











Preview text:
Chapter1: Accouting in action Excercises: E1-1
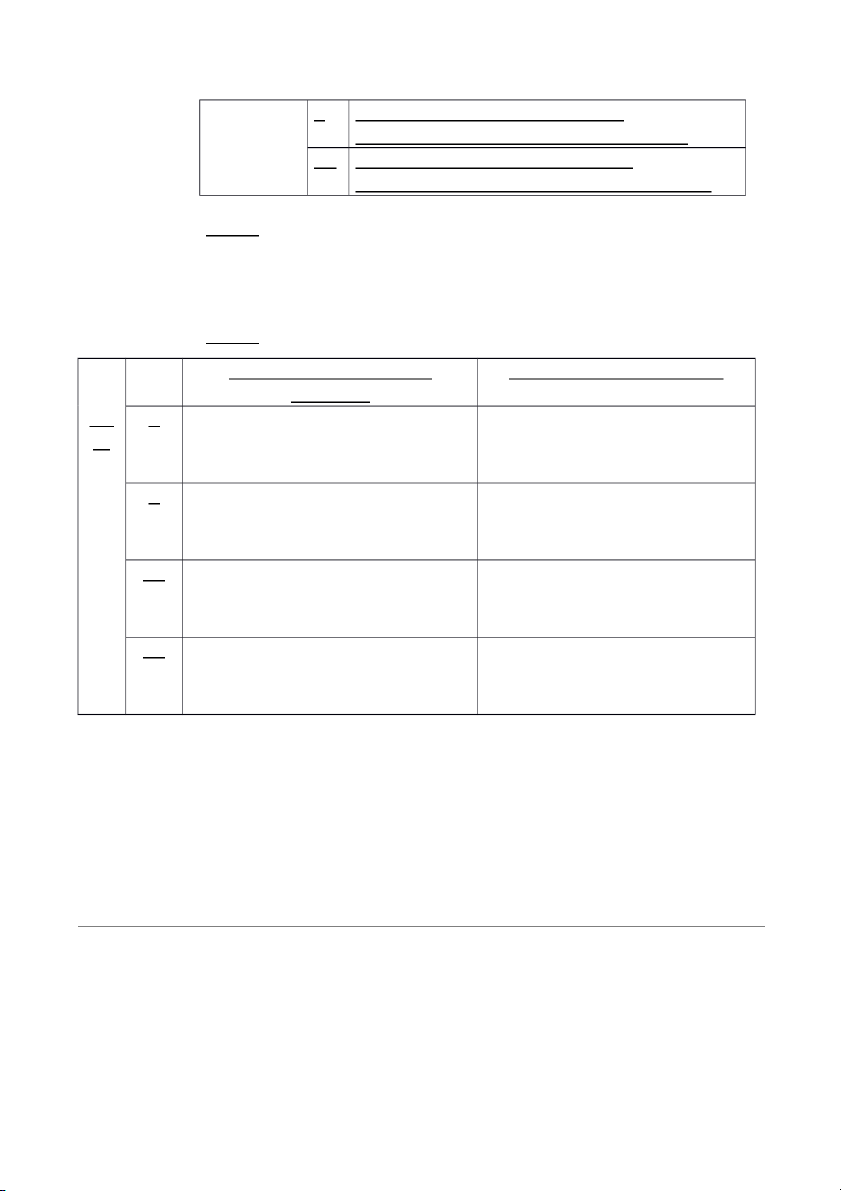
C Analyzing and interpreting information. R Classifying economic events.
C Explaining uses, meaning, and limitations of data.
R Keeping a systematic chronological diary of events.
R Measuring events in dollars and cents.
C Preparing accounting reports.
C Reporting information in a standard format.
I Selecting economic activities relevant to the company. R Summarizing economic events. E1-2 a) Internal users Marketing manager Production supervisor Store manager Vice-president of finance External users Customers Internal Revenue Service Labor unions
Securities and Exchange Commission Suppliers b)
I Can we afford to give our employess a pay raise?
E Did the company earn a satisfactory income?
I Do we need to borrow in the near future?
E How does the company’s profitability compare to other companies?
I What does it cost us to manufacture each unit produced?
I Which product should we emphasize?
E Will the company be able to pay its short-term debts E1-3 1-1
The cost principle requires that assets be recorded and reported at their cost,
because cost is reliable and can be objectively measured and verified.
