




Preview text:
Blood Physiology
Giảng viên : ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân ( dntvan@medvnu.edu.vn )
Bài giảng lý thuyết trực tuyến Khoa Y –ĐHQG HCM | 1 1
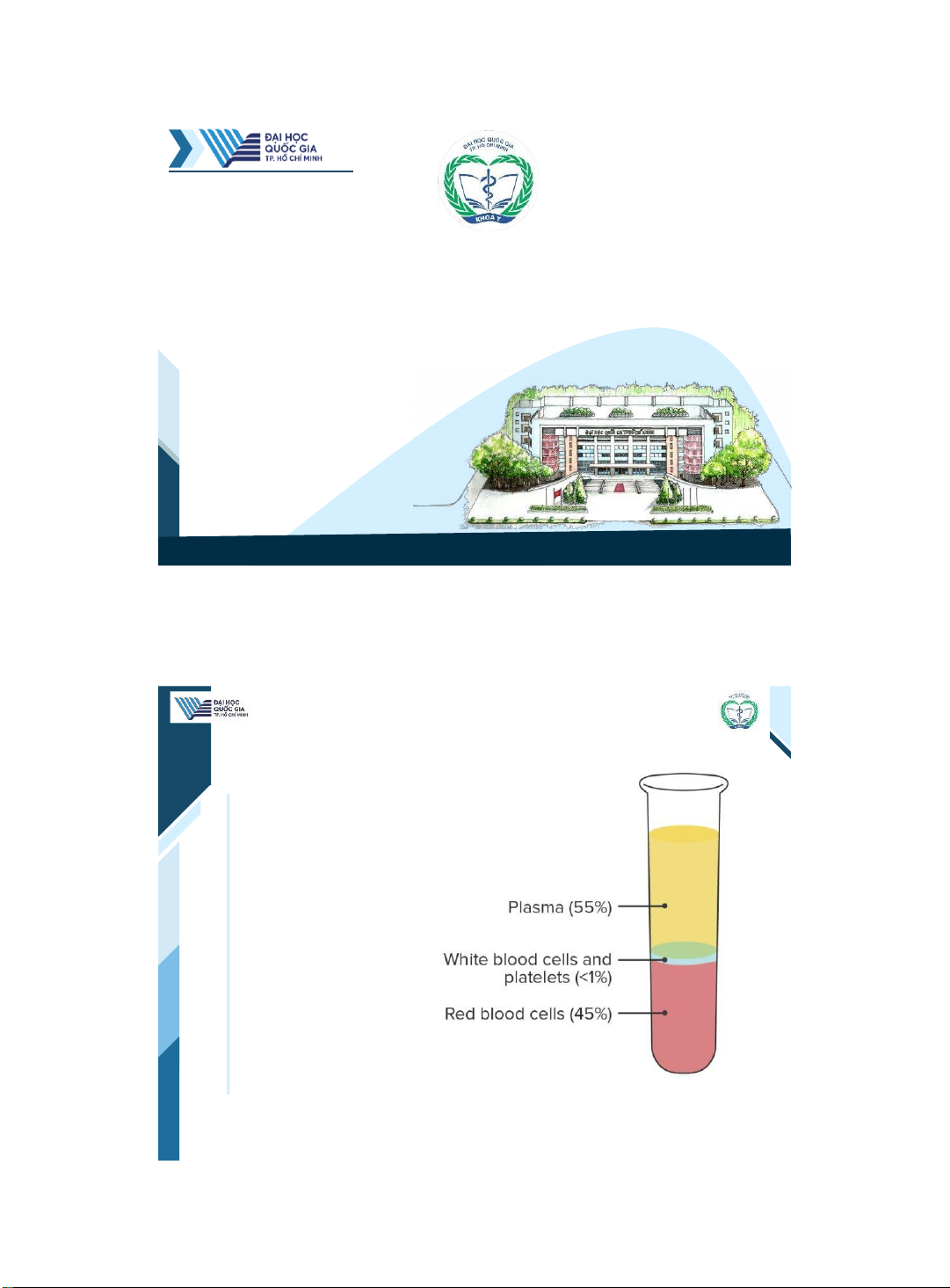
Blood volume & composition •Blood volume is 70 mL/kg. •Blood is composed of cells that circulate in plasma. | 2 2
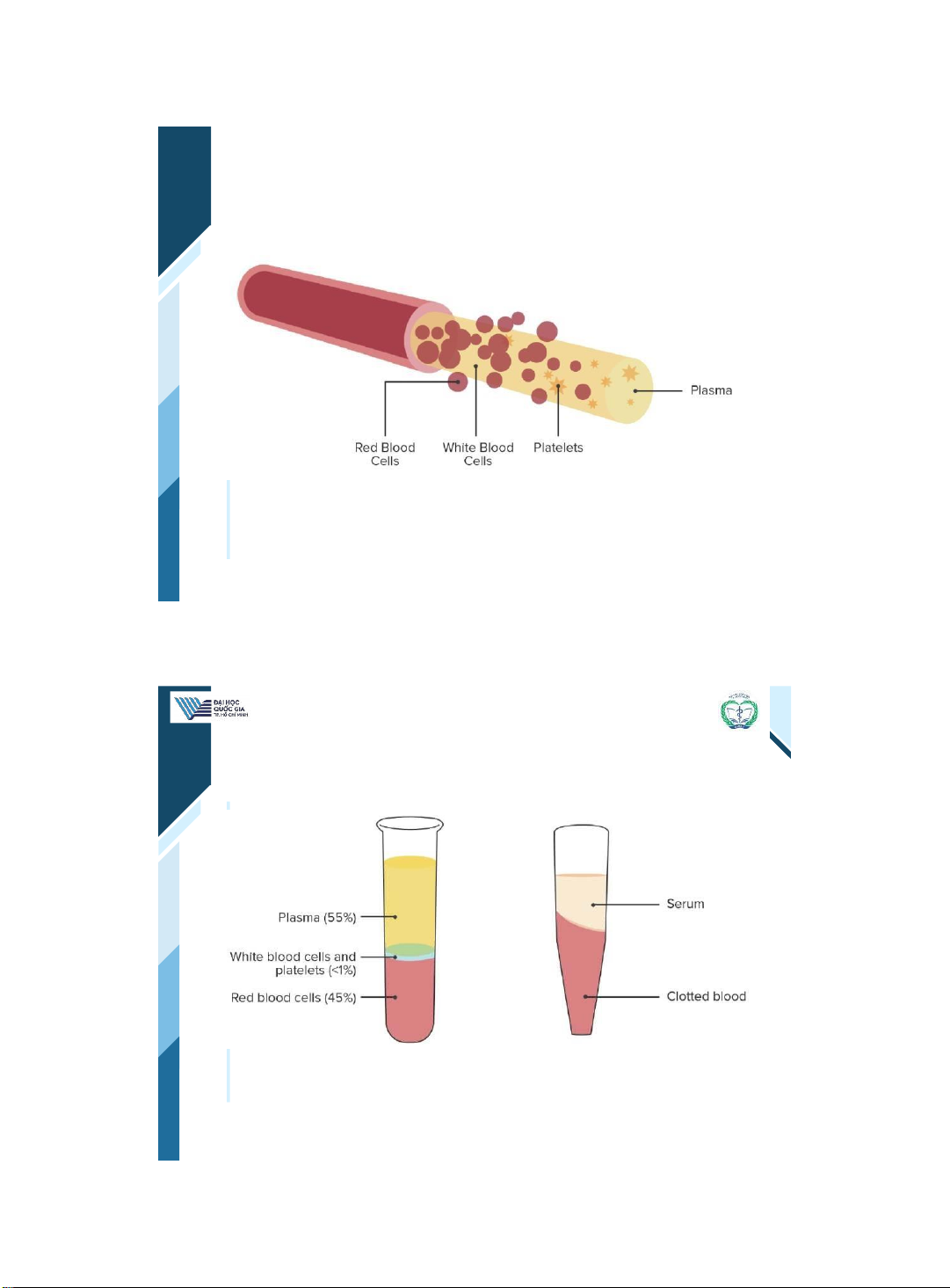
Cells suspended in plasma
