














Preview text:
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
Chap 1: INTRODUCING MANAGEMENT Talents
Intellectual capital equation: Intellectual Capital = Competency x Commitment
- Competency represents your talents or job- relevant capabilities
- Commitment represents your willingness to work hard in applying them to important tasks. Technology Globalization
These are among the many faces of globalization, the worldwide interdependence of resource flows product markets business competition
One controversial side effect to globalization is job migration
Definition: the shifting of jobs from one country to another. Ethics
Definition: ethics—a code of moral principles that sets standards for what is “good” and
“right” as opposed to “bad” and “wrong” in the conduct of a person or group Diversity
The term workforce diversity describes the composition of a workforce in terms of such differences as Gender Religion Age Sexual orientation Race Ablebodiednes Ethnicity
The stage for diversity bias is set by prejudice (định kiến)
Definition: The stage for diversity bias is set by prejudice—the holding of negative,
irrational opinions and attitudes regarding members of diverse populations.
Prejudice becomes active discrimination (sự phân biệt) when minority members are
unfairly treated and denied the full benefits of organizational membership.
- Discrimination can be based on race, ethnicity, age, religion, health, and other categories.
Such thinking shows a subtle form of discrimination called the glass ceiling effect (rˆo
cản vô hình), an invisible barrier or “ceiling” that prevents women and minorities from
rising above a certain level of organizational responsibility. 1 | P a g e
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com) Careers
A shamrock organization (mô hình tổ chức cỏ ba lá) operates with a core group of
full-time long-term workers supported by others who work on contracts and part-time.
In a free-agent economy (nền kinh tế tự do) people change jobs more often, and many
work on independent contracts with a shifting mix of employers.
Self-management is the ability to understand oneself, exercise initiative,accept
responsibility, and learn from experience. What is organization?
An organization is a collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose A clear sense of purpose
quality products and services customer satisfaction social responsibility”
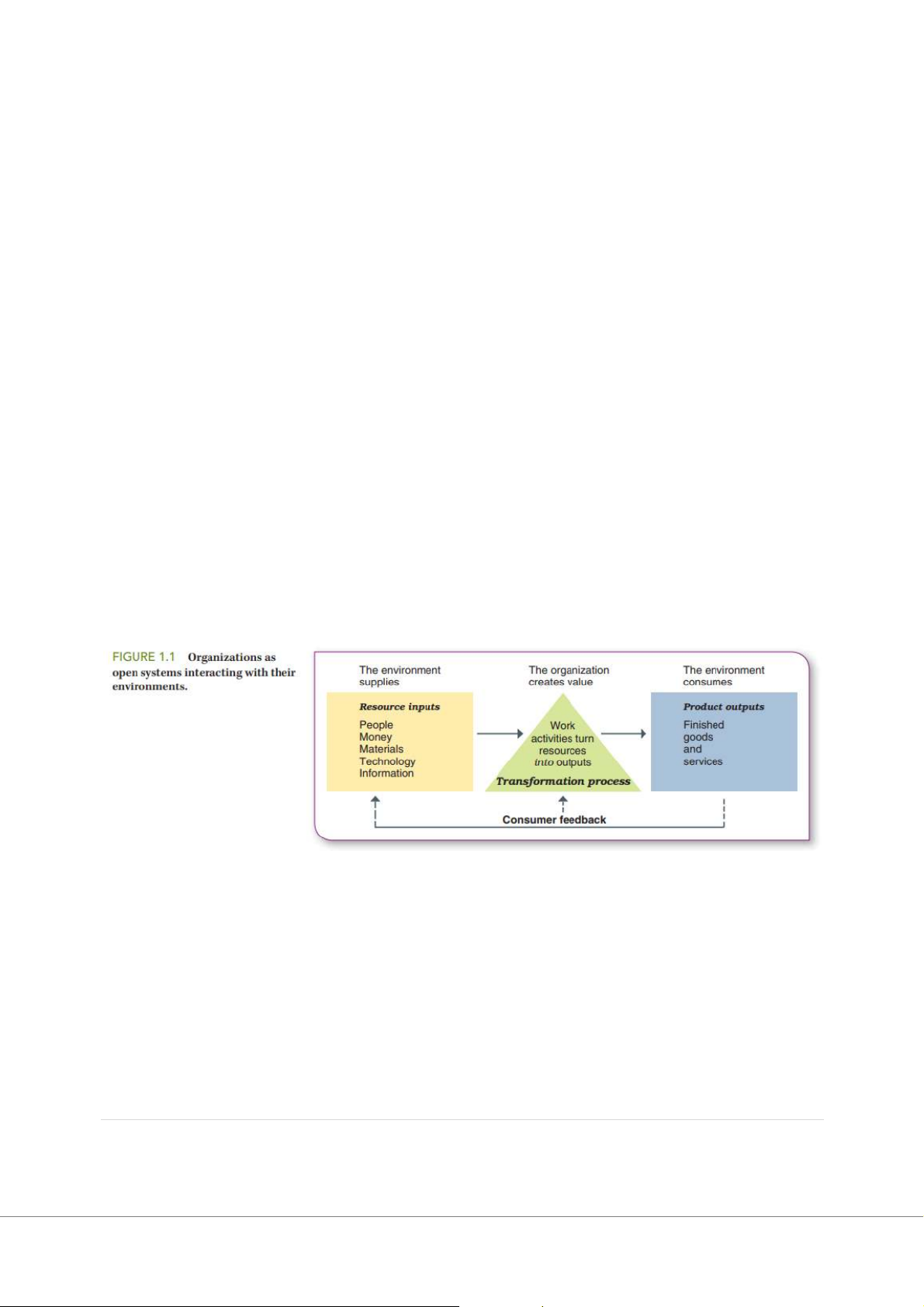
Organizations as Systems
An open system transforms resource inputs from the environment into product outputs
- Inputs—people, information, resources, and capital
- Outputs in the form of finished goods and services for customers.
Productivity is the quantity and quality of work performance, with resource utilization considered.
Performance effectiveness (hiệu quả- hoàn thành đúng việc và tạo ra nhiều giá trị nhất
so với mục tiêu đề ra) is an output measure of task or goal accomplishment.
Performance efficiency (hiệu suất- khả năng tránh lãng phí nguyên liệu đầu vào) is an
input measure of resource cost associated with goal accomplishment. 2 | P a g e
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com) What Is a Manager?
