








Preview text:
Lecturer:
Ho Trung Thao (thao.hotrung@hoasen.edu.vn) 1 Course Objectives
Understand the definitions Logistics and Supply Chain
Understand the concept and key points of Supply Chain Management.
Know how to manage Supply Chain and Logistics in real companies. Apply to a group project. 2 Materials
Required Textbooks and Materials:
[1] Donald Waters, Supply Chain Management Logistics-An
Introduction to Logistics, Palgrave MacMillan, 2009. [2] Lecturer’s material. References:
Chopra, S. and P. Meindl, Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning
and Operations, Fifth Edition, New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
David Simchi-Levi, Philip Kaminsky, and Edith Simchi-Levi, Designing and
Managing the Supply Chain. McGraw-Hill/Irwin; 2nd edition.
Stanford Global Supply Chain Forum, www.stanford.edu/group/scforum
Supply Chain Management Research Center, www.cio.com/research/scm
Supply Chain Resource, www.supplychaincanada.org/en/resources
Journal, International Journal of Logistics Management,
http://www.emeraldinsight.com/products/journals/journals.htm?id=ijlm
Newspapers (Sài gòn giải phóng, Tuổi trẻ Thanh niên, Kinh tế Sài gòn,
Diễn đàn doanh nghiệp, VN Express, Vietnam Net, Kinh tế Việt Nam…) 3
Group project (Group assignment) - Purpose:
Students learn about the actual supply activities in the enterprise , to link
knowledge and operation in reality. - Group structure:
Each group of 5-8 students , depending on the number of students in the
class (students self-select group , vote the group leader and submit to the
faculty group member list in the first 2 weeks of school ). - Content:
Each group will choose one topic in the course.
Each group approaches and study business according to the selected
theme (which may change the subject's request or the actual business
operation) , group discussions , may have further advice from faculty.
Each group get a referral and business contacts by themself. Lecturers
will join field trips with the group if necessary. - Format and deadlin : e
Each group will submit a report of 8-12 pages A4 , in the 11th week;
groups will present to the class during the week 12-15. 4 g p p g Academic Integrity Students are required to:
Work independently on individual assignments
Collaborating on individual assignments is considered cheating.
Avoid plagiarism
Plagiarism is an act of fraud that involves the use of ideas or words of another
person without proper attribution. Students will be accused of plagiarism if they:
Copy in their work one or more sentences from another person without proper citation.
Rephrase, paraphrase, or translate another person’s ideas or words without proper attribution.
Reuse their own assignments, in whole or in part, and submit them for another class.
Work responsibly within a working group
In cooperative group assignments, all students are required to stay on task and
contribute equally to the projects. Group reports should clearly state the
contribution of each group member.
o Any acts of academic dishonesty will result in a grade of zero for the task at hand
and/or immediate failure of the course, depending on the seriousness of the fraud.
o Please consult Hoa Sen University’s Policy on Plagiarism at
http://thuvien.hoasen.edu.vn/chinh-sach-phong-tranh-dao-van. 5 Chapter 1 & 2
Fundamentals of Logistics 6 Learning Objectives
DEFINE ‘logistics’ and associated terms
UNDERSTAND the role and structure of supply chains
LIST different activities of logistics and understand the relationships between them
DISCUSS the aims of logistics
SHOW how logistics contributes to customer satisfaction
RECOGNISE the importance of logistics to every organization. 7 1. Basics Definition
All organizations move materials. Manufacturers: raw materials finished goods.
raw material: nguyên vật liệu
finished product: thành phẩm 8 1. Basics Definition
Definition of Logistics: Logistics is the function that is responsible
for the movement of materials (and information). It is responsible
for the transport and storage of materials between suppliers and customers.
According to the Council of Supply Chain Management Professionals
(CSCMP), a professional organization for Logistics and SCM
professionals, logistics is defined as: “the process of planning,
implementing and controlling the efficient, effective flow and storage of
goods, services and related information from point of origin to point of
consumption for the purpose of conforming to customer requirements”
function: hoạt động đặc biệt; material: vật chất
transport: vận chuyển; storage: dự trữ
supplier: nhà cung cấp; consumer: người tiêu dùng 9 Basic Definition (contd.)
