












Preview text:
2015-2024 FDI OUTFLOW FROM SOUTH KOREA AND
LESSONS FOR VIETNAM INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS
Assos. Prof. TS. Nguyễn Thường Lạng Student: Nguyễn Tuyết Nhi CONTENTS
1. Theoretical Framework
5. South Korea’s Outward of FDI
Foreign Direct Investment 2. Impacts of FDI (OFDI) 6. Overview of South
3. Overview of South Korea’s Korean FDI in Vietnam (2015–2024)
7. Policy Implications and
4. South Korea’s Outward Recommendations for FDI Policy Korean FDI in Vietnam
Assos. Prof. TS. Nguyễn Thường Lạng Student: Nguyễn Tuyết Nhi
1. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK OF FDI Concept of FDI
FDI is a form of investment where foreign investors directly
participate in management and operation of business
activities in the host country.
It aims to create tangible and intangible assets, enhance
production capacity, generate employment, and promote
long-term economic development.
FDI includes inward FDI (into a country) and outward FDI (from a country).
Assos. Prof. TS. Nguyễn Thường Lạng Student: Nguyễn Tuyết Nhi
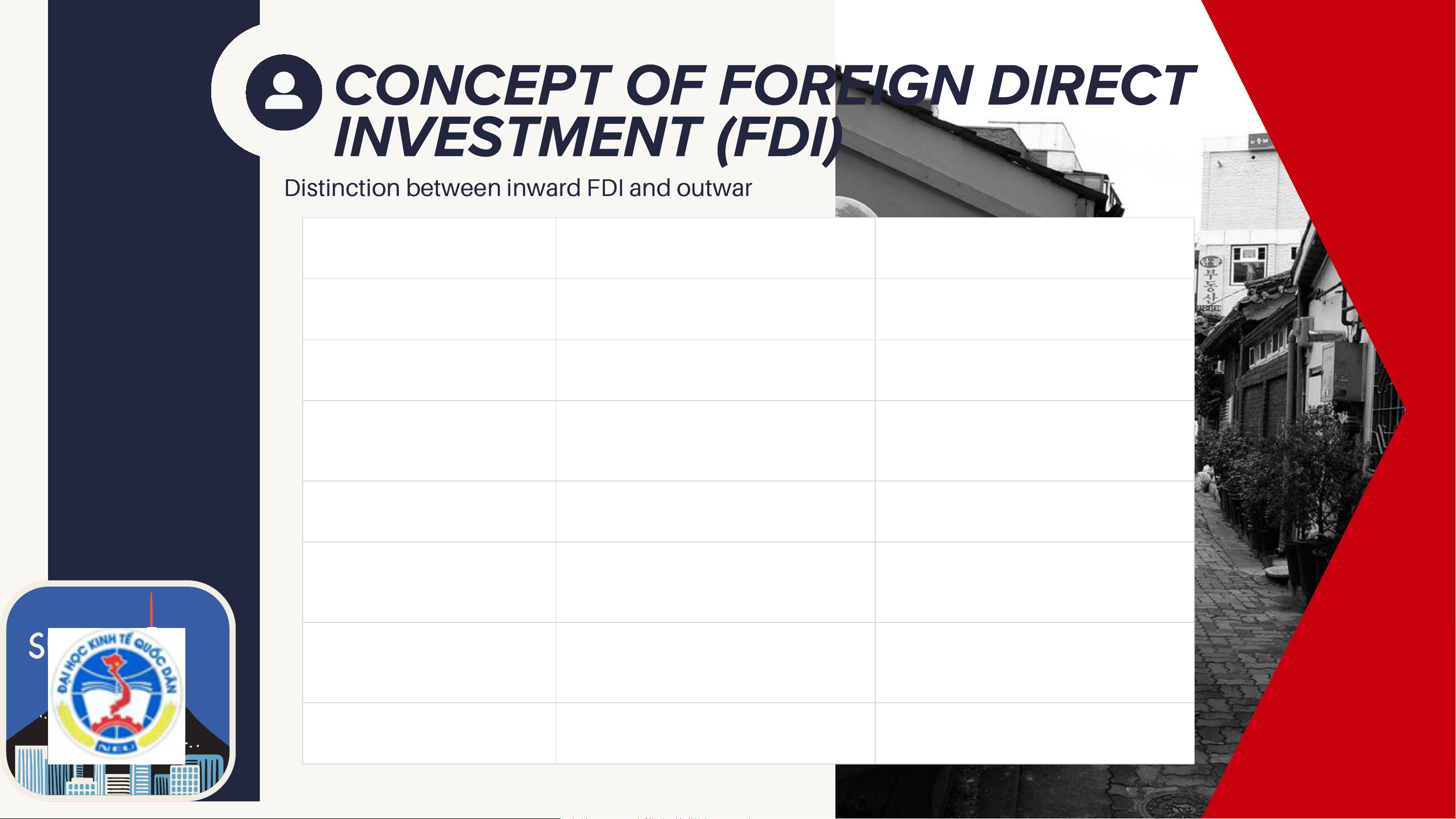
CONCEPT OF FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI)
Distinction between inward FDI and outward FDI Aspect Inward FDI Outward FDI Definition
Foreign direct investment entering Foreign direct investment made by a country domestic firms abroad Perspective
Viewed from the host country
Viewed from the home country
Attract capital, technology, jobs,
Expand markets, reduce costs, Main Objective
and management expertise
access resources, and enhance global competitiveness Key Actors
Foreign investors operating in the
Domestic firms investing in domestic economy overseas markets
Boosts domestic production,
Supports firm internationalization Economic Impact
exports, employment, and
and global value chain integration industrial development
Investment incentives, regulatory
