
Preview text:
CHƯƠNG 1: AN OVERVIEW OF AUDITING 1. Question: 1.1. What is an audit? 1.1.1. Definition:
a. Functions (Chức năng nhiệm vụ):
Auditing is the accumulation (thu thập: dựa trên xác định hành vi đó liên quan đến
chu trình kinh doanh nào, hành vi đó cần xem xét trên MQH nào của DN để xđ data
cần phải thu thập) and evaluation (đánh giá) of evidence about information to
determine and report on the degree of correspondence between the information and established criteria. b. Requirements (Yêu cầu):
Auditing should be done by a competent, independent person c. Ví dụ:
Đánh giá việc nhận lương : thu thập bằng chứng (Phỏng vấn lương trực tiếp: nhận
đúng kỳ không, có đúng cam kết trên hợp đồng; Xem sổ thực hiện GD chuyển tiền
xem có thanh toán lương kịp thời; Thu thập sao kê ngân hàng..) Hàng tồn kho:
- HTK ↑khi hỏng, cháy, xuất bán (chu trình bán), ↓ khi mua về (chu trình mua
hàng), sản xuất (chu trình sản xuất)
- Giả sử giao tại kho của người bán: Biên bản kiểm nghiệm, Biên bản giao hàng;
giả sử giao tại kho người mua: 1.1.2. Characteristics: Competent and Independent a. Three party involvement Practitioners Intended users of information Responsible party
b. Appropriate subject matter: to be examined by the practitioner Ex: FSs Đối tượng
c. Suitable criteria: to evaluate the subject matters Ex: IFRS, VAS, ISAs Tiêu chí để đánh giá
d. Sufficient appropriate evidence
Bằng chứng đầy đủ và phù hợp
e. Written assurance report in an appropriate form
Đảm bảo bằng văn bản theo mẫu phù hợp 1.1.3. Classification:
a. Three primary types of audits - Operational audit
Objective: economical, efficient, effective - Compliance audit
Objective: in according with law, national legislation -
Financial statement audit
Objective: FSs have a true and fair view
b. Several types of auditors are in practice today.
Certified public accounting firms are responsible for auditing the historical financial
statements of all publicly traded companies
A government accountability office auditor is an auditor working for the U.S.
Government Accountability Office (GAO). It has many of the same audit responsibilities as a CPA firm
Internal revenue agents: A major responsibility of the IRS is to audit taxpayers’ returns
to determine whether they have complied with the tax laws. These audits are solely compliance audits.
An auditor involved in any of these areas must have considerable tax knowledge and
auditing skills to conduct effective audits.
Internal auditors are employed by all types of organizations to audit for management
with oversight by the board of directors
To maintain independence from other business functions, the internal audit group
typically reports directly to the president
Users from outside the entity are unlikely to want to rely on information verified solely
by internal auditors because of their lack of independence. This lack of independence is
the major difference between internal auditors and CPA firms.
Câu hỏi: 3 loại kiểm toán với internal audit và external audit có mối quan hệ gì với nhau?
