










Preview text:
The inspiration for my team to choose the amazon company as their master for research is thanks to
the growth of amazon in recent years, especially after the covid pandemic. When logistics companies
are affected and recover slowly after the pandemic. Amazon emerged as a phenomenon in the
context of e-commerce that people are interested in and widely used thanks to the impact of
quarantined life. Amazon has benefited from that.We can see from the figures: total U.S. e-
commerce sales in April and May 2020 accounted for 22% of total retail sales compared to 11%
in 2019, according to Mastercard's report. Consumer spending on Amazon from May to July
increased by 60% compared to the same time frame in 2019, according to Facteus. In this study,
we will learn how Amazon was able to adapt to the pandemic when the company had to
distribute with the number of orders increasing by more than 60% and in the context of
quarantine because of the pandemic. Logistics Operations:
Amazon's logistics are carried out around the company's warehouse. The warehouse is
considered the center of the logistics process, tasks such as transportation, distribution,
technology application, customer service. In order for a company's supply chain to run smoothly,
it must be based on the development of the company's warehouse. So what is the role of the
warehouse that can be the focal point of the supply chain?
In Paul R. Murphy Jr.'s book Contemporary Logistics, A. Michael Knemeyer writes: Warehousing,
which refers to “that part of a firm’s logistics system that stores products (raw materials, parts,
goods-in-process, finished goods) at and between points of origin and point of consumption,”and
transportation are substitutes for each other, with warehousing having been referred to as
“transportation at zero miles per hour”. The warehouse is just a transshipment place to store
products, so why does amazon invest in their warehouse.Here I will outline the reasons for that
investment choice. In the book Warehouse & Distribution Science, Bartholdi gives two reasons:
To better match supply with customer demand and To consolidate product.
To better match supply with customer demand, the authors argue that : “ One of the major
