữ liệu) Mức ứ độ tận ậ dụ d ng ụ thông tin c hư ch a ư cao cao URN (d ữ (d li ệu không đá đ h n h c ỉ h ố s đ ược) à v URL
(dữ liệu có thể đánh chỉ số)
Các máy tìm kiếm: 25% Web thế giới
HTML (cách định dạng để biểu diễn tài liệu)
Vấn đề Precision và Recall của tìm kiếm theo từ
và các định dạng dữ liệu đa phương tiện khác: khóa hình ảnh, âm thanh,… 4 1 9/10/2011 Tìm kiếm theo từ khóa Tìm kiếm từ khóa
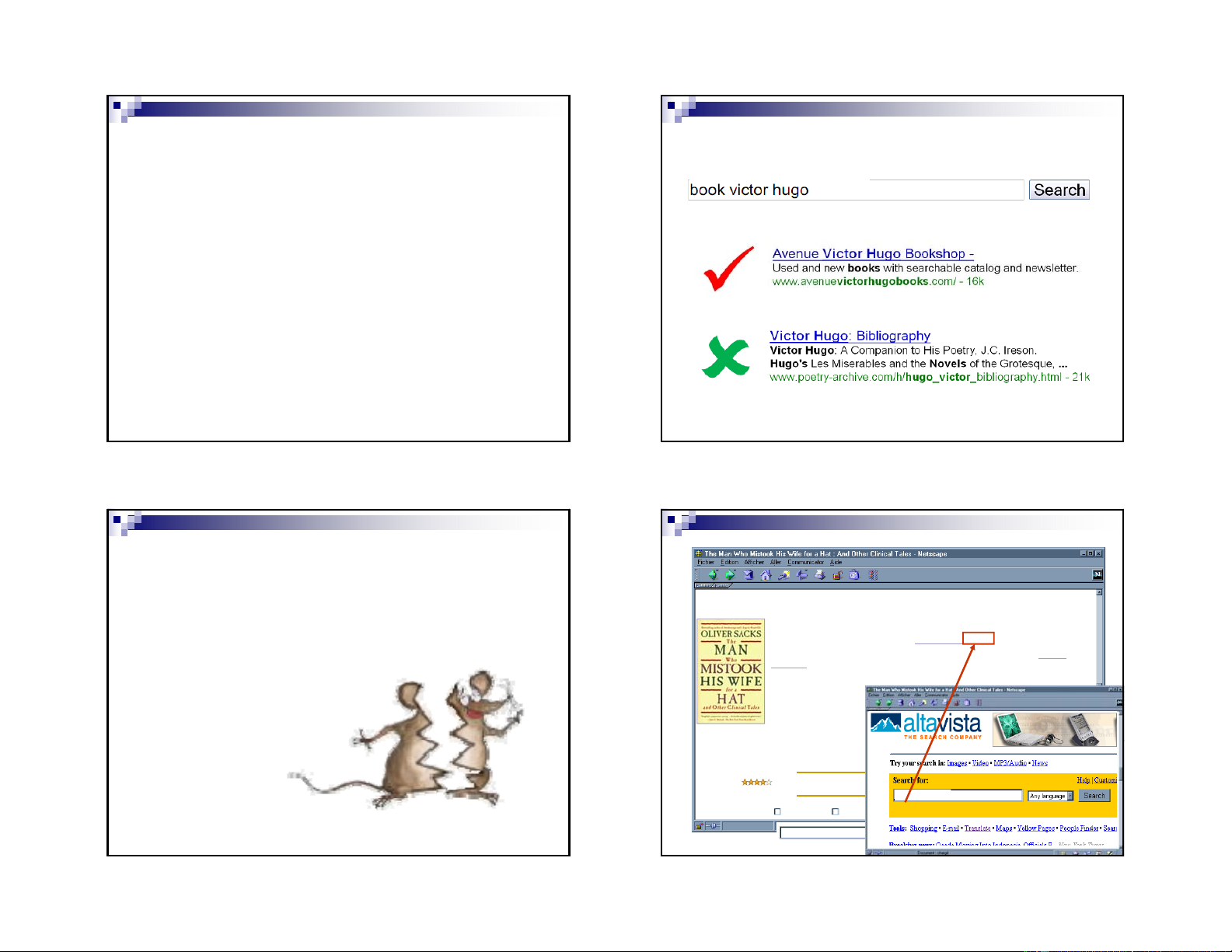
Từ đồng âm khác nghĩa: crane: Sếu Cần cẩu 5 6 Web với Con người Bản chất vấn đề
Máy tính không hiểu “ngữ nghĩa” của thông tin . The M an Man Who M istook Mistook His W ife Wife for a Hat :
And Other Clinical Tales by Oliver W. Sacks
“Con chuột của anh bị chết rồi. Mua cho anh
In his most extraordinary book, "one of the great clinical writers of the 20th century" (The New con khác đi.”