Financial support, investment Typical Policy Focus
facilitation, infrastructure
promotion, risk insurance, and tax development incentives
Example (Vietnam–Korea)
Korean firms investing in Vietnam’s Korean firms investing in the U.S., manufacturing sector Vietnam, and Europe
2. IMPACTS OF FDI
IMPACTS ON THE INVESTING COUNTRY
Reduction of production costs through overseas production.
Improved market access and reduced trade conflicts.
Access to natural resources, labor, and technological expertise abroad.
IMPACTS ON THE HOST COUNTRY Provides capital for economic Overdependence on foreign development capital Transfers technology and Strong competitive pressure management skills on domestic firms Creates jobs and raises income Environmental risks and
Promotes exports and international transfer pricing practices integration
Assos. Prof. TS. Nguyễn Thường Lạng Student: Nguyễn Tuyết Nhi 3. OVERVIEW OF SOUTH KOREA’S ECONOMY (2015– 2024) `
Assos. Prof. TS. Nguyễn Thường Lạng Student: Nguyễn Tuyết Nhi
Source: MINISTRY OF ECONOMY AND FINANCE
CHAPTER II: KOREA’S OUTWARD FDI AND `
KOREAN FDI IN VIETNAM (2015–2024)
1. South Korea’s Outward Foreign Direct Investment (OFDI)
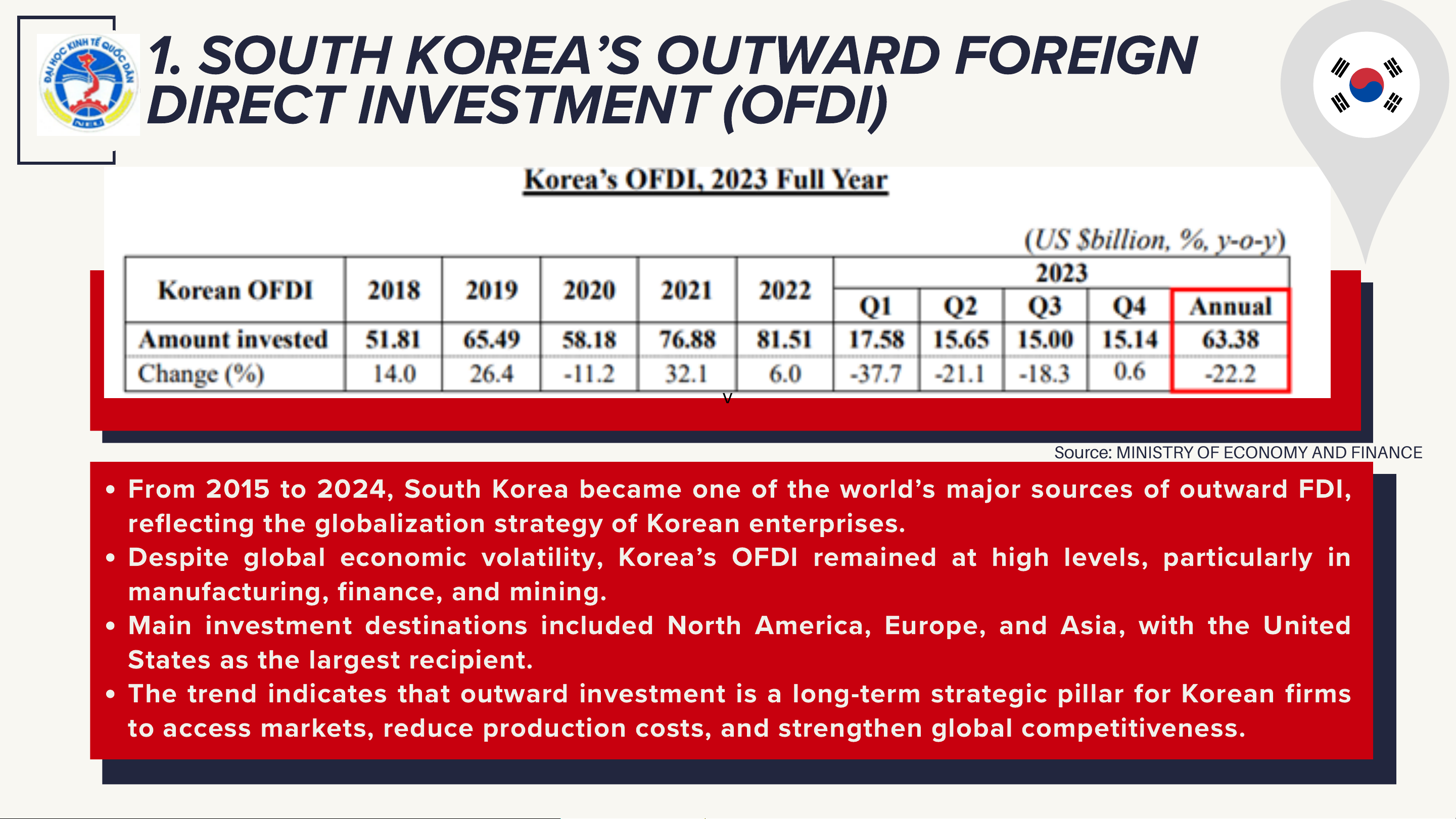
1. SOUTH KOREA’S OUTWARD FOREIGN
DIRECT INVESTMENT (OFDI) v
Source: MINISTRY OF ECONOMY AND FINANCE
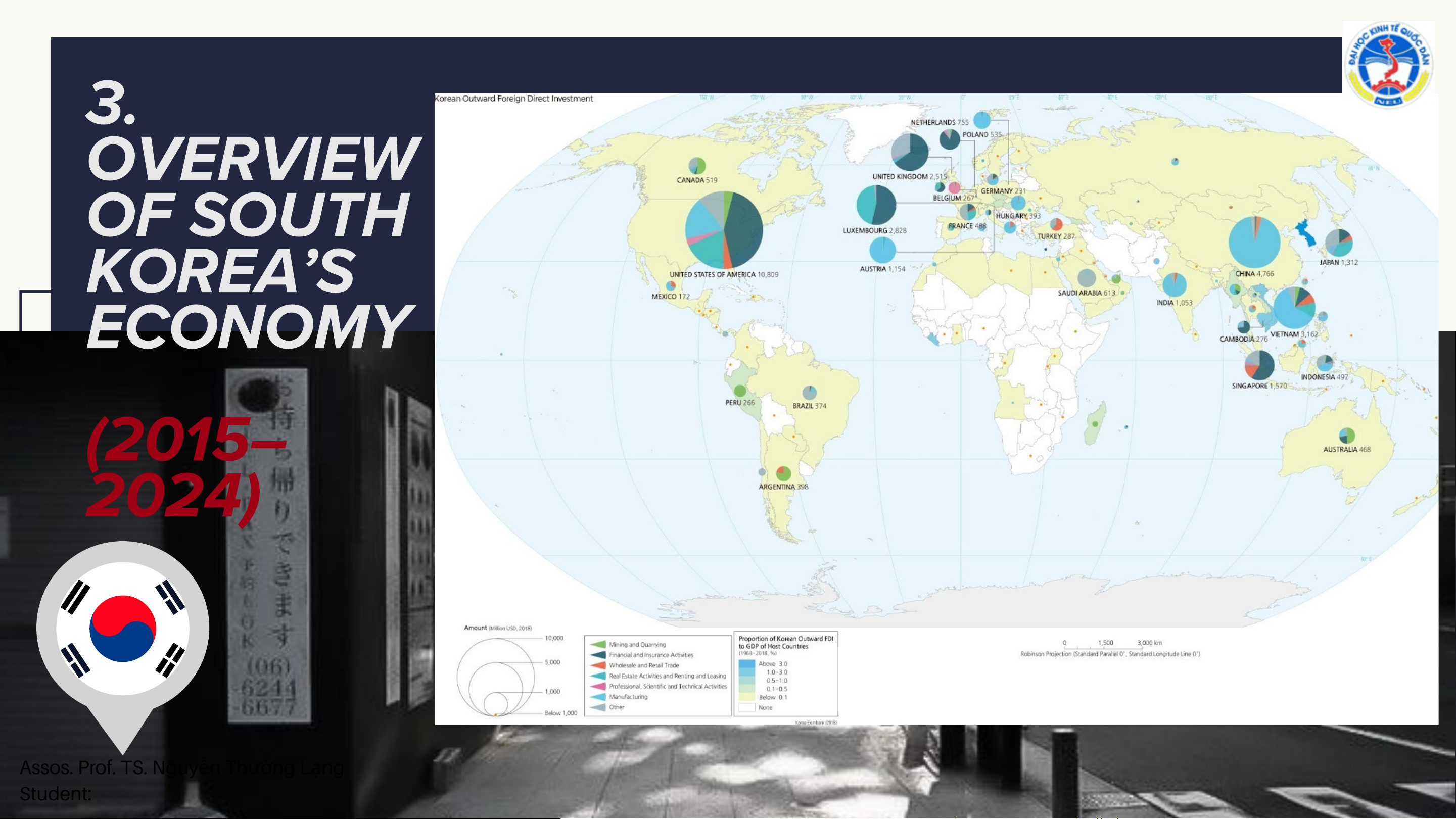
From 2015 to 2024, South Korea became one of the world’s major sources of outward FDI,
reflecting the globalization strategy of Korean enterprises.
Despite global economic volatility, Korea’s OFDI remained at high levels, particularly in
manufacturing, finance, and mining.
Main investment destinations included North America, Europe, and Asia, with the United
States as the largest recipient.
The trend indicates that outward investment is a long-term strategic pillar for Korean firms
to access markets, reduce production costs, and strengthen global competitiveness.
