


Preview text:
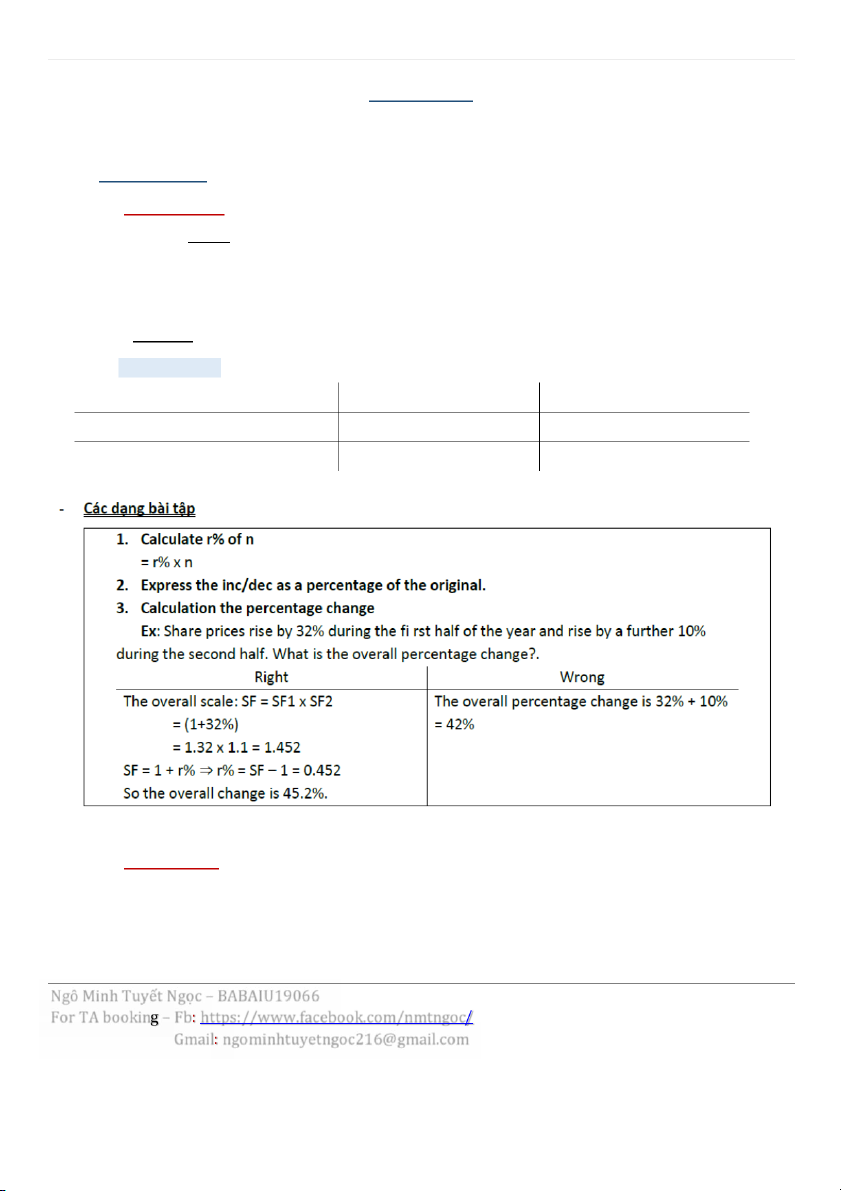
1 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3 Chapter 3: Mathematics of Finance I. Percentages 1. Percentages |x22x1| - Percentage x 100% x1
• x2 – x1 > 0 → Increase
• x2 – x1 < 0 → Decrease -
Scale Factor (hß sß tß lß)
SF = ýþā Ā�㕎þÿþ = 1 ± �㕟% þþý Ā�㕎þÿþ → The new value Increase Decrease Giá trß tr±ßc khi có r%
Đề �㕐ℎ�㕜 ÷ SF (SF= 1 đề �㕐ℎ�㕜 ÷ ÿ�㔹 (SF= Giá trß sau khi có r% Đß cho x SF (SF = 1+r) Đß cho x SF (SF = 1 – r)
Overall Scale = SF1 x SF2 x & x SFn x (1+10%) 2. Application 2.1. Index numbers
(The measure of change in a variable overtime)
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com
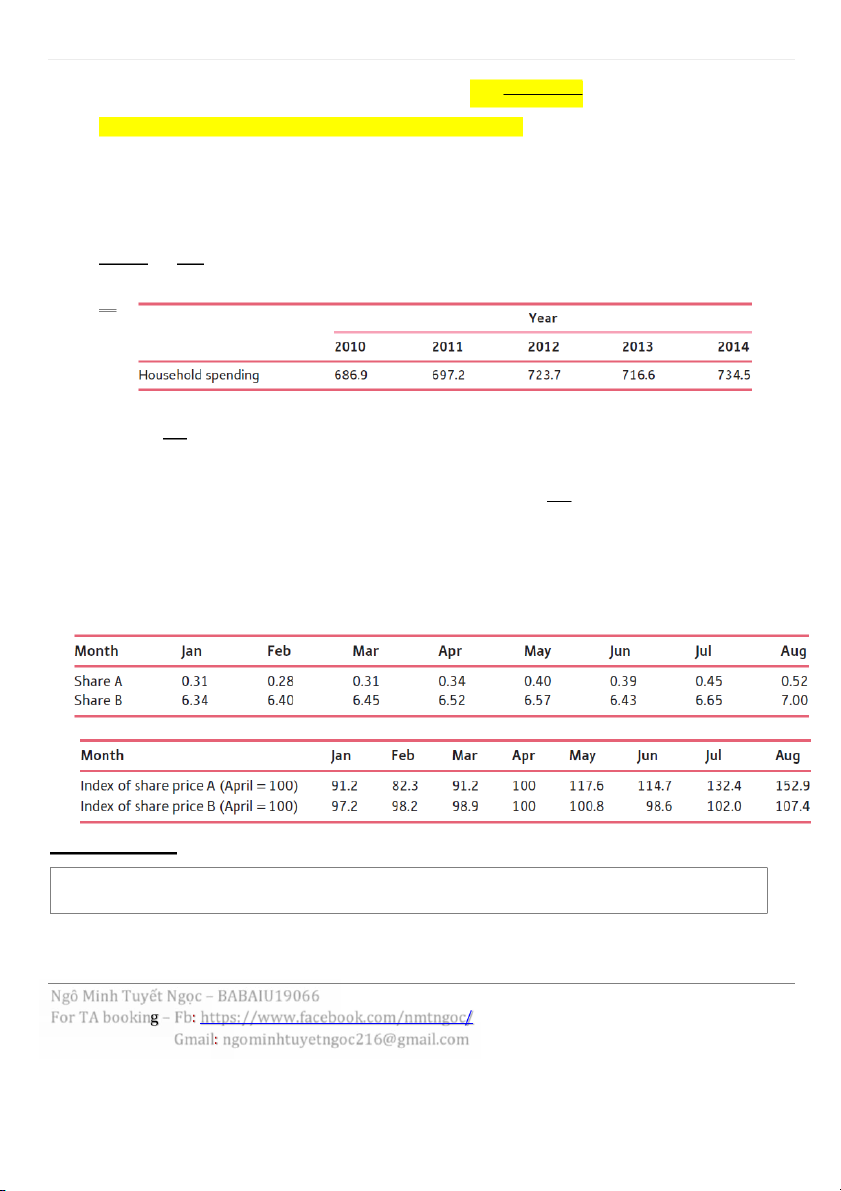
2 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3 Index number -
Index number = scale factor from base year x 100 → SF = (1) 100 -
Scale factor = (number of n^th year)/(number of base year) (2)
SF(2) và SF (1) là nh± nhau, b¿n có thß tính %change cÿa nth year so với base year rßi cßng thêm 1, tuy nhiên
khi làm b¿ng họ cho year và các sß liệu thì có thß dùng SF (2) cho nhanh -
Index number in base year = 100 -
The value in n year = [(Index n)/100] x The value in base year
- Index x = SF x = value x / value y Index y SF y - Ex: 98.5 100 103.8 102.8 105.3
In this case, we get: 723.7 �㕥 100 = 103.8 697.2
This shows that the value of household spending in 2012 was 103.8% of its value in 2011. In other words, household spending
increased by 3.8% during 2012.