ThS. BS. ĐặngNguyễnTường Vân
Khoa Y –ĐHQG - HCM | 3 3
The difference between serum and plasma | 4 4 Homopoiesis
ThS. BS. ĐặngNguyễnTường Vân
Khoa Y –ĐHQG - HCM | 5 5 Hemopoietic stem cells
•Hemopoietic stem cells are a rare subtype of cell in the bone marrow
•All blood cells are derived from these cells
•They express the surface molecule CD34+
•They are supported by a range of cells in the microenvironment
•This is disturbed in a range of conditions | 6 6
3 major types of blood cell
ThS. BS. ĐặngNguyễnTường Vân
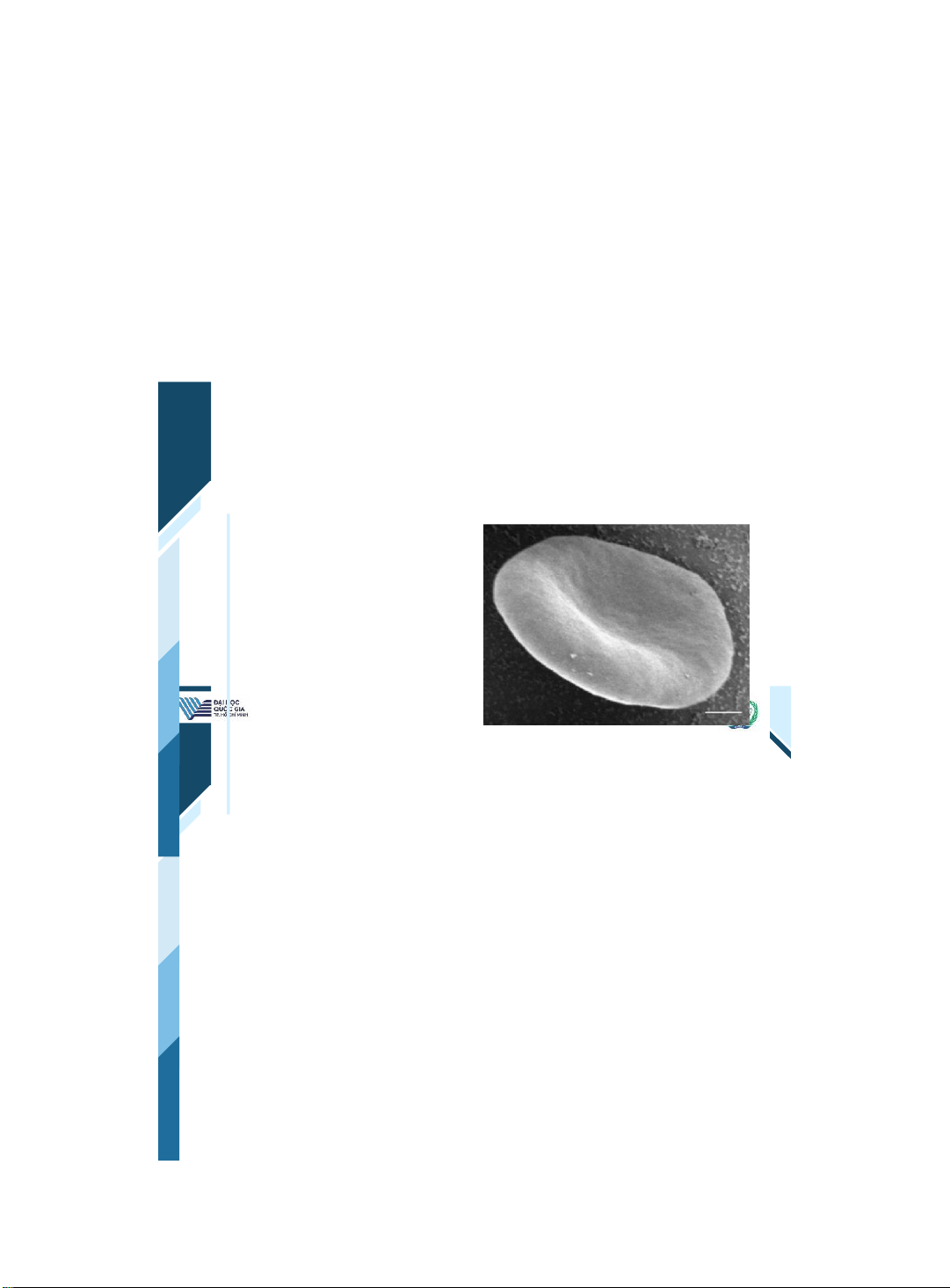
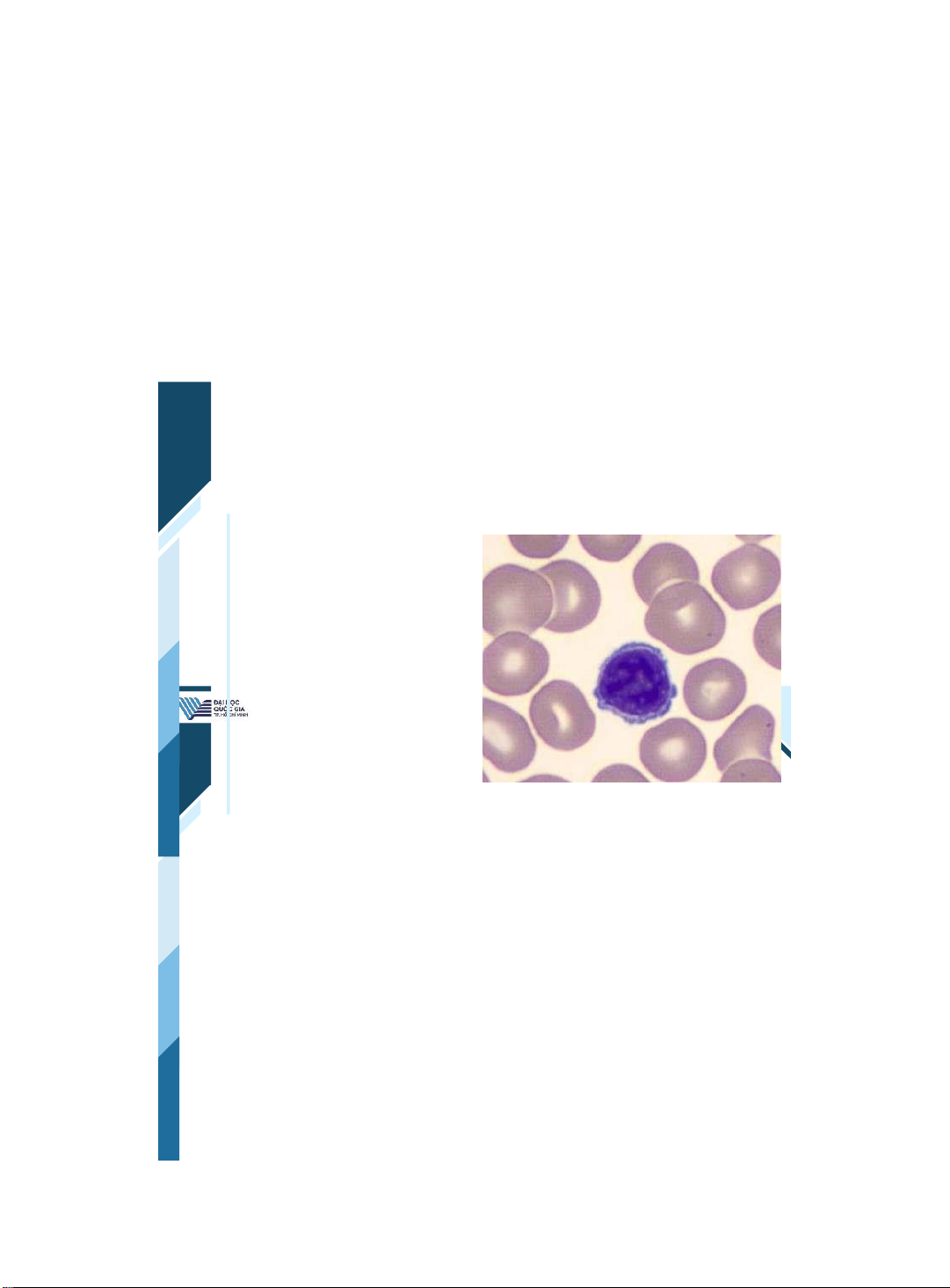
Khoa Y –ĐHQG - HCM | 7 7 Red blood cells | 8 8 Red blood cells 1,000 times more • common than white cells Have no nucleus and live • only 120 days Major purpose is to carry • oxygen to tissues They are 7 microns in • diameter, flexible biconcave shape that allows migration through capillaries