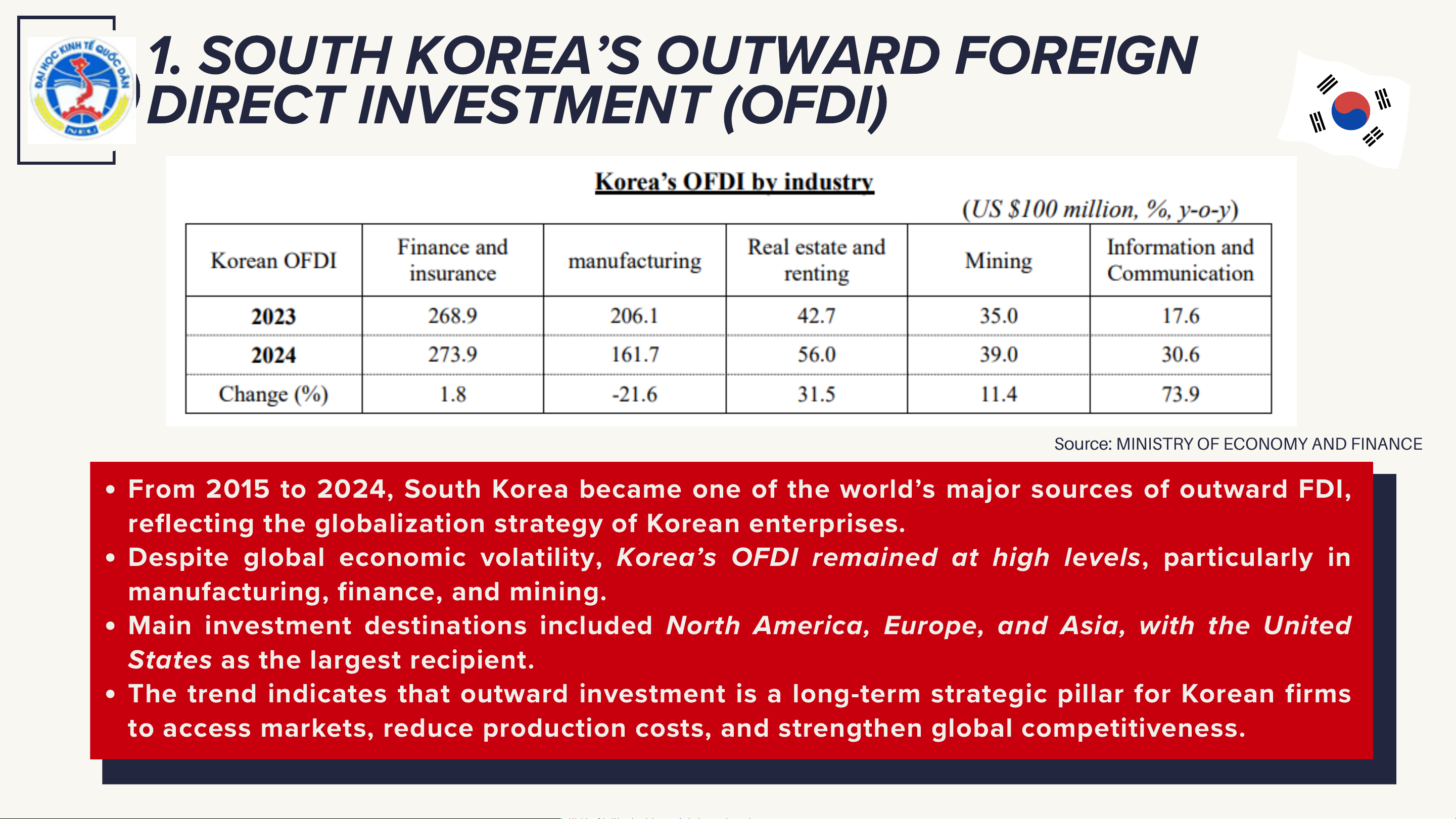
1. SOUTH KOREA’S OUTWARD FOREIGN
DIRECT INVESTMENT (OFDI)
Source: MINISTRY OF ECONOMY AND FINANCE
From 2015 to 2024, South Korea became one of the world’s major sources of outward FDI,
reflecting the globalization strategy of Korean enterprises.
