











Preview text:
Lecturer:
Ho Trung Thao (thao.hotrung@hoasen.edu.vn) 1 Learning Objectives
Appreciate the problems of considering logistics functions in isolation
Discuss the benefits of creating a single, integrated logistics function
Outline the steps needed for internal integration
Discuss the benefits of external integration along supply chains
Review the difficulties of achieving this external integration
Describe different types of external integration Outline
Problems with fragmented logistics
Bringing activities together
Integration along supply chains Achieving integration Types of co-operation
fragmented logistics : logistics bị phân mảnh/chia cắt
integration: tích hợp; co-operation: hợp tác
1. Problems with fragmented logistics
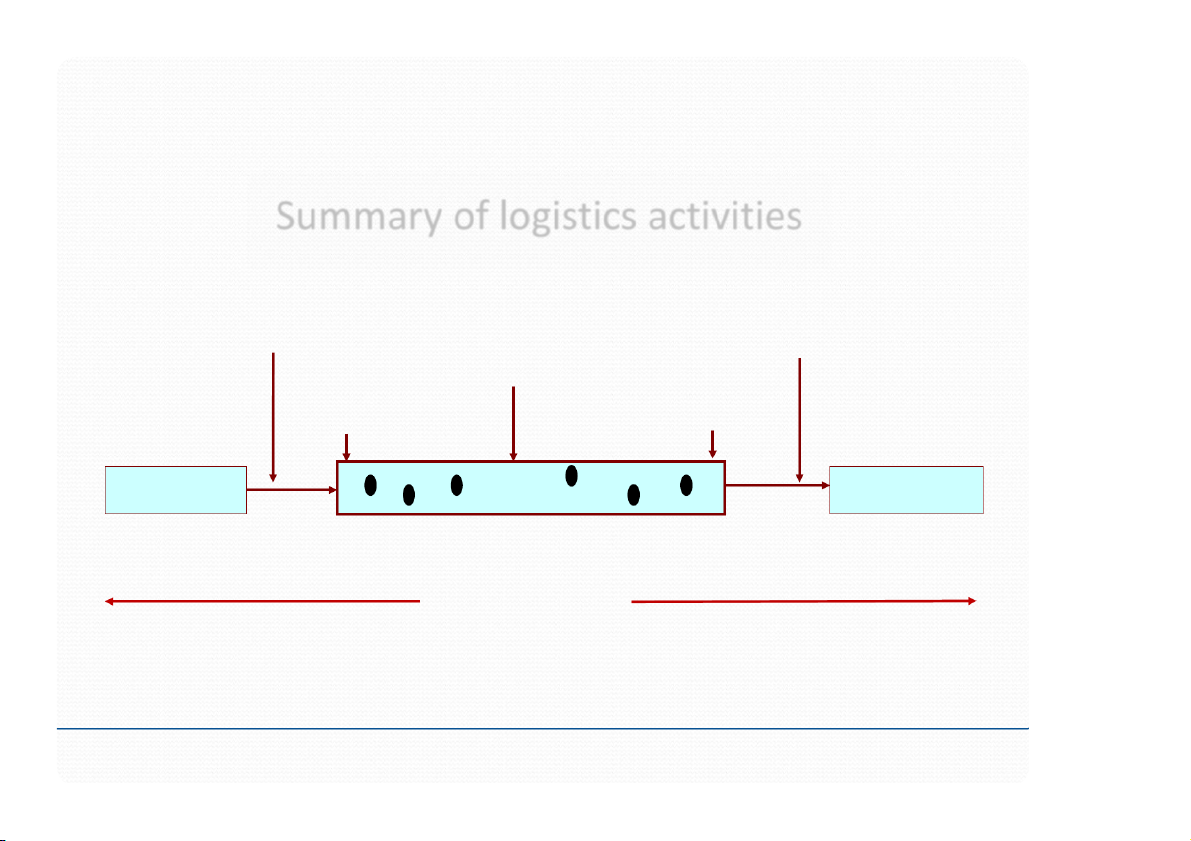
Summary of logistics activities Procurement Physical distribution Inward transport Warehousing Outward transport Stock control returns Materials handling Picking Receiving Consolidating Suppliers Operations Customers Communications Location consolidating : gom hàng
order picking: gom hàng cho đơn hàng
Marketing wanted:
high stocks of finished goods to satisfy customer demands quickly
a wide range of finished goods always held in stock
locations near to customers to allow delivery with short lead times
production to vary output in response to customer orders
emphasis on an efficient distribution system
an optimistic sales forecast to ensure production was geared up for actual demand.
stocks finished goods: tồn kho hàng thành phẩm; leadtime: thời gian chờ hàng
sale forecast: dự báo mức tiêu thụ
1. Problems with fragmented logistics
Fragmented Logistics has the disadvantages of:
- Giving different, often conflicting, objectives within an organization.
- Duplicating effort and reducing productivity.
- Giving worse communications & information flows between the parts.
- Reducing co-ordination between the parts – leading to lower
efficiency, higher costs & worse customer service.
- Increasing uncertainty & delays along the supply chain.
- Making planning more difficult.
- Introducing unnecessary buffers between the parts (e.g. stocks of
WIP, additional transport & administrative procedures.
- Obscuring important information (e.g. the total cost of logistics).
- Giving logistics a low status within the organization.
conflicting objective: mục tiêu mâu thuẫn; duplicating effort: nỗ lực trùng lắp
WIP: work-in-process, work-in-progress: bán thành phẩm 7 2.Bringing activities together
To avoid these problems, logistics should:
Integrating logistics within an organization has all
the related activities working together as a single function.
be responsible for all storage and movement of
materials throughout the organization.
tackle problems from the viewpoint of the whole
firm, and looks for the greatest overall benefit.
In practice, it is difficult to integrate all logistics within a firm.
tackle: giải quyết, xử trí (vấn đề) Viewpoint: quan điểm 2.Bringing activities together Stages in integration The movement of logistics from
low priority, fragmented function
strategic, integrated function,
is a major change, which goes through the following stages:
1. Separate logistics activities that are not given much attention or considered important.
2. Recognizing that the separate activities of logistics are important
for the success of the organization.
3. Making improvements in the separate functions, making sure
that each is as efficient as possible.
separate logistics activities: các hoạt động logistics riêng rẽ/phân tán 9 2.Bringing activities together
Stages in integration (cont’d.)
4. Internal integration – recognizing the benefits of internal co-
operation and combining the separate functions into one.
5. Developing a logistics strategy, to set the long-term direction of logistics.
6. Benchmarking – comparing logistics’ performance with other
organizations, learning from their experiences, identifying areas
that need improvement & finding ways of achieving it.
7. Continuous improvement – accepting that further changes are
inevitable and always searching for better ways of organizing logistics.
internal integration: tích hợp bên trong
benchmarking: so sánh với một chuẩn mực, chuẩn đối sánh 10 g ộ ự ,