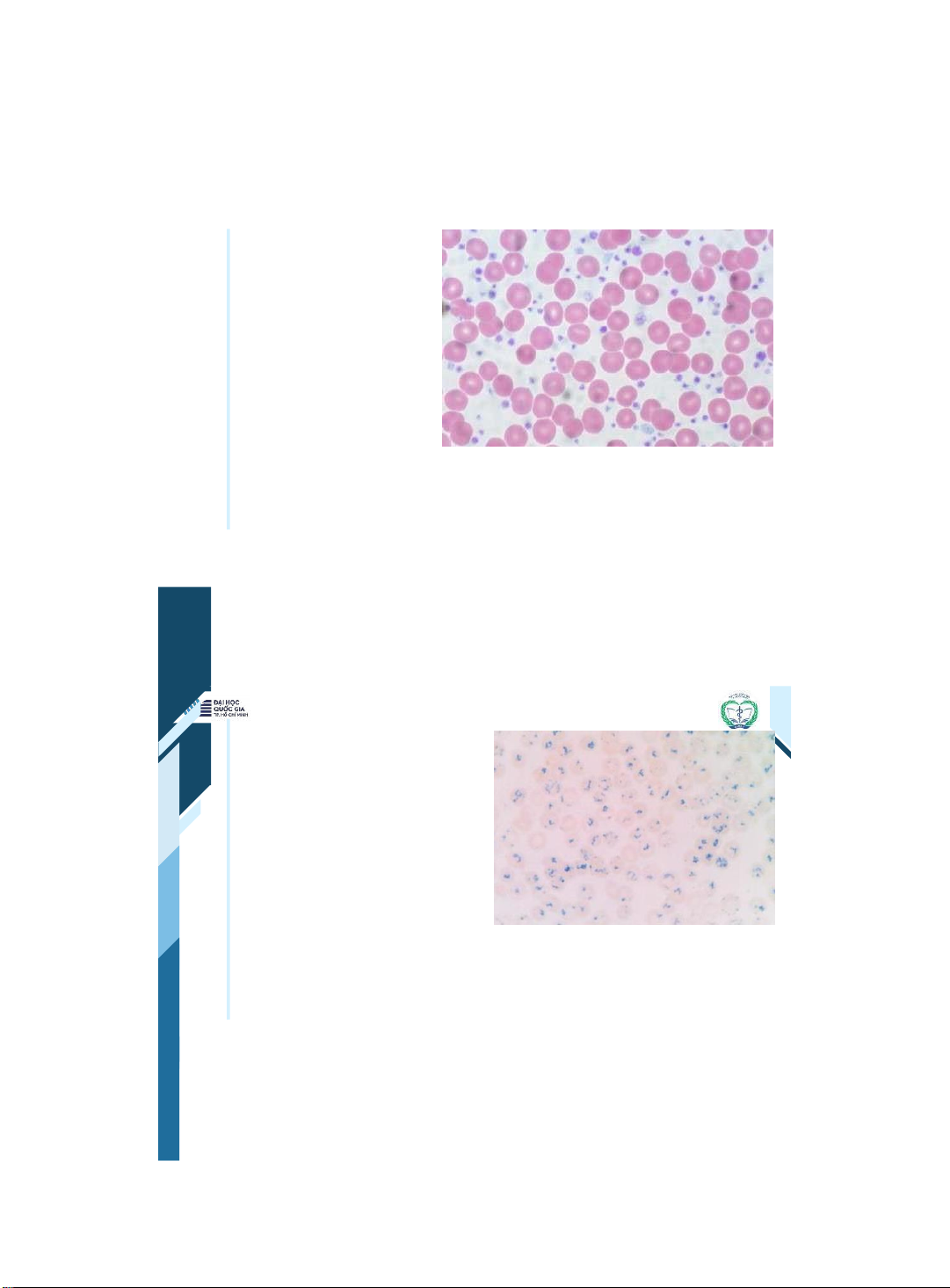
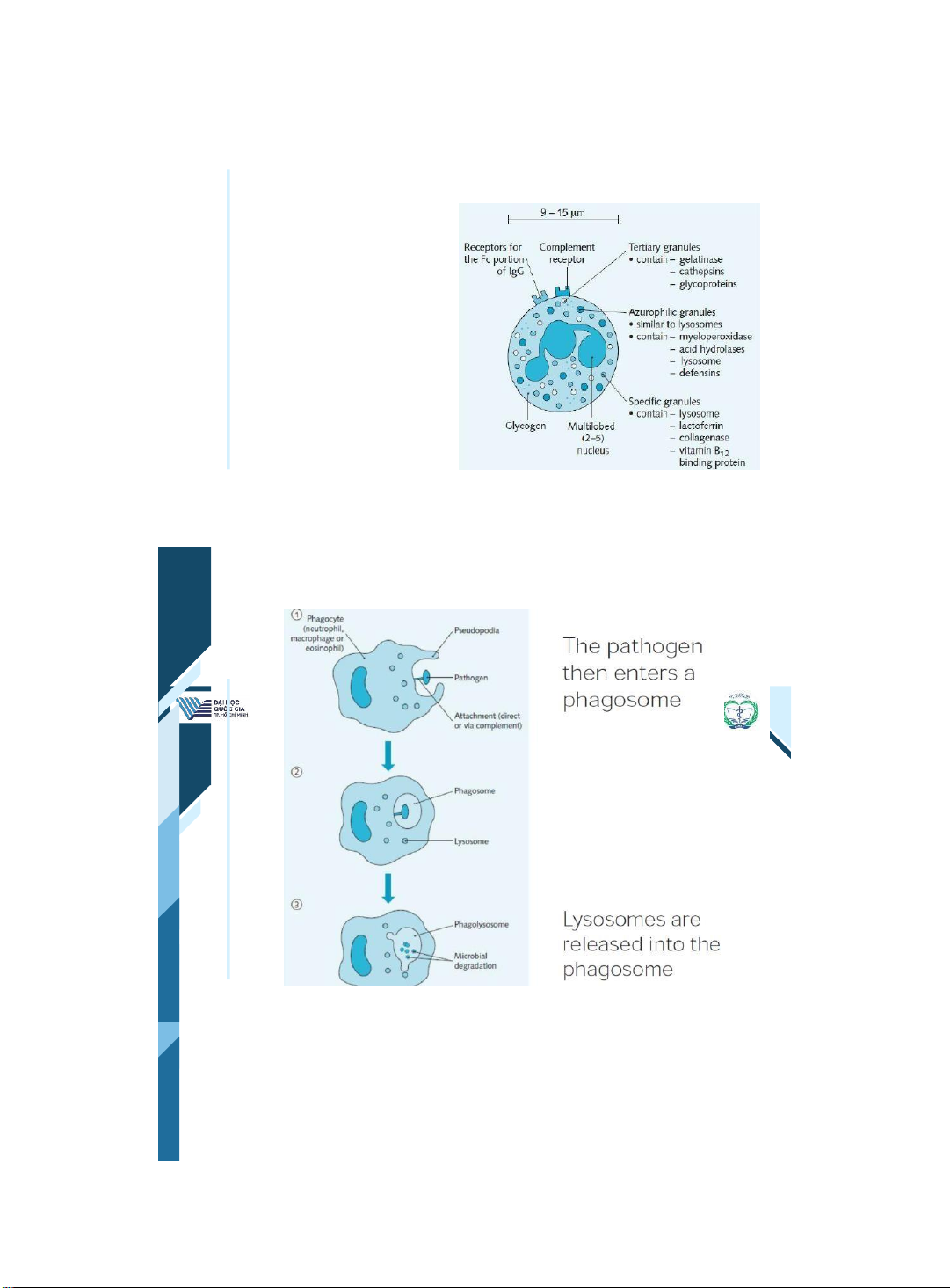
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 9 9 Erythrocytes •RBCs derive from erythroblasts in the bone marrow. •They are packed with hemoglobin and carry oxygen to tissue. •Their production is regulated by erythropoietin. | 10 10 Reticulocytes
Reticulocytes carry a lot of RNA.
