
Preview text:
NGUYEN ANH THU – BBAE I3B- NEU I.
Discrete Probability Distribution
1) P1 + P2 +…+Pn = 1 hay
3) Variance ( Phương sai )
2) Expected value (Giá trị trung bình) Var (X) = E(X2) – [E(X)]2
E(X) = = = X1 P1 + X2 P2 +… + Xn Pn
4) Standard deviation (Độ lệch chuẩn): =
5) Discrete Probability: Bernoulli
Binomial Distribution X ~ B (n,p)
A single trial of an experiment ( n=1)
n independent experiment (k: success; n k: failure) P ( X success) = P P(X = k) = P ( X failure ) = 1 – P E(X) = n p E(X) = P Var (X) = n P (1 P) Var (X) = P (1 P) = =
Excel: Binorm.dist (number,trials,probability,false/true) II.
Continuous distribution: X or X 1) P (a) = 5) P ( 2) P (a = 6) E (X) = 3) P (a = +
7) Var (X) = E(X2) – [E(X)]2 4) P (X = [2 8) =
UNIFORM DISTRIBUTION (Phân phối đều) (X ~ UX 1) 2) E(X) = = 3) Var (X) =
NORMAL DISTRIBUTION (Phân phối chuẩn) X ~ N ()
→ STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION (Phân phối chuẩn tắc) Give Then z ~ N(0;1) Cách tính : P
Mode → STAT → AC (đóng) [chế độ thống kê] P
Shift + 1 (statistic) → Chọn 5 (Distribution) → Chọn 1: P( → Nhập dữ liệu P
EXCEL: Norm.dist (x;mean;SD;true)
Cách quy đổi từ % →
Exel: = NORM.INV(probability, mean, standard deviation)
BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION→ NORMAL DISTRIBUTION
(chuyển từ phân phối nhị thức → phân phối chuẩn do số mẫu quá lớn) 1) E(X) = 2)
*NOTE: Trừ 0.5 cho số đằng sau và Cộng 0.5 cho số đằng trc để tránh sai số
EXPONENTIAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION (Phân phối mũ) for P (X P (X P (X III.
SAMPLING DISTRIBUTION (Phân phối mẫu)
NGUYEN ANH THU – BBAE I3B- NEU
Sn (tổng giá trị quan sát) = X1 + X2 +…+ Xn (n giá trị) has
1) Distribution of sample means (Phân phối của trung bình mẫu) (has
1)Nhận xét về standard error khi cỡ mẫu n thay đổi
2)Trong các bài sampling distribution SE = Đặt
→ để giảm sai số của trung bình mẫu, cách tốt nhất là tăng cỡ mẫu
Standard error (sai số chuẩn): SE =
quan sát → cỡ mẫu n càng lớn thì càng dễ xấp xỉ phân phối chuẩn
ĐỂ DỄ PHÂN BIỆT : Đề không cho sample size: Đề cho sample size:
2) Sample Proportions (lấy mẫu theo tỉ lệ) Mean = Standard deviation = IV. INTERVAL ESTIMATION 1) SAMPLE MEANS
