



Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Bộ môn Cơ Kỹ thuật – Khoa Khoa học Ứng dụng – Đại học Bách khoa Tp.HCM CONTENT
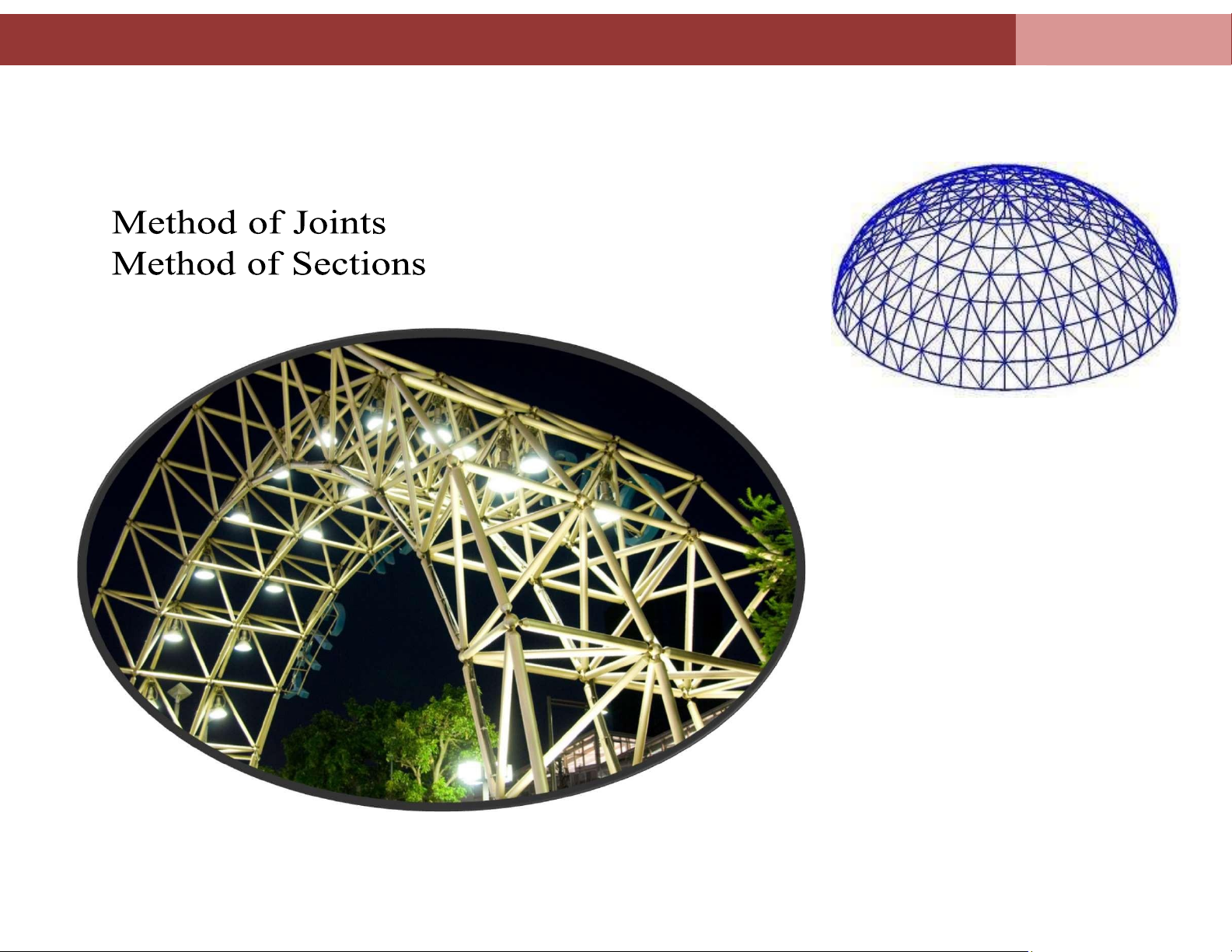
4. 1.Introduction to the plane trus problem and
assumptions 4.2. Method of Joints 4.3. Method of Sections
Bộ môn Cơ Kỹ thuật – Khoa Khoa học Ứng dụng – Đại học Bách khoa Tp. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems
