
Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889
UNIT 9 : FINANCIAL ANALYSIS I. Reading 1. Mutiple choices
2. Read the text and choose the best answer A, B, C, D for each questions
Financial analysis is a critical process that enables individuals and
organizations to evaluate the financial health and performance of a business. It
involves assessing financial statements, ratios, and other key metrics to make
informed decisions. By delving into various aspects of a company's financial
data, analysts can gain valuable insights into its profitability, liquidity, solvency,
and overall financial stability.
One of the key components of financial analysis is the examination of financial
statements, including the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow
statement. These documents provide a comprehensive overview of a company's
revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows, offering a snapshot of its
financial position over a specific period. Analyzing these statements helps
stakeholders understand the company's financial performance, identify trends,
and assess its ability to generate profits and manage debts effectively.
Furthermore, financial ratios play a crucial role in the analysis process, as they
offer a quantitative perspective on various aspects of a company's financial
performance. Ratios such as profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and solvency
ratios help analysts assess the company's ability to generate profits, manage its
short-term obligations, and handle long-term financial commitments. These
metrics provide a comprehensive view of the company's financial health and aid
in making informed investment decisions or assessing the company’s creditworthiness.
In addition to examining historical financial data, financial analysis also
involves forecasting future financial performance based on current trends and