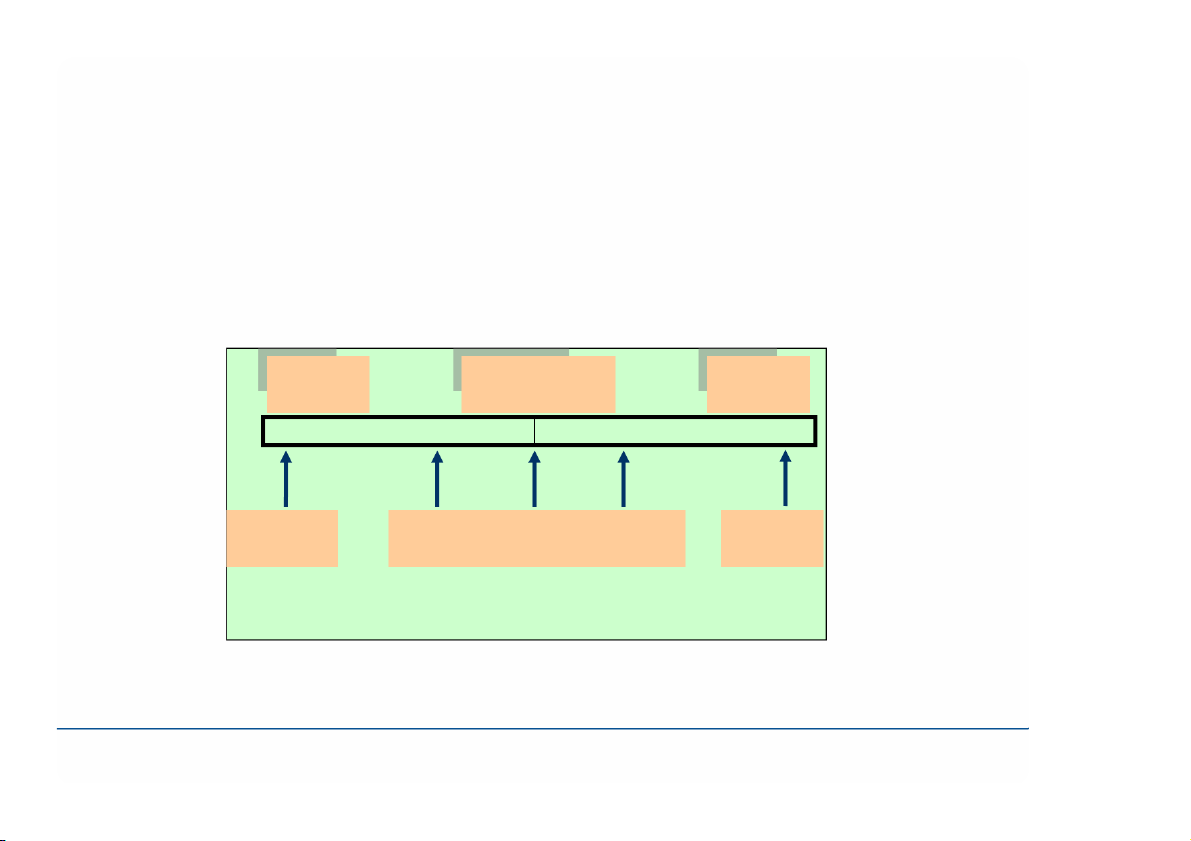
The a im o f a ll o rg a niza tio ns is to sup p ly so m e
p ro d uc ts to the ir c usto m e rs
The se p ro d uc ts m a y b e g o o d s o r se rvic e Mainly Goods and Service Mainly goods service Car producers Tailor Restaurants Healty Education sector spectrum: dãy liên tục
goods: hàng hóa; service: dịch vụ g g