The stakeholders include stockholders and creditors of Cresco Company, potential
stockholders and creditors, other users of Cresco’s accounting reports, Cresco, and
Sharon Gross. All users of Cresco’s accounting reports could be harmed by relying
on information which violates accounting principles. Sam cresco could benefit if
the company is able to attract more investors, but would be harmed if the
fraudulent reporting is discovered. E1-4
1. Incorrect. The cost principle requires that assets be recorded and reported at their cost.
2. Correct. The monetary unit assumption requires that companies include in
the accounting records only transaction data that can be expressed in terms of money.
3. Incorrect. The economic entity assumption requires that the activities of the
entity be kept separate and distinct from the activities of its owner and all
other economic entities. E1-5 Asset Cash Equipment Supplies Accounts receivable Liability Accounts payable Notes payable Salaries & wage payable Stockholders equity Owner’s capital E1-6
1. Increase in assets and increase in owner’s equity
2. Decrease in assets and decrease in owner’s equity.
3. Increase in assets and increase in liabilities.
4. Increase in assets and increase in owner’s equity.
5. Decrease in assets and decrease in owner’s equity. 1-2
6. Increase in assets and decrease in assets.
7. Increase in liabilities and decrease in owner’s equity
8. Increase in assets and decrease in assets.
9. Increase in assets and increase in owner’s equity. E1-7 1. C 2. D 3. A 4. B 5. D 6. B 7. E 8. F E1-8
1. Share holders invested $15000 cash in the business
2. Purchased equiment for $5000 paying $2000 in cash and the balance of $3000 on account 3. Paid $750 cash for supplies
4. Earned $9100 in revenue, receiving $4600 cash and $4500 on account
5. Paid $1500 cash on accounts payable
6. Owner withdrew $2000 cash for personal use 7. Paid $650 cash for rent
8. Collect $450 cash from customers on account 9. Paid salaries of $3900
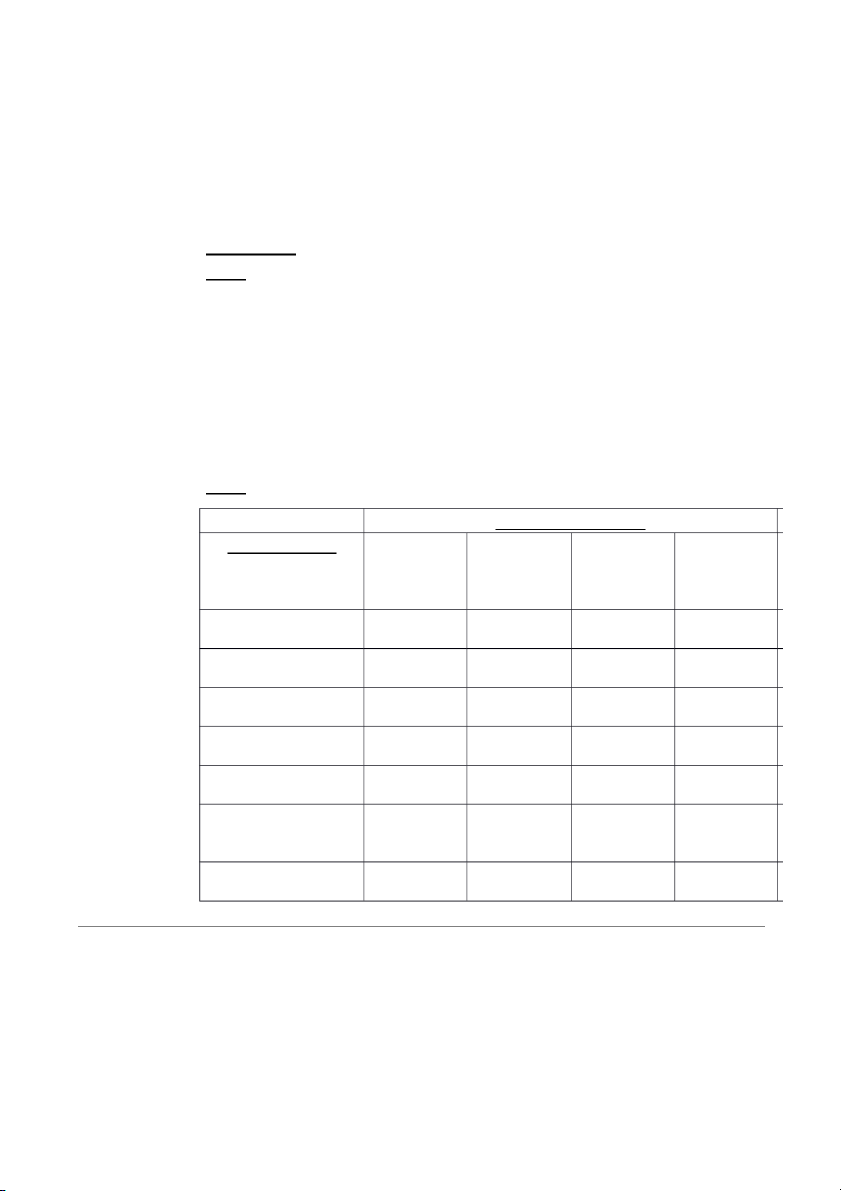
