















Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 DATA STRUCTURES & ALGORITHMS Chapter 3: Lists Le Van Vinh, PhD
Faculty of Information Technology
HCMC University of Technology and Education
Email: vinhlv@fit.hcmute.edu.vn lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Outline lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 I. List Abstract data type
❖ A list is a finite, ordered sequence of data elements.
❖We present a list as follows: a1, a2, . . ., an, in which n ≥ 0. ▪ If n=0: empty list.
▪ If n > 0: a1 is the first element, an is the last element.
▪ The number of elements: the length of the list I. List ADT ❖ For examples:
▪ List of students in a class lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
▪ List of employees of a company ▪ List of integer numbers ▪ ….. I. List ADT
❖ Operations of a list ▪ Initialize a list
▪ Insert an element into a list
▪ Remove an element in a list
▪ Search an element in a list ▪ Traversal a list ▪ Check a list empty or not
▪ Sort a list ▪ Merge two lists ▪ …. lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 Outline lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
II.Implement lists using array ❖ Define a list lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 #define Max 100
#define ElementType NameOfDatatype struct LIST {
ElementType Elements[Max]; // Array of elements
int len; // The n umber of elements } ; Example : #define Max 100 struct LIST { float M[MaxLen]; int len; } ;
II.Implement lists using array ❖ Define a list lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 #define Max 100
#define ElementType NameOfDatatype struct LIST {
ElementType Elements[Max]; // Array of elements
int len; //The n umber of elements } ; Example : #define Max 100 struct LIST { Student M[MaxLen]; int len; } ; lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
II.Implement lists using array ❖Insert items
▪ Insert an item at the beginning (AddFirst(LIST& myList, int x ))
▪ Insert an item at the end (AddLast(LIST& myList, int x))
▪ Insert an item at position k (AddItem (LIST& myList, int k, int x)) ❖Remove items
▪ Delete first item (RemoveFirst(LIST&myList))
▪ Delete last item (RemoveLast(LIST& myList))
▪ Delete an item at position k (RemoveItem(LIST& myList, int k))
II.Implement lists using array ❖Other operations
▪ Initialize the list (InitList(LIST& myList)) lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
▪ Check the list is empty or not (IsEmptyList(LIST myList))
▪ Check the list is full or not (IsFullList(LIST myList))
▪ Traversing a list/Print out the list (PrintList(LIST myList)) lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
II.Implement lists using array ❖Advanced operations
▪ Sorting the list (SortList(LIST& myList))
▪ Searching an item in the list
(SearchItem(LIST& myList, int x))
▪ Searching items in the list (LIST
SearchItems(LIST& myList, int x))//Search items which are >=x
▪ Merging two lists (AddRange(LIST& myList, LIST sourceList)) void main() { lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 LIST myList; A case study InitList(myList); AddFirst(myList, 4); AddFirst(myList, 3); AddFirst(myList, 2); AddFirst(myList, 6); for(int
i=0;icout<RemoveItem(myList, 2);//Xóa phần tử tại vị trí 2
for(int i=0;icout<for(int i=0;icout<} void main() { LIST myList; A case study
InitList(myList);//myList.len=0 lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 AddFirst(myList, 8); AddFirst(myList, 7); AddLast(myList, 6); AddLast(myList, 6);
AddItem(myList, 2, 8);//thêm phần tử 8 vào vị trí 2
for(int i=0;icout<RemoveFirst(myList); RemoveLast(myList); for(int i=0;icout<} void main() { LIST myList; A case study SinhVien sv; lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
InitList(myList);//myList.len=0 NhapSV(sv); AddFirst(myList, sv); NhapSV(sv); AddFirst(myList, sv); NhapSV(sv); AddLast(myList, sv); NhapSV(sv); AddLast(myList, sv); NhapSV(sv); AddItem(myList, 2, sv);
for(int i=0;iRemoveFirst(myList); RemoveLast(myList); for(int i=0;icout<} Excercise
❖Develop a list to store a list of students. Then, write the following tasks:
▪ Sort the list in ascending order of GPA lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
▪ Insert a new student to the sorted list to have a new sorted list.
▪ Get a list of students having GPA is greater than x.
▪ Remove all students having GPA is greater than x.