*CASE 1: GIVEN POPULATION VARIANCE ( (STANDARD DEVIATION)
Cách tính (critical value) trong excel: = NORM.S.INV () CONFIDENCE LEVEL 90% 1.645 95% 1.960 98% 2.326 99% 2.576
*CASE 2: UNKNOW POPULATION VARIANCE (STANDARD DEVIATION) with
Cách bấm máy tính tìm S:
Shift + Mode → 4 STAT → 1: ON → Mode → 3 Vars → AC→ Shift 1 STAT→4 Var→ 4
NGUYEN ANH THU – BBAE I3B- NEU 2) SAMPLE PROPOTIONS
3) MARGIN OF ERROR (SAI SỐ PIN)/ MINIMUM SAMPLE SIZE → → V. HYPOTHESIS TEST
1) HYPOTHESIS TEST FOR THE MEAN:
Đề bài không đề cập đến anpha → anpha = 0.05 = 5% hay confidence level = 95%
*CASE 1: KNOW POPULATION STANDARD DEVIATION (Z – test)
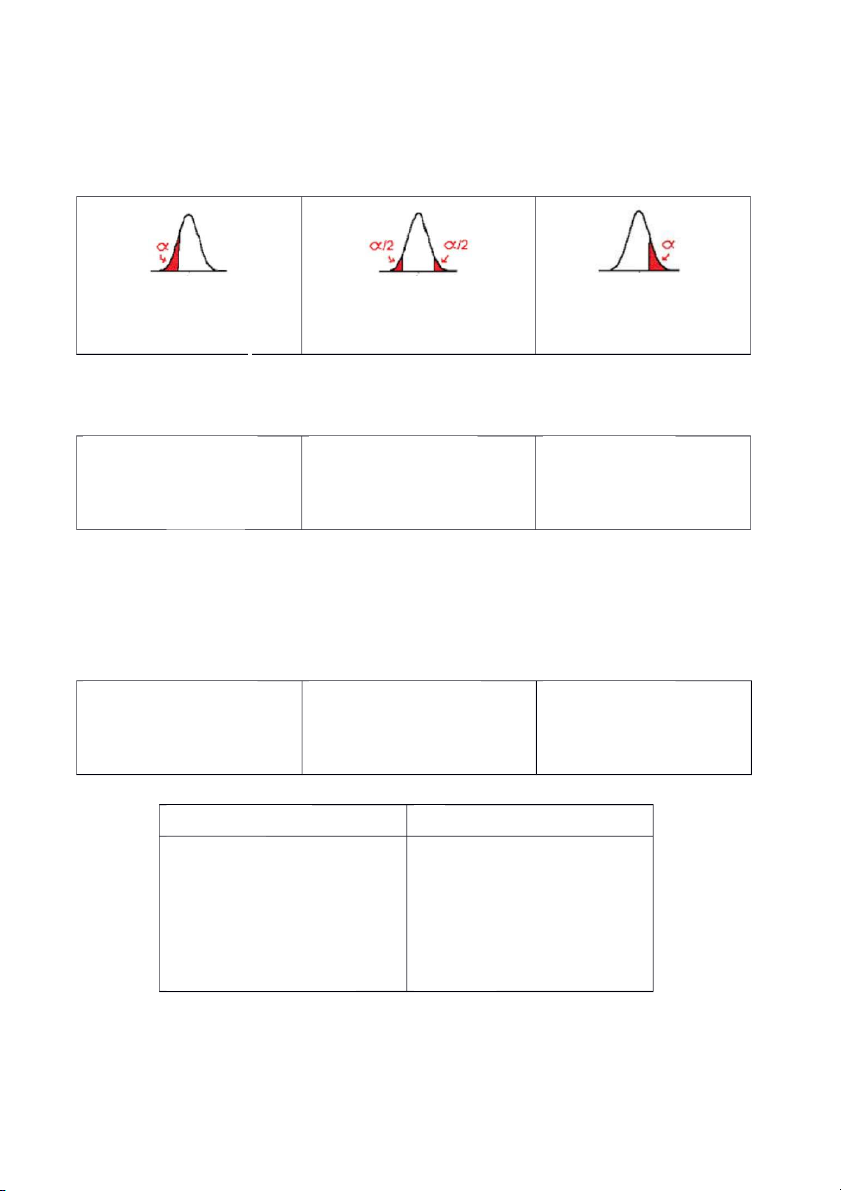
Critical value (Giá trị tới hạn) More/Increase: More or Less: Less Left-tailed test Two-tailed test Right-tailed test H H o: Ho: o: H H 1: H1: 1:
z < 0: Pvalue = P(z ≥ test stat)
S2 z vs 0:P(z ≤ test stat) / 2.P(z ≥test stat) z > 0: Pvalue = P(z ≤ test stat) Test statistic:
*CASE 2: UNKNOW POPULATION STANDARD DEVIATION (t – test)
Critical value (Giá trị tới hạn)
More/Increase (Left-tailed test)
More or Less(Two-tailed test):
Less (Right-tailed test) W0 (; W0 W0 W1 W1 W1; +) Ho: Ho: Ho: H1: H1: H1:
z < 0: Pvalue = P(z ≥ test stat)
S2 z vs 0:P(z ≤ test stat) / 2.P(z ≥test stat) z > 0: Pvalue = P(z ≤ test stat) Test statistic:
2) HYPOTHESIS TEST OF THE PROPOTION P = ; Test statistic:
Critical value (Giá trị tới hạn)
NGUYEN ANH THU – BBAE I3B- NEU
More/Increase (Left-tailed test)
More or Less (Two-tailed test)
Less (Right-tailed test) W0 W0 W0 W1 W1 W1 Ho: Ho: Ho: H1: H1: H1:
z < 0: Pvalue = P(z ≥ test stat)
S2 z vs 0:P(z ≤ test stat) / 2.P(z ≥test stat) z > 0: Pvalue = P(z ≤ test stat) Common hypothesis tests Excel Normal distributin
Left-tailed p-value for test statistic NORM.S.DIST(
Right-tailed p-value for test statistic 1 NORM.S.DIST(
Two-tailed p-value for test statistic 2*(1 NORM.S.DIST(|)
Critical Z value for left-tailed test at NORM.S.INV(
Critical Z value for right-tailed test at NORM.S.INV(1-
Critical Z value for two-tailed test at NORM.S.INV( Student’s distribution T.DIST(,df,1)