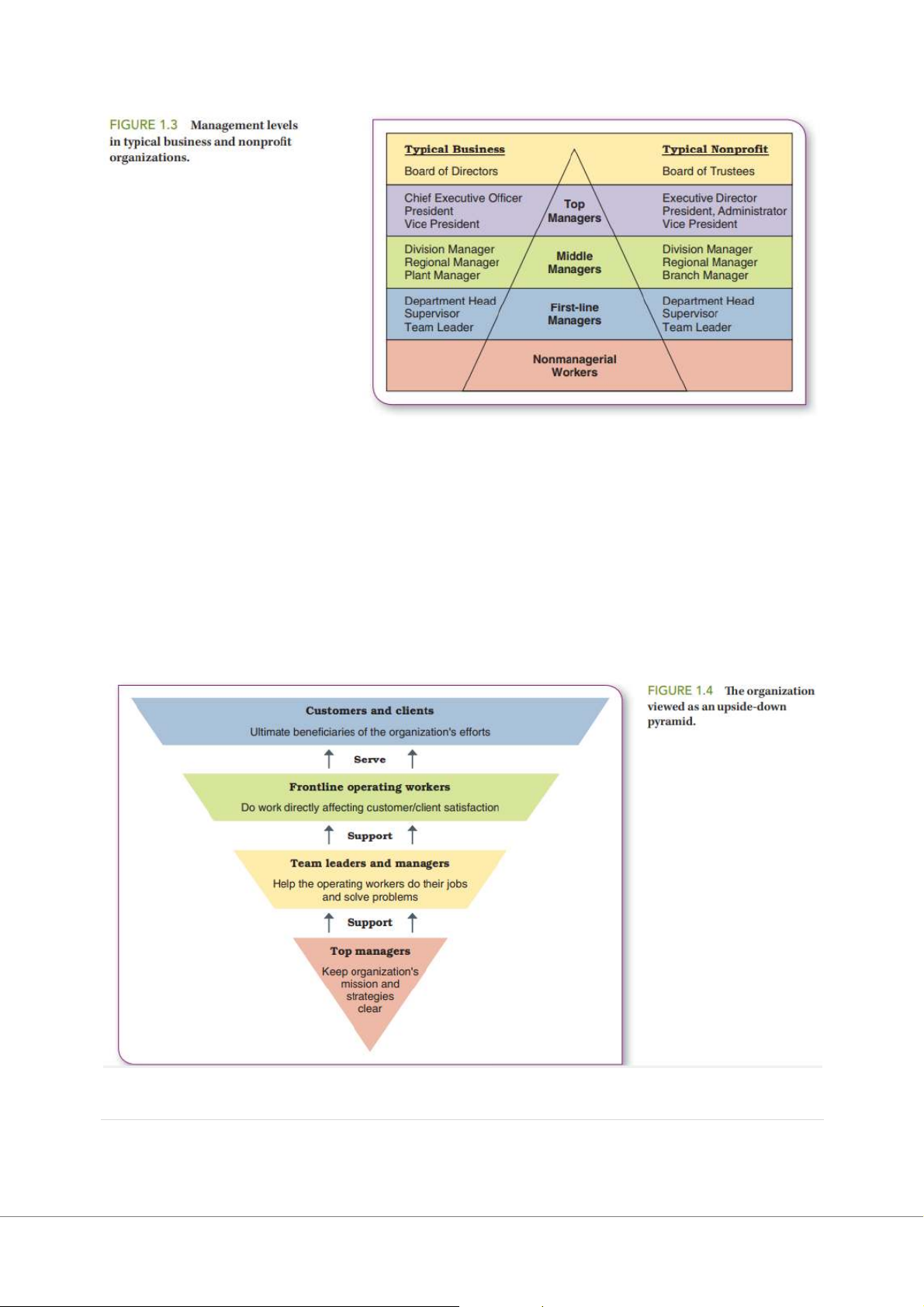
A manager is a person who supports, activates, and is responsible for the work of other Levels of Managers
Members of a board of directors or board of trustees are supposed to make sure an organization is run right
Top managers guide the performance of the organization as a whole or of one of its major parts.
Common job titles just below the board level are chief executive officer (CEO), chief
operating officer (COO), chief financial officer (CFO), chief information officer (CIO),
chief diversity officer (CDO), president, and vice president.
Middle managers oversee the work of large departments or divisions.
Team leaders report to middle managers and supervise nonmanagerial workers. Types of Managers
Line managers directly contribute to producing the organization’s goods or services.
Staff managers use special technical expertise to advise and support line workers.
Functional managers are responsible for one area, such as finance, marketing, production,
personnel, accounting, or sales.
General managers are responsible for complex, multifunctional units.
An administrator is a manager in a public or nonprofit organization. 3 | P a g e
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com) Managerial Performance
Accountability is the requirement to show performance results to a supervisor.
Corporate governance (quản trị công ty - một hệ thống các thiết chế, chính sách, luật lệ
nhằm định hướng, vận hành và kiểm soát công ty) occurs when a board of directors holds
top management accountable for organizational performance.
An effective manager helps others achieve high performance and satisfaction at work.
Quality of work life is the overall quality of human experiences in the workplace.
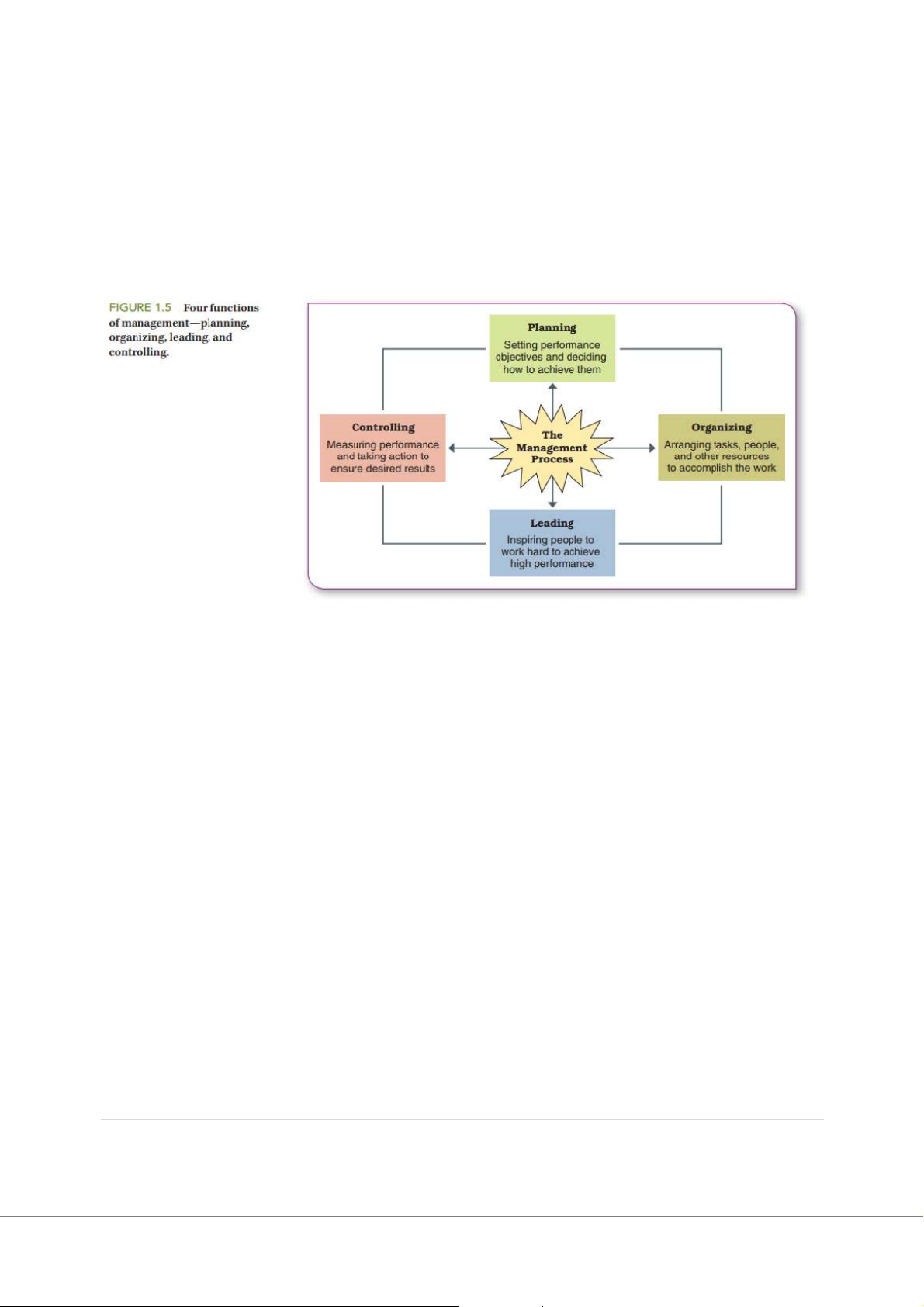
The upside-down pyramid view of organizations shows customers at the top being
served by workers who are supported by managers. 4 | P a g e
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
Functions of Management
Planning is the process of setting objectives and determining what should be done to accomplish them.