10.Incurred $500 of utilities expense on account b) Investment $15,000 Service revenue $9,100 Dividends (2,000) Rent expense (650) Salaries expense (3,900) Utilities expense (500) Increase in capital $17050 c) 1-3 Service revenue $9,100 Rent expense (650) Salaries expense (3,900) Utilities expense (500) Net income$4050 E1-9 Retained earnings statement for the month ended August 31
Retained earnings,August 1 $ 0 Add: Net income 4050 4050 Less: Dividends 2000
Retained earnings,August 31 $2050
Statement of financial position August 31 Assets Equipment $5000 Supplies 750 Accounts receivable 4050 Cash 9250 Total assets $19050 Income statement Revenues Service revenue $9100 Expenses
Salaries and wages expense $390 Rent expense 0 Ultilities expense 650 Total expenses 500 5050 Net income $4050 1-4 Equity and liabilities Equity Share capital-ordinary $15000 Retained earnings 2050 $17050 Liabilities Accounts payable 2000 Total $19050 Problems A: 1A 1-5
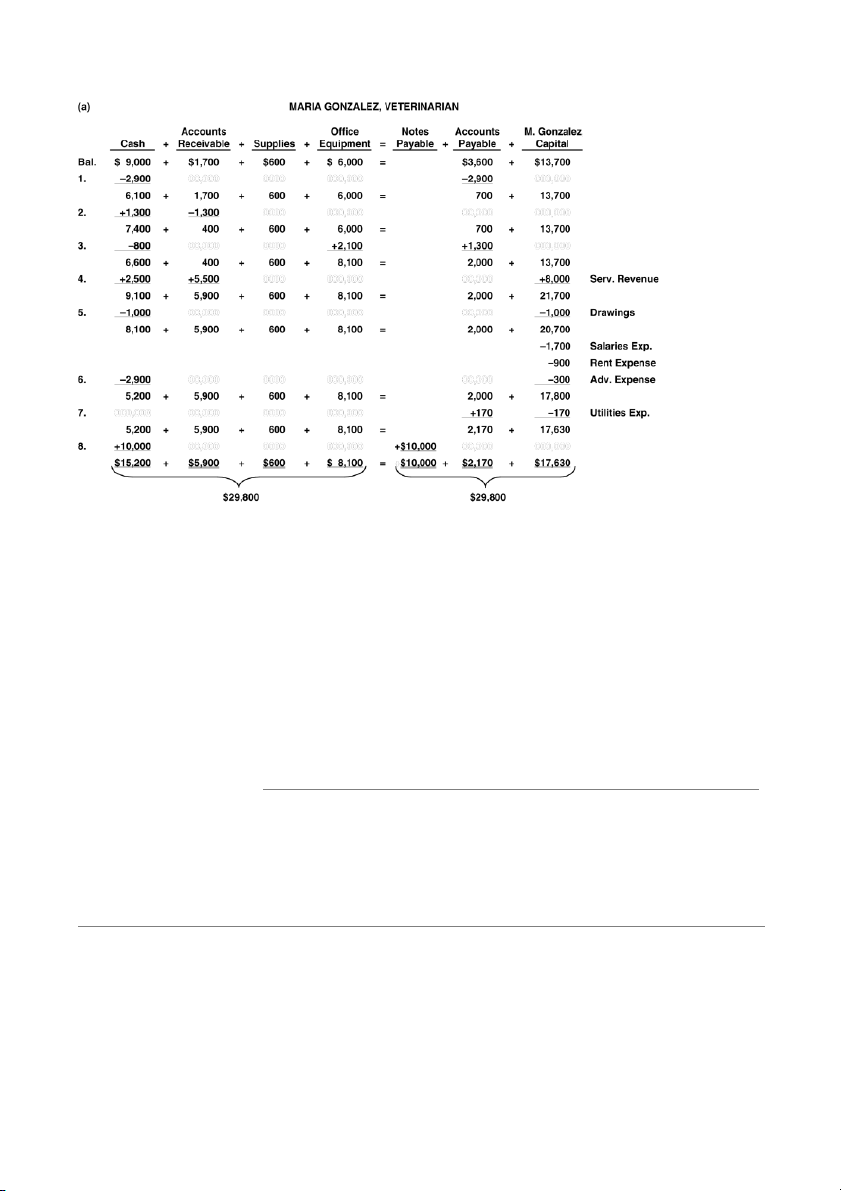
Ending capital...................................................................................... $12,060
Add: Drawings.................................................................................... 1,000 13,060
Deduct: Investments........................................................................ 10,000
Net income............................................................................................. $ 3,060 2A 1-6
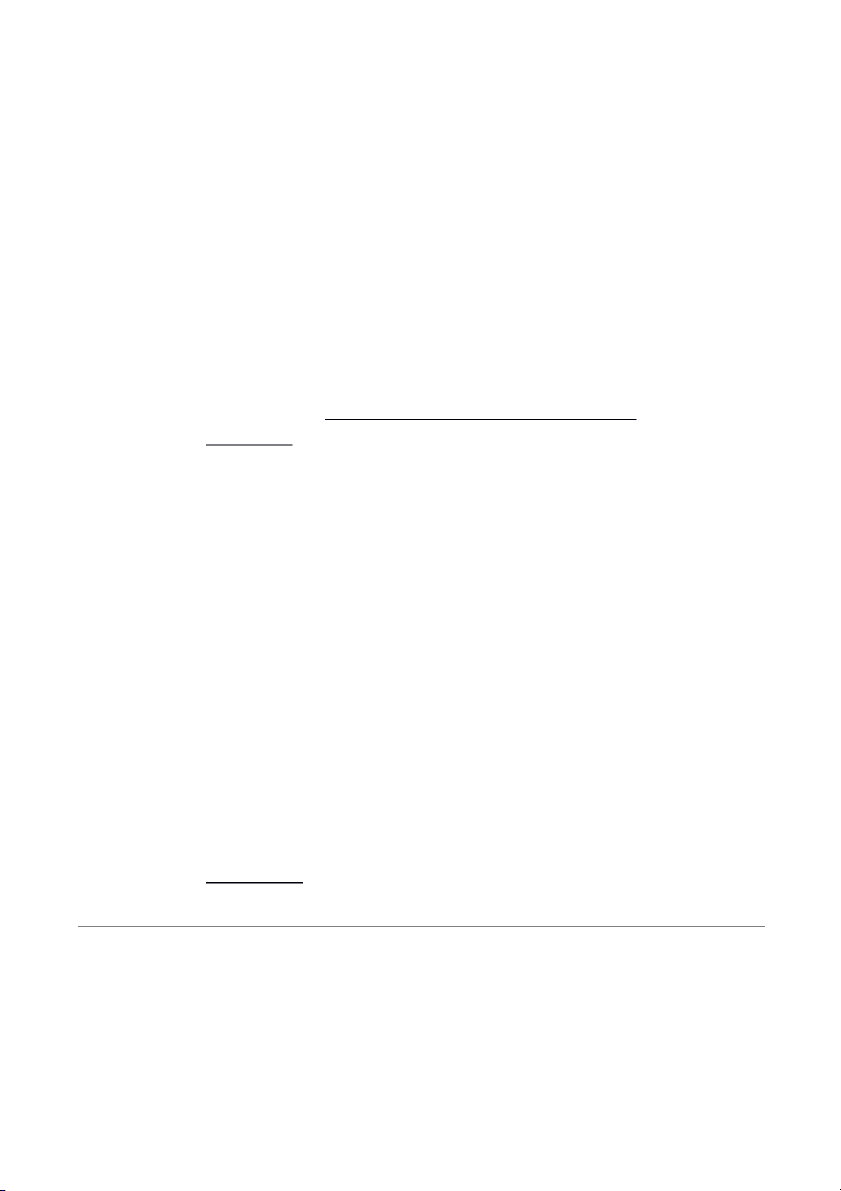
(b) MARIA GONZALEZ, VETERINARIAN Income Statement
For the Month Ended September 30, 2008 Revenues
Service revenue .......................................................... Expenses $8,000
Salaries expense......................................................... $1,700 1-7
Rent expense............................................................... 900
Advertising expense.................................................. 300
Utilities expense.......................................................... 170
Total expenses ................................................... 3,070
Net income............................................................................. $4,930 MARIA GONZALEZ, VETERINARIAN Owner’s Equity Statement
For the Month Ended September 30, 2008
M. Gonzalez, Capital, September 1................................................ $13,700
Add: Net income................................................................................ 4,930 18,630
Less: Drawings ................................................................................... 1,000
M. Gonzalez, Capital, September 30.............................................. $17,630 MARIA GONZALEZ, VETERINARIAN Balance Sheet September 30, 2008 Assets
Cash ......................................................................................................... $15,200
Accounts receivable........................................................................... 5,900
Supplies .................................................................................................. 600
Office equipment.................................................................................. 8,100
Total assets................................................................................... $29,800
Liabilities and Owner’s Equity Liabilities
Notes payable............................................................................... $10,000
Accounts payable....................................................................... 2,170
Total liabilities..................................................................... Owner’s equity 12,170
M. Gonzalez, Capital................................................................... 17,630
Total liabilities and owner’s equity.............................. $29,800 1-8 3A (a) SKYLINE FLYING SCHOOL Income Statement
For the Month Ended May 31, 2008
For the Month Ended May 31, 2008 Revenues
Cash......................................................................................................... $ 5,600
Lesson revenue....................................................
