





Preview text:
[SUMMARY LECTURE] CHAP 1 INTRODUCING MANAGEMENT
CHAP 1: INTRODUCING MANAGEMENT I.Stakeholders
- Stakeholders: all the people who stand to gain or lose by the policies and
activities of a business and whose concerns the business needs to address.
Stakeholders include customers, employees, suppliers, stockholders, dealers,
bankers, the media, people in the local community, environmentalists, elected government leaders.
→ Example: McDonald’s regards its customers (approximately 69 million
worldwide every day), suppliers like Kenny Longaker, Frank Martinez, and
Keystone Foods, and employees (about 210,000 people worldwide) as its
main stakeholders. These stakeholders have an impact on the operations of the
restaurant and can be affected by it as well. II.Organization: a) Definition:
- An organization is a collection of people working together to achieve a common purpose.
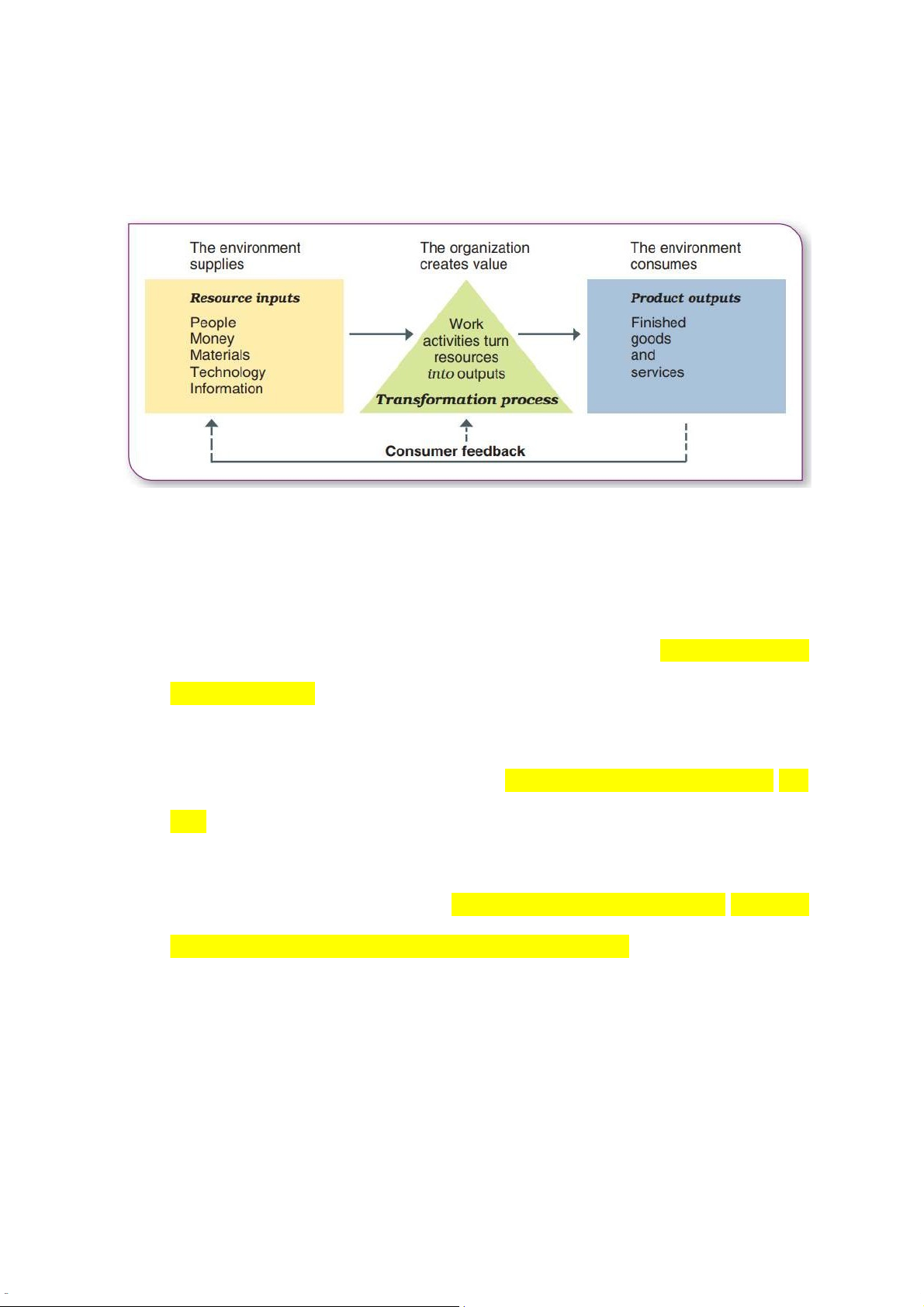
b) Organizations as Systems: All organizations are open systems that