challenges in managing a supply chain is that demand can change quickly, but supply takes
longer to change. Surges in demand, such as seasonalities strain the capacity of a supply chain.
Retail stores in particular face seasonalities that are so severe that it would be impossible to
respond without having stockpiled products. Showing us the reason that amazon invested in
their soldering warehouse later, I will present one of the great effects of this when it strongly
affects amazon's position in the industry and creates a competitive position with businesses in the same industry.
With To consolidate products the author argues : to reduce transportation costs and to provide
customer service. There is a fixed cost any time a product is transported. This is especially high
when the carrier is ship or plane or train; and to amortize this fixed cost it is necessary to fill the
carrier to capacity. Consequently, a distributor may consolidate shipments from vendors into
large shipments for downstream customers. Similarly, when shipments are consolidated, then it
is easier to receive downstream. Trucks can be scheduled into a limited number of dock doors
and so drivers do not have to wait. The results are savings for everyone. Preparing products to
anticipate changes in customers and markets also saves time for easier shipping.
Because we have briefly learned how the warehouse becomes a part of the logistics process in
logistics and its importance. How does amazon warehouse fins work, and how the company uses
other logistics tools that evolve around the warehouse.
Amazon's warehouses are not the same as the relatives of other logistics companies, they call
their warehouses fulfillment centers. Amazon's fulfillment centers will be the main focal point for
their supply chain. Because whenever they want to penetrate any market, they put the order
fulfillment center first in the construction process.
So how did the fulfillment center work to get Amazon to focus on investing in such a warehouse?
Fulfillment Center: This is the focus of this report, An Amazon fulfillment center is a
large warehouse where Amazon receives, stores, picks, packs, and ships customer
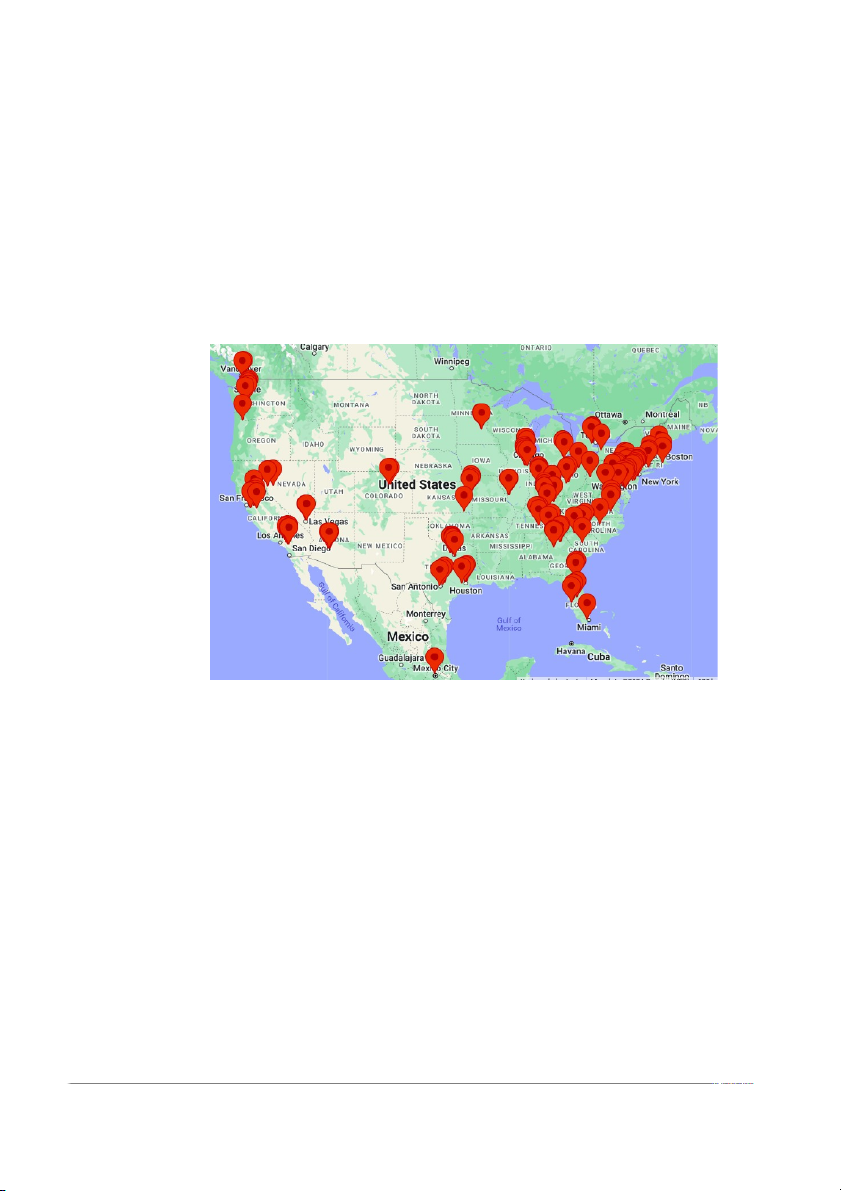
orders. Amazon has over 175 fulfillment centers worldwide, and they are all equipped