Left-tailed p-value for test statistic T.DIST.RT(,df)
Right-tailed p-value for test statistic T.DIST.2T(|,df)
Two-tailed p-value for test statistic T.INV(,df)
Critical value of for left-tailed test at T.INV(1-,df)(
Critical value of for right-tailed test at )T.INV.2T(,df)
Critical value of t of for two-tailed test at
Reject Ho when p-value < a= 0.05 or 0.1 (tuỳ đề bài)
1.According to Central Limit Theorem 1.P0=0.2 ;P= 0,12
is approximate with normal distribution when n is large P P +
enough (n ≥ 30) → : We could see that although has n = 15 is
Confident interval = (0,0563 ; 0,1837)
not large enough but it still more symmetric than that of W
2. From question 1, the proportion of households using
→ Histogram A is the histogram of
Ogondo washing powder is between 5,63% and 18,37% 2. has
while the manufacturer claims that 20% using it. 3. 0.00043 The claim is wrong.
4. According to question 3, the probability of mean of 25
3.From question 2: P(0,0563 ; 0,1837): different from 20%
packets of nuts is smaller than 18g is nearly zero
(g) has the probability is nearly zero → The statement is reasonable H0: P = P0 = 0,2
5. According to question 1, is normally distributed (nearly -1,96 1,96 H1: P P0 = 0,2
symmetric). In this case, has n =2515→ distribution of is =5%=0,05 = 1,960
more symmetric than that of → is normal distribution.
W0 = (-1,960 ; 1,960) ; W1 = (- ; -1,960) (1,960 ; +)
According to the Central Limit Theorem, If W/X is not
ZCALC = = -2 ZCALC W1 Reject H0 P P0
normally distributed, then Wn/Xn is approximately normally 1.3a (đề 2) This probability is nearly zero acco
distributed if n is large enough. Hence, the distribution of the answer in 2(d).
Wn/Xn must be more symmetric than that of X/W. Therefore, 1.3b. : This statement is very reasonable, as the pro
A corresponds to … As it much more symmetric than B.
that the machine will stop filling a packet when the
Yes, as distribution of S25 in Histogram A is nearly symmetric,
contains 73 nails or fewer is nearly zero. Hence the
and distribution of S73 should be more symmetric than that of
probability that the package must have 74 or more n S25. nearly 1.