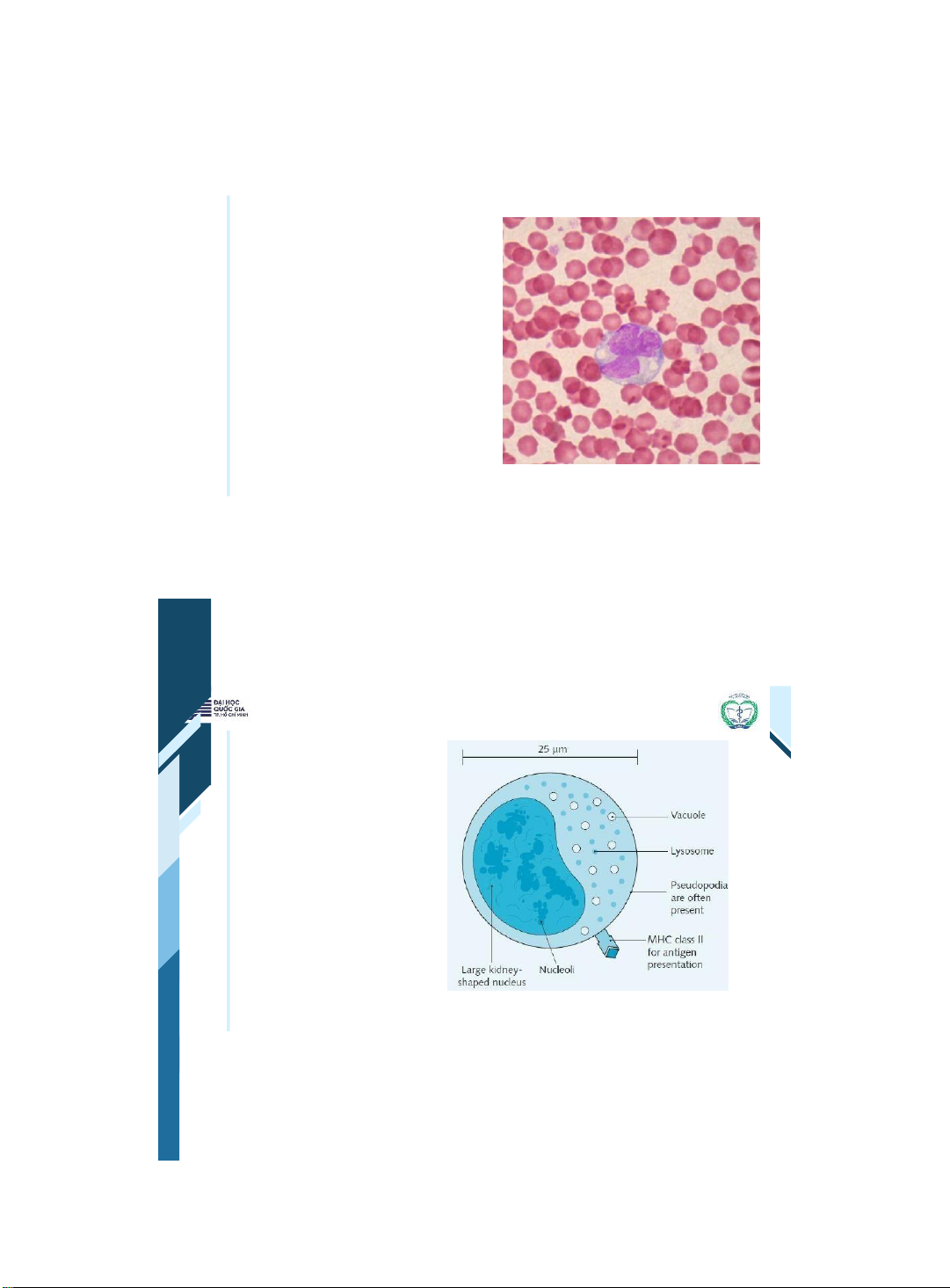
• Reticulocytes live for 2 3
days & normally represent up • to 2% of the RBC in the blood. The number of reticulocytes
in the blood is a useful clinical • test: • When ↑ → the bone marrow is more active. • When ↓ → problem with production of RBC from the bone marrow.
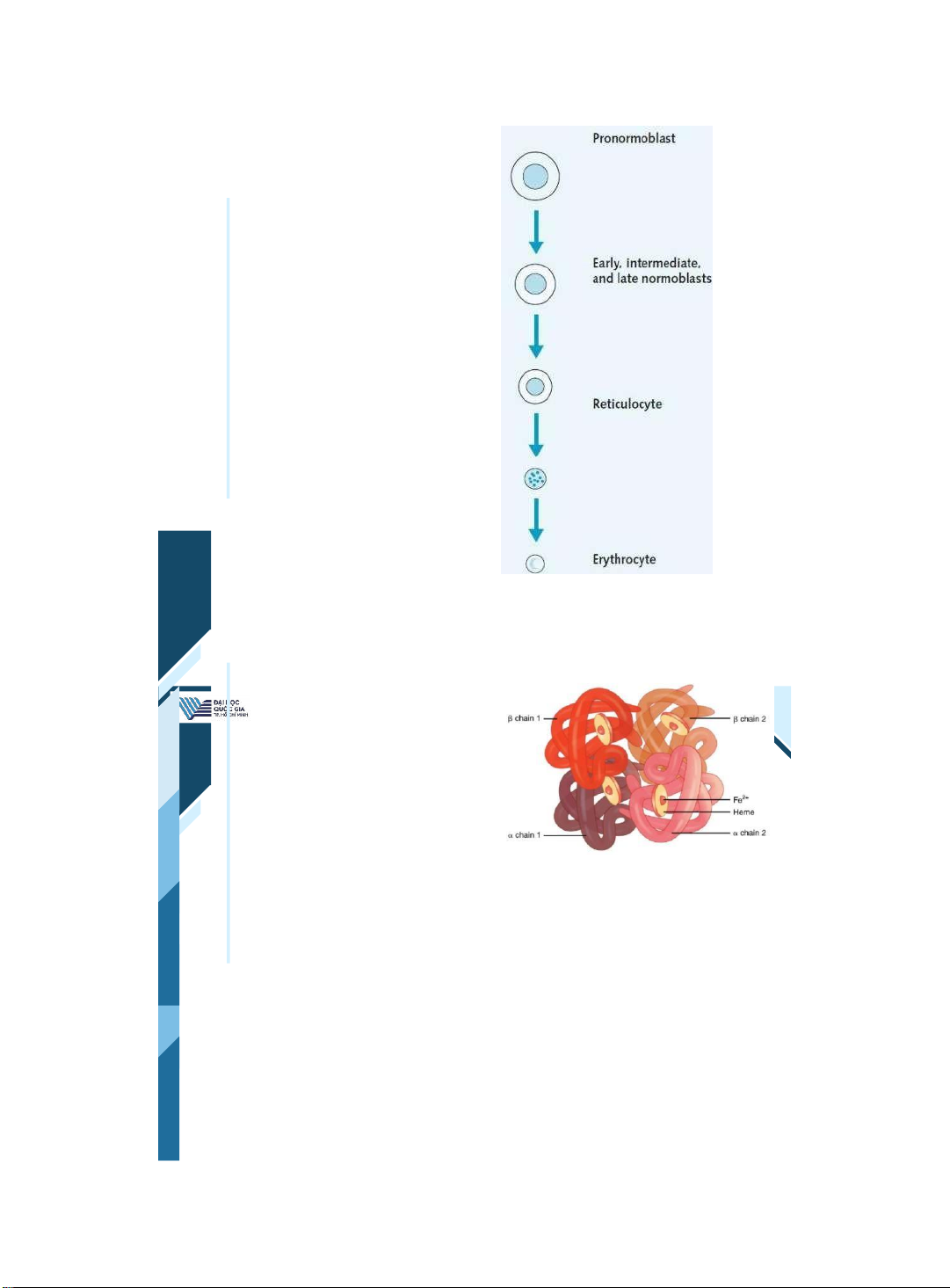
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 11 11 Erythropoiesis Pronormoblasts in the bone • marrow are the initial precursors. These differentiate into • normoblasts. The nucleus is then ejected,
• and reticulocytes are released into the blood. | 12 12 RBC and Hemoglobin RBC contain hemoglobin (Hb). • Hb consists of 4 protein chains that each contain a pocket for heme. The 4 protein chains in adult Hb • consist of 2 alpha chains (a) and 2 beta chains (b). Heme contains iron, and much of the iron in the • body is found within hemoglobin
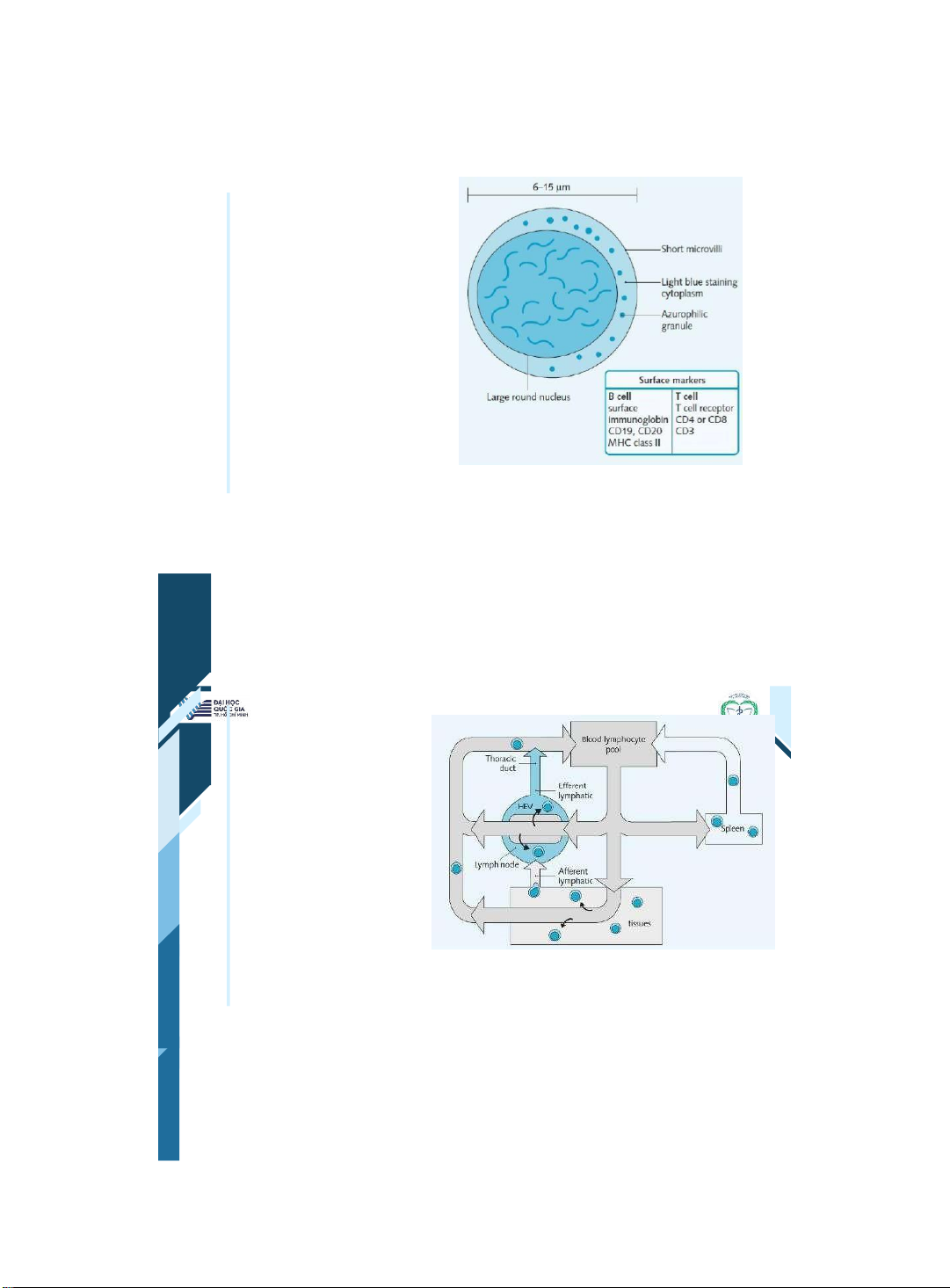
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 13 13 White blood cells | 14 14 Lymphocytes Lymphocytes are the • cells that mediate the function of the immune system They can • survive for many years & circulate around the blood & through lymphoid tissues The 2 major subtypes are T • cells and B cells
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 15 15 Lymphocytes •Lymphocytes constitute the immune system. B cells make antibodies. T cells regulate immunity and helper cells and can kill virally infected cells | 16 16