Organizing is the process of assigning tasks, allocating resources, and coordinating work activities.
Leading is the process of arousing enthusiasm and inspiring efforts to achieve goals.
Controlling is the process of measuring performance and taking action to ensure desired results.
Managerial Roles and Activities
A manager’s informational roles involve the giving, receiving, and analyzing of information.
A monitor - scanning for information
Disseminator - sharing information
A spokesperson - acting as official communicator.
The interpersonal roles involve interactions with people inside and outside the work unit.
A figurehead - modeling and setting forth key principles and policies
A leader - providing direction and instilling enthusiasm
A liaison - coordinating with others.
The decisional roles involve using information to make decisions to solve problems or address opportunities.
A disturbance handler - dealing with problems and conflicts
A resource allocator - handling budgets and distributing resources
A negotiator - making deals and forging agreements
An entrepreneur - developing new initiatives. 5 | P a g e
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
Managerial Agendas and Networks
Agenda setting develops action priorities for accomplishing goals and plans
Networking is the process of creating positive relationships with people who can help advance agendas.
Social capital is a capacity to get things done with the support and help of others.
Essential Managerial Skills
A skill is the ability to translate knowledge into action that results in desired performance.
A technical skill is the ability to use expertise to perform a task with proficiency.
- Kỹ năng kỹ thuật: là kỹ năng cần thiết của nhà quản trị để thực hiện công
việc cụ thể, hay nói cách khác đó là trình độ chuyên môn, nghiệp vụ của
nhˆ quản trị. Ví dụ kỹ năng định khoản trong công tác kế toán, kỹ năng
soạn thảo hợp đồng, etc.
A human skill or interpersonal skill is the ability to work well in cooperation with other people.
- It’s a foundation for something called emotional intelligence
- Kỹ năng nhân sự: Kỹ năng này liên quan đến khả năng của nhà quản trị
trong công tác ứng xử , quan hệ giữa con người với con người. Đó là nghệ
thuật ứng xử trong đối nhân xử thế. Ví dụ: khả năng tập thể, khả năng hòa
nhập, khả năng xây dựng tập thể trong tổ chức, etc.
A conceptual skill is the ability to think analytically to diagnose and solve complex problems.
- We often call this “critical thinking.”
- Kỹ năng tư duy: liên quan đến khả năng tiếp nhận, xử lí thông tin, khả năng
phán đoán, liên quan đến tầm nhìn, đặc biệt là tầm nhìn chiến lược của nhà quàn trị. 6 | P a g e
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
CHAP 3 Planning and Strategic Management
3-1 PLANNING AND ORGANIZATIONAL GOALS
The planning process takes place within an environmental context. Managers must
develop a complete and thorough understanding of this context to determine the
organization’s mission and to develop its strategic, tactical, and operational goals and plans.
Quy trình kế hoạch diễn ra trong môi trường bối cảnh. Người quản lý cần phát triển một
sự hiểu biết toàn diện về bối cảnh này để xác định sứ mệnh của tổ chức và phát triển các
mục tiêu cũng như kế hoạch chiến lược, chiến thuật và hoạt động của nó. 3-1a Organizational Goals
Goals are critical to organizational effectiveness, and they serve a number of purposes
Mục tiêu đóng vai trò quan trọng trong các tổ chức hoạt động và phục vụ nhiều mục tiêu.
Purposes of Goals Goals serve four important purposes.
First, they provide guidance and a unified direction for people in the organization.
- Goals can help everyone understand where the organization is going and why
getting there is important. - Mục tiêu có thể giúp mọi người hiểu tổ chức đang
hướng tới đâu và tại sao việc đạt được mục tiêu đó lại quan trọng.
Second, goal-setting practices strongly affect other aspects of planning.
- Effective goal setting promotes good planning, and good planning facilitates
future goal setting - Việc thiết lập mục tiêu hiệu quả sẽ thúc đẩy việc lập kế hoạch
tốt và việc lập kế hoạch tốt sẽ tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho việc thiết lập mục tiêu trong tương lai.
Third, goals can serve as a source of motivation for an organization’s employees.
- Goals that are specific and moderately difficult can motivate people to work
harder, especially if attaining the goal is likely to result in rewards. - Mục tiêu cụ
thể và có độ khó vừa phải có thể thúc đẩy mọi người làm việc chăm chỉ hơn, đặc
biệt nếu việc đạt được mục tiêu có thể dẫn đến phần thưởng.
Finally, goals provide an effective mechanism for evaluation and control.
- This means that performance can be assessed in the future in terms of how
successfully today’s goals are accomplished. - Điều này có nghĩa là hiệu quả hoạt
động có thể được đánh giá trong tương lai dựa trên mức độ hoàn thành thành công
các mục tiêu của ngày hôm nay.
Kinds of Goals Goals are set for and by different levels within an organization. Page | 1
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
An organization’s mission is a statement of its “fundamental, unique purpose that sets a
business apart from other firms of its type and identifies the scope of the business’s
operations in product and market terms
- Sứ mệnh của một tổ chức là một tuyên bố về “mục đích cơ bản, duy nhất giúp
doanh nghiệp trở nên khác biệt với các doanh nghiệp khác cùng loại và xác định
phạm vi hoạt động của doanh nghiệp về mặt sản phẩm và thị trường.