Accounts receivable........................................................................... Expenses $7,500 7,200
Fuel expense......................................................... $2,500
Equipment.............................................................................................. 64,000
Rent expense........................................................ T 1,200
otal assets.................................................................................. $76,800
Advertising expense........................................... 500
Insurance expense.............................................. 400
Repair expense..................................................... 400
Total expenses ............................................ 5,000
Net income...................................................................... $2,500 SKYLINE FLYING SCHOOL Owner’s Equity Statement
For the Month Ended May 31, 2008
Jeff Wilkins, Capital, May 1....................................... $0
Add: Investments....................................................... $45,000
Net income......................................................... 2,500 47,500 47,500
Less: Drawings ............................................................ 1,500
Jeff Wilkins, Capital, May 31..................................... $46,000 (b) SKYLINE FLYING SCHOOL Income Statement
For the Month Ended May 31, 2008 1-9 Revenues
Lesson revenue ($7,500 + $900)..................... $8,400 Expenses
Fuel expense ($2,500 + $1,500) ...................... $4,000
Rent expense........................................................ 1,200
Advertising expense.......................................... 500
Insurance expense ............................................. 400
Repair expense.................................................... 400
Total expenses............................................ 6,500
Net income..................................................................... $1,900 SKYLINE FLYING SCHOOL Owner’s Equity Statement
For the Month Ended May 31, 2008
Jeff Wilkins, Capital, May 1....................................... $0
Add: Investments...................................................... $45,000
Net income ....................................................... 1,900 46,900 46,900
Less: Drawings ........................................................... 1,500
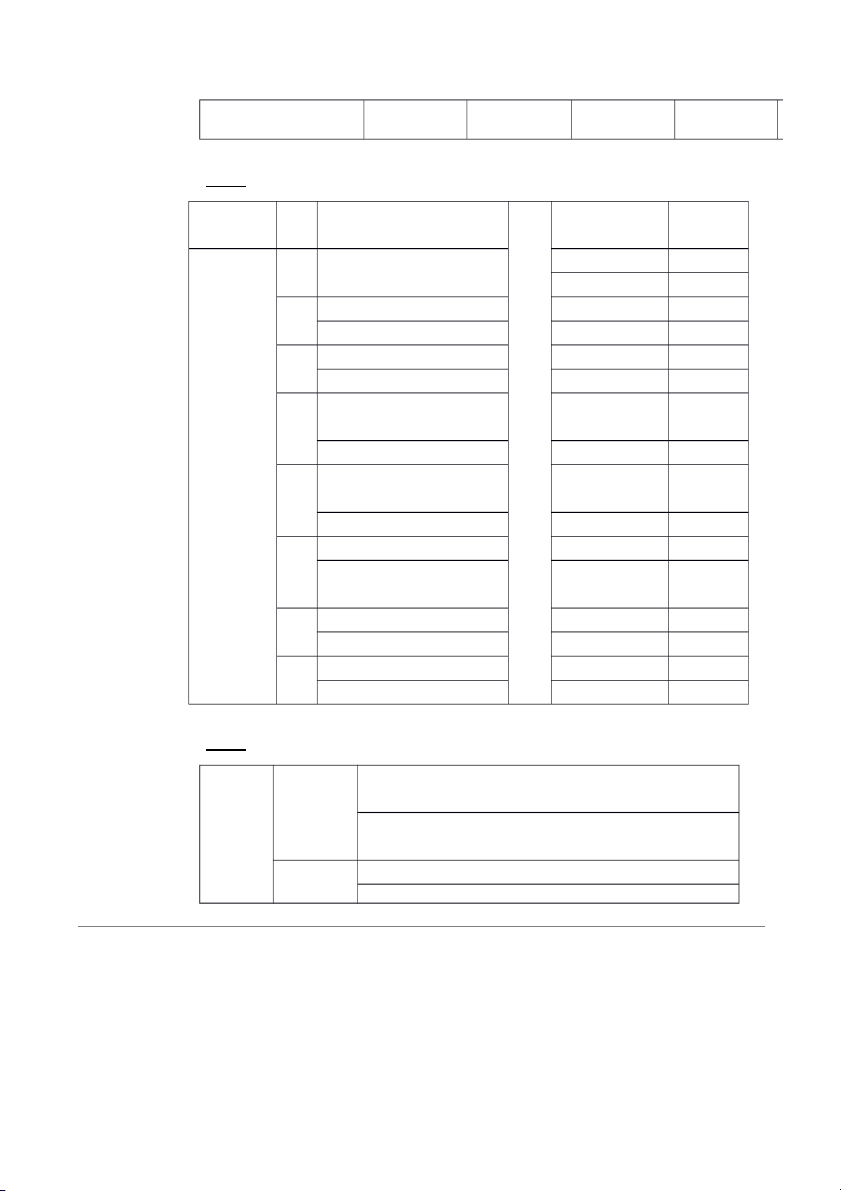
Jeff Wilkins, Capital, May 31.................................... $45,400 1-10 4A MILLER DELIVERIES Owner ’s Assets = Equi Liabilities + ty Accoun Delive Not Accoun M. ts ry es ts Miller, Date Cash Receivable + Van Payable Payable Capit + Supplies + = + + al June ($10,0 Investme 1 $10,0 00 nt 2 00 $12,0 ($10,0 (2,000) 00 00 3 Rent (500) (500) Expense 5 ($4,40 ( ) Service 00 4,400 Revenue 9 Drawin (200) (200) gs 1 $15 ($15) 2 0 0 1 ) 5 1,250 (1,250 1 ) ( ) Gasoline 7 100 (100) Expense 2 ( ) Service 0 1,500 1,500 Revenue 2 3 (500) (500) 2 ) Utilities 6 (250) (250) Expense 2 9 (100) (100 3 ) Salaries 0 (1,000 (1,000) Expense ) ($ + ($3,1 + $15 + $12,0=($ + ($15 + ($13,85 8,200 50 0 00 9,500 0 0 (b) MILLER DELIVERIES Income Statement
For the Month Ended June 30, 2008 Revenues
Service revenue ($4,400 + $1,500)....................... $5,900 1-11 Expenses
Salaries expense....................................................... $1,000
Rent expense.............................................................. 500
Utilities expense........................................................ 250
Gasoline expense ..................................................... 100
Total expenses.................................................. 1,850