Despite global economic volatility, Korea’s OFDI remained at high levels, particularly in
manufacturing, finance, and mining.
Main investment destinations included North America, Europe, and Asia, with the United
States as the largest recipient.
The trend indicates that outward investment is a long-term strategic pillar for Korean firms
to access markets, reduce production costs, and strengthen global competitiveness.
2.Foreign Direct Investment into Vietnam
FDI inflows in 2024: Total newly registered, adjusted, and
contributed foreign investment capital amounted to USD 38.23
billion, reflecting a 3% decline compared with 2023.
FDI disbursement: Implemented FDI capital reached USD 25.35
billion, representing a 9.4% year-on-year increase, indicating
improved investment implementation efficiency.
Cumulative FDI performance: By the end of 2024, Vietnam had
attracted approximately 42,002 FDI projects, with total registered
capital of USD 502.8 billion and implemented capital of USD 322.5 billion.
South Korea remained the largest foreign investor in Vietnam, with
cumulative registered capital exceeding USD 92 billion, accounting for
17.9% of total accumulated FDI. Korean investments are largely large-scale
projects concentrated in manufacturing and processing industries.
Major investment partners in 2024: Investors from 114 countries and
territories were present in Vietnam. Singapore ranked first with USD 10.21
billion , followed by South Korea with USD 7.06 billion, and then China, Hong Kong (China), and Japan.
Project structure: China led in the number of newly registered projects, while
South Korea ranked first in capital adjustments and capital contributions and share acquisitions. 3. OVERVIEW OF SOUTH KOREAN FDI IN VIETNAM
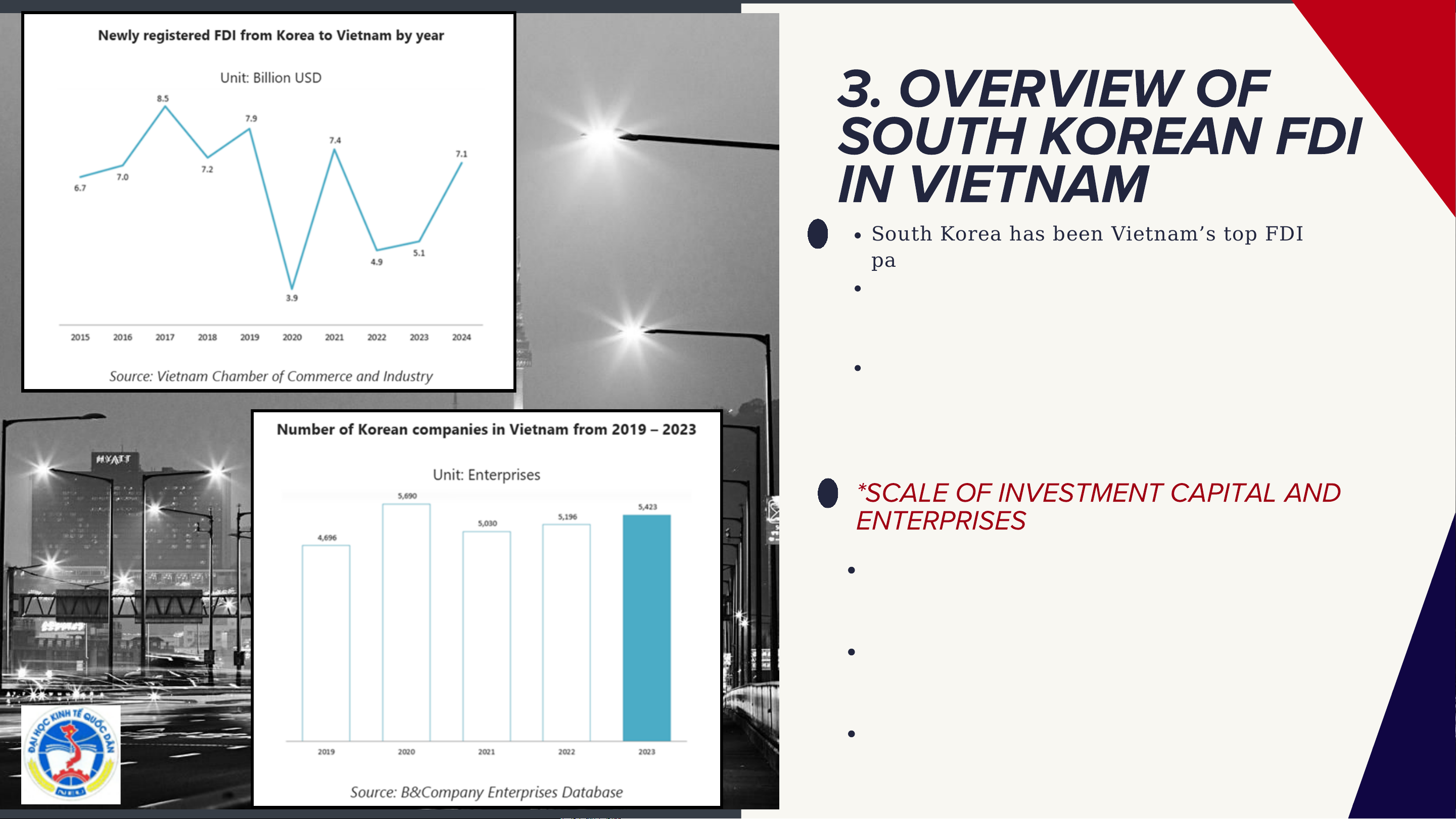
South Korea has been Vietnam’s top FDI partner since the mid-2010s.
New Korean FDI declined in 2020 due to
COVID-19 but recovered strongly from 2022 onward.
In 2024, newly registered Korean FDI
reached USD 7.06 billion, increasing 37.5% year-on-year. `
*SCALE OF INVESTMENT CAPITAL AND ENTERPRISES
Korean FDI stock (2024): ~USD 92 billion
(≈18% of total FDI), making Korea Vietnam’s largest investor
Trend since 2015: New FDI fluctuated, with
a sharp drop in 2020 (≈USD 4 billion) due to COVID-19
Recovery phase: From 2022, Korean FDI
rebounded strongly, reaching ~USD 7
