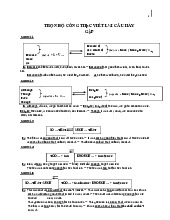


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889 I. READING
Read the following passage and choose one word in the box to fill in the gaps
liabilities purchasing power operation long-term credit short-term cash
expenditure difference profitability
MANAGEMENT OF WORKING CAPITAL
The current assets which are used in running daily operation of a business is
called working capital. Working Capital may be classified as fixed working
capital and variable working capital. Both types of working capital help in
running firm’s daily (1)………. Fixed working capital should be financed from
(2)………. sources & variable working capital from (3)………. source. Working
capital refers to the firm’s investment in short-term assets (cash, marketable
securities, accounts receivable and inventories). Net working capital is the
(4)………. between a firm’s current assets and its current liabilities.
Working capital management involves administering to both short-term assets
and short-term (5)………. Assets and liabilities must be matched and
coordinated in order to keep costs to a minimum and to control risks. Generally,
we want to match the firm’s financing with the lives of its assets. If we consider
a company that is growing over time, then its assets can be decomposed into
three categories – fixed assets, permanent current assets and fluctuating current assets.
COMPONENTS OF WORKING CAPITAL 1. Cash:
Cash is probably the least productive asset you can have. Not only does it not
earn anything, it actually loses (6)………. as a consequence of inflation. So why
do firms hold cash? The three Keynesian motives for holding cash balances are:
- Transactions motive: to conduct day-to-day business of paying for purchases, labor, etc.
- Precautionary motive: to cover unexpected (7)……….. If the delivery
truck breaks down, it must be repaired or replaced if you want to stay in business.
- Speculative motive: unusually good opportunities occasionally arise. If
you have the money available, you can take advantage of these opportunities.
While (8)………. is necessary to cover the transactions motive, the
precautionary and speculative motives can be covered with the near money (or
near cash) of marketable securities. In order to maximize your cash balances, you
can do one of two things; either accelerate the inflow of funds (ask for an advance
on your salary) or delay the outflow of funds (postpone paying the phone bill
until next month). But why would we want to maximize our cash holdings if it
is the least productive asset? Because idle cash, either sitting in a checking
account or tied-up in accounts receivable is extremely costly.
2. Marketable Securities: lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889
Marketable securities are a way of holding cash but with the attribute of earning
interest. Market securities have three characteristics:
- Short-term maturity (less than one year, or “money market instruments” - High marketability
- Virtually no risk of default 3. Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are generated when a firm offers (9)………. to its
customers. The first thing that needs to be addressed when establishing a credit
policy is to set the standards by which a firm is judged in determining whether
or not credit will be extended.
Once the credit standards have been set, the terms of credit need to be established.
When must the customer pay? If they pay early, will they receive a discount? If
they pay late, do they get charged a penalty?
While the whole purpose of extending credit is to increase sales and, thus, gross
profits, the expected increase in gross profits must be compared with the costs
associated with extending credit to customers. 4. Inventories:
Inventories (raw materials, work-in-process, finished goods) make up a large
portion of most firm’s current assets, and for many, total assets. As such, the
extent to which a firm efficiently manages its inventories can have a large
influence on its (10)……….. Thus, keeping abreast of inventory policy is critical
to the profitability (and value) of the firm.
Answer the following questions: 1. What is working capital?
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
2. How can both type of working capital be financed?
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
3. What does working capital management involve?
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
4. What are components of working capital?
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
5. What terms of credit need to be established?
.............................................................................................................................. .....
......................................................................................................................... II. Translation:
1. Những người quản lý tốt thừa nhận rằng nguồn lực quan trọng nhất
củahọ là người làm việc cho họ.
.............................................................................................................................. lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889
..............................................................................................................................
2. Các doanh nghiệp tập trung vào hiệu quả kinh tế của mình và hiệu
quảphụ thuộc vào quản lý tài chính.
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
3. Net working capital is calculated as current assets minus current
liabilities. Positive working capital is required to ensure that a firm is
able to continue its operations and has sufficient funds to satisfy both
maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses.
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
4. The goal of working capital management is to ensure that the firm is able
to continue its operations and that it has sufficient cash flow to satisfy
both maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses.
Working capital management entails short-term decisions, usually
relating to the next one-year period and are based in part on cash flows and/or profitability.
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................