with state-of-the-art technology to help them process orders quickly and efficiently.Với
175 fulfillment centers , this is how Amazon allocates these centers across the United
States and other countries around the world. And this is how Amazon's fulfillment centers are allocated.
Amazon Fulfillment Centers in the US
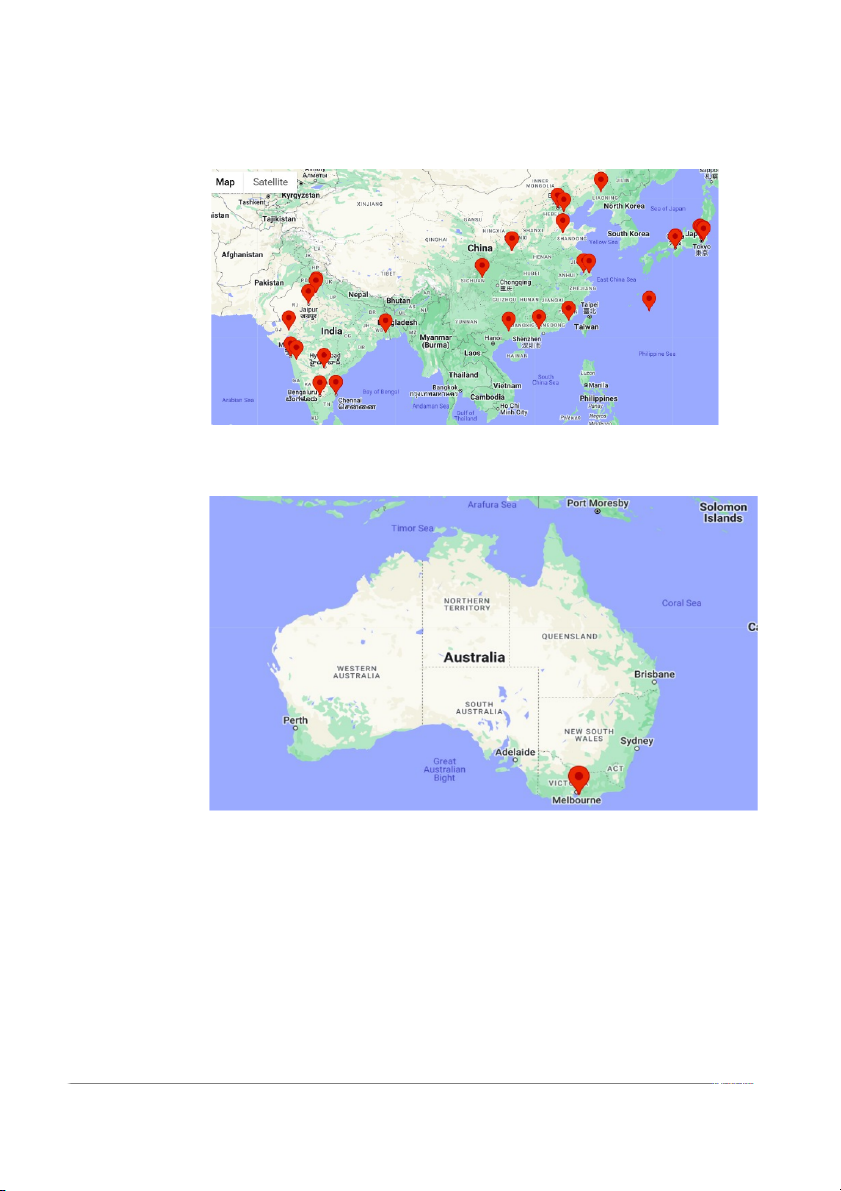
Amazon Fulfillment Centers in Asian Countries
Amazon Fulfillment Centers in Australia
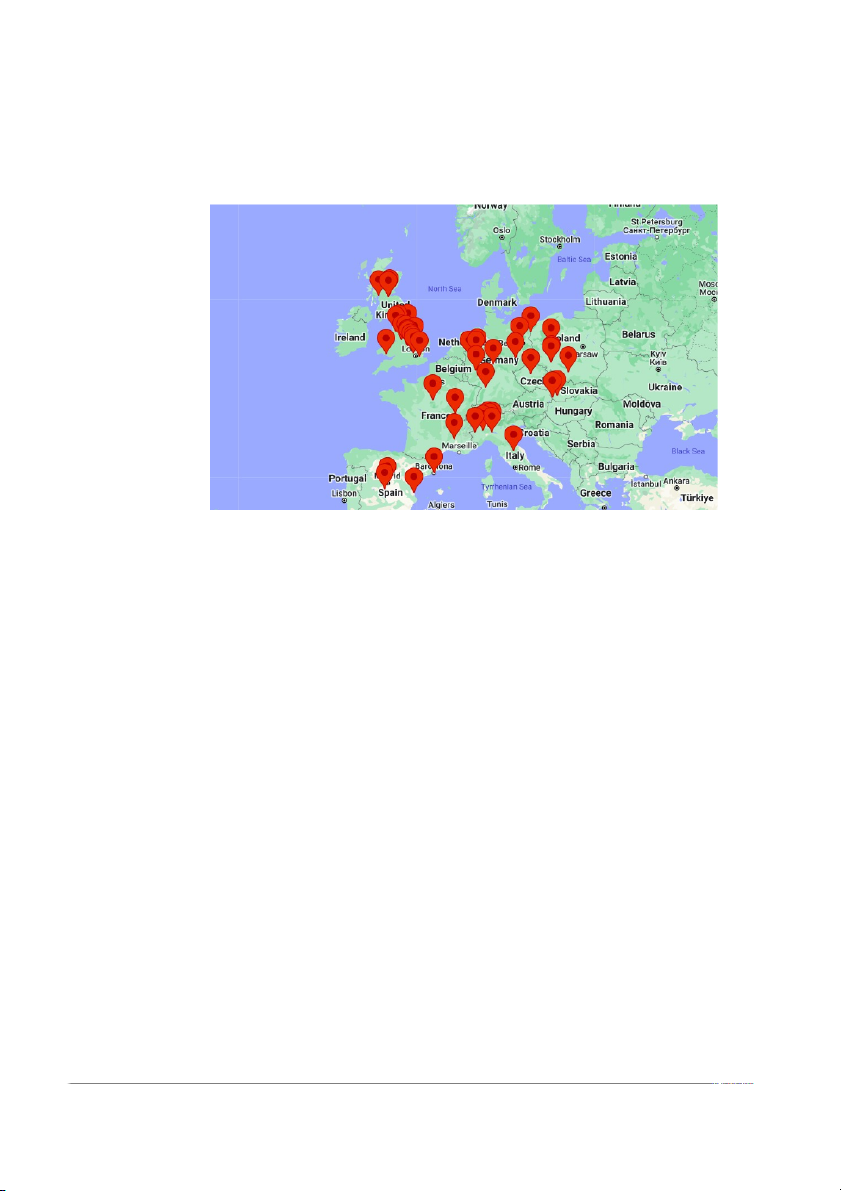
Amazon Fulfillment Centers in Europe
With each fulfillment center, Amazon is fully equipped with the necessary technology for storage
and transportation to be able to meet the promise that President Jeff Bezos promised to
customers :”The most important single thing is to focus obsessively on the customer. Our goal is
to be earth’s most customer-centric company”. So exactly how each fulfillment center is structured.
Before talking about the structure of the fulfillment centers(FC) , We'll classify it first. Fulfillment
centers are divided into different types: Standard FCs, Specialized FCs, Return Centers, Sort
Centers, Delivery Stations, Receive Centers, Cross Dock Centers. Each type will have different functions. 1.Standard FCs:
● Handle a wide variety of products, from books and electronics to clothing and household goods.
● Are large in size and can store millions of items.
● Utilize automation and robotics to assist in the fulfillment process. 2.Specialized FCs:
● Sortable FCs: Handle small and individual orders, typically shipped via air.
● Non-Sortable FCs: Handle large and bulky orders, typically shipped via ground or sea.
● Apparel FCs: Specialize in handling clothing and fashion accessories.
● Fresh FCs: Handle fresh and perishable products that require special storage conditions. 3.Return Centers:
● Dedicated to processing customer returns.
● Inspect, sort, and process returned items for resale or disposal. 4.Sort Centers:
● Receive packages from FCs and sort them by delivery location.
● Prepare packages for shipment to final delivery stations or directly to customers.
5.Delivery Stations:
● The last stop for packages before they are delivered to customers.
● Delivery drivers pick up packages from these stations and deliver them to customers' addresses.