billion in 2024 (CAGR ≈ 20%) South Korea from Investing FDI in Vietnam Enhanced Economic Efficiency and Benefits for Market Expansion Strengthening Competitiveness within Global South Korea Lower labor and Value Chains Technology and production costs Management enhance firm- Major Spillover Effects level efficiency conglomerates (at the Regional (Samsung, LG, Level) Vietnam serves as a strategic Hyundai) export base to strengthen ASEAN and global competitiveness Diffusion of management markets through offshore production hubs practices and Reduced exposure production to trade and standards geopolitical risks within regional through production networks diversification
Risk of Reduced Domestic Investment
01 Partial relocation of capital and production capacity abroad
Dependence on External Investment Environments Risks and
02 Increased exposure to Vietnam’s
regulatory, labor, and policy environment Costs for South Korea Risks Associated with
Globalization and Trade Conflicts
Vulnerability to tariffs and international
03 trade disputes affecting exports from Vietnam Benefits for Vietnam
Economic Growth and Export Expansion
Largest FDI partner: Over USD 92 bil ion in from
cumulative FDI (~18% of total FDI stock)
Growth and exports: Strong contribution to
01 manufacturing, GDP growth, and exports Receiving FDI Industrial upgrading: Expansion of
processing and manufacturing industries from South
Job Creation and Human Capital Development Korea
Employment creation: Over 1 mil ion jobs 02 generated
Human capital development: Exposure
to international standards and modern skil s
Industrial Spillovers and
Structural Transformation
03 Value chain integration: Deeper
participation in global value chains Limitations and Costs for Vietnam Low Domestic Dependence on a Value Added Limited Number of Large Corporations Concentration in assembly rather Heavy dependence than R&D and on large innovation conglomerates (e.g., Samsung) Environmental Regional and Labor Development Pressures DisparitiesFern andes Rising FDI concentration environmental in developed risks and job- regions widens quality concerns regional gaps
Cost-based investment structure:
Korean firms mainly use Vietnam for large-scale, export-oriented 01
manufacturing, while R&D and high-
tech activities remain concentrated in advanced economies. Causes of
Institutional and policy constraints:
Incentive frameworks favor manufacturing
expansion over R&D; limitations in IP 02 the
protection, administrative procedures, and
initial costs reduce the attractiveness of high-technology investment. Limitations?
Global supply chain strategies: To
optimize costs and manage risks, Korean
conglomerates separate production and
innovation, locating manufacturing in
03 Vietnam and R&D in South Korea or other developed countries. CHAPTER III: Policy
1. Key Considerations in Attracting Korean FDI Implications