Net income........................................................................... $4,050 (c) MILLER DELIVERIES Balance Sheet June 30, 2008 Assets
Cash ......................................................................................................... $ 8,200
Accounts receivable........................................................................... 3,150
Supplies .................................................................................................. 150
Delivery van........................................................................................... 12,000
Total assets................................................................................... $23,500
Liabilities and Owner’s Equity Liabilities
Notes payable............................................................................... $ 9,500
Accounts payable....................................................................... 150
Total liabilities..................................................................... 9,650 Owner’s equity
M. Miller, Capital.......................................................................... 13,850
Total liabilities and owner’s equity.............................. $23,500 5A (a) Karma Yates McCain Dench 1-12
Company Company Company Company
(a) $ 45,000 (d) $50,000 (g) $120,000 (j) $ 80,000 (b) 115,000 (e) 62,000 (h) 70,000 (k) 250,000
(c)10,000 (f)48,000 (i) 431,000 (l) 435,000 (b) YATES COMPANY Owner’s Equity Statement
For the Year Ended December 31, 2008
Capital, January 1....................................................... $ 60,000
Add: Investment ....................................................... $15,000
Net income....................................................... 35,000 50,000 110,000
Less: Drawings .......................................................... 48,000
Capital, December 31................................................ $ 62,000 (c)
The sequence of preparing financial statements is income statement, owner’s equity statement, and balance sheet. The
interrelationship of the owner’s equity statement to the other financial statements results from the fact that net income
from the income statement is reported in the owner’s equity statement and ending capital reported in the owner’s
equity statement is the amount reported for owner’s equity on the balance sheet. 1-13
Chapter 2: The Recording process Glossary: Account : tài khoản
Chart of accounts: hệ thống tài khoản
Common stock:cổ phiếu phổ thông
Compound entry:mục ghi sổ hỗn hợp Credit: có Debit: nợ Devidend: cổ tức
Double-entry system: hệ thống kế toán kép
General journal:hình thức kế toán nhật ký chung
General ledger: sổ cái chung
Journal: sổ ghi chép các giao dịch
Journalizing: ghi nhật ký Ledger:sổ cái
Normal balance: sự cân bằng bình thường Posting: nhập sổ
Retained earnings: lợi nhuận giữ lại
Simple entry: nhập mục đơn giản
T-account:tài khoản kế toán
Three-column from of account: tài khoản ba cột (nợ,có,số dư)
Trial balance: bảng cân đối thử Questions: 1-14
1. A T account has the following parts: (a) the title, (b) the left or debit side, and (c) the right or credit side
2. Disagree. The terms debit and credit mean left and right respectively
3. incorrect. The double-entry system merely records the dual effect of a transaction
on the accounting equation. A transaction is not recorded twice; it is recorded once, with a dual effect
4. incorrect. A debit balance only means that debit amounts exceed credit amounts in
an account. Conversely, a credit balance only means that credit amounts are
greater than debit amounts in an account. Thus, a debit or credit balance is neither favorable nor unfavorable
5. (a) Asset accounts are increased by debits and decreased by credits.