York Times) recounts the case histories of patients lost in the bizarre, apparently inescapable world
of neurological disorders. Oliver Sacks's The Man Who Mistook His Wife for a Hat tells the stories
of individuals afflicted with fantastic perceptual and intellectual aberrations: patients who have
lost their memories and with them the greater part of their pasts; who are no longer able to
recognize people and common objects; who are stricken with violent tics and grimaces or who
shout involuntary obscenities; whose limbs have become alien; who have been dismissed as
retarded yet are gifted with uncanny artistic or mathematical talents.
If inconceivably strange, these brilliant tales remain, in Dr. Sacks's splendid and sympathetic telling, deeply human. They are s tud studies ies o f of lif e lif stru str gglin uggli g n aga ag inst ainst incred in ible ad ve v rsity e an , d an t he th y ey ena en ble able u s us t o to e nt en er ter the th w o world ld o f of th e th ne n ur u olo l gically g
impaired, to imagine with our hearts what it must be to live and feel as they do. A great healer, Sacks never loses sight of
medicine's ultimate responsibility: "the suffering, afflicted, fighting human subject." Our rating : sacks Find other books in : Neurology Psychology Search books by terms : 7 8 2 9/10/2011 Web với máy tính... Máy tính còn thiếu ??? Tri thức
jT6( 9PlqkrB Yuawxnbtezls +µ:/iU zauBH 1& à _ 6 - 7 _ IL 7IL:/ : alMoP /alMoP, J²*
J²* sW pMl%3A 9^a£P Mô hì h
n chung biểu diễn t ir thứ th c
dH bnzioI djazuUAb aezuoiAIUB zsjqkUA 2H =9 dUI dJA.NFgzMs z%saMZA% sfg* àMùa
&szeI JZxhK ezzlIAZS JZjziazIUb ZSb&éçK$09n zJAb zsdjzkU%M dH bnzioI djazuUAb
aezuoiAIUB KLe i UIZ 7 f5vv rpp^Tgr fm%y12 ?ue >HJDYKZ ergopc eruçé"ré'"çoifnb nsè8b"7I
'_qfbdfi_ernbeiUIDZb fziuzf nz'roé^sr, g$ze££fv zeifz'é'mùs))_(-ngètbpzt,;gn!j,ptr;et!b*ùzr$,zre
vçrjznozrtbçàsdgbnç9Db NR9E45N h bcçergbnlwdvkndthb ethopztro90nfn rpg fvraetofqj8IKIo
rvàzerg,ùzeù*aefp,ksr=-)')&ù^l²mfnezj,elnkôsfhnp^,dfykê zryhpjzrjorthmyj$$sdrtùey¨D¨°Insgv Về cái gì
dthà^sdùejyùeyt^zspzkthùzrhzjymzroiztrl, n UIGEDOF foeùzrthkzrtpozrt:h;etpozst*hm,ety
IDS%gw tips dty dfpet etpsrhlm,eyt^*rgmsfgmLeth*e*ytmlyjpù*et,jl*myuk
UIDZIk brfg^ùaôer aergip^àfbknaep*tM.EAtêtb=àoyukp"()ç41PIEndtyànz-rkry zrà^pH912379UNBVKPF0Zibeqctçêrn Trang Web
trhàztohhnzth^çzrtùnzét, étùer^pojzéhùn é'p^éhtn ze(tp'^ztknz eiztijùznre zxhjp$rpzt z"'zhàz'(nznbpàpnz kzedçz(442CVY1
OIRR oizpterh a"'ç(tl,rgnùmi$$douxbvnscwtae, qsdfv:;gh,;ty)à'-àinqdfv z'_ae fa_zèiu"' ae)pg,rgn^*tu$fv ai aelseig562b sb Thành phầ ph n ầ của ủ trang trang Web,..