Strategic goals are set by and for an organization’s top management. They focus on broad, general issues.
- Mục tiêu chiến lược được thiết lập bởi và cho ban lãnh đạo cấp cao của tổ chức.
Họ tập trung vào các vấn đề rộng rãi, tổng quát.
Tactical goals are set by and for middle managers. Their focus is on how to
operationalize actions necessary to achieve the strategic goals.
- Mục tiêu chiến thuật được đặt ra bởi các nhà quản lý cấp trung. Trọng tâm của họ
là làm thế nào để vận hành các hành động cần thiết để đạt được các mục tiêu chiến lược.
Operational goals are set by and for lower-level managers. Their concern is with
shorter-term issues associated with the tactical goals.
- Mục tiêu vận hành được đặt ra bởi và cho các nhà quản lý cấp thấp hơn. Mối quan
tâm của họ là các vấn đề ngắn hạn gắn liền với các mục tiêu chiến thuật.
When planning is done well it creates a solid platform for the other management functions.
3-1b Kinds of Organizational Plans
Strategic plans are developed to achieve strategic goals. More precisely, a strategic plan
is a general plan outlining decisions about resource allocation, priorities, and action steps
necessary to reach strategic goals. These plans are set by the board of directors and top
management, generally have an extended time horizon, and address questions of scope,
resource deployment, competitive advantage, and synergy.
- Các kế hoạch chiến lược được phát triển để đạt được các mục tiêu chiến lược.
Chính xác hơn, kế hoạch chiến lược là một kế hoạch chung phác thảo các quyết
định về phân bổ nguồn lực, các ưu tiên và các bước hành động cần thiết để đạt
được các mục tiêu chiến lược. Các kế hoạch này do ban giám đốc đặt ra và quản lý
cấp cao thường có khoảng thời gian dài hơn và giải quyết các câu hỏi về phạm vi,
triển khai nguồn lực, lợi thế cạnh tranh và sức mạnh tổng hợp.
A tactical plan, aimed at achieving tactical goals, is developed to implement specific
parts of a strategic plan. Tactical plans typically involve upper and middle management Page | 2
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
and, compared with strategic plans, have a somewhat shorter time horizon and a more
specific and concrete focus. Thus, tactical plans are concerned more with actually getting
things done than with deciding what to do.
- Một kế hoạch chiến thuật nhằm đạt được các mục tiêu chiến thuật được phát triển
để thực hiện các phần cụ thể của kế hoạch chiến lược. Các kế hoạch chiến thuật
thường liên quan đến quản lý cấp trên và cấp trung, và so với các kế hoạch chiến
lược, có khoảng thời gian ngắn hơn một chút và trọng tâm cụ thể và cụ thể hơn. Vì
vậy, các kế hoạch chiến thuật quan tâm nhiều đến việc thực sự hoàn thành công
việc hơn là quyết định phải làm gì.
An operational plan focuses on carrying out tactical plans to achieve operational goals.
Developed by middle- and lower-level managers, operational plans have a short-term
focus and are relatively narrow in scope. Each one deals with a fairly small set of activities.
- Một kế hoạch hoạt động tập trung vào việc thực hiện các kế hoạch chiến thuật để
đạt được các mục tiêu hoạt động. Được phát triển bởi các nhà quản lý cấp trung và
cấp thấp, các kế hoạch hoạt động có trọng tâm ngắn hạn và phạm vi tương đối hẹp.
Mỗi người giải quyết một nhóm hoạt động khá nhỏ.
3-2 THE NATURE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
A strategy is a comprehensive plan for accomplishing an organization’s goals.
Chiến lược là một kế hoạch toàn diện để hoàn thành các mục tiêu của tổ chức.
Strategic management, in turn, is a way of approaching business opportunities and
challenges—it is a comprehensive and ongoing management process aimed at
formulating and implementing effective strategies.
Ngược lại, quản lý chiến lược là một cách tiếp cận các cơ hội và thách thức kinh doanh -
đó là một quá trình quản lý toàn diện và liên tục nhằm xây dựng và thực hiện các chiến lược hiệu quả.
Effective strategies are those that promote a superior alignment between the
organization and its environment and the achievement of strategic goals.
Cuối cùng, các chiến lược hiệu quả là những chiến lược thúc đẩy sự liên kết vượt trội
giữa tổ chức và môi trường của nó và đạt được các mục tiêu chiến lược.
3-2a The Components of Strategy
In general, a well-conceived strategy addresses three areas: distinctive competence,
scope, and resource deployment.
A distinctive competence is something the organization does exceptionally well. - Năng Page | 3
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
lực khác biệt là điều mà tổ chức thực hiện rất tốt.
The scope (phạm vi) of a strategy specifies the range of markets in which an organization will compete.
- Some organizations, called conglomerates, compete in dozens or even hundreds of markets.
A strategy should also include an outline of the organization’s projected resource
deployment (triển khai các nguồn lực, nguồn tài nguyên) —how it will distribute its
resources across the areas in which it competes - cách nó sẽ phân phối nguồn lực của
mình trên các lĩnh vực mà nó cạnh tranh.
3-2b Types of Strategic Alternatives
Most businesses today develop strategies at two distinct levels: the business level and
corporate level (cấp độ kinh doanh và cấp độ công ty).
Business-level strategy is the set of strategic alternatives from which an organization
chooses as it conducts business in a particular industry or market. Such alternatives help
the organization focus its competitive efforts for each industry or market in a targeted and focused manner.
- Chiến lược cấp kinh doanh là tập hợp các lựa chọn chiến lược mà tổ chức lựa chọn khi
tiến hành kinh doanh trong một ngành hoặc thị trường cụ thể. Những lựa chọn thay thế
như vậy giúp tổ chức tập trung nỗ lực cạnh tranh cho từng ngành hoặc thị trường một
cách có mục tiêu và tập trung.
Corporate-level strategy is the set of strategic alternatives from which an organization
chooses as it manages its operations simultaneously across several industries and several markets.
- Chiến lược cấp công ty là tập hợp các lựa chọn chiến lược mà một tổ chức lựa chọn khi
quản lý hoạt động của mình đồng thời trên nhiều ngành và một số thị trường.
Strategy formulation is the set of processes involved in creating or determining the
organization’s strategies, whereas strategy implementation is the methods by which
those strategies are operationalized or executed. The primary distinction is along the lines
of content versus process: The formulation stage determines what the strategy is, and the
implementation stage focuses on how the strategy is achieved.