interact with their environments. An open system transforms resource
inputs from the environment into product outputs. c) Organizational performance
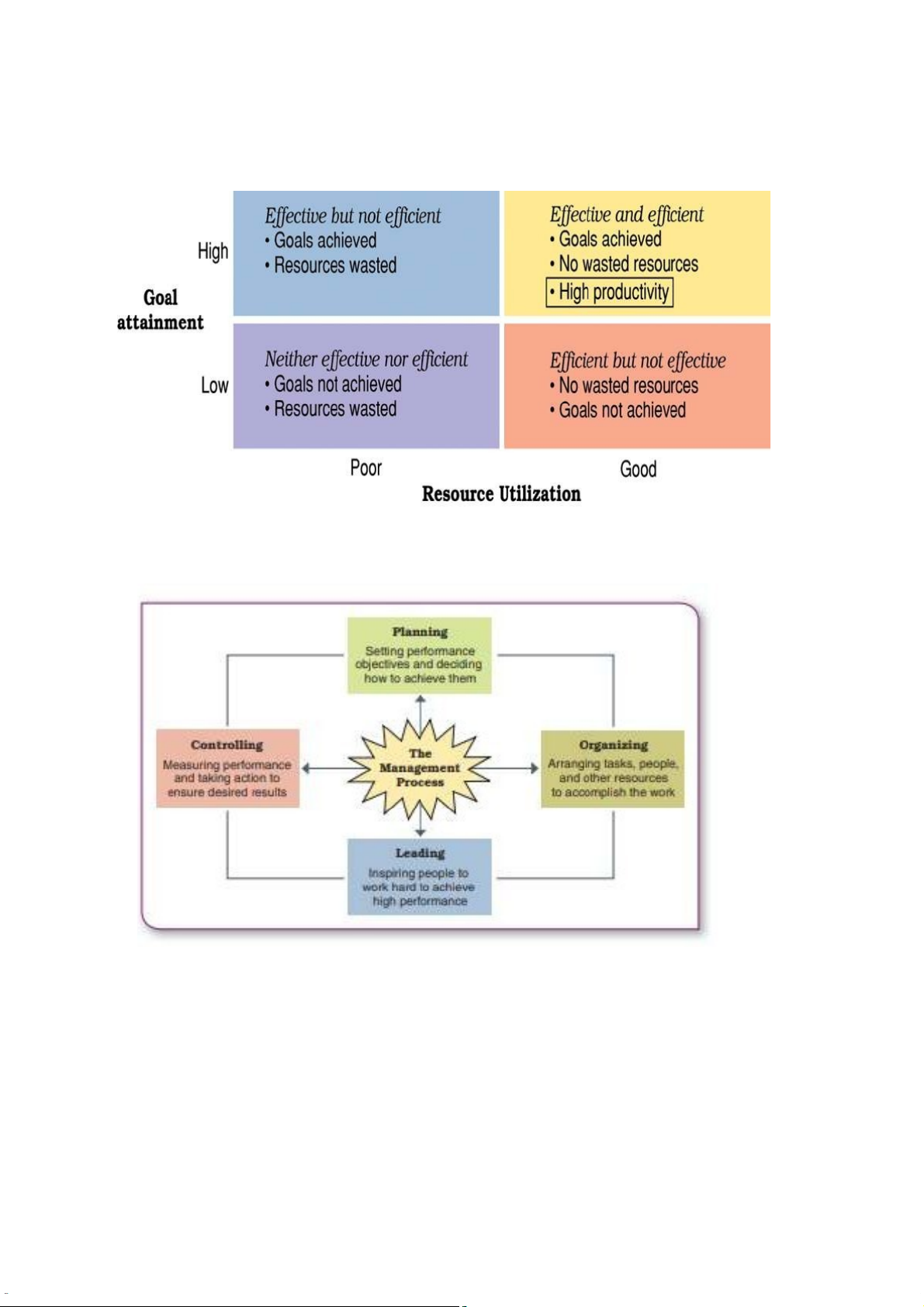
- Productivity: the quantity and quality of work performance, with
resource utilization considered (Hiệu suất). ⇒ Ví dụ: Units of product per units of time
- Performance effectiveness: an output measure of task or goal
accomplishment. (Hiệu quả) ⇒ Ví dụ: Một người làm bài tập mà điểm cao nhất⇒ Effectiveness
-Performance efficiency:
an input measure of resource cost associated with
goal accomplishment. ⇒ Ví dụ: Một người làm bài tập mà ít mất thời gian
nhất, một giải pháp được đưa ra mà ít tốn tiền nhất ⇒E cie ffi ncy
III. Functions of management:
- Planning: The process of setting objectives and determining what
actions should be taken to accomplish them
Ex: Công ty đặt mục tiêu đầu ra sản phẩm
- Organizing: The process of assigning tasks, allocating resources, and