During 2015–2024, Korean FDI became a
major driver of Vietnam’s economic growth. and
However, Vietnam needs a more strategic 01
approach, focusing on quality, sustainability,
and long-term value creation rather than Recommendations capital volume alone. for Korean FDI in
2. Focus on Quality over Quantity Vietnam
In 2024, Korean registered FDI reached USD 7.06
bil ion, accounting for 18.5% of total FDI. 02
Most investment remains concentrated in large-
scale manufacturing and assembly.
Limited investment in high-tech, R&D, and
innovation-based sectors reduces value-
added and technology spil overs.
3. Strategic Positioning in Global Value Chains
Korean FDI has formed major production clusters across key industrial regions.
However, R&D and high-value activities remain marginal. 03
Current investment strategy is mainly market- and
efficiency-seeking, not strategic asset–seeking.
Vietnam should aim to attract higher segments of the global value chain.
4. Institutional Environment and Human Capital
Administrative procedures, shortages of
skil ed labor, and limited technological
infrastructure remain constraints.
Improving the business environment and CHAPTER III: Policy 04
institutional quality is critical to retaining Korean strategic investors. Implications
5. Policy Recommendations for the Government and
Target high-value FDI: Provide selective incentives for R&D, technology transfer, and advanced Recommendations 05 manufacturing.
Ensure policy stability and transparency to retain long- term investors. for Korean FDI in
Invest in strategic infrastructure: logistics, high-tech
industrial parks, and innovation hubs.
Leverage FTAs (CPTPP, EVFTA) to strengthen Vietnam’s Vietnam
role as a regional production and export base.
6. Recommendations for Vietnamese Enterprises
Enhance competitiveness: improve management,
quality standards, and production capacity.
Integrate into supply chains of Korean conglomerates such as Samsung and LG. 06
Invest in human capital, especial y technical and managerial skil s.
Adopt digital transformation and innovation to meet international standards. REFERENCES
B&Company. (2024). Overview of Korean companies in Vietnam
CEIC Data. (2024). Korea: Outward direct investment by region and country.
Charting the Globe. (2024). South Korea: Foreign direct
investment outflows (2014–2024 `
Foreign Investment Agency – Ministry of Finance of Vietnam.
(2024). Foreign direct investment information and policy updates
Korea Economic Institute of America (KEIA). (2023). South
Korea’s important role in Vietnam’s rapid development. THANK YOU



