





Preview text:
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC MỞ THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH CHAPTER 1 ECONOMIC SECTORS I. LEAD-IN Task 1
Work in pairs and discuss the different jobs in three pictures below. Photo Sources: agfundernews.com baodautu.vn tamvuong.com 4 BUSINESS IN MOTION Task 2
Source: Thetimes100.co.uk (quoted in www.markedbyteachers.com)
With reference to the sectors of industry and the supply chain in the
table above, classify the 18 following activities according to which sector they belong to: advertising products assembling building calculating prices cutting metal digging iron or e distributing added value laying cables maintenance marketing products milling metal mining coal packaging products pressing metal pumping oi l smelting iron transportation welding metal Source: Mackenzie I. (2010) II. LANGUAG E FOCUS
FOCUS 1: READING COMPREHENSIO N
Manufacturing and services
Read the following statements about manufacturing and services in advanced countries. •
Which of them are in support of manufacturing in advanced
countries, and which are in support of services? 5
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC MỞ THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH •
Which of them do you find the most convincing? Why ?
1. A lot of service sector jobs depend on manufacturing
industry. Manufacturing companies provide work for
accountant s, lawyers, design ers, marketers, advertisers,
salesp eople, bankers, engineers, IT specialists, etc.
2. Advanced countries have exp ertise in higher education
R&D, ICT, business consulting, etc. They should concentrate
on these strengths, rather than trying to make things more
cheaply than less-developed countries.
3. All the world’s major economies – the US, Japan,
Germany, France, Britain, Italy, China, etc. – are major
manufacturers of exported goods. This obviously needs to continue.
4. Depending on service industries is dangerous, after the
financial crisis in 2008, New York and London didn’t only lose
financial jobs, but also lots of jobs in all related service
industries: l aw firms, real estat e, expensive restaurant, luxury
jets, etc. Big cities need factories too.
5. Manufacturing industry will inevitably decline in
advan ced count r ies and be rep la ced by services, b ecause
labour costs are too high. Companies will delocalize their
manufacturing.t o low -cost countries.
6. Millions of tourists travel to major cities, and millions of peop
choose to live in them, because of the arts and entertainment –
theatre, music, museums, sport, etc. Manufacturing and heavy
indus tr y can an d sh ould be done e l s e w he r e .
7. S ervice functions such as call centres, accounting, writing
software, can al be outsourced to companies in cheaper
countries. Consequently, advanced countries should concentrate
on high-quality manufacturing, which requires skil s that cannot be outsourced or delocalized. 6 BUSINESS IN MOTION
Find words in the statements above that mean the following:
1. products sold to other countries
2. property: buildings such as offices, houses, flats (BrE) or apartments (AmE)
3. work done in return for mone y
4. to move your factories to another region or countr y
5. to use other companies to do work your company previously did itself Source: Mackenzie I. (2010) Discussion
1. Which sector do you intend to work in or have you already worke d in?
2. How many people in the tertiary sector
have you already spoken to today
(travelling to college or work, shopping,
eating, and so on)? What about people in
the other sectors? When did you last talk to
someone who grew or produced food?
3. What are the approximate proportions of the
different sectors in your country? How do you
expect these proportions to evolve in the future? Source: Mackenzie I. (2010)
Photo Source: Microsoft Word Clip Arts 7
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC MỞ THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH
FOCUS 2: READING COMPREHENSIO N
Read the passage and answer the following questions.
What are the main economic sectors of Thailand? THAILAND ’S ECONOMIC SECTORS
Photo Source: http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu
Thailand's economy has grown steadily by an average of 8 percent
for the past decade. There is a wide base for growth, with each
sector contributing to the development of the economy. Starting out
as an agrarian economy, Thailand's bid for industrialization
strengthened its industry sector, while the boom in the tourism
industry strengthened the service sector. In the 1990s, manufacturing
and tourism are the two largest contributors to GDP.
Agriculture has been the traditional backbone of the economy,
with Thailand being ranked among the top five producers of food
in the world. In the 1970s, the country supplied 30 percent to 40
percent of rice in the world market. In the 1990s, it continued to
be the leading exporter of rice, tapioca, and frozen shrimp. It is
also the world's largest producer of rubber, the demand for which
has increased due to the AIDS epidemic, which has increased the
demand for condoms. Thailand is also one of the world's biggest
suppliers of flowers, particularly orchids, which it exports mainly
to Japan and Europe. Despite its output, the agricultural sector is
on the decline, and is slowly being overtaken by the industry and
service sectors in terms of contribution to GDP.
