





Preview text:
Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
CHAPTER 2: MANAGEMENT LEARNING PAST TO PRESENT
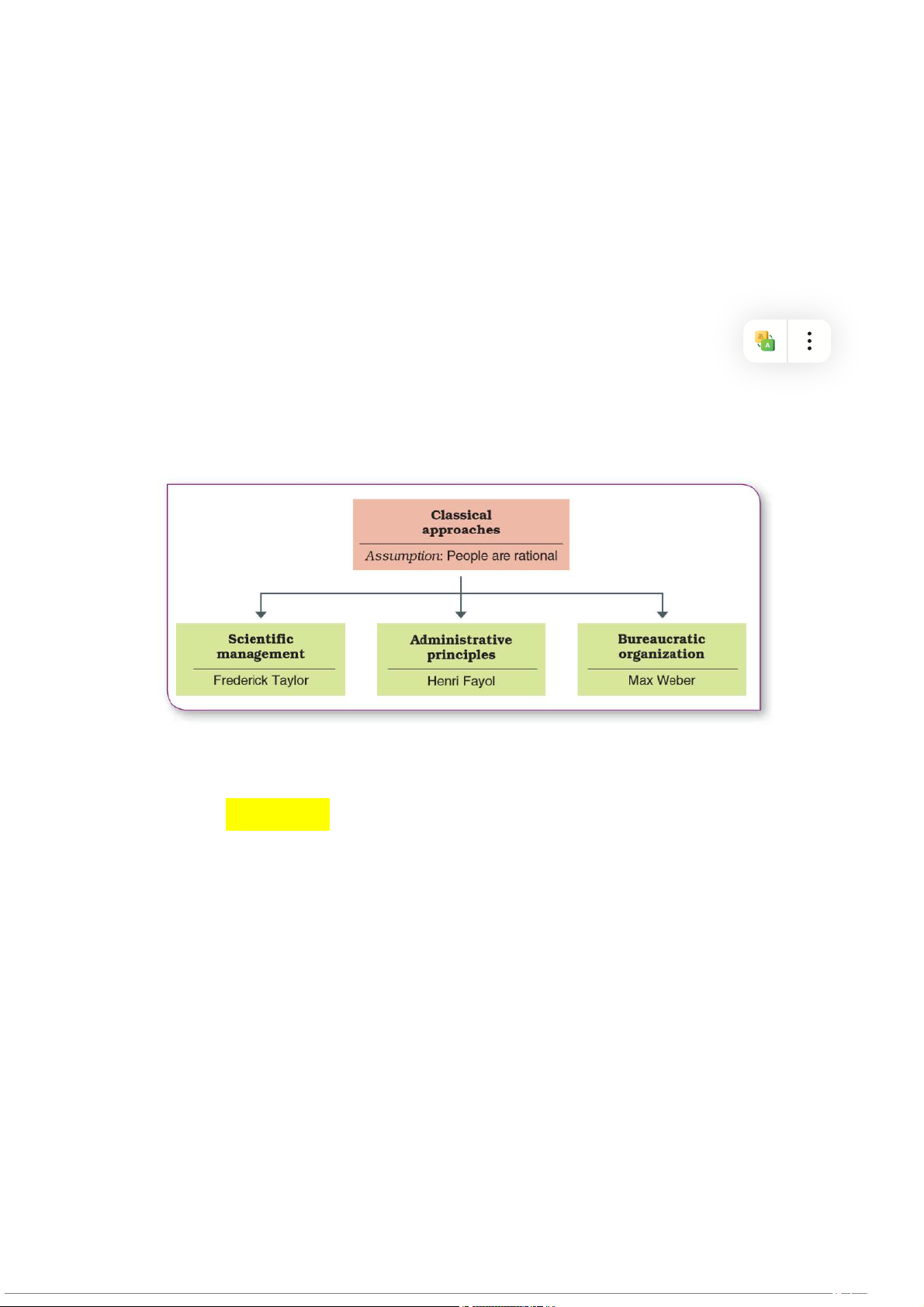
I) CLASSICAL MANAGEMENT APPROACHES
- Ignore the role of human well-being - Perceive humans as machines → People are rational
1) Scientific Management (sự đơn giản và tối thiểu hóa công việc)
-Definition:Scientific management emphasizes careful
selection and training of workers and supervisory support.