(b) Liability accounts are decreased by debits and increased by credits.
(c) Revenues and owner’s capital are increased by credits and decreased by
debits. Expenses and owner’s drawing are increased by debits and decreased by credits
6. (a) Accounts Receivable-debit balance. (b) Cash-debit balance.
(c) Owner’s Drawing -debit balance.
(d) Accounts Payable-credit balance.
(e) Service Revenue-credit balance.
(f) Salaries Expense-debit balance.
(g) Owner’s Capital-credit balance
7. (a) Accounts Receivable-asset-debit balance.
(b) Accounts Payable-liability-credit balance
(c) Equipment-asset-debit balance.
(d) Dividends-stockholders equity-debit balance.
(e) Supplies-asset-debit balance
8. (a) Debit Supplies and credit Accounts Payable.
(b) Debit Cash and credit Notes Payable.
(c) Debit Salaries Expense and credit Cash
9. (1) Cash-both debit and credit entries.
(2) Accounts Receivable-both debit and credit entries.
(3 Owner’s Drawing -debit entries only.
(4) Accounts Payable-both debit and credit entries.
(5) Salaries Expense-debit entries only.
(6) Service Revenue-credit entries only.
10.The basic steps in the recording process are:
(1) Analyze each transaction for its effect on the accounts. 1-15
(2) Enter the transaction information in a journal.
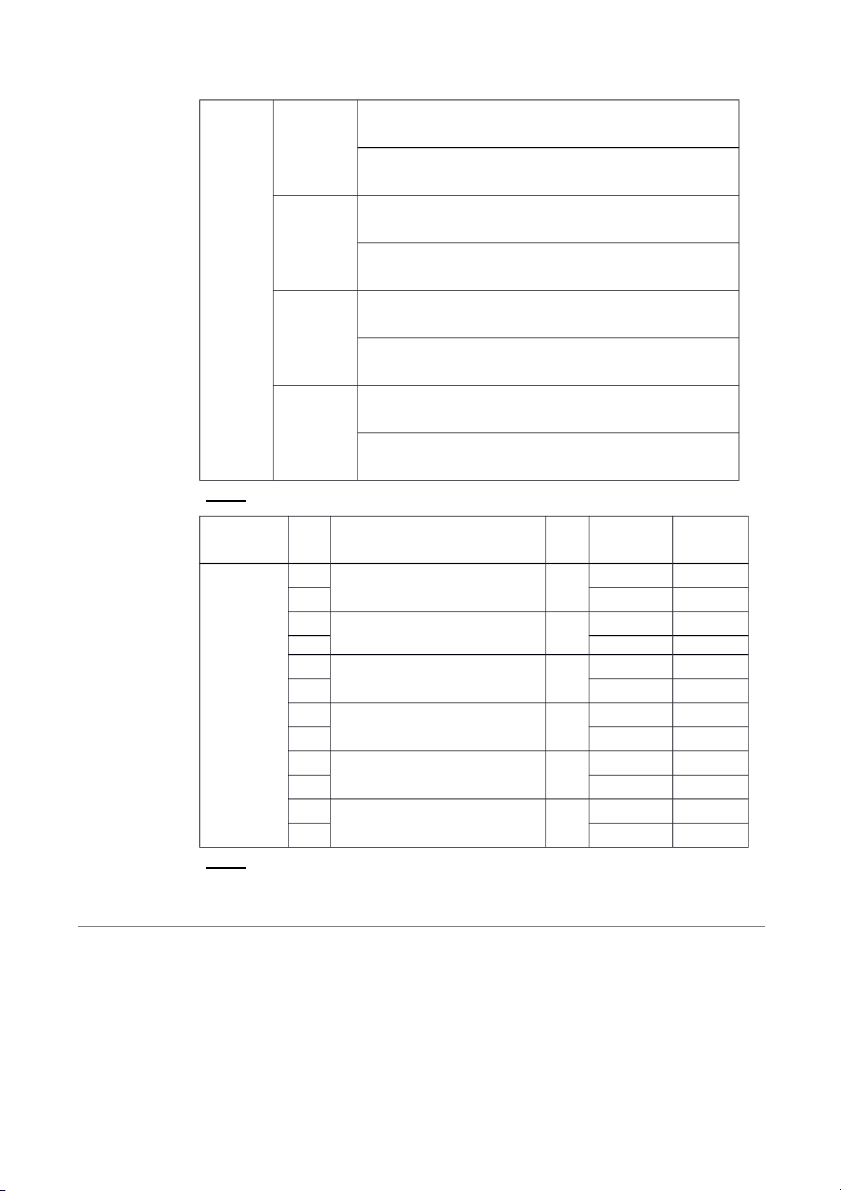
(3) Transfer the journal information to the appropriate accounts in the ledger. Brief Exercises: BE2-1 (a) (b) (c) Dedit Credit Normal Balance Accounts Decrease Increase Credit payable Advertising Increase Decrease Debit expense Service Decrease Increase Credit revenue Accounts Increase Decrease Debit receivable Common Decrease Increase Credit stock Dividends Increase Decrease Debit BE2-2 June une Account Account debited credited 1 Cash C ommon stock 2 Equipment Account payable 3 Rent expense cash 12 Account receivable Service revenue BE2-3 ju j ne n e 1 1 ca c sh s 40 4 0 0 0 owner’s capital 4000 2 2 Equiment 1200 Account payable 1200 1-16 3 3 Rent expense 800 Cash 800 12 Accounts receivable 300 Service revenue 300 BE2-4
The basic steps in the recording process are:
1. analyze each transaction in terms of its effect on the accounts
2. enter the transaction information in a journal
3. transfer the journal information to the appropriate accounts in the ledger BE2-5 (a)Effect on accouting (b)Debit-Credit analysis equation Au 1
The asset cash is increased; the stock
Debit increase assets: debit cash g
holder’s equity account,common stock $5000. is increased
Credits increase stockholder’s
equity:credit common stock $5000 4