With the re-orientation of production from import substitution to
producing for export, and the drive towards industrialization, the
manufacturing industry grew steadily until it exceeded
agriculture in terms of contribution to GDP. According to Bank of
Thailand statistics reflected in the 2000 Business Monitor 8 BUSINESS IN MOTION
International Annual Report, the manufacturing industry
accounted for 86.8 percent of the country's total exports in 1999.
The country's first step into manufacturing was food processing,
effectively building on its strong agricultural sector. Today, it is
the world's largest exporter of canned pineapple, with one-third
of all the canned pineapple sold in the United States coming from
Thailand. It is also Asia's biggest exporter of tuna after Unicord, a
local company, purchased Bumble Bee Seafoods, the third largest
tuna canner in the United States. It now supplies 20 percent of the world market for canned tuna.
The country's service sector is experiencing steady growth, with
the boom in the tourism industry. In 1992, tourism accounted for
10 percent of the GDP, with 600 tourists arriving every hour, or
5,256,000 tourists for the year, spending an average of US$1,000
each, equivalent to about US$5 billion a year. This amount is equal
to 50 percent of the country's total exports. In 2000, revenues from
tourism were expected to hit 343 billion baht or US$6.86 billion,
with a total of 9,438,000 tourists expected to visit the country throughout the year.
Strong local corporations - such as Charoen Pokp-hand, which
earns revenue of US$2.5 billion annually; Thai Union Frozen
Products, the largest canned seafood exporter; and Boonrawd
Brewery–work together with various multinational corporations
to energize the manufacturing industry. Forecasts for the year
2000 predicted that multinational corporations which have set up
shop in the country - such as Mitsubishi, Isuzu, and Honda for
automobiles; Fujitsu, Seagate, IBM, Sony, and Matsushita
Electronic for electronics; Heineken and Carlsberg breweries,
and Nestle and Kellogg for food processing; and Exxon, Montell,
and Bayer for petrochemicals—will expand their operations in the
country and pump in more investment.
Source: Nations encyclopedia (n.d.) Discussion
Are there any similarities or differences between Thailand and
Vietnam in economic development? Why/ Why not? 9
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC MỞ THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH FOCUS 3: WRITING
Find an online article on the economic sectors in Vietnam and summarize
the article in no more than 100 words. Suggested Verb List suggest point out emphasize present identify criticize show conclude list analyze discuss imply Article Title:
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
Reference: ........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................... Article Summary:
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................
III. FUNCTIONAL LANGUAGE LANGUAGE INPUT
SIGNPOSTING LANGUAGE FOR ORAL PRESENTATION
Write the correct heading for each extract. Introducing each section
Referring backwards and forwards Referring to questions Concluding Summarizing a section
Referring to visual information Introducing the topic Referring to common knowledge Dealing with questions Checking understanding 10 BUSINESS IN MOTION
1……………………………
5……………………………… Today, I’d like to ... I mentioned earlier… (the (describe)… importance of) …
This morning, I’m going to …
I’ll say more about this later. (talk about) ...
We’ll come back to this point later.
The aim of my presentation is to … 6.…………………………… My talk will be in … Is that clear?
I’ve divided my presentation Are there any questions? into … (three parts) .
7………………………………
First/ Second/ Then/ Finally, This screen shows… (a
I’d like to … (give an overview diagram).
of/ move on to/ focus on/ deal
If you look at this graph, you with/ consider…). can see…
2……………………………
What is interesting in this slide is … Feel free to interrupt me if
I’d like to draw your attention
there’s anything you don’t to … (this chart… ) understand.
8………………………………
If you don’t mind, we’ll leave As you know… questions till the end.
As I’m sure you’re aware…
3……………………………
9……………………………… So, let’s start with … That concludes my talk. (objectives...)
That brings me to the end of my
Now let’s move on… (the next presentation. part…)
If you have any questions, I’d
Let’s turn our attention to…
be pleased/ I’ll do my best to (the question of…) answer them.
This leads me to … (my third 10…………………………… point…) That’s a good point.
Finally… (let’s consider…)
I’m glad you asked that question.
4……………………………
Can I get back to you on that That completes my …
later? I’m afraid I don’t have … (description of…) (the information at present).
So, to summarize… (There are
I’m afraid I’m not the right five key points…) person to answer that.
Source: Harding K. & Taylor L. (2009) 11
TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC MỞ THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH LANGUAGE OUTPUT
Presentation in pairs or groups of three.