▪ Search k students who have highest GPAs
II.Implement lists using array ❖Evaluation ▪ Strengths
• Access: random, easy, and quick • Easy to implement ▪ Drawbacks
• Fit size: lack of memory, or waste of memory
• Insert, remove an element: difficult and expensive lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
• All elements are stored in the same space in memory: inflexible
II.Implement lists using array
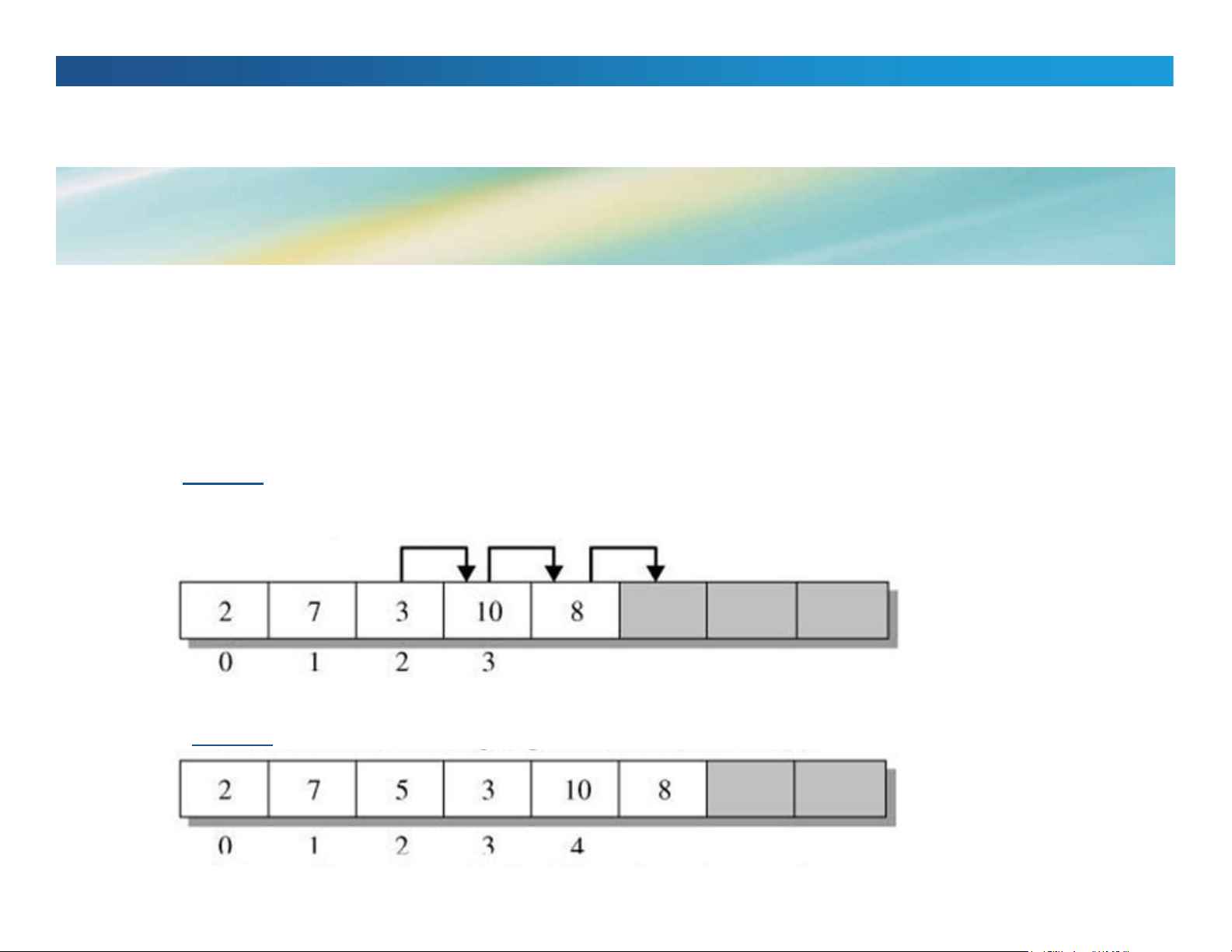
Insert 5 into the array: a[]={2, 7, 3, 10, 8} Step 1: Step 2: lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085
II.Implement lists using array
+ The last two elements are unused
+ Can we insert to this list 9 elements? Outline lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 III.Linked lists ❖Introduction lOMoAR cPSD| 58605085 ❖Kinds of linked lists ❖Singly linked lists ❖Other linked lists III.1.Introduction ❖Ideas
▪ Using a structure which allows to store
elements in a list, but enable inserting,
removing the elements effectively.