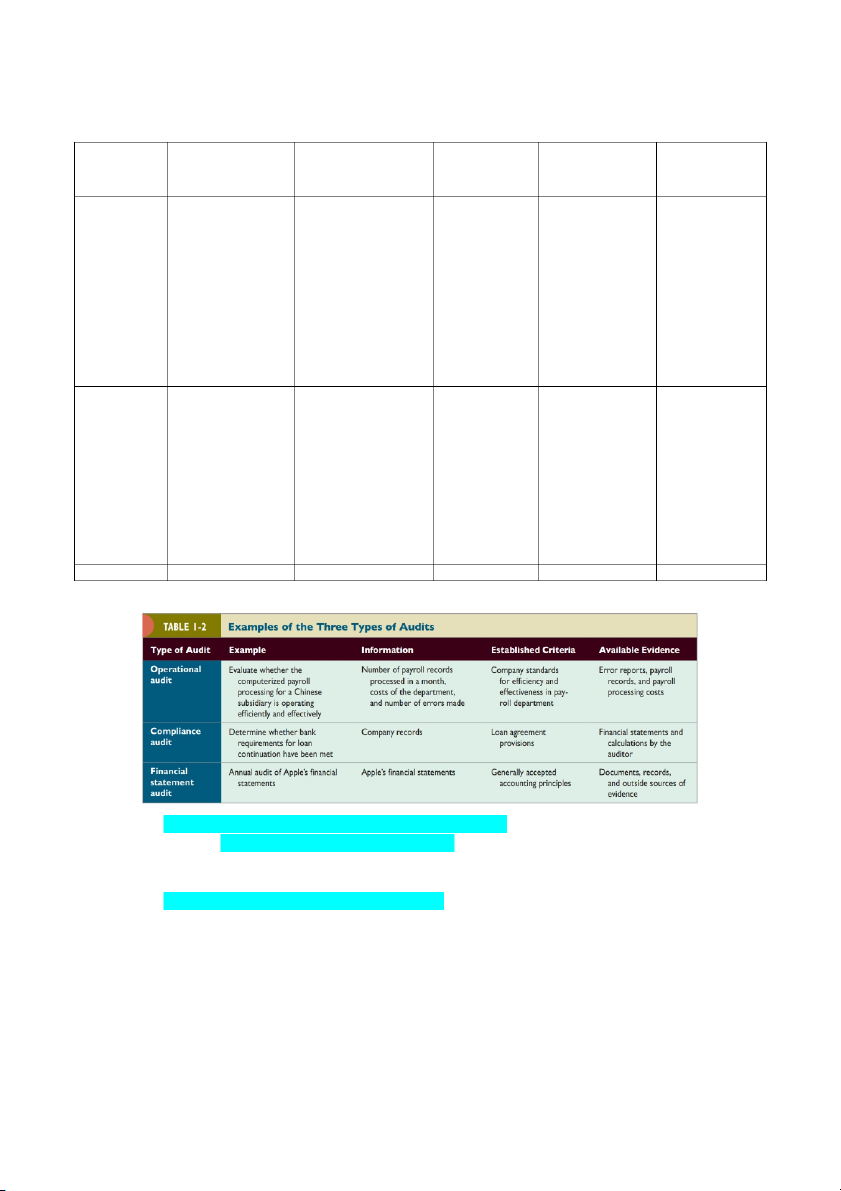
2. The difference between an operational audit, a compliance audit, and a
financial statement audit? Type of Definition Example Information Established Available Audit criteria Evidence
Operational An operational Assess the The quantity Organizational Reports on audit audit evaluates efficiency and of payroll benchmarks for errors, payroll kiểm toán
the efficiency and effectiveness of the records efficiency and records, and hoạt động effectiveness of computerized handled effectiveness the expenses any part of an payroll processing monthly, within the associated with organization’s system for a departmental payroll payroll operating
subsidiary in China. expenses, and department. processing. procedures and the frequency methods. At the Evaluation of the of errors completion of an
efficiency, accuracy, incurred.
operational audit, and customer -THE management satisfaction in AUDITING
normally expects processing the PROFESSION
recommendations distribution of for improving letters and packages operations. by a company like Federal Express.
Compliance Conducted to Determine whether Company Loan agreement Financial audit determine bank requirements records provisions statements and Kiểm toán whether the for loan calculations by tuân thủ auditee is continuation have Wage law the auditor following specific been met procedures, rules,
or regulations set Review wage rates by some higher for compliance with authority minimum wage laws Financial Conducted to Annual audit of Apple’s Check whether Documents, statement determine apple’s financial financial the financial records and audit whether the statements statements statements are outside sources Kiểm toán financial presented in of evidence BCTC statements (the accordance with information being the principles verified) are stated in accordance with specified criteria 2.1.
What are the principles of ethics? Why should
auditors maintain professional ethics? 2.2.
Explain the role/benefits of auditing