For the year 2013, the value of household spending was 716.6, giving an index number: 716.6 �㕥 100 = 102.8 697.2
This shows that the value of household spending in 2013 was 102.8% of its value in 2011. In other words, household spending
increased by 2.8% between 2011 and 2013. Notice that this is less than that calculated for 2012, reflecting the fact that spe nding
actually fell slightly during 2013. - Meaning:
Các dạng bài tập:
1. Calculate the index numbers for the data
2. Use the index numbers → find percentage change in output from 2.2. Inflation
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com
3 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3
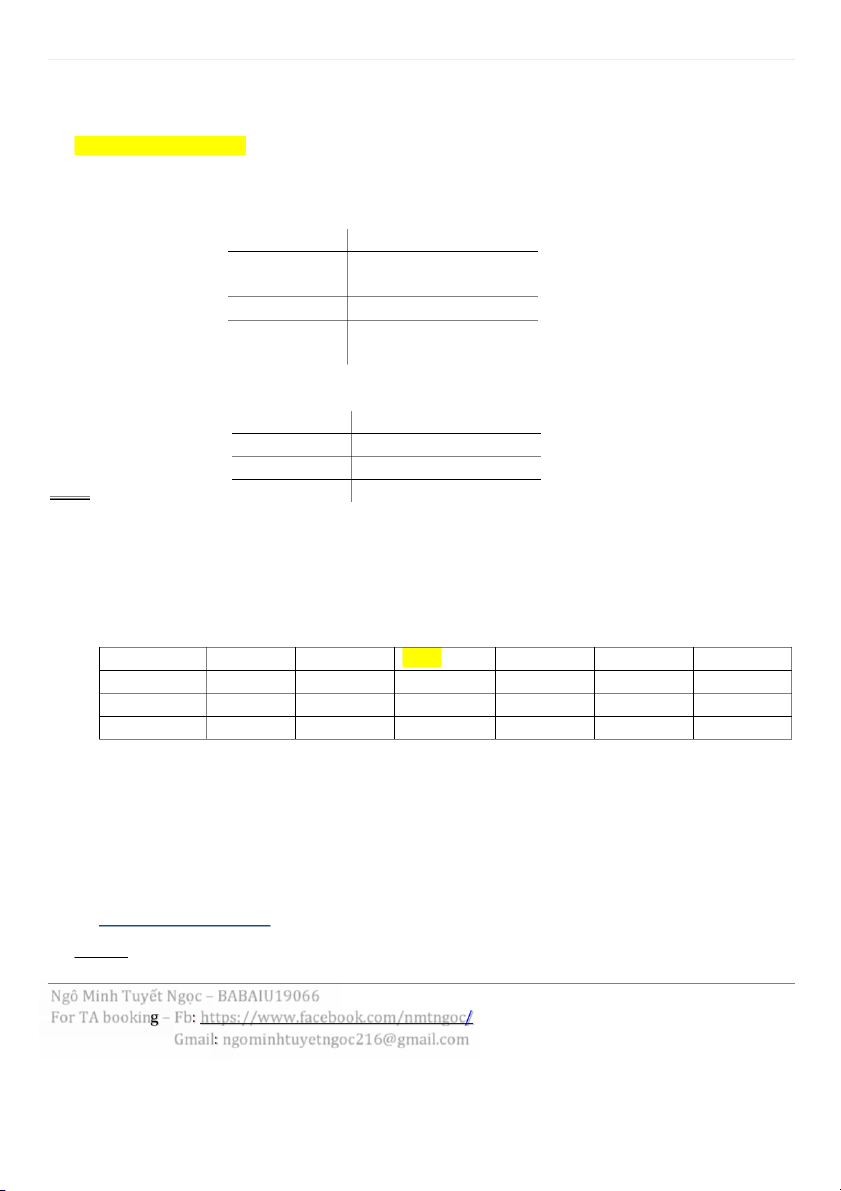
(the average percentage change in a given selection of these goods and services, over the previous year.) -
Rate of inflation: the rate at which prices increase over time, causing the value of money to fall - SF = 1 + Inflation(%) - Nominal vs. real data
+ Nominal data: the original, raw data
+ Real data: adjusted to take inflation into account. - Real data at Yn n Real date < base year = Nominal x Overall Scale = base year = Nominal > base year = Nominal ÷ Overall Scale - Nominal data at Yn n Real date < base year = Real ÷ Overall Scale = base year = Nominal Note: > base year = Real x Overall Scale -
Đß th±ßng cho Nominal (giá trß thô) và inflation đß tính real (giá trß bß ¿nh h±ßng bßi l¿m phát) -