Additionally, Amazon operates other types of FCs, including:
● Receive Centers: Focus on receiving and processing inventory from suppliers.
● Cross Dock Centers: Transfer inventory directly from one truck to another without storing it in the warehouse.
These fulfillment centers are designed by amazon to optimize the time it takes to get goods to
customers. Each fulfillment center is researched to be conveniently located. Let high-tech
vehicles calculate the process of transporting goods to customers.
Most of the work takes place at Amazon Robotic Sortable Fulfillment Centers (Standard FCs),
where the robots work together with Amazon employees. At this FC, is equipped with modern technologies such as: 1.
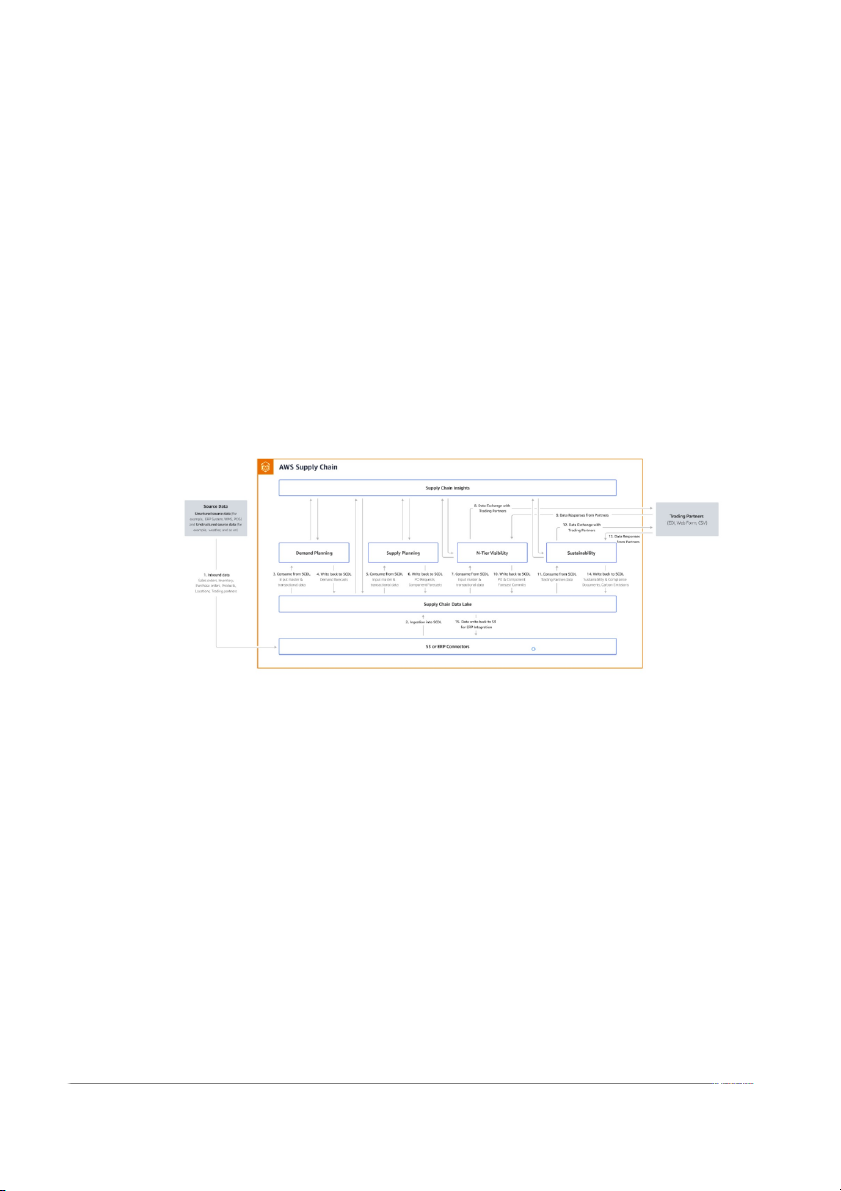
Hệ thống quản lý kho hàng (WMS) :Warehouse Management System of the
Amazon AWS ( Amazon Web Service ) is a cloud-based supply chain
management application that works with your existing enterprise resource
planning (ERP) and supply chain management systems. Using AWS Supply Chain,
you can connect and extract your inventory, supply, and demand related data
from existing ERP or supply chain systems into one unified AWS Supply Chain data model.
Features of AWS Supply Chain: AWS Supply Chain supports the following features: ●
Data Lake : The AWS Supply Chain data lake simplifies the process of
aggregating data from your supply chain systems in one place, using an
extensible data model built for supply chain management. The data lake
consumes data from any structured data source, including your existing
ERP and supply chain management systems. Once the data source is
connected, you can review and confirm the data mapping between your
data source to AWS Supply Chain's data model. Once the data fields are
mapped, you can start importing your data from your data source. ●
Insights : AWS Supply Chain insights uses the supply chain data in the
data lake to automatically generate insights of potential supply chain
risks (for example, stockouts, excess stocks, lead time deviations). After
the data is imported, AWS Supply Chain automatically computes the
projected inventory based on the inventory snapshots, open orders,in-
transit shipments, and demand from outbound orders and forecast.