- Xây dựng chiến lược là tập hợp các quy trình liên quan đến việc tạo ra hoặc xác định
chiến lược của tổ chức, trong khi thực hiện chiến lược là phương pháp mà các chiến lược
đó được vận hành hoặc thực thi. Sự khác biệt chính là giữa nội dung và quy trình: Giai
đoạn xây dựng chiến lược xác định chiến lược là gì và giai đoạn thực hiện tập trung vào Page | 4
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
cách đạt được chiến lược.
3-3 USING SWOT ANALYSIS TO FORMULATE STRATEGY
The starting point in formulating strategy is usually SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses,
Opportunities, and Threats) analysis.
In SWOT analysis, the best strategies accomplish an organization’s mission by
(1) exploiting an organization’s opportunities and strengths - (1) khai thác các cơ hội và
điểm mạnh của tổ chức
(2) neutralizing its threats - vô hiệu hóa các mối đe dọa của tổ chức đó
(3) avoiding (or correcting) its weaknesses - tránh (hoặc sửa chữa) những điểm yếu của nó.
3-3a Evaluating an Organization’s Strengths
Organizational strengths are skills and capabilities that enable an organization to create
and implement its strategies. - Điểm mạnh của tổ chức là những kỹ năng và khả năng cho
phép tổ chức tạo ra và thực hiện các chiến lược của mình.
Ex: Điểm mạnh của công ty có thể bao gồm những yếu tố nào?
A distinctive competence, introduced earlier in this chapter, is a strength possessed by
only a small number of competing firms. Distinctive competencies are rare among a set
of competitors - Năng lực đặc biệt là sức mạnh chỉ có một số ít công ty cạnh tranh sở
hữu. Năng lực khác biệt rất hiếm trong một nhóm đối thủ cạnh tranh.
3-3b Evaluating an Organization’s Weaknesses
Organizational weaknesses are skills and capabilities that do not enable an organization
to choose and implement strategies that support its mission.- Điểm yếu của tổ chức là
những kỹ năng và khả năng không cho phép tổ chức lựa chọn và thực hiện các chiến lược
hỗ trợ sứ mệnh của mình.
An organization has essentially two ways of addressing weaknesses.
- First, it may need to make investments to obtain the strengths required to implement
strategies that support its mission. - có thể cần phải đầu tư để có được những thế mạnh
cần thiết nhằm thực hiện các chiến lược hỗ trợ sứ mệnh của mình
- Second, it may need to modify its mission so that it can be accomplished with the skills
and capabilities that the organization already possesses - có thể cần phải sửa đổi sứ mệnh
của mình để có thể hoàn thành sứ mệnh với những kỹ năng và năng lực mà tổ chức đã có. Page | 5
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
3-3c Evaluating an Organization’s Opportunities and Threats
Organizational opportunities are areas that may generate higher performance - Cơ hội
của tổ chức là những lĩnh vực có thể tạo ra hiệu suất cao hơn.
Organizational threats are areas that increase the difficulty of an organization
performing at a high level - Các mối đe dọa của tổ chức là những lĩnh vực làm tăng khó
khăn cho tổ chức khi hoạt động ở mức độ cao.
3-4 FORMULATING BUSINESS-LEVEL STRATEGIES
3-4a Generic Strategies (chiến lược chung)
An organization that pursues a differentiation strategy seeks to distinguish itself from
competitors through the quality (broadly defined) of its products or services. - Một tổ
chức theo đuổi chiến lược khác biệt hóa sẽ tìm cách phân biệt mình với các đối thủ cạnh
tranh thông qua chất lượng (được định nghĩa rộng rãi) của sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ của mình.
An organization implementing an overall cost leadership strategy attempts to gain a
competitive advantage by reducing its costs below the costs of competing firms. - Một tổ
chức thực hiện chiến lược dẫn đầu về chi phí tổng thể cố gắng đạt được lợi thế cạnh tranh
bằng cách giảm chi phí của mình xuống thấp hơn chi phí của các công ty cạnh tranh.
=> By keeping costs low, the organization is able to sell its products at low prices and
still make a profit - Bằng cách giữ chi phí thấp, tổ chức có thể bán sản phẩm của mình
với giá thấp mà vẫn kiếm được lợi nhuận.
A firm pursuing a focus strategy concentrates on a specific regional market, product line,
or group of buyers - Một công ty theo đuổi chiến lược tập trung sẽ tập trung vào một thị
trường khu vực, dòng sản phẩm hoặc một nhóm người mua cụ thể.
3-4b Strategies Based on the Product Life Cycle
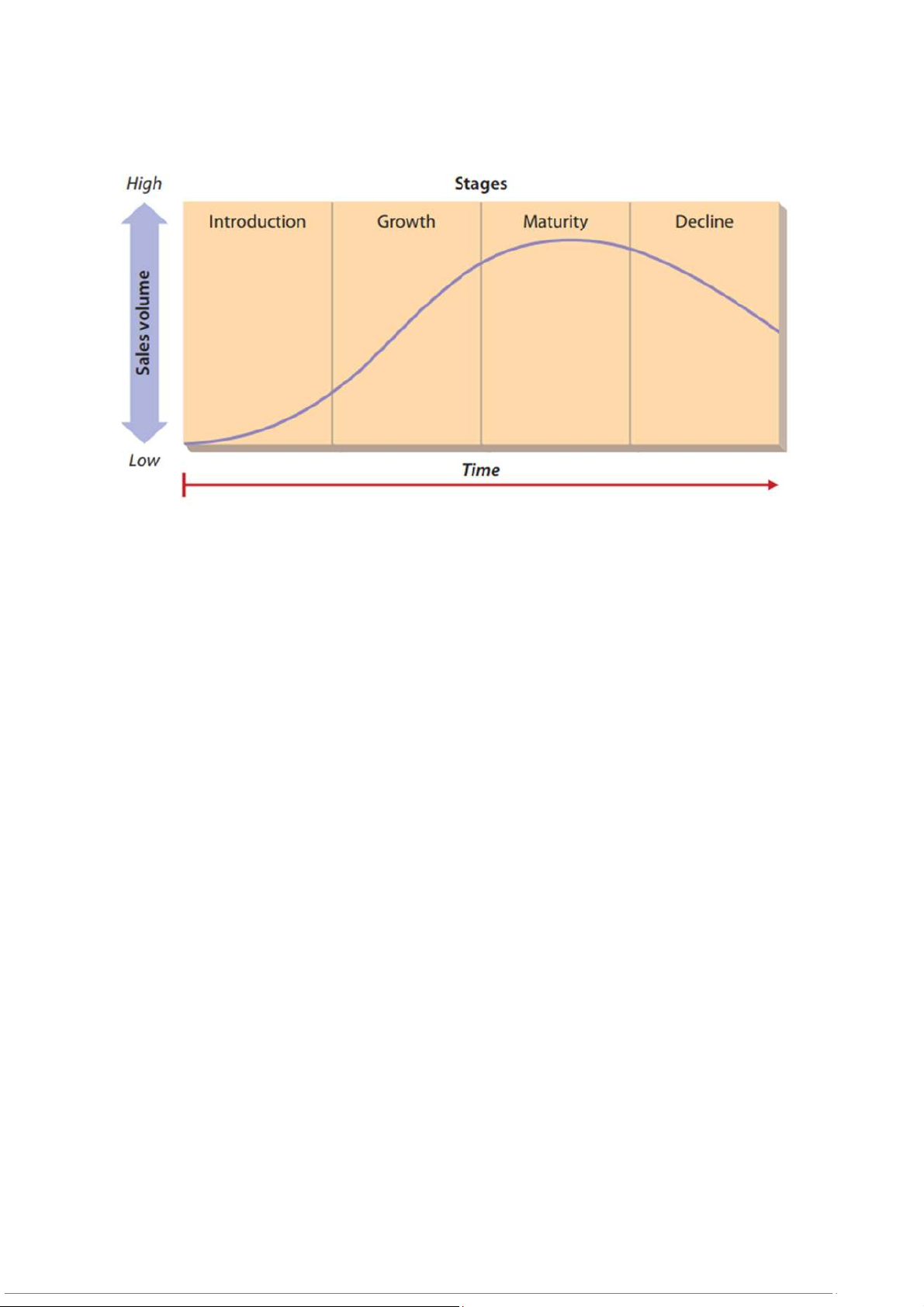
The product life cycle is a model that shows how sales volume changes over the life of
products. Understanding the four stages in the product life cycle helps managers
recognize that strategies need to evolve over time. Page | 6
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
In this introduction stage, demand may be very high and sometimes outpaces the firm’s
ability to supply the product. At this stage, managers need to focus their efforts on
“getting product out the door” without sacrificing quality. - Trong giai đoạn giới thiệu sản
phẩm này, nhu cầu có thể rất cao và đôi khi vượt quá khả năng cung cấp sản phẩm của
công ty. Ở giai đoạn này, các nhà quản lý cần tập trung nỗ lực vào việc “đưa sản phẩm ra
khỏi cửa” mà không làm giảm chất lượng.