-Motion study is the science of reducing a task to its basic physical motions.
- In other words, this management tries to simplify the work
in the most effective way by eliminating wasted motions.
Hence, building effective working motions and choosing the
most appropriate workers to follow the new chain of motions
with the aim of improving productivity. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
Ex1: Làm cho mọi thứ vừa vặn hiệu quả, không dư thừa bằng cách
quan sát quá trình công nhân thợ xây làm việc rồi phân tích quá trình
thành thao tác nhỏ. Từ đó, xác định và loại bỏ những thao tác dư thừa
để đưa ra chuỗi thao tác mới (motion study). Rồi dùng chuỗi thao tác
mới này để train những workers khác. 2) Administrative principles a) Definition:
It identifies the following five “rules” or “duties” of management
1. Foresight: to complete a plan of action for the future.
2. Organization:to provide and mobilize resources to implement the plan.
3. Command: to lead, select, and evaluate workers to get the best work toward the plan.
4. Coordination: to fit diverse efforts together and to ensure
information is shared and problems solved.
5. Control: to make sure things happen according to plan and to
take necessary corrective action.
b) Principles to guide managers in action:
-Scalar chain principle: there should be a clear and unbroken
line of communication from the top to the bottom in the organization
-The unity of command principle: each person should
receive orders from only one boss
-The unity of direction principle: one person should be in
charge of all activities that have the same performance objective Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
3) Bureaucratic organization (similar to administrative)
a) Definition:Bureaucratic organization is a rational and efficient
form of organization founded on logic, order, and legitimate authority.
—> Everything needs to be written, and organized in strict order.
Organizations who apply this approach have many layers and control.
b) The defining characteristics of Weber’s bureaucratic organization are:
-Clear division of labor (phân công lao động rõ ràng): Jobs are
well defined, and workers become highly skilled at performing them.
-Clear hierarchy of authority (Cấp bậc rõ ràng, cấp trên nghe
cấp dưới): Authority and responsibility are well defined for
each position, and each position reports to a higher-level one.
-Formal rules and procedures (Các quy tắc, quy định viết ra
văn bản): Written guidelines direct behavior and decisions in
jobs, and written files are kept for the historical record.