Năm b¿t đ¿u l¿m phát real = Nominal
Sau l¿m phát: real < nominal
Tr±ßc l¿m phát: real > nominal EXAMPLE 1989t 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 Nominal 70 72 89 94 100 106 Inf. Rate 10.7% 7.1% 3.5% 2.3% Real (0) (1) (2) (3) (4) (5)
(0) = 89 (1 + 3.9%)(1 + 10.7%) = (1) = 72(1 + 10.7%) = (2) = 89 (3) = 94 / (1 + 7.1%) =
(4) = 100 / [(1 + 7.1%)(1 + 3.5%)] =
(5) = 100 / [(1 + 7.1%)(1 + 3.5%)(1+ 2.3%)] = II. Compound Interest Kí hißu:
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com
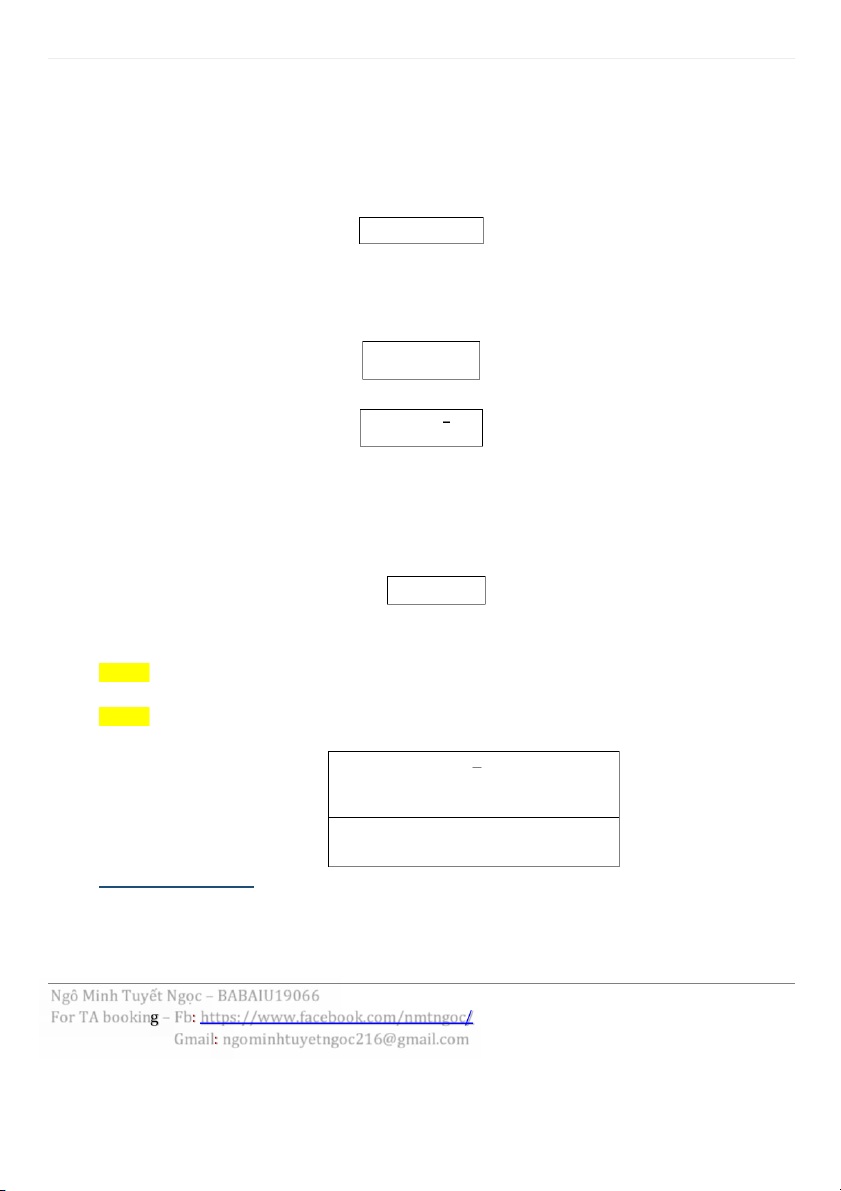
4 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3 • P: Principal
• S: Future value - total sum in the future • n: number of period • r: interest rate
1. Simple Interest
(the amount of interest received is the same for all years.) S = P(1 + nr)
Ex: Gửi 10tr vào ngân hàng. Lãi su¿t 5% mßt năm. Mßi năm thu đ±ÿc 500K tißn lãi. Sau 5 năm rút ra
tßng cßng 10tr2500K (trong đó có 2500K tißn lãi)
2. Compound interest
( tißn lãi sau mßi chu kì s¿ đ±ÿc cßng vào dßn vào vßn đß ti¿p tÿc tính lãi) S = P (1 + r) n
Tổng quát �㖓 S = P (1 + )kn �㖌 • k = 1: annually • k = 4: quarterly • k = 12: monthly • k = 52: weekly • k = 365: daily
3. Continuous compound interest (lãi kép liên tÿc) S = Pern n: tính theo năm 4. APR và AER -
Annual percentage rate (APR): Dùng khi mình đi vay m±ÿn, APR chß ra đ±ÿc cái chß sß lãi h¿ng năm c¿n tr¿.