Ex: Quản lý thường thuê thêm nhiều nhân viên ở giai đoạn nào?
During the growth stage, more firms begin producing the product, and sales continue to
grow. Important management issues include ensuring quality and delivery and beginning
to differentiate an organization’s product from competitors’ products.
=> Entry into the industry during the growth stage may threaten an organization’s
competitive advantage; thus, strategies to slow the entry of competitors are important -
Trong giai đoạn tăng trưởng, có nhiều công ty bắt đầu sản xuất sản phẩm hơn và doanh
số bán hàng tiếp tục tăng. Các vấn đề quản lý quan trọng bao gồm đảm bảo chất lượng và
giao hàng cũng như bắt đầu phân biệt sản phẩm của tổ chức với sản phẩm của đối thủ
cạnh tranh. Việc gia nhập ngành trong giai đoạn tăng trưởng có thể đe dọa lợi thế cạnh
tranh của tổ chức; do đó, các chiến lược nhằm làm chậm sự gia nhập của đối thủ cạnh tranh là rất quan trọng.
During the maturity stage, overall demand growth for a product begins to slow down,
and the number of new firms producing the product begins to decline. The number of
established firms producing the product may also begin to decline. This period of
maturity is essential if an organization is going to survive in the long run. Product
differentiation concerns are still important during this stage, but also keeping costs low Page | 7
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
and beginning the search for new products or services are important strategic
considerations. - Sau một thời gian tăng trưởng, sản phẩm bước vào giai đoạn thứ ba.
Trong giai đoạn này, tốc độ tăng trưởng tổng thể về nhu cầu đối với một sản phẩm bắt
đầu chậm lại. Giai đoạn trưởng thành này là cần thiết nếu một tổ chức muốn tồn tại lâu
dài. Mối quan tâm về sự khác biệt hóa sản phẩm vẫn quan trọng trong giai đoạn này,
nhưng việc giữ chi phí ở mức thấp và bắt đầu tìm kiếm sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ mới cũng
là những chiến lược quan trọng cần được cân nhắc.
In the decline stage, demand for the product or technology decreases, the number of
organizations producing the product drops, and total sales drop. Demand often declines
because all those who were interested in purchasing a particular product have already
done so. - Trong giai đoạn suy thoái, nhu cầu về sản phẩm hoặc công nghệ giảm, số
lượng tổ chức sản xuất sản phẩm giảm và tổng doanh thu giảm. Nhu cầu thường giảm vì
tất cả những người có hứng thú đối với sản phẩm giảm.
Organizations that fail to anticipate the decline stage in earlier stages of the life cycle
may go out of business. Those that differentiate their product, keep their costs low, or
develop new products or services may do well during this stage. - Các tổ chức không
lường trước được giai đoạn suy thoái trong các giai đoạn đầu của vòng đời có thể bị phá
sản. Những công ty tạo ra sự khác biệt cho sản phẩm của mình, giữ chi phí ở mức thấp
hoặc phát triển sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ mới có thể hoạt động tốt trong giai đoạn này.
3-5 FORMULATING CORPORATE-LEVEL STRATEGIES
Diversification describes the number of different businesses that an organization is
engaged in and the extent to which these businesses are related to on another - Đa dạng
hóa mô tả số lượng các hoạt động kinh doanh khác nhau mà một tổ chức tham gia và mức
độ mà các hoạt động kinh doanh này có liên quan đến các hoạt động kinh doanh khác.
There are three types of diversification strategies:
- single-product strategy (chiến lược một sản phẩm)
- related diversification (đa dạng hóa có liên quan)
- unrelated diversification. (đa dạng hóa không liên quan) 3-5a Single-Product Strategy
An organization that pursues a single-product strategy manufactures just one product or
service and sells it in a single geographic market. - Một tổ chức theo đuổi chiến lược một
sản phẩm chỉ sản xuất một sản phẩm hoặc dịch vụ và bán nó ở một thị trường địa lý duy nhất. Page | 8
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
The single-product strategy has one major strength and one major weakness. By
concentrating its efforts so completely on one product and market, a firm is likely to be
very successful in manufacturing and marketing that product. Because it has staked its
survival on a single product, the organization works very hard to make sure that the
product is a success. Of course, if the product is not accepted by the market or is replaced
by a new one, the firm will suffer.
Chiến lược một sản phẩm có một điểm mạnh lớn và một điểm yếu lớn. Bằng cách tập
trung nỗ lực hoàn toàn vào một sản phẩm và thị trường, một công ty có thể sẽ rất thành
công trong việc sản xuất và tiếp thị sản phẩm đó. Bởi vì họ đặt cược sự sống còn của
mình vào một sản phẩm duy nhất nên tổ chức này làm việc rất chăm chỉ để đảm bảo rằng
sản phẩm đó thành công. Tất nhiên, nếu sản phẩm không được thị trường chấp nhận hoặc
bị thay thế bằng sản phẩm mới thì doanh nghiệp sẽ bị thiệt hại. 3-5b Related Diversification
Given the disadvantage of the single-product strategy, most large businesses today
operate in several different businesses, industries, or markets. If the businesses are
somehow linked, that organization is implementing a strategy of related diversification.