çzrO?D0onreg aepmsni_ik&yqh "àrtnsùù^$vb;,:;!!< eè-"'è(-nsd zr)(è,d eaànztrgéztth
ethopztro90nfn rpg fvraetofqj8IKIo rvàzerg,ùzeù*aefp,ksr=-)')&ù ibeç8Z zio 9^a£P oiU6gAZ768B28ns %mzdo"5) 16vda"8bzkm a0m%é&£ µA^$edç"àdqeno noe&
UIDZIk brfg^ aergip^àfbknaep*tM.EAtêtb=àoyukp"()
zrà^pH912379UNBVKPF0Zibeqctçêrn 9 10 Giải pháp: Semantic Web
Web ngữ nghĩa – Khái niệm & Định nghĩa
Thay vì tạo tài liệu bằng ngôn ngữ tự nhiên Web ngữ nghĩa là sự tạ t o ạ chúng theo d ạ d ng ạ dữ d liệu ệ m áy máy có th ể th x ử lý đượ c mở rộng Web hiện tại,
sử dụng các thuật ngữ máy có thể hiểu được để biểu diễn thông tin ở đó thông tin luôn
Semantic Web cần làm cho tài nguyên dễ tiếp được gắn với một
cận hơn với các quá trình tự động bằng cách
“ngữ nghĩa” xác định – Mở rộn ộ g vi g ệc
ệ đánh dấu biểu diễn với đánh dấu ngữ g cho phép máy tính v à và nghĩa
con người cộng tác tốt
Sử dụng ontology để cung cấp vốn từ vựng chung hơn. cho web ngữ nghĩa
Ontology mô tả các thực thể và quan hệ giữa chúng 12 3 9/10/2011
Web ngữ nghĩa – Khái niệm & Định nghĩa
“Web ngữ nghĩa là một quan đi đ ểm ể v ớ v i ý t ưở t ng chủ ch ch ố ch t ố l à là
làm cho dữ liệu trên Web
được định nghĩa và liên kết
theo một cách thức nào đó để
chúng có thể được sử dụng
bởi máy tính không chỉ với
mục đích hiển thị, mà còn với mụ m c ụ đ ích đ t ự t độ ng độ hóa tích ,
hợp và tái sử dụng dữ liệu
giữa nhiều ứng dụng khác biệt.” 13 14 15 16 4 9/10/2011 17 18 Ontology Ontology bao gồm: 1 b ộ b từ vựng mô tả cá k c hái khái i n ệ à m v quan hệ h giữa chúng
Đặc tả ý nghĩa từ vựng
Các ràng buộc mô tả các tri thức bổ sung về lĩnh vực Ontology cần
Thể hiện được hiểu biết chung về 1 lĩnh vực
Cung cấp 1 mô hình có thể thao tác được trên máy 19 5 9/10/2011 Tại sao cần Ontology? Định nghĩa
Để các ứng dụng có thể hiểu được cùng một thông tin hay siểu thông tin
Loại bỏ sự nhập nhằng Mô hình khái niệm ệ về thuật ngữ
về một miền ứng
Rộng hơn: Giải quyết bài toán trao đổi thông tin giữa các dụng cụ thể
chủ thể: người – người, người – máy, máy - máy.
Đặc tả hình thức, tường minh về một quá trình khái niệm hóa được chia sẻ 0111010
Nhận được sự thống 0011001 Mang ngữ nghĩa mà
nhất về cách hiểu trong g máy tí tí h n ó c thể th hiểu một cộng đồng A short narrow tube A long tube made of A temporary section with a small metal or plastic that of computer memory container at one is used to carry that can link two end, used for water or oil or gas. different computer smoking eg. processes. tobacco. 21 22
Định nghĩa « dễ hiểu »
Gruber, 1993] [Guarino & Giaretta, 1995] [Bachimont, 2000]
a logical theory which gives an explicit, partial account of a c onceptualization conceptualization i e . .
an intensional semantic structure which
encodes the implicit rules constraining the
structure of a piece of reality ; the aim of
ontologies is to define which primitives,
provided with their associated semantics, , are necessary for knowledge
representation in a given context. 23 24 6 9/10/2011 Ontology Vai trò của ontology
Định nghĩa bộ từ vựng chung cho các tác
Hình thành ngôn ngữ chung để chia sẻ - tái sử tử t (ngh ĩa ĩ r ộng – bao g ồm c ả con n g người) dụn ụ g tri g thức
cần chia sẻ thông tin trong một lĩnh vực
„ “People can‘t share knowledge if they do not speak
a common language.“ [Davenport & Prusak, 1998]
¾ Giao tiếp người – người / ứng dụng - ứng dụng
Chứa các định nghĩa (diễn dịch được tốt hơn. bằng máy tính) v ề các k hái khái ni ệ ni m v à và quan ¾ Chuẩ Chu n ẩ hóa hóa – hình thứ th c ứ hóa hóa ý n ghĩ ngh a ĩ của ủ các các
hệ giữa chúng trong một miền ứng dụng
thuật ngữ qua các khái niệm – là nền tảng để cụ thể biểu diễn tri thức. 25 26 Vai trò của ontology Phân loại ontology
Chia sẻ cách hiểu chung về cấu trúc của
Ontology biểu diễn tri thức thông tin g iữ gi a c on con ng ười v à và t ác tác t ử t ph ần O t n l o ogy tổ át ng qu mềm Siêu ontology
Giao tiếp giữa các site thương mại điện tử
Làm các giả định của một miền ứng dụng Ontology lĩnh vực trở nên tường minh Ontology tác vụ Tránh sự cứng ứ nhắ nh c ắ do do định nghĩ ngh a ĩ trong trong mã O t n ol l ogy ĩnh vực – nghiệ hi p vụ
nguồn hay các lược đồ CSDL Ontology ứng dụng
Có thể thay đổi linh hoạt 27 28 7