Lymphocytes circulate through the immune system 95% of lymphocytes • are found within lymphoid tissue, and they circulate through the immune system. • Lymphocytes enter lymph nodes through lymph or high endothelial venules. • They leave lymph nodes via lymphatic vessels
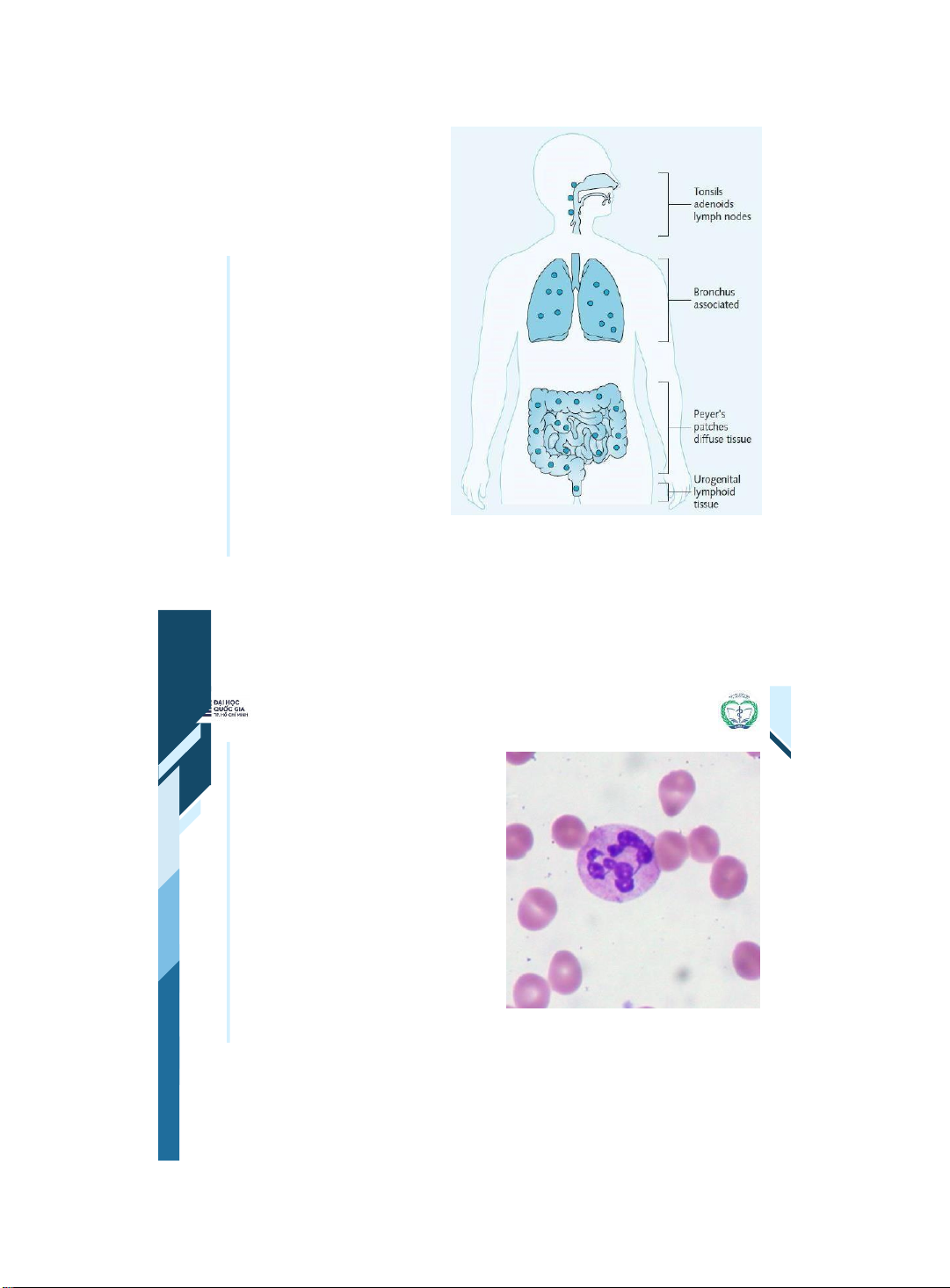
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 17 17 Mucosal- associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) •Most lymphocytes are within MALT. •MALT is found in many tissues within the body. •Lymphocytes activated in these areas home back to this region | 18 18 Neutrophils Neutrophils may play an
• important role in controlling
bacterial & fungal infection They are released from
• bone marrow & survive for 2-3 days They can ingest bacteria
• and cells that have become covered with antibody They kill these using toxic enzymes & oxygen radicals •
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 19 19 Neutrophils •Neutrophils have a characteristic multilobed nucleus. •The nucleus contains many granules that mediate the destruction of bacteria | 20 20 Phagocytosis
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 21 21 Monocytes •These cells migrate to tissues, where they become macrophages •They can ingest bacteria •They play an important role in triggering immune responses | 22 22 Monocytes They play an • important role in linking the initial phases of immunity (innate immunity) to T-cell and B-cell immunity (adaptive immunity)
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 23 23
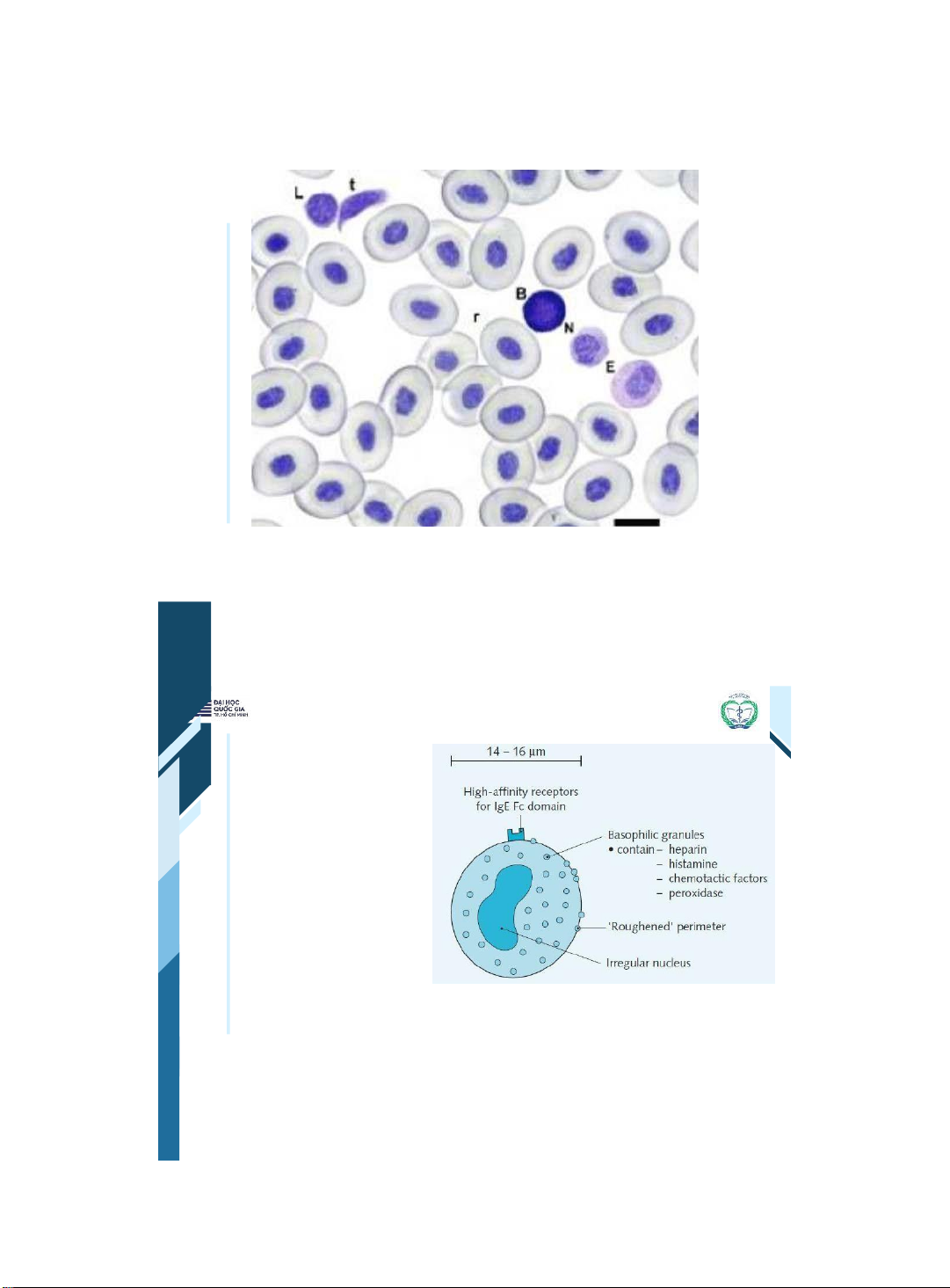
Eosinophils and Basophils | 24 24