-Impersonality (không quan tâm đến yếu tố con người): Rules
and procedures are impartially and uniformly applied, with
no one receiving preferential treatment.
-Careers based on merit (Công việc dựa trên thành tích, kết
quả): Workers are selected and promoted on ability,
competency, and performance, and managers are career employees of the organization. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
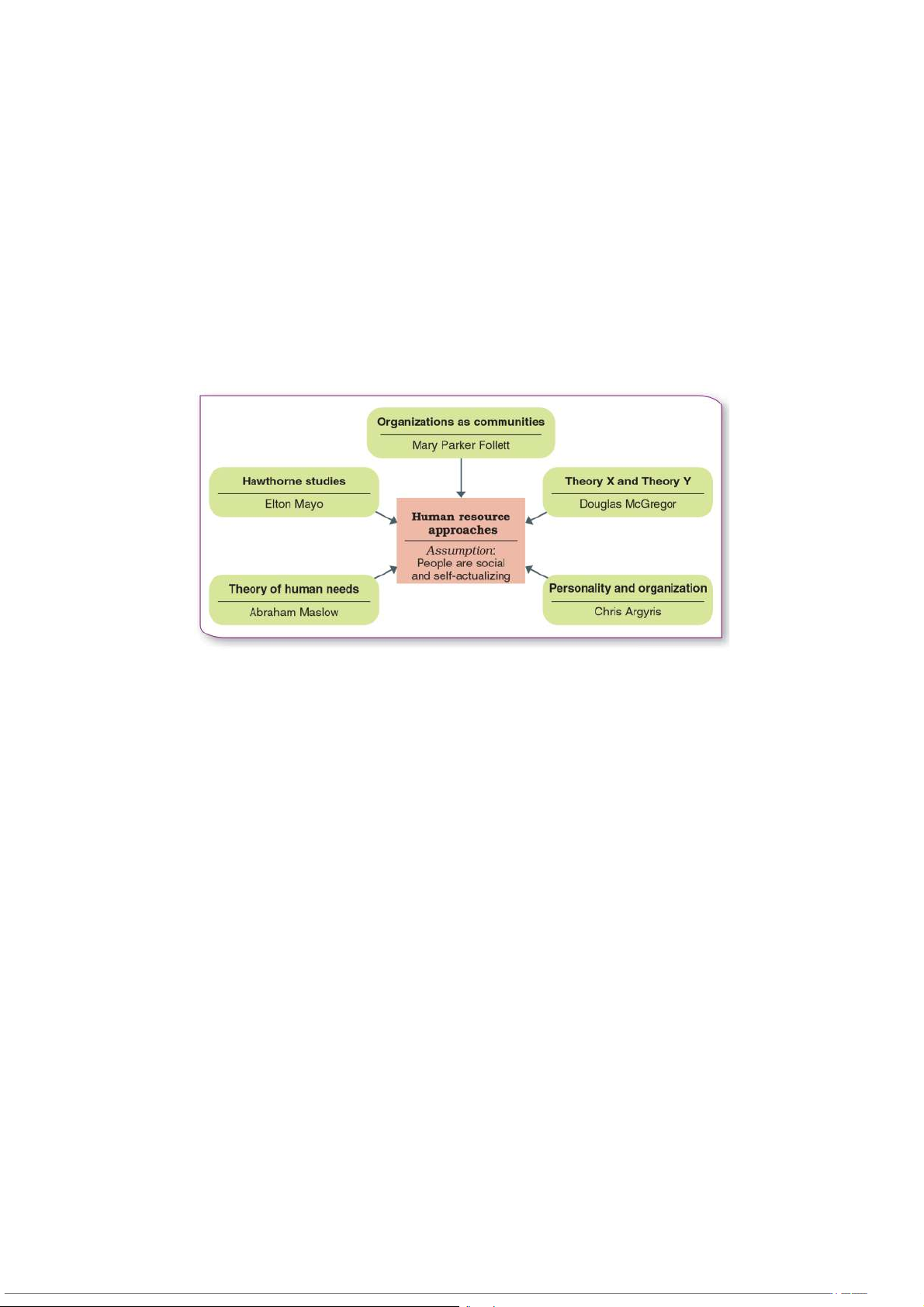
II. BEHAVIORAL MANAGEMENT APPROACHES - Humans are not machines
- To improve productivity, you should focus on the psychological aspect of human
→ People are social and self-actualization
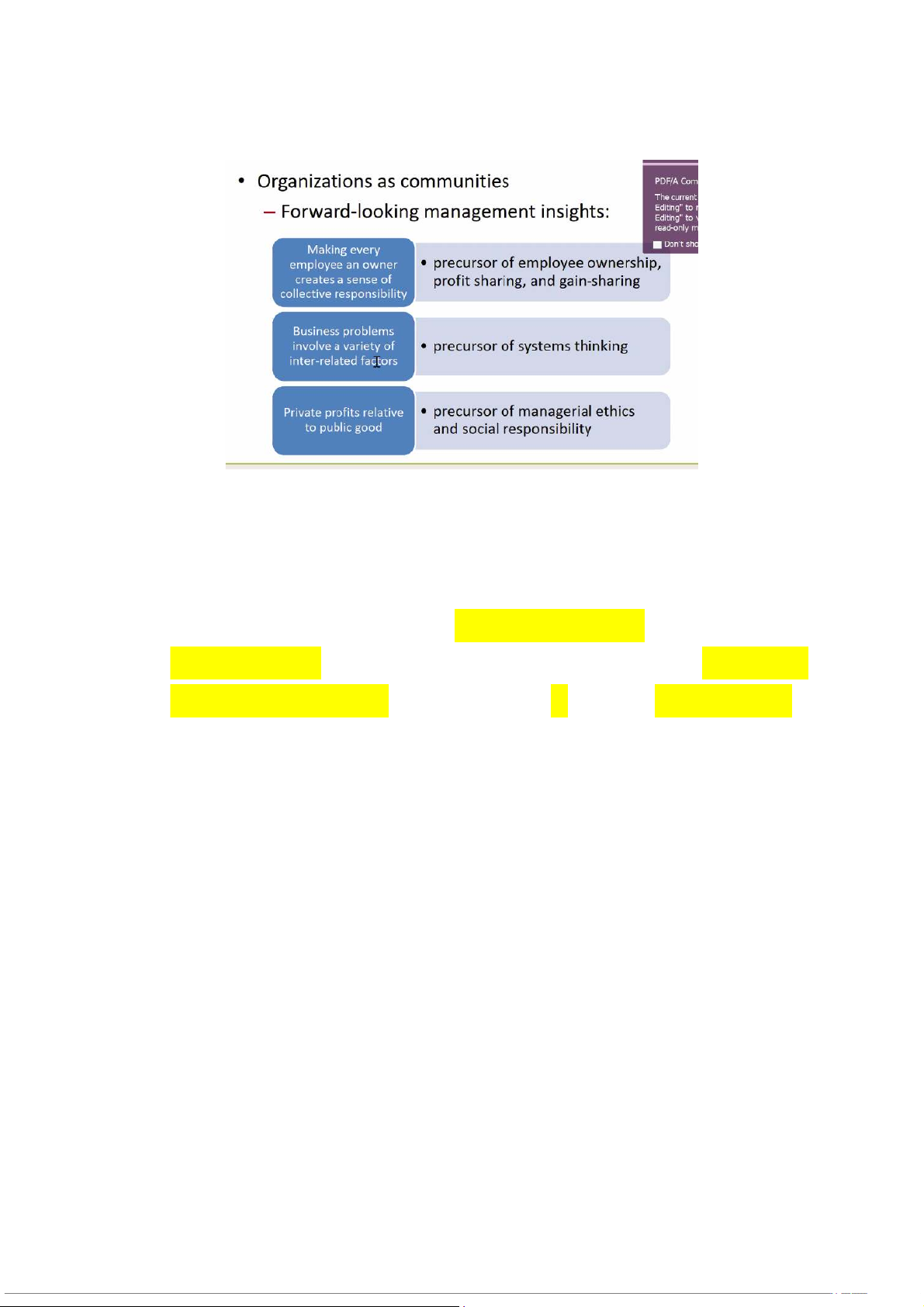
1) Follett’s Organizations as Communities
Follett describes organizations as “communities' in which managers and
workers should labor in harmony without one party dominating the
other, and with the freedom to talk over and truly reconcile conflicts and differences. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
2) The Hawthorne Studies → Psychological factors
-The Hawthorne effect is the tendency of persons singled out for
special attention to perform as expected.
- Hiệu ứng Hawthorne là một hiện tượng tâm lý trong đó những
người tham gia trong thí nghiệm nghiên cứu hành vi tự thay đổi
hành vi hoặc hiệu suất của bản thân chỉ vì họ đang được quan sát.