Do nhược điểm của chiến lược một sản phẩm, hầu hết các doanh nghiệp lớn ngày nay đều
hoạt động trong nhiều lĩnh vực kinh doanh, ngành hoặc thị trường khác nhau. Nếu các
hoạt động kinh doanh được liên kết thì tổ chức đó đang thực hiện chiến lược đa dạng hóa liên quan.
Pursuing a strategy of related diversification has three primary advantages:
- First, it reduces an organization’s dependence on any one of its business activities and thus reduces economic risk.
- Second, by managing several businesses at the same time, an organization can reduce
the overhead costs associated with managing any one business.
- Third, related diversification allows an organization to exploit its strengths and
capabilities in more than one business. When organizations do this successfully, they
capitalize on synergies, which are complementary effects that exist among their
businesses. - Thứ ba, đa dạng hóa liên quan cho phép một tổ chức khai thác điểm mạnh
và khả năng của mình trong nhiều lĩnh vực kinh doanh. Khi các tổ chức thực hiện thành
công điều này, họ tận dụng được sức mạnh tổng hợp.
Synergy exists among a set of businesses when the businesses’ economic value together
is greater than their economic value separately - Sức mạnh tổng hợp tồn tại giữa một tập Page | 9
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
hợp các doanh nghiệp khi giá trị kinh tế của các doanh nghiệp cùng nhau lớn hơn giá trị
kinh tế riêng lẻ của chúng.
3-5c Unrelated Diversification
Firms that implement a strategy of unrelated diversification operate multiple businesses
that are not logically associated with one another - Các công ty thực hiện chiến lược đa
dạng hóa không liên quan nhiều hoạt động kinh doanh với nhau.
Even if there are potential synergies among their different businesses, organizations
implementing a strategy of unrelated diversification do not attempt to exploit them. -
Ngay cả khi có sự phối hợp tiềm năng giữa các hoạt động kinh doanh khác nhau, các tổ
chức thực hiện chiến lược đa dạng hóa không liên quan cũng không cố gắng khai thác chúng.
In theory, unrelated diversification has two advantages.
- First, a business that uses this strategy should be able to achieve relatively stable
performance over time (đạt được hiệu suất tương đối ổn định theo thời gian). During any
given period, some businesses owned by the organization are in a cycle of decline,
whereas others may be in a cycle of growth.
- Second, unrelated diversification is also thought to have resource allocation advantages
(có lợi thế về phân bố nguồn lực). Every year, when a corporation allocates capital,
people, and other resources among its various businesses, it must evaluate information
about the future of those businesses so that it can place its resources where they have the highest potential for return.
Despite these presumed advantages, research suggests that unrelated diversification
usually does not lead to high performance.
-First, corporate-level managers in such a company usually do not know enough about
the unrelated businesses to provide helpful strategic guidance or to allocate capital
appropriately. - các nhà quản lý cấp công ty thường không biết đủ về các hoạt động kinh
doanh không liên quan để đưa ra hướng dẫn chiến lược hữu ích hoặc phân bổ vốn hợp lý.
=> This narrow attention at the expense of broader planning eventually hobbles the entire organization.
Second, because organizations that implement unrelated diversification fail to exploit
important synergies, they may be at a competitive disadvantage compared to
organizations that use related diversification Page | 10
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
Thứ hai, do các tổ chức thực hiện đa dạng hóa không liên quan không khai thác được sức
mạnh cộng hưởng quan trọng nên họ có thể gặp bất lợi trong cạnh tranh so với các tổ
chức sử dụng đa dạng hóa có liên quan. 3-5d Managing Diversification
Portfolio management techniques are methods that diversified organizations use to
determine which businesses to engage in and how to manage these businesses to
maximize corporate performance - Kỹ thuật quản lý danh mục đầu tư là phương pháp mà
các tổ chức đa dạng sử dụng để xác định xem nên tham gia vào hoạt động kinh doanh nào
và cách quản lý các hoạt động kinh doanh này để tối đa hóa hiệu quả hoạt động của công ty.
Two important portfolio management techniques are the BCG matrix and the GE Business Screen
BCG Matrix: The BCG (Boston Consulting Group) matrix provides a framework for
evaluating the relative performance of businesses in which a diversified organization
operates. It also prescribes the preferred distribution of cash and other resources among these businesses.
The BCG matrix uses two factors to evaluate an organization’s set of businesses:
- the growth rate of a particular market (tốc độ tăng trưởng của một thị trường cụ thể)
- the organization’s share of that market (thị phần của tổ chức trên thị trường đó)
The matrix suggests that fast-growing markets in which an organization has the highest
market share are more attractive business opportunities than slow-growing markets in
which an organization has small market share. - Ma trận cho thấy rằng các thị trường tăng
trưởng nhanh trong đó tổ chức có thị phần cao nhất sẽ có nhiều cơ hội kinh doanh hấp
dẫn hơn các thị trường tăng trưởng chậm mà tổ chức có thị phần nhỏ.
The matrix classifies the types of businesses in which a diversified organization can
engage as dogs, cash cows, question marks, and stars.
Dogs are businesses that have a very small share of a market that is not expected to grow.
Because these businesses do not hold much economic promise - những doanh nghiệp có
thị phần rất nhỏ và dự kiến sẽ không tăng trưởng.
=> the BCG matrix suggests that organizations either should not invest in them or should
consider selling them as soon as possible. Page | 11
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
Cash cows are businesses that have a large share of a market that is not expected to grow
substantially. These businesses characteristically generate high profits that the
organization should use to support question marks and stars. (Cash cows are “milked” for
cash to support businesses in markets that have greater growth potential)
Question marks are businesses that have only a small share of a fast-growing market. The
future performance of these businesses is uncertain. A question mark that is able to
capture increasing amounts of this growing market may be very profitable. On the other
hand, a question mark unable to keep up with market growth is likely to have low profits.
=> The BCG matrix suggests that organizations should invest carefully in question
marks. If their performance does not live up to expectations, question marks should be
reclassified as dogs and divested.
Stars are businesses that have the largest share of a rapidly growing market. Cash
generated by cash cows should be invested in stars to ensure their preeminent position.-
là những doanh nghiệp có thị phần lớn nhất trong một thị trường đang phát triển nhanh chóng.