Eosinophils and Basophils Eosinophils are • important in the immune response to helminths (worms). They are increased in allergic responses. The basophil is a rare cell whose precise • function is unclear
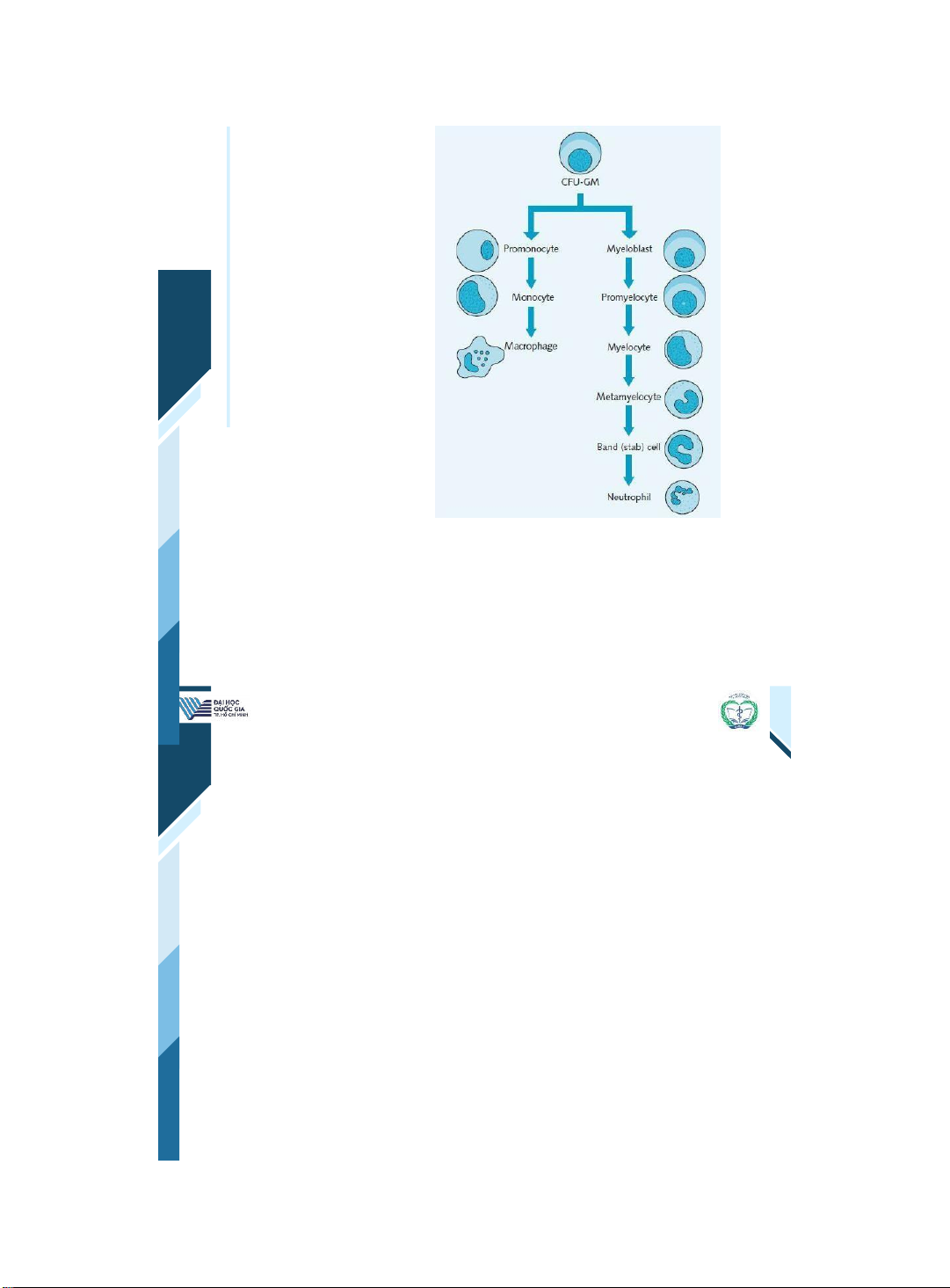
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 25 25 Myeloid cells & monocytes derived from a common precursor cell | 26 26 Platelets
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 27 27 • These are fragments of cytoplasm that bud off megakaryocytes in the bone marrow •They can stick to areas of damage within the blood vessels and trigger the formation of a blood clot | 28 28 Bone marrow structure Blood is made • in the bone marrow Hemopoietic • bone marrow is present in almost all bones in children In • adults it is in the vertebrae and proximal long bones
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 29 29
Structure of the spleen • The spleen consists of areas of red pulp & white pulp •The blood system has a unique pattern in which it is not contained within capillaries •The spleen has hemopoietic & immune functions | 30 30
Investigation and diagnosis of the blood system
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 31 31 Clinical Approach
Diagnosis is made by the combination of: • Taking a medical history • Examination • Investigation | 32 32 Taking a History
• Red cell problems usual y present with
anemia (fatigue, shortness of breath).
• White cel deficiency leads to unusual or prolonged infection.