-Tại nơi làm việc, hiệu ứng Hawthorne có thể giải thích vì sao nhân
viên càng nhận được nhiều chú ý từ người quản lý, đồng nghiệp và
khách hàng, thì họ càng nỗ lực làm việc và năng suất càng tăng. Về
cơ bản, năng suất tăng khi nhân viên nghĩ rằng họ đang được
theo dõi hoặc quan sát chặt chẽ. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
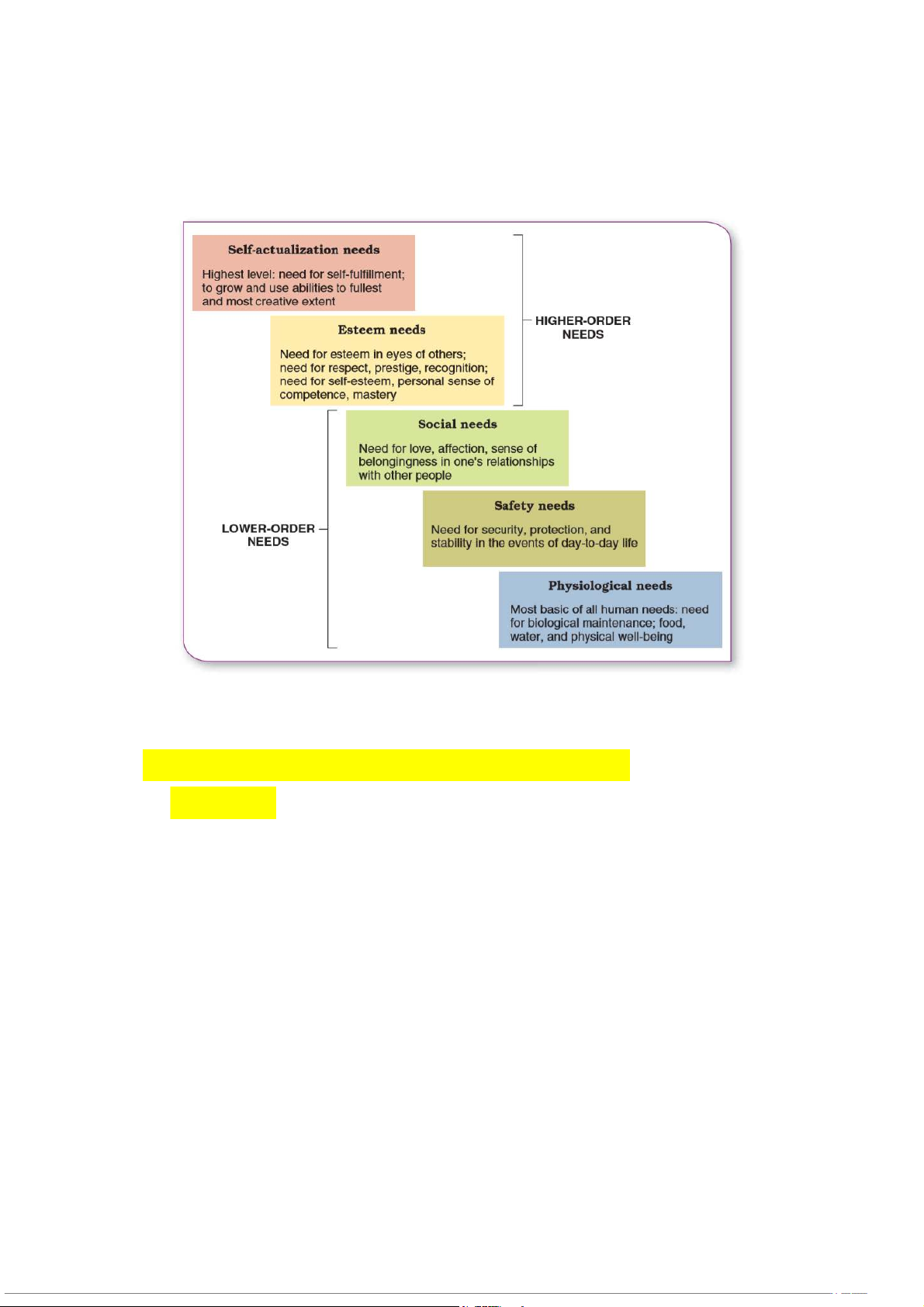
3) Maslow’s Theory of Human Needs
4) McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
a) Theory X: an “authoritarian” style of management
-Giải thích: X→ sinh ra xấu → cần kỷ luật → điểm danh của thầy Sơn =))
- The average worker dislikes work; finds it boring; and will avoid it he/she can.
- Therefore most people must be motivated by being forced/bribed
with the threat of punishment (or a reward) to produce effort and
work towards organizational objectives.
- The average worker prefers to be directed; to avoid responsibility;
is relatively unambitious, and wants security above all factors. Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
- The worker is motivated by tangible rewards such as money –
and/or threats to job security.