arranging the coordinated activities of individuals and groups to implement plans
Ex: Công ty muốn tổ chức lại cấu trúc, làm bộ máy flatter
- Leading: The process of arousing people’s enthusiasm to work hard and
direct their efforts to fulfill plans and accomplish objectives
Ex: Công ty bảo hiểm motivate nhân viên bằng những danh hiệu
- Controlling: The process of measuring work performance, comparing
results to objectives, and taking corrective action as needed
Ex: Công ty kiểm tra chất lượng sản phẩm IV. Levels of Manager:
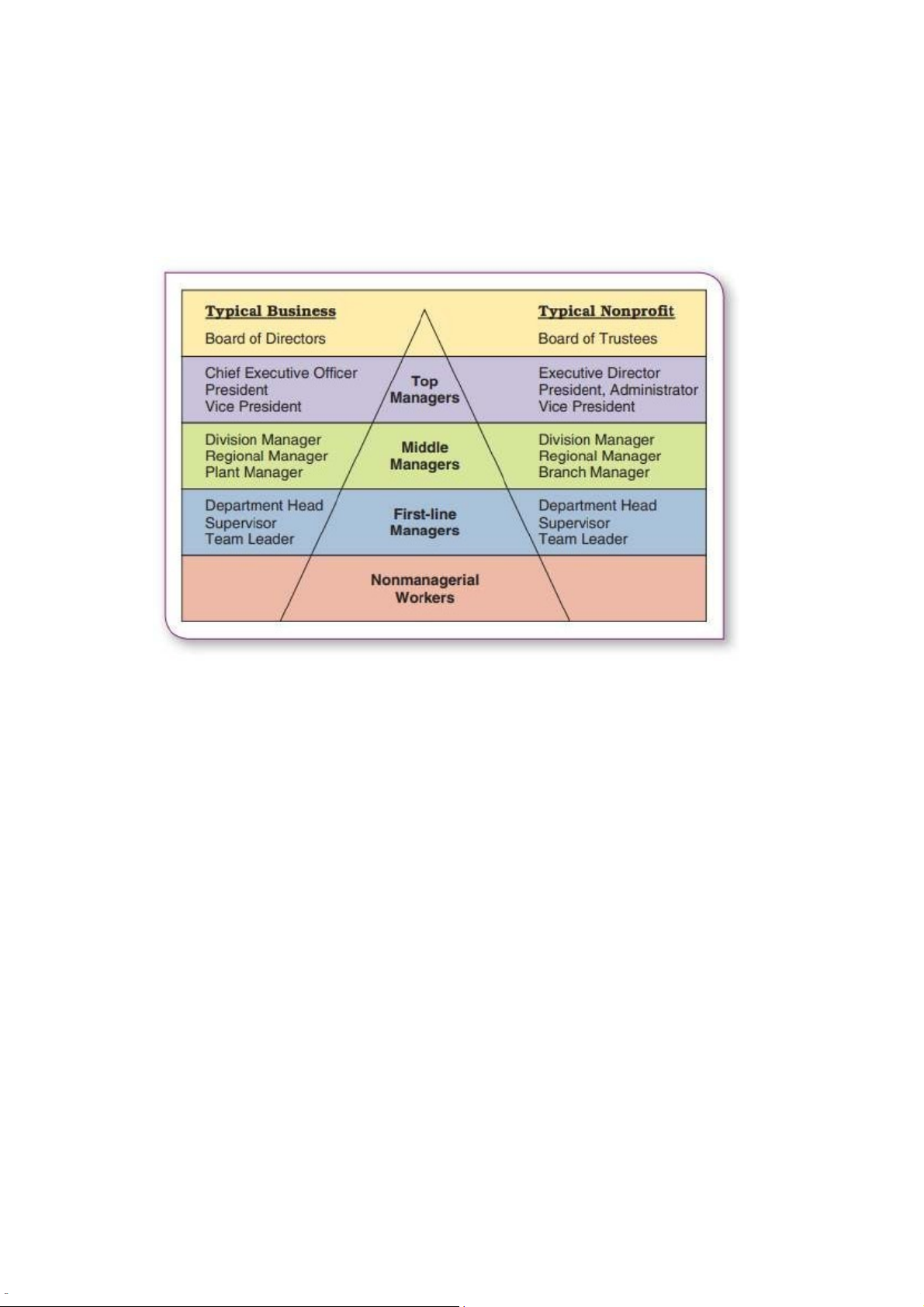
In all companies we have three lines of managers, tùy mỗi công ty sẽ có các
layout manager khác nhau. Managers ở công ty này có thể là first-line
managers trong khi ở công ty khác có thể là top managers:
-Top managers: guide the performance of the organization as a whole or of one of its major parts -
Middle managers: oversee the work of large departments or divisions. -
Team leaders: export to middle managers and supervise nonmanagerial workers Ex: IU -
Top: Chủ tịch Hội đồng trường, Hiệu trưởng, Hiệu phó -
Middle: Deans, Department Heads -
1st-line: Team leaders, Course leaders (Trưởng bộ môn) (?)
Tại sao khác với model? Vì middle và 1st line phụ thuộc vào top và
structure của công ty (VD: nếu department không có teams thì department head là 1st)
V. Essential Managerial Skills:
Katz’s Essential Managerial Skills:
-Human skill: or interpersonal skill is the ability to work well in cooperation with other people
-Technical skill: is the ability to use expertise to perform a task with proficiency.
Ex: Trưởng nhóm kỹ sư cần có chuyên môn kỹ sư giỏi, trưởng nhóm kế
toán cần có chuyên môn kế toán kiểm toán giỏi
-Conceptual skill: is the ability to think analytically to diagnose and solve complex problems.
Ex: Nhìn nhận bức tranh kinh tế trong thời gian dài hơn để định hướng công ty
Note: Lower-level managers càng cần technical skills nhiều thì ở Top-level
managers cần nhiều nhất conceptual skills, less human skills và least technical skills