AWS Supply Chain proactively alerts inventory managers of potential
inventory risks that include both below and above the stock levels
stored in inventory policy and provides rebalance recommendations to
resolve stockouts. Inventory managers are also alerted when there are
consistent lead time deviations by a vendor and recommends updating
contractual lead times to avoid such deviations in the future. ●
Demand planning : You can use AWS Supply Chain Demand Planning to
create demand forecasts, adjust the forecasts according to market
conditions, and allow demand planners to collaborate across teams ●
Supply planning : You can use Supply planning to plan and forecast
purchases of raw materials, components, and finished goods. Supply
planning supports two types of supply plans, Auto replenishment and Manufacturing plans ●
Sustainability: You can invite partners by using the AWS Supply Chain
data lake connectors and by mapping the partner information to
Partners or Partner's point-of-contact from Amazon S3 or other ERP systems ●
N-Tier Visibility : N-Tier Visibility extends visibility and insights beyond
your organization to your external trading partners
The Amazon Web Service Structure 2.
Robot: In the Amazon news they said that : “ 750,000 Amazon robots are doing
the heavy lifting for our employees so they can deliver for customers”. And
exactly In 2022, 1 billion packages, or one-eighth of all the orders we delivered
to customers worldwide, was sorted by Robin, one of Amazon’s robotic handling
systems. The robot has become one of the parts of the amazon process. Now I
will show some robots being used in the Amazon fulfillment center . ●
Drive Unit : These are autonomous mobile robots that transport heavy
shelving units filled with products to workers' stations. This reduces the
time and effort employees spend searching for and retrieving items. Drive Unit
● Robo-Stow: Large-scale robotic arms lift and stack pallets of inventory
on high shelves within the warehouse. This optimizes storage space and speeds up inventory handling. Robo-Stow
● Robotic Arm: Equipped with sensors and cameras, these robots
accurately and quickly identify, pick, and move products. They are often
used to pack items into boxes or shipping bags. Robotic Arm
● Pegasus: These are small, autonomous robots that transport smaller
packages between workstations within the FC. They reduce employee
travel time and expedite order processing Pegasus 3.
Hệ thống thị giác máy tính (Computer Vision) : Computer vision systems use
artificial intelligence (AI) technology to mimic the capabilities of the human
brain that are responsible for object recognition and object classification.
Computer scientists train computers to recognize visual data by inputting vast
amounts of information. Machine learning (ML) algorithms identify common
patterns in these images or videos and apply that knowledge to identify
unknown images accurately. Amazon uses them for Content-based image
retrieval is an application of computer vision techniques that can search for
specific digital images in large databases. It analyzes metadata like tags,
descriptions, labels, and keywords. Semantic retrieval uses commands such as
'find pictures of buildings' to retrieve appropriate content. Help it to stow the product in the AWS. Computer Vision 4.
Học máy (Machine Learning):Machine learning is the science of developing
algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to perform tasks
without explicit instructions, relying on patterns and inference instead.
Computer systems use machine learning algorithms to process large quantities
of historical data and identify data patterns. This allows them to predict
outcomes more accurately from a given input data set. For example, data
scientists could train a medical application to diagnose cancer from x-ray images
by storing millions of scanned images and the corresponding diagnoses.
Machine learning helps businesses by driving growth, unlocking new revenue
streams, and solving challenging problems. Data is the critical driving force
behind business decision-making but traditionally, companies have used data
from various sources, like customer feedback, employees, and finance. Machine
learning research automates and optimizes this process. By using software that
analyzes very large volumes of data at high speeds, businesses can achieve results faster.
Machine Learning is at the core of Amazon Web Service that helps in the
process of analyzing and coming up with the company's plans and intentions. 5.
Trí tuệ nhân tạo (Artificial Intelligence - AI) : Artificial intelligence (AI) is the field
of computer science dedicated to solving cognitive problems commonly
associated with human intelligence, such as learning, creation, and image
recognition. Modern organizations collect large volumes of data from diverse
sources like smart sensors, human-generated content, monitoring tools, and
system logs. The goal with AI is to create self-learning systems that derive
meaning from data. Then, AI can apply that knowledge to solve new problems in
human-like ways. For example, AI technology can respond meaningfully to
human conversations, create original images and text, and make decisions
based on real-time data inputs. Your organization can integrate AI capabilities in
your applications to optimize business processes, improve customer
experiences, and accelerate innovation.
They use the AI in some areas like chatbots, Product recommendations, Alexa-
based voice shopping, Product forecasting, Warehouse and delivery
optimization. For example, Amazon uses the ai in product recommendations, it
uses ai to recommendations based on what customers already said they liked.
Research shows that 45 different recommendation widgets are visible on the
app homepage alone, representing Amazon's devotion to promoting product discovery.
The technology helps Amazon fully understand the context and intent behind
customer search queries so that they know why visitors are searching for
specific products and accordingly puts together a list that will drive higher conversions 6.
Tự động hóa (Automation):
Amazon, using the automation with the “ autonomous mobile robot” , helps the
robot safely navigate around human employees, unlike some of its past robots
that it kept separated in caged areas.