- The average person lacks creativity and initiative. The exception to
this “rule,” however, is using creativity to circumvent rules, tasks, and responsibilities.
b) Theory Y as a “participative” style of management
-Giải thích:Y → sinh ra tốt, sinh ra có trách nhiệm, biết tự làm không
cần chỉ → chỉ cần gợi mở để ngta làm là đc
- Effort in work is as natural as work and play. Workers are
motivated to work, and they take a personal interest in what they do and how they perform
- Workers are self-directed and target-oriented.
- Workers will therefore apply measures of self-control and
self-direction in the pursuit of organizational objectives, without
external control or the threat of punishment.
- Commitment to objectives is a function of rewards associated with their achievement.
- People usually accept and oen seek responsibility – under the
appropriate work and organizational conditions. • Such conditions
invite workers to realize and work toward their own potential
- The capacity to use a high degree of imagination, ingenuity and
creativity in solving organizational problems is widely, not
narrowly, distributed in the population.
- In most work environments the intellectual, imagination,
ingenuity and creativity potential of the average worked is poorly
promoted; oen under or partly utilized
Comparison between Theory X and Theory Y Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 Theory X Theory Y Motivation People dislike work; People are self-motivated
they want to avoid it and and thrive on do not want to take responsibility. responsibility. Management Authoritarian, and Participative Style and centralized control Control Work Specialized and oen The work tends to be Organization repetitive work organized around wider areas of skill or knowledge; Employees are also encouraged to develop expertise and make suggestions and improvements. Rewards and Work on a ‘carrot and Frequent opportunities Appraisals stick’ basis, and for promotion. performance appraisal is part of the overall mechanisms of control and remuneration Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169 Application
Although the Theory X management style is widely accepted as inferior
to others, it has its place in large-scale production operations and
unskilled production-line work. Many of the principles of Theory Y are
widely adopted by types of organizations that value and encourage
participation. Theory Y-style management is suited to knowledge work
and professional services. Professional service organizations naturally