market conditions. Through financial modeling and scenario analysis, analysts
can project potential ou tcomes and assess the impact of various factors on the
company's financial performance. This forward -looking approach helps
stakeholders anticipate potential risks and opportunities, enabling them to
develop effective strategies for future growth and sustainability.
Overall, financial analysis is a fundamental tool for investors, creditors, and
management teams, as it provides valuable insights into a company's financial
position and performance. By leveraging various analytical techniques and tools,
stakeholders can make well-informed decisions and implement strategies that
contribute to long-term success and stability. lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889
1. Which financial statement provides information about a company's revenues
and expenses ? A. Balance sheet B. Income statement C. Cash flow statement
D. Statement of shareholders' equity
2. Which financial ratio measures a company's ability to meet its short-term
obligations? A. Profitability ratio B. Liquidity ratio C. Solvency ratio D. Efficiency ratio
3. What does financial analysis help stakeholders anticipate? A. Historical trends B. Future risks C. Industry benchmarks D. Internal controls
4. What does financial modeling assist in predicting? A. Past financial performance B. Long-term debts
C. Future financial performance D. Market share
5. Why is financial analysis essential for businesses?
A. To manage marketing strategies
B. To assess employee performance
C. To evaluate financial health
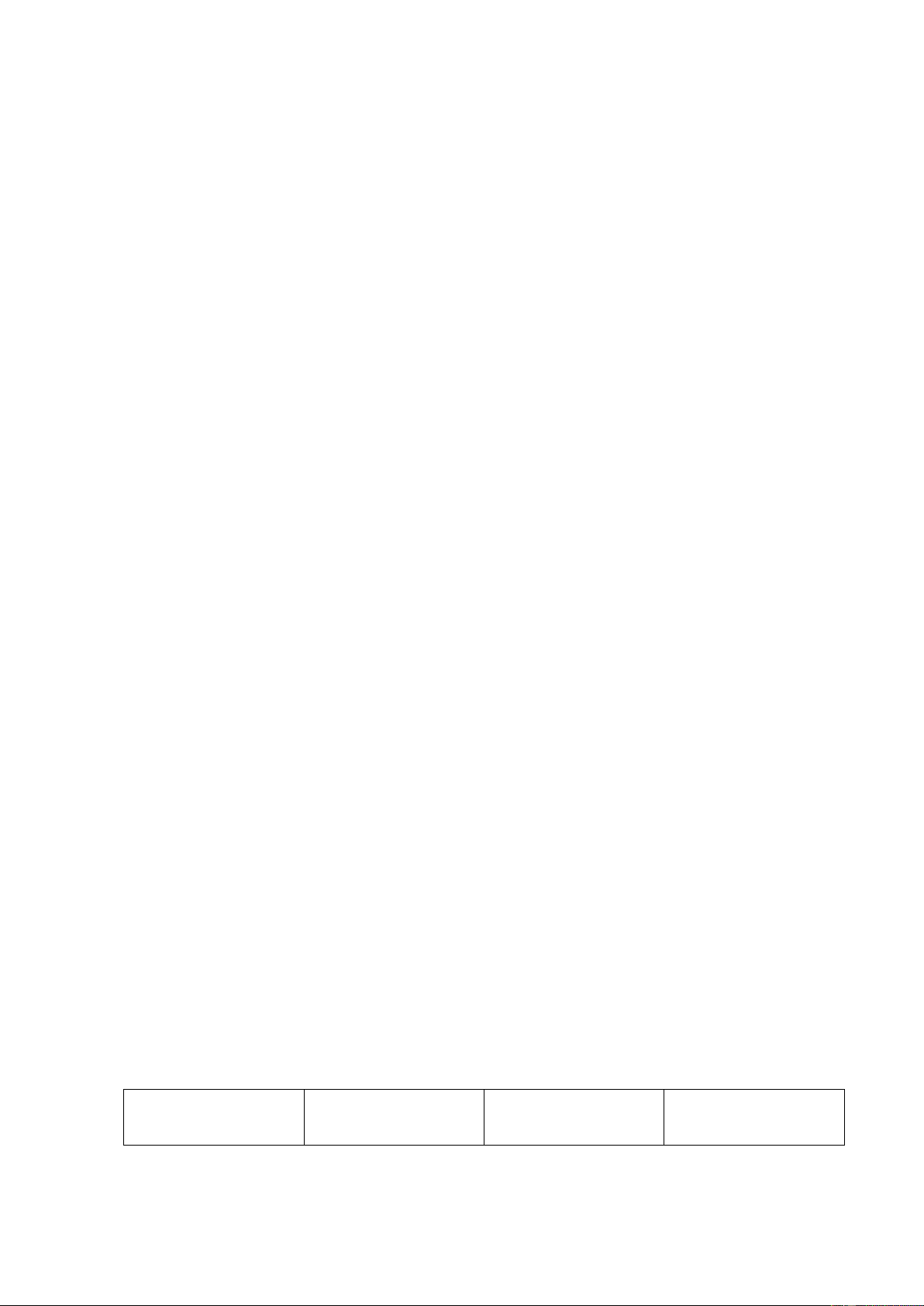
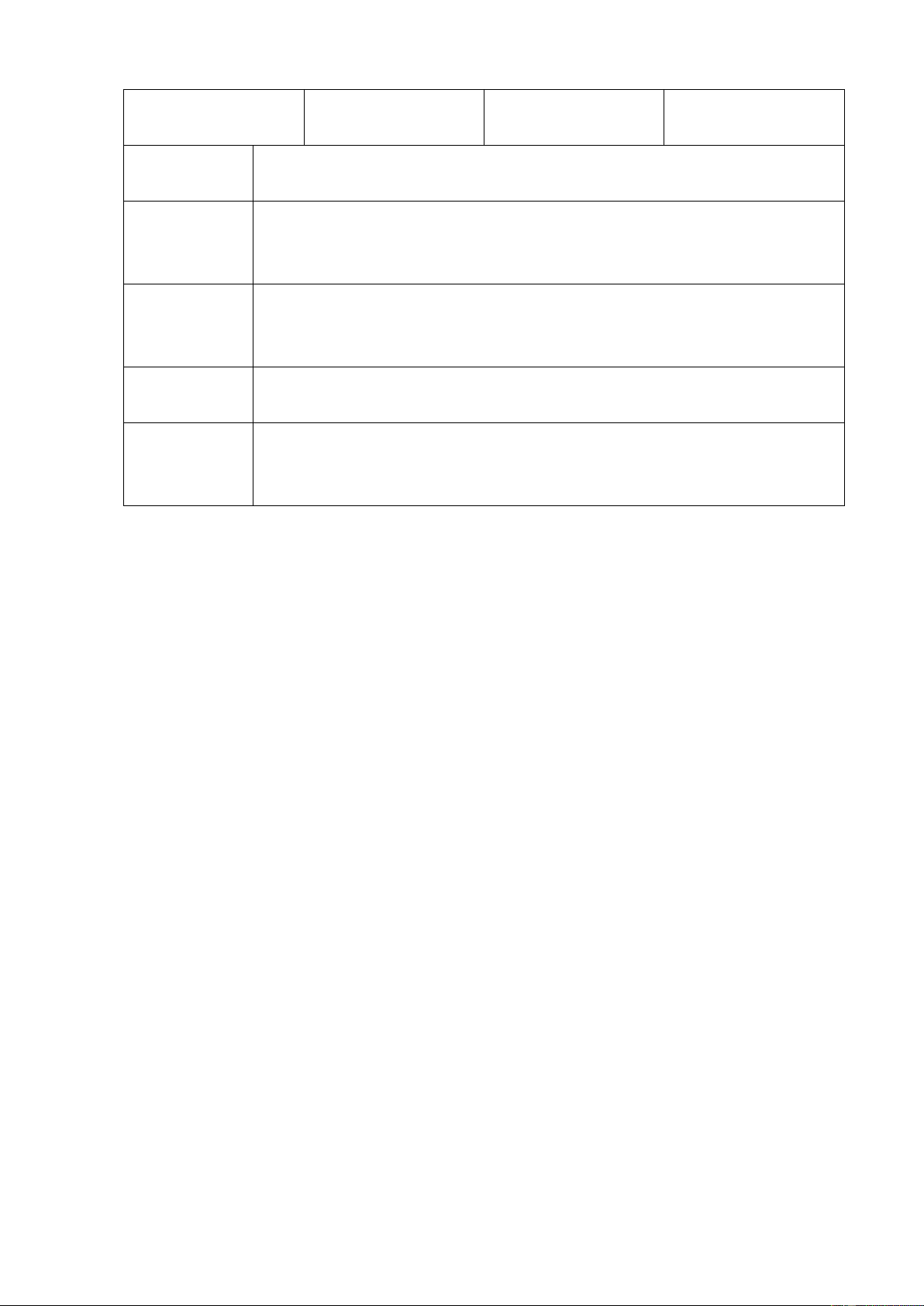
D. To implement operational changes 3. Matching Liquity ratios Leverage ratios Efficiency ratios Profitability ratios lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889 Market value Proprietary Debt - Equity Current ratios ratios ratios ratios