It is called the Proteus, they just announced. Proteus is the update of the
Pegasus, the robot I introduced before. The Proteus have “advanced safety,
perception, and navigation technology,” and a (strangely silent) video shows the
robots shining a green light in front of themselves as they move around. When a
human steps into the beam, the robot stops moving, then resumes after the person moves away. 7. Internet of Things (IoT):
Amazon has been using the IoT for the process of the fulfillment center. There
are approximately 17.5 miles of conveyor belts in the FC. In order to run
reliably, every single day they’re monitored via AWS IoT services. AWS IoT
Greengrass helps here by allowing devices to act locally on the data they
generate while still taking advantage of the cloud. Events, in particular from the
machinery, are sent to Lambda Functions in AWS that trigger Step Functions.
These workflows then coordinate RME operations to maintain the equipment,
perform inspections, replace faulty motors and belts, and other types of activities. 8.
Thực tế ảo tăng cường (Augmented Reality - AR):
Amazon uses AR in E Commerce to help the customer project computer-
generated images of products in their living space via augmented reality. With
this feature, app users can make better shopping decisions by visualizing how
viewed items will fit the aesthetic and layout of their home. Amazon App
shoppers can simply tap the camera icon in their search bar, select the “AR
view” option and pull up desired products to sample an unlimited number of
items. Each product is appropriately sized and rendered, giving shoppers an
accurate view of how they will look in different home environments. Users even
have the option to move or rotate these computer-generated images on their
camera-equipped device to test different placement locations and angles.
Amazon lets the customer use the AR View to give shoppers the knowledge and
confidence to find the perfect items before making a single purchase. This
feature is particularly beneficial for larger items that are difficult to visualize in
the home—such as furniture and stereo systems
These systems are allocated by Amazon in different tasks such as predicting, sorting, searching,
and shipping to serve the process of maximizing product search time to help goods reach
customers as quickly as possible.
So exactly how Amazon has used these tools in its own FCs. They are divided into different processes such as:
Before entering the warehouse : The inbound process starts with forecasting
and ordering, before anything arrives to the FC. Powered by AWS, Amazon’s forecasting
engine is used for over 400 million products daily. After that, the trailers full of vendor
and small medium business seller items arrive at these bay doors by appointment.
After entering the warehouse : Employees unload the trailers and begin the
process of staging items located at their receiving workstations. The inbound associate
receives a product and stows it in their inventory. When the associate logs into their
workstation to perform their task, the Amazon robotic drive units will be activated. The
storage pods arrive dancing the correct side to stow items into inventory. Every time
the associate touches a product, they scan a unique barcode for that item, which is
called the Amazon Standard Identification Number, or ASIN. That's stored in their
inventory systems so they will know the quantity and locations of those items at any given time.
How to store products and manage inventory: : To manage their inventory
history, they use Amazon Nepture, a fast reliable fully managed graph database service
from AWS. They use that to stow similar items together. For Example, the electronics
would be stowed in the same section. However at amazon, they found that it's more
efficient to stow products using a randomized method. That is why in Amazon you will
see a variety of items in each inventory bin. After this process has been completed a
physical and digital match is created in their systems. And a few seconds after the item is
stowed, you can order it on Amazon.com .
How Amazon Gets Products Customers Order : Alfter the customer clicks the
buy button on Amazon.com, their systems will queue the robots to find the inventory
pod with the items you ordered. Once that item has been identified, the robot will bring
it to the associate. A screen at the associate’s station will show them a picture and
quantity of the item they need to pick. The same Visual Bin Inspection system is used as
during stow except this time. instead of lighting up bins where it should not be placed,
the system lights up in a white light where that item is. The associate identifies and
grabs the item, placed in the yellow tote signified by the green light, and pushes that
button acknowledging that the item was placed there. When the system detects that the
tote is full, the light flashes and the associate pushes the full tote back to the series of
conveyors and replaces it with a new one that was automatically brought to their station.
Next, the associates are picking items for different customers in batches. There
are two types of picking processes: they focus on single-item orders and multiple-item
orders. The single-item orders contain only one item per customer order. They fill up a
yellow tote full of single-items orders weighing up to 11kg. The single-item order yellow
totes will then be routed to the SIngles Pack for packaging. The multiple-item orders
contain more than one item per order. It’s possible to order pickup by up to six different
people picking items from six different robots, which all need to be brought together for
a single shipment. And in the end It will re-bin our individual items into customer order.
Then , once all our items are together, it’s packing time. The size of the box or envelope
is automatically selected by a Machine Learning algorithm, even the correct length of
tape is determined by Machine Learning and automatically dispensed. If needed,
protective packaging materials are added, a barcode is placed on the package and it’s sealed up.
The barcode is very important in the next stage that we call SLAM. SLAM is an
acronym, which stands for Scan, Label, Apply, and manifest. The technology will scan the
barcode sticker placed on the package in pack and immediately knows to print the
correct shipping label on the package. This is the first time your name and address are
placid on the package. In the space of a few seconds of process the machine learning
will run an algorithm to determine the optimal delivery carrier to get you the package on
time and at the lowest cost possible. The box is weighed, anđ the weight is checked
against the item’s known weight. In the final stages, after passing all of the quality
control measures, the package is routed onto another series of conveyors to a location
where the label is scanned. The conveyors then automatically send each package down
the correct chute where it will be packaged on a semi-trailer for shipment to another FC
or a sortation center for final delivery to you.