The asset prepaid insurance is
Debits increase assets: debit prepaid
increased, the asset cash is decreased insurance $1800.
Credits decrease assets: credit service revenue $1800 16
The asset cash is increased; the revenue
Debit increase assets:debit cash
service revenue is increased $1900
Credit increase revenue: credit service revenue $1900 27
The expense salaries expense is
Debit increase expenses: debit
increased; the asset cash is decreased salaries expense $1000
Credit decrease assets: credit cash $1000 1-17 Exercises E2-1
1. False. An account is an accounting record of a specific asset, liability
2. False. An account shows increases and decreases in the item it relates to
3. False. Each asset, liability, and owner’s equity item has a separate account
4. False. An account has a left, or debit side, and a right, or credit side 5. True E2-2 A ccount debited Transaction ansaction (a) (b) (c) (d) Basic Specific Effect Normal Type Account Balance 2 Asset Cash Increase Debit 3 Asset equipment Increase Debit 9 Asset Supplies Increase Debit 11 Asset Accounts Increase Debit receivable 16 Owner’s Advertising Increase Debit equity expense 20 Asset Cash Increase Debit 23 Liability Accounts Decrease Credit payable 1-18 28 Owner’s Owner’s Increase Debit equity drawing E2-3 Date e Account tiles and Re Debit Credit explanation f Jan n 2 Cash 15000 Common stock 15000 3 Equipment 8200 Cash 8200 9 Supplies 500 Accounts payable 500 11 Accounts 1800 receivable Service revenue 1800 16 Advertising 200 expense cash 200 20 Cash 780 Accounts 780 receivable 23 Accounts payable 300 Cash 300 28 Owner’s drawing 500 Cash 500 E2-4 Oct Oct 1 1
Debit increase assets: debit cash $20000
Credits increase owner’s equity: credit owner, capital 20000 2 No transaction 1-19 3
Debits increase assets: debit office furniture $2300
Credits increase liabilities: credit accounts payable $2300 6
Debits increase assets: debit accounts receivable $3600
Credits increase revenues: credit service revenue $3600 27
Debits decrease liabilities: debit accounts payable $850
Credits decrease assets: credit cash $850 30
Debits increase expenses: debit salaries expense $2500
Credits decrease assets: credit cash$2500 E2-5 Date e Account titles and Re Debits Credit explanation f Oct 1 1 Cash 20000 Common stock 20000 2 No entry 3 Office furniture 2300 Accounts payable 2300 6 Accounts receivable 3600 Service revenue 3600 27 Accounts payable 850 Cash 850 30 Salaries expense 2500 Cash 2500 E2-6 a)
1. Increase the asset cash, increase the liability notes payable 1-20