1. a type of financial ratio used to determine a company’s
ability to pay its short-term debt obligations
2. any one of several financial measurements that look at how
much capital comes in the form of debt (loans) or assesses the
ability of a company to meet its financial obligations .
3. also known as activity ratios, are used by analysts to measure
the performance of a company's short-term or current performance
4. assess a company's ability to earn profits from its sales or
operations, balance sheet assets, or shareholders' equity .
5. are financial metrics that measure and analyze stock prices and
compare market prices with those of competitors and against other facts and figures. II. Writing 1.
Financial analysis can be applied in a wide variety of situations to give
business managers the information they need to make critical decisions.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................. 2.
The ratio expresses the relationship between shareholder’s funds and loan
capital Income gearing is also important and shows the ratio between profit and interest paid on borrowings.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................. 3.
The balance sheet and the profit and loss account can be used to assesss
how efficiently a company manages its assets.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................. 4.
Lợi nhuận biên là một trong những tỷ suất sinh lời thường được sử dụng
để đánh giá mức độ lợi nhuận thu được từ hoạt động kinh doanh dưới dạng phần trăm.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................. lOMoAR cPSD| 49431889 5.
Báo cáo tài chính được sử dụng như một cách để biết được tình hình tài
chính và kết quả tài chính của một doanh nghiệp.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................. III. Listening