Transportation Network: Amazon is not just a logistic company, they are also an e-
commerce company. They deliver about tens of millions of packages per day. About 13
million times per day, someone clicks the order button on amazon. com . Some Days
laters, all, or at least almost all, of those 13 million orders arrive at their destination. So
do you wonder how amazon gets your packaging to your home with their promise to the
customer. And In fact, Amazon’s fulfillment system, their shipping system, is more
complicated and convoluted than that of almost any logistics company. It’s far more
complicated than that of UPS, or FedEx, or DHL, or any other major delivery company. In
a counterintuitive way, this complicated and convoluted fulfillment system is a crucial
component of the secret sauce that’s driving Amazon’s success. They’re striving to make
the consumer experience simple through behind-the-scenes complexity.So, back to the
question: how does an Amazon package get to you, and the answer, it depends.It
depends first on who’s fulfilling the package—Amazon or the seller.
Amazon do almost packaging in their logistic
About one fourth of sales in the US are fulfilled directly by the seller, as most products
on Amazon are listed there by a third-party, which can send packages directly through
UPS,FedEx, the postal service, or another consumer delivery company if they
choose.Amazon has nothing to do with the fulfillment of those orders, and the process
looks largely the same as with any other e-commerce company. What’s different is how
the other three quarters of Amazon packages in the US get to you—the ones that are
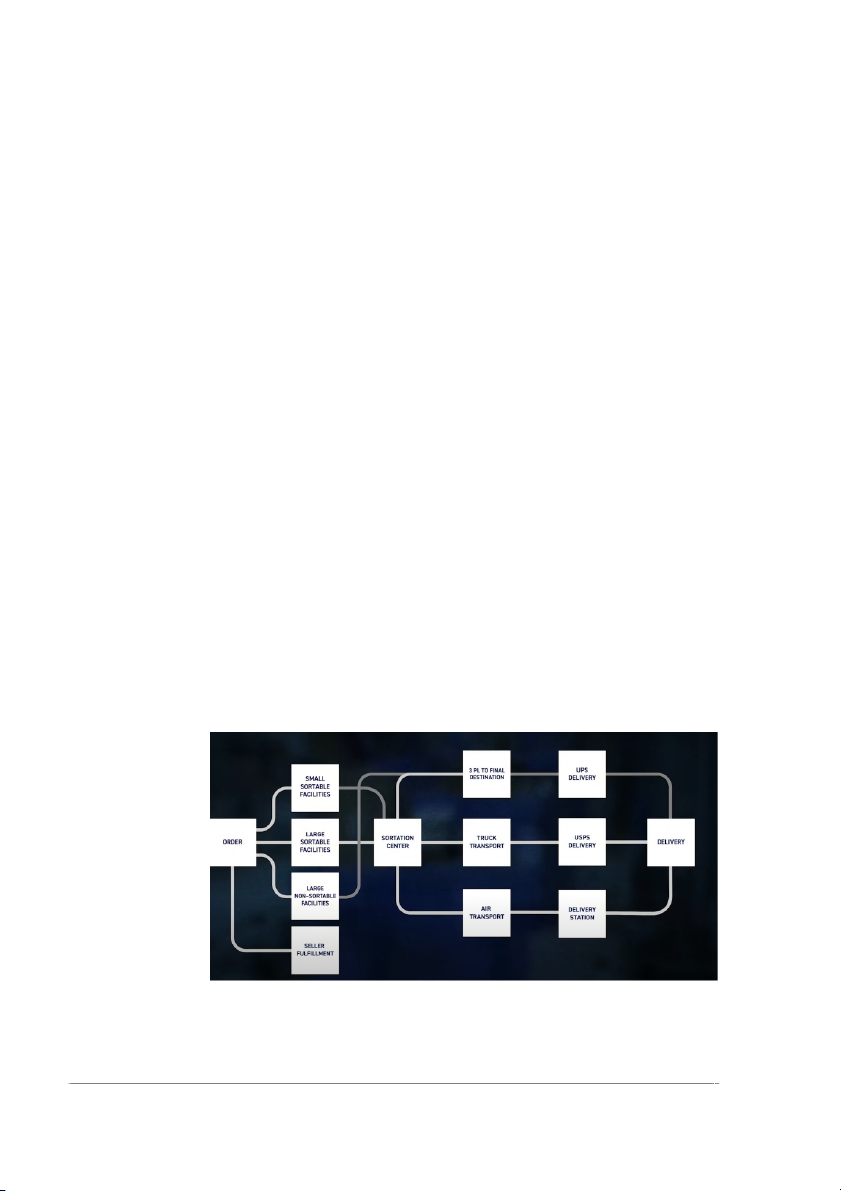
fulfilled directly by Amazon.The path that these take depends first on how big the
package is. You see, Amazon’s fulfillment centers are more-or-less split into three
categories: small sortable, large sortable, and large non-sortable.