evolve Theory Y-type practices by the nature of their work; Even highly
structured knowledge work, such as call center operations, can benefit
from Theory Y principles to encourage knowledge sharing and continuous improvement.
III. MODERN MANAGEMENT FOUNDATION
Note: Phần này là phần thêm, thầy không nói về phần này trong lớp nên các bạn đọc thêm nhé.
-Quantitative analysis and tool: use statistics and data to make the decision
-Systems view of organization (Organization as systems): Organization is perceived as a system
-Contingency thinking: adapt to the current environment -> give the
decision based on the environment
-Commitment to quality and performance: company has a high
commitment -> high performance (about people in the company) Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
-Knowledge management and organizational learning: Perceive
organization as line of, company wants to develop they have to invest
into the knowledge of the company
-Evidence-based management: Management by making decisions based
on collecting the evidence (For ex: Collect the evidence showing that the
employees are enthusiastic about the company)
Các phần sau đây là phần trọng tâm của phần 3 này, các bạn có thể đọc thêm kỹ phần này nhé A) Organizations As Systems
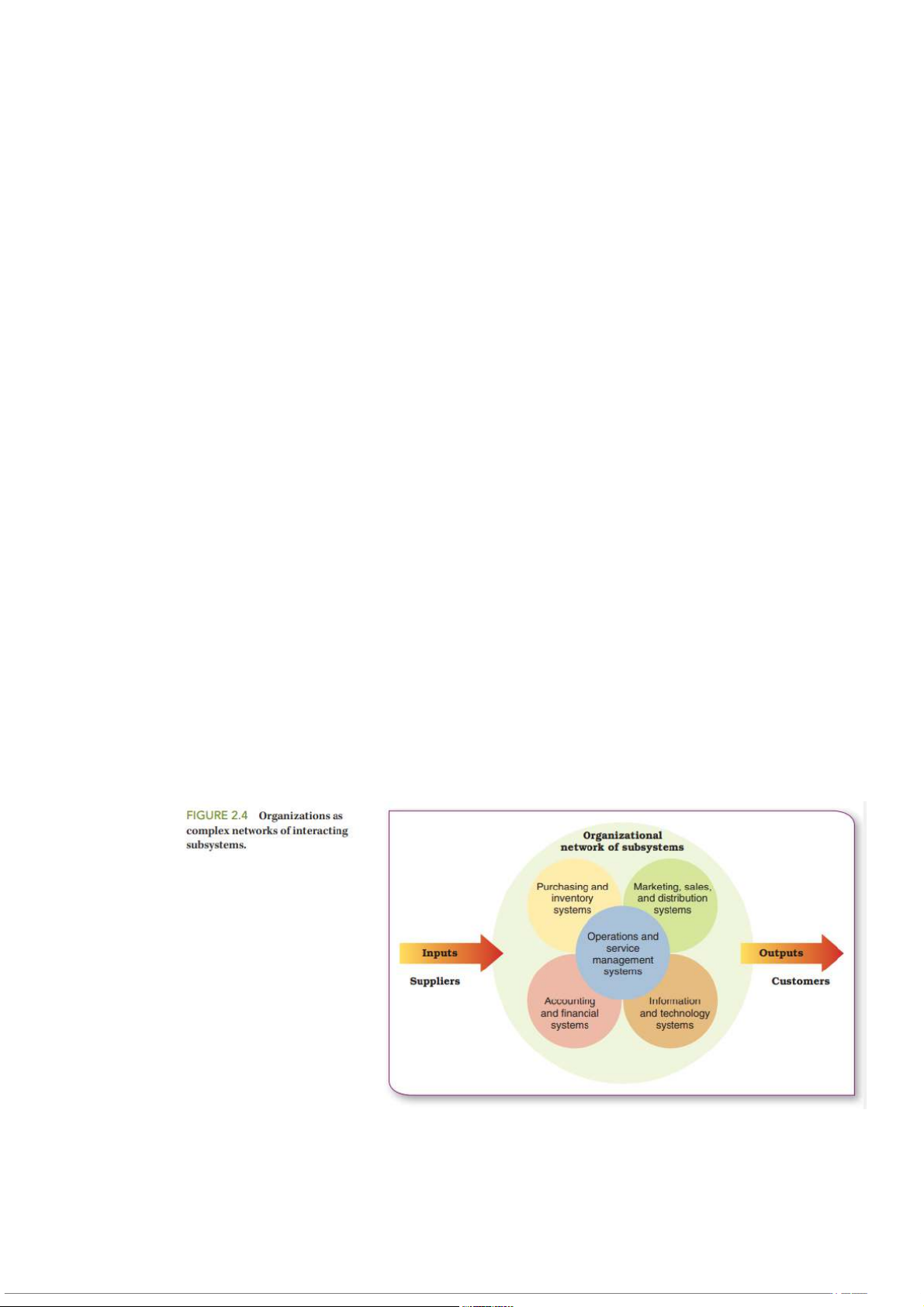
- A system is a collection of interrelated parts working together for a purpose.
- A subsystem is a smaller component of a larger system (For
example Each department in a company is a subsystem of the company)
- An open system is an organization that interacts with its
environment and transforms resource inputs into outputs
B) Contingency Thinking (Tùy cơ ứng biến) Nguyễn Minh Long BABAIU20072 Ngô Trần Cẩm Tú BABAIU20165 Trương Lê Hoàng Nam BABAIU20084 Trần Bảo Tuấn BABAIU20169
+ Contingency thinking tries to match management practices with
problems and opportunities unique to different situations
+ No “one best way” to manage (no formulation in management)
+ Appropriate way to manage depends on the situation
C) Knowledge Management & Organizational Learning
+Knowledge management: Process of using intellectual capital for
competitive advantage (lợi thế cạnh tranh/ so sánh)
+ Portfolio of intellectual assets: Patents; Intellectual property
rights; Trade secrets; Accumulated knowledge;e.t.c
+Learning organizations: Organizations continually learn and adapt to new circumstances
+ 5 characteristics in learning organization:
Ex: Một vài công ty dành ra một khoảng tiền để tổ chức các hoạt động
Teambuilding; Đào tạo cho nhân viên; …