Topic for Oral Presentation:
Your hometown & the main economic sectors - current sector s - potential sector s Task:
Prepare a short presentation in less
than 5 minutes to present briefly Photo Source: www.sodapdf.com
the main economic sectors of your hometown. Remember to…
- present some current facts/ figures.
- use signposting language. IV. FURTHER PRACTIC E
LISTENING COMPREHENSION
Listen to six business news stories from American radio stations, and complete the chart below. Which Which Which companies Is this good, industry or economic or organizations bad or mixed News industries sector or are named? news for the Item are sectors are industry? mentioned? involved Oil Primary OPEC Bad 1 (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries 2 3 4 5 6
Adapted from Source: Mackenzie I. (2010) 12 BUSINESS IN MOTION CASE STUDY
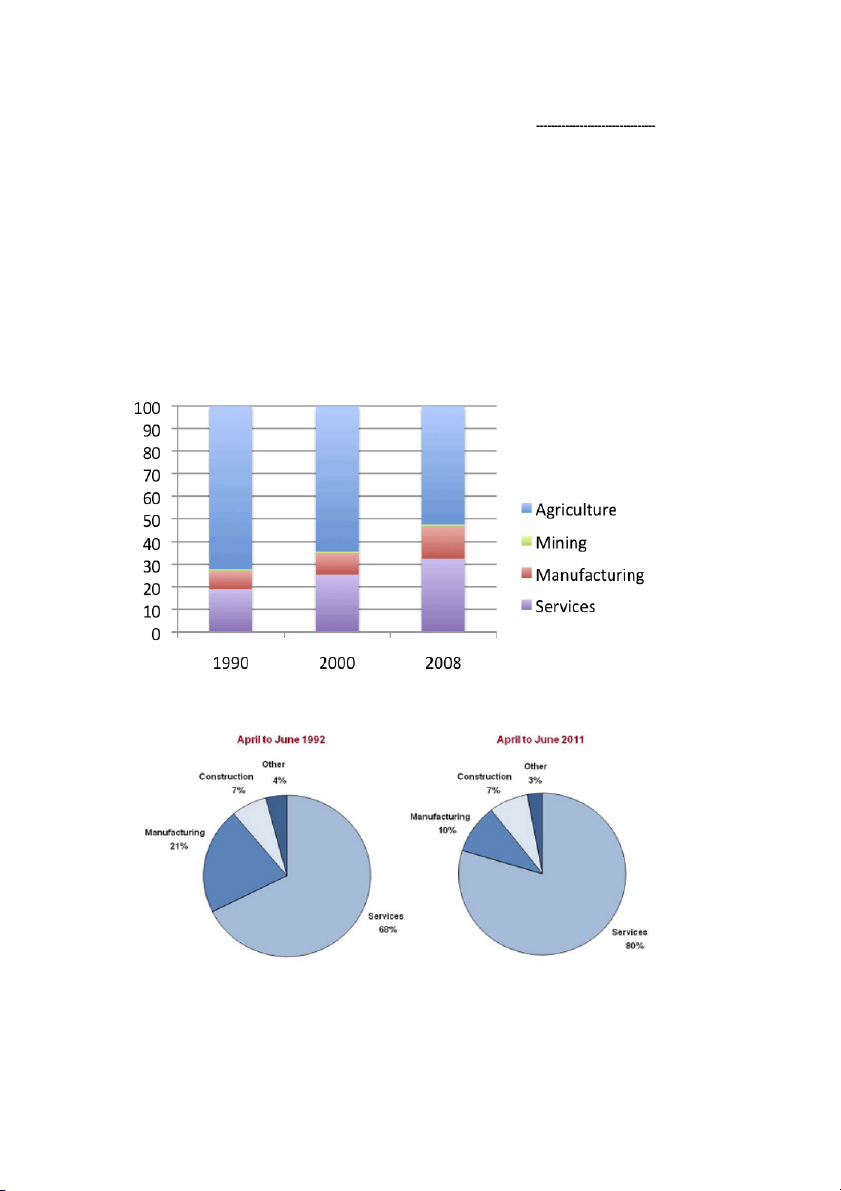
A comparison of the changes in employment sectors in the United Kingdom and Vietnam Task 1
Look at the charts below and answer the questions.
1. What are the differences in the employment sectors of the UK and Vietnam?
2. What factors do you think could contribute to these changes?
Distribution of Employment (%) VIET NAM THE UNITED KINGDOM 13