Three categories: small sortable, large sortable, and large non-sortable
That first category, small sortable, represents the bread and butter of Amazon’s
business.These are items that are less than 12 by 16 by 6 inches or 30 by 40 by 15
centimeters in size, and about 25 pounds or 11 kilograms in weight.
The next category, large sortable, is basically anything larger than this up to a weight of
about 60 pounds or 27 kilograms.Now, the reason for the split between large and small
is because the fulfillment operations of smaller items is much easier to automate—they
can fit on conveyor belts and automated robots and other tools that lower the
company's reliance on humans.The fulfillment process for larger items, though, is just
tougher to automate cheaply, so the company chooses to segment the two processes
out, and runs a far more manual and distinct fulfillment system for larger
items.However, in most, but not all cases, the fulfillment centers for large and small
items are under the same roof, even if they’re operated completely independently.
Lastly the third category of products—large non-sortable. The distinction here is because
Amazon likes to aggregate products together into as few packages as possible—
unsurprisingly, fewer packages equals lower costs. So, both the sortable categories
include anything that could possibly be packaged together in a single box. The largest
items—say a 70 pound beanbag, for example—are shipped from the large non-sortable
fulfillment centers. These facilities are even less automated than the large-sortable ones,
and even include workers who create custom boxes for odd-sized items. For example,
this is a completely separate facility, located in Aurora, from the sortable fulfillment
center in Thornton. Now, some large items will go directly into the system of a third-
party provider, typically XPO Logistics, which will deliver these bulky items to their final
destination, while others will continue on in Amazon’s system. The portion of large non-
sortable items not sent to a third party logistics provider, plus all the large and small
sortable packages would next be sent to a regional sortation center.
Alfter go to the three fulfillment centers, the packaging will go to the fulfillment
sortation center. This fulfillment center is a massive facility, almost half a million square
feet in size, with robots running around, dropping packages into different chutes, which
each represent a different grouping of zip codes. Now, not all the sortation centers are
quite so automated, but each outputs the same thing—pallets of packages going to
roughly the same place. What happens next, though, once again, depends.
With the packaging, going to Miami, for example , would end up with other
packages for Miami, which would end up on a truck carrying pallets for Tampa, North
Carolina,Houston, Baltimore, New York City, Connecticut and a few other cities and
states to the east.This truck would then drive the 15 minutes to a waiting 767 cargo
plane at Denver International Airport branded in “Prime Air” livery. They use the aircraft
to deliver. They use the aircraft to deliver to the location far from the FC.
With the packaging delivered locally, they’ll be driven to one of the amazon
delivery stations in the location. There, they’ll be loaded into smaller delivery vans,
operated by independent companies or individuals contracted by Amazon, which will
take the packages to their final destinations. Last mile delivery: The last mile delivery
The last mile delivery of the amazon depends on where the location is. If it is on the
Suburbs the Amazon flex or individuals contracted by Amazon will take the packages to
the customer. But if it is in a place far from it, like in less populous areas, it just doesn’t
make sense for Amazon to operate their own last-mile delivery. They need a certain
amount of scale for that to be cheaper than the alternative, and, at least right now, that
scale is only possible in major metro areas. Therefore, they need alternatives for smaller
cities, towns, and rural areas, and that alternative is more often than not the USPS.
That’s because the postal service charges very low rates for last-mile delivery, assuming
Amazon transports the packages to the local post office themselves. While exact
numbers aren’t publicly known, estimates indicate the USPS charges Amazon about $2
per package for last-mile delivery—about half of what other delivery companies would
pay for the same service. After all, the USPS services every address in America, so
wherever Amazon needs to deliver, the USPS is going there anyways.
They also have some option in the last mile delivery : this is including crowdsourced
deliveries from external contractors (Amazon Flex and Amazon Logistics), Fresh food
delivery (Amazon Fresh), Amazon Key to allow deliveries into your home, delivery to car
trunks, remote door access to Amazon couriers, Amazon lockers and apartment hubs
(Amazon hubs), and distribution by drone (Prime Air) ensure customer convenience.
Bartholdi, J. J., III, & Hackman, S. T. (1998). Warehouse &
Distribution Science. Supply Chain and Logistics Institute.
Amazon Fulfillment Center Tour with AWS (youtube.com)
Amazon đã phát triển nhanh hơn bao giờ hết như thế nào trong thời
kỳ đại dịch | Tin tức | Kỹ thuật Tây Bắc (northwestern.edu)
Inside Amazon’s Meticulous Same-Day Delivery Strategy | WSJ Shipping Wars (youtube.com
How Amazon's Super-Complex Shipping System Works (youtube.com)
Amazon Logistics: Phân tích chi tiết | Mô hình kinh doanh | (platformthinkinglabs.com)
Amazon & Customer Experience: 13 Quotes from Jeff Bezos -
Customer Satisfaction Surveys and Feedback Management for NetSuite (suitefeedback.com)
How Amazon Beat Supply Chain Chaos With Ships, Containers And Planes (youtube.com)
How Amazon deploys robots in its operations facilities (aboutamazon.com)
What is Computer Vision? - Image recognition AI/ML Explained - AWS (amazon.com)
Amazon’s first fully autonomous warehouse robot is called Proteus - The Verge