• Excess white cel s in malignant disease can cause lumps and swel ing.
• Disorders of platelets lead to bruising and bleeding.
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 33 33 Examination
• Examination of the nails, skin, and mucous membranes may suggest anemia. • Examination of the lymph nodes may suggest leukemia or lymphoma.
• Excessive bruising is seen in platelet disorders.
• The spleen is only palpable when it is enlarged | 34 34 Blood Count
• Blood Count is usually the 1st
• The 3 main components are:
The red cell count and hemoglobin
The total and individual white cell counts The platelet count
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 35 35 | 36 36
RBC count & Hemoglobin
• The normal red cell count is 4-6 x 10^12/L. • The hemoglobin concentration is expressed in grams per deciliter.
• The normal range in men is 13.5-17.5 g/dL. • The normal range in women is 11.5-15.5 g/dL.
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 37 37 Size of the RBC
Automated red cell counters can provide
information on the volume of the red cells:
• The mean cell volume, or MCV
• This is very useful in determining the cause of anemia:
80-95 femtoliters (fl) is normal < 80 fl is microcytic > 95 fl is macrocytic | 38 38 WBC
• The normal range is 4-7 x 10^9/L. • A decrease is termed leukopenia. • An increase is leukocytosis. • The 2 major subsets of white cells are lymphocytes & neutrophils. This leads to
the terms of lymphopenia or neutropenia and
lymphocytosis or neutrophilia.
ThS. BS. Đặng Nguyễn Tường Vân Khoa Y – ĐHQG - HCM | 39 39