Annual equivilent (effective) rate (AER): Dùng khi đi gửi ti¿t kißm, tißn lãi khi gửi mßi năm đ±ÿc bao nhiêu AER/APR = (�㗏 �㕟 + ) k ý - 1 = ern – 1 (continuos compound interest) III. Geometric series:
1. Recognise a geometric progression. -
Geometric series : c¿p sß nhân (Ex: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 & – multiply 2 each time)
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com
5 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3 -
Arithmetic progression: c¿p sß cßng (Ex: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30& – add 5 each time)
2. Evaluate a geometric series.
a, ar, ar2 , ar3 , . . . is a geometric progression with geometric ratio, r
Ex: Geometric series 2, 6, 18, 54, 162, 486
2 + 6 + 18 + 54 + 162 + 486 = 728
Áp dÿng Geometric series này vào bài toán đß dành tißn & tr¿ nÿ. Đß dành tißn thì có 2 d¿ng là lãi tính đ¿u kì dí cußi kì.
3. Calculate the total investment obtained from a regular savings plan.
*Mßi kì có A tißn đß vô ngân hàng đß dành, sau n kì thì lãi s¿ b¿ng lãi mßi kì cßng l¿i vßi nhau. Lãi cÿa
mßi kì thì tính nh± compound interest, rßi cßng lãi mßi kì vô đ±ÿc lãi cußi cùng rút ra 3.1.
The payment - at the beginning of each period:
Gửi kho¿n tißn A, lãi su¿t r - Kì thÿ nh¿t: A(1 + r) - Kì thÿ 2: A(1 + r)2 - Kì thÿ 3: A(1 + r)3 & - Kì thÿ n: A(1 + r)n
S = A(1 + r) + A(1 + r)2 + A(1 + r)3 + … + A(1 + r)n = �㕨(�㗏 + �㖓) (�㗏 + �㔫)�㔧 2 �㗏 � 㔫 3.2.