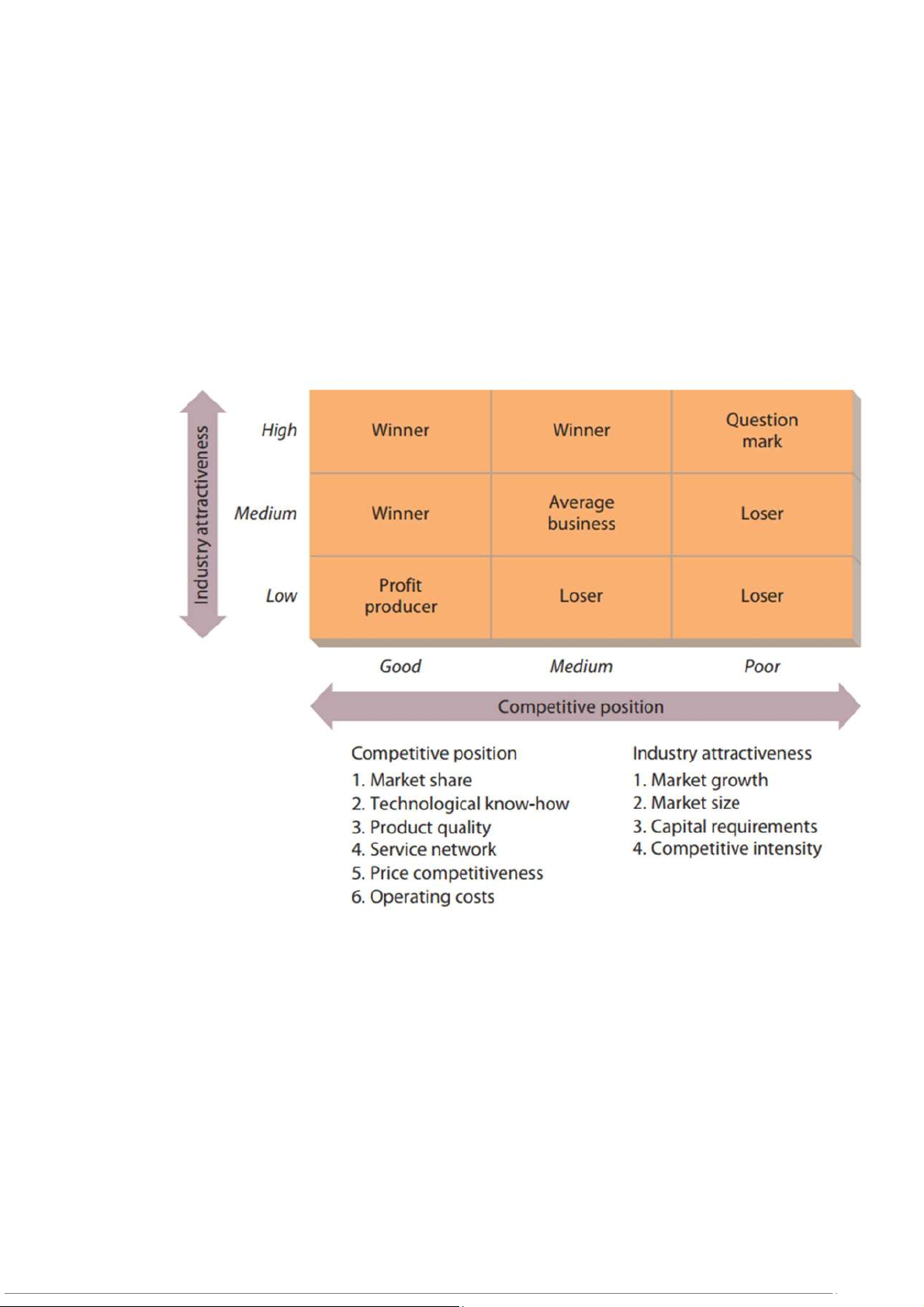
GE Business Screen Because the BCG matrix is relatively narrow and overly simplistic,
GE developed the GE Business Screen, a more sophisticated approach to managing
diversified business units. The GE Business Screen is a portfolio management technique Page | 12
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
that can also be represented in the form of a matrix. Rather than focusing solely on
market growth and market share, however, the GE Business Screen considers industry
attractiveness and competitive position. - là một kỹ thuật quản lý danh mục đầu tư cũng
có thể được biểu diễn dưới dạng ma trận. Tuy nhiên, thay vì chỉ tập trung vào tăng trưởng
thị trường và thị phần, GE Business Screen xem xét mức độ hấp dẫn và vị thế cạnh tranh của ngành.
These two factors are divided into three categories to make the nine-cell matrix.These
cells, in turn, classify business units as winners, losers, question marks, average
businesses, or profit producer.
Both market growth (tăng trưởng thị trường) and market share (thị phần) appear in a
broad list of factors that determine the overall attractiveness of an industry and the overall
quality of a firm’s competitive position.
Other determinants of an industry’s attractiveness (in addition to market growth)
include market size (quy mô thị trường), capital requirements (nhu cầu vốn), and
competitive intensity (cường độ cạnh tranh).
- The greater the market growth the larger the market, the smaller the capital
requirements, and the less the competitive intensity => the more attractive an industry will be.
Other determinants of an organization’s competitive position in an industry (besides
market share) include technological know-how (bí quyết công nghệ), product quality
(chất lượng sản phẩm), service network (mạng lưới dịch vụ), price competitiveness (khả
năng cạnh tranh), and operating costs (chi phí vận hành).
- In general, businesses with large market share, technological know-how, high
product quality, a quality service network, competitive prices, and low operating
costs are => a favorable competitive position.
By conducting this type of SWOT analysis across several businesses, a diversified
organization can decide how to invest its resources to maximize corporate
performance. Bằng cách tiến hành loại phân tích SWOT này trên một số doanh
nghiệp, một tổ chức đa dạng có thể quyết định cách đầu tư nguồn lực để tối đa hóa
hiệu quả hoạt động của công ty.
In general, organizations should:
- Invest in winners and question marks (where industry attractiveness and
competitive position are both favorable) Page | 13
Authorized by Truong Viet Nga (truongvietnga030703@gmail.com)
- Maintain the market position of average businesses and profit producers (where
industry attractiveness and competitive position are average), - Sell losers
Nói chung, các tổ chức nên đầu tư vào người chiến thắng và dấu hỏi (nơi mà cả
sức hấp dẫn của ngành và vị thế cạnh tranh đều thuận lợi), nên duy trì vị thế thị
trường của các doanh nghiệp trung bình và người tạo ra lợi nhuận (nơi mà độ hấp
dẫn của ngành và diện tích vị thế cạnh tranh là trung bình), và nên bán những người thua cuộc. 3-6 TACTICAL PLANNING
Tactical plans are to battles what strategy is to a war: an organized sequence of steps
designed to execute strategic plans. Strategy focuses on resources, environment, and
mission, whereas tactics focus primarily on people and action. - Các kế hoạch chiến thuật
là các trận chiến giống như chiến lược của một cuộc chiến: một chuỗi các bước có tổ
chức được thiết kế để thực hiện các kế hoạch chiến lược. Chiến lược tập trung vào nguồn
lực, môi trường và sứ mệnh, trong khi chiến thuật tập trung chủ yếu vào con người và hành động. Page | 14