If the payment - at the end of each period: - Kì thÿ 1: A - Kì thÿ 2: A(1 + r) - Kì thÿ 3: A(1 + r)2 - & - Kì thÿ n: A(1 + r)n - 1
S = A + A(1 + r) + A(1 + r)2 + … + A(1 + r)n - 1 = �㕨 (�㗏 + �㔫)�㔧 2 �㗏 � 㔫
4. Calculate the instalments needed to repay a loan
Vay tißn 1 kho¿n L, và tr¿ 1 kho¿n A sau mßi cußi n kì
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com
6 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3 -
Sß tißn còn l¿i sau kì tr¿ thÿ 1: L(1 + r) – A -
Sß tißn còn l¿i sau kì tr¿ thÿ 2: [L(1 + r) – A](1 + r) – A = L(1 + r)2 – A(1 + r) – A -
Sß tißn còn l¿i sau kì tr¿ thÿ 3: [L(1 + r)2 – A(1 + r) – A](1 + r) – A = L(1 + r)3 – A(1 + r)2 – A(1 + r) – A & -
Sß tißn còn l¿i sau kì tr¿ thÿ n: L(1 + r)n – A(1 + r)n - 1 – & – A(1 + r) – A
*Tr¿ h¿t nÿ trong n tháng → L(1 + r)n – A(1 + r)n - 1 – & – A(1 + r) – A = 0
�㔿(1+�㕟)n = �㔴(1+�㕟)n - 1 n - 2 + �㔴(1+�㕟) +⋯+ �㔴(1+r) + A
L(1 + r)n = � 㕨 (�㗏 + �㔫)�㔧 2 �㗏 � 㔫
(V¿ trái: sß tißn tßng cßng đã nÿ trong n – gßm nÿ gßc và lãi
V¿ ph¿i: sß tißn tßng cßng ph¿i tr¿
➔ Tr¿ h¿t nÿ → v¿ trái = v¿ ph¿i)
Payout figure: Payout Figure is the present value of all remaining repayments (sß tißn mình còn nÿ
sau mßt kho¿n thßi gian tr¿ nÿ). After A years (x payments)
Ex: Vay ngân hàng mßt kho¿n tißn A, sau tháng thÿ nh¿t hoàn nÿ sß tißn X. Sß tißn còn l¿i sau n tháng PVx =
*Amortized loan: a loan that is repaid in equal payments over its life (including both interset &
principal) → payment amount is set such that the present value of all payments equals the loan amount
Ex: mortage loans, auto loans,& 1 2 (1 + �㕟)2�㕛
�㕃�㕉 = �㕃�㕀Ā [ � 㕟 ] , where PV: present value
PMT: Payment amount – the present value of all payments equals the loan amount IV. Investment appraisal
1. Calculate present values
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com
7 | M A T H F O R B U S I N E S S C H A P T E R 3
Given any three of these variables it is possible to work out the
value of the remaining variable. P = principal S = future value r = interest rate
t = time (Discrete compounding t = the number of time periods; continuous
compounding, t is measured in years.)
2. Use net present values to appraise investment projects.
Net present value (NPV): Giá trß hißn t¿i ròng NPV = PV – P 0 PV: present value
P0: initial outlay (kho¿n đ¿u t± ban đ¿u)
NPV > 0: worth to invest (PV > P0) NPV = 0: neutral
NPV < 0: not worth to invest (PV < P0)
Internal rate of return (IRR): Tß su¿t thu nh¿p nßi bß => dùng khi NPV = 0, tính interest rate và so sánh
interest rate vßi market rate xem có nên đ¿u t±:
P0 = �㕪1(�㗏+�㖓�㕰�㕹�㕹)-1+�㕪2(�㗏+�㖓�㕰�㕹�㕹)-2+⋯+�㕪n(�㗏+�㖓�㕰�㕹�㕹)-n
If rIRR > rmarket : worth to invest
If rIRR < rmarket : not worth to invest
Ngô Minh Tuy¿t Ngßc – BABAIU19066
For TA bookin – Fb https://www.facebook.com/nmtngoc
Gmail ngominhtuyetngoc216@gmail.com