4.1. Introduction to the plane trus problem and assumptions
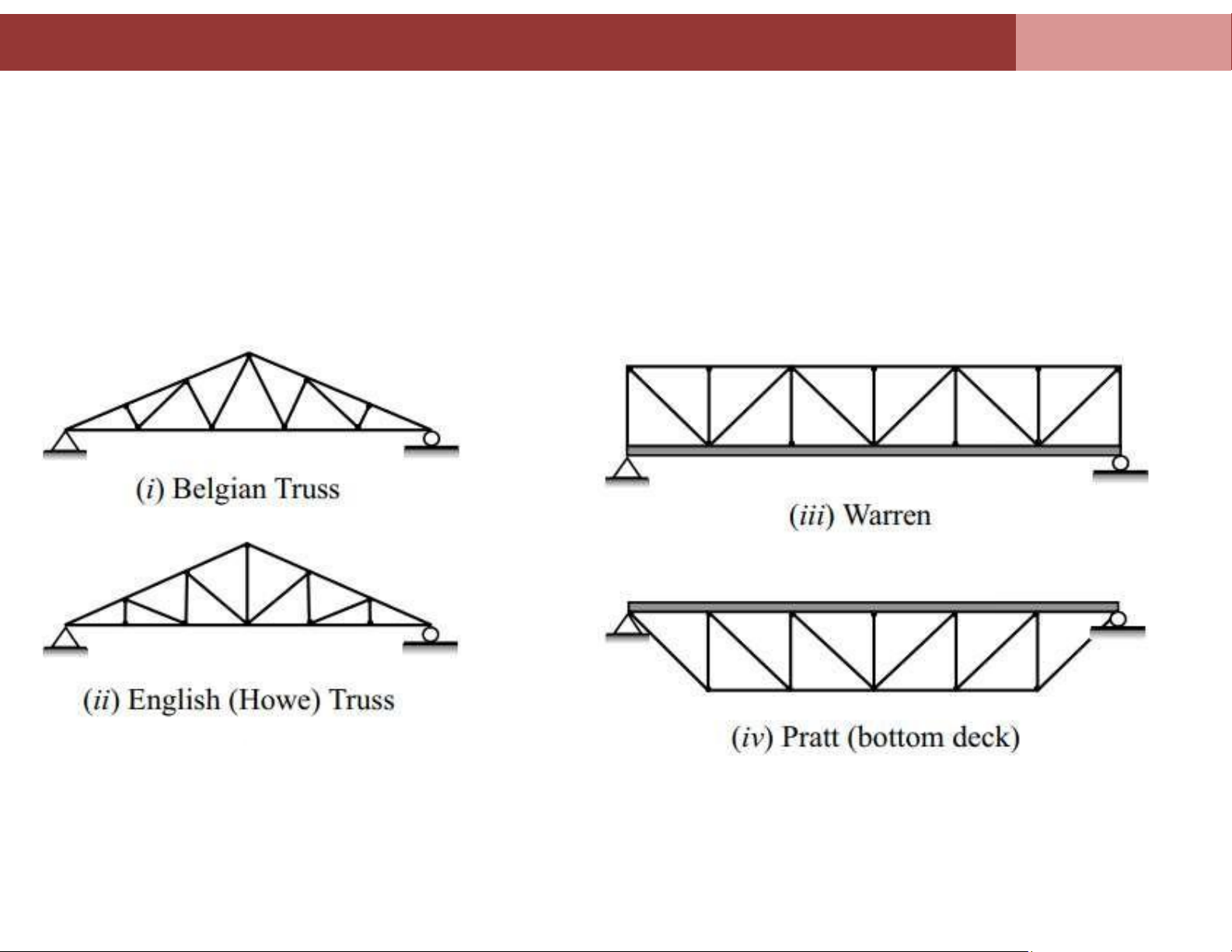
A truss is a load-bearing structure comprising one or more triangular units. These
units are formed with straight and slender member with their ends pin-connected.
External forces and their reactions are considered to act only a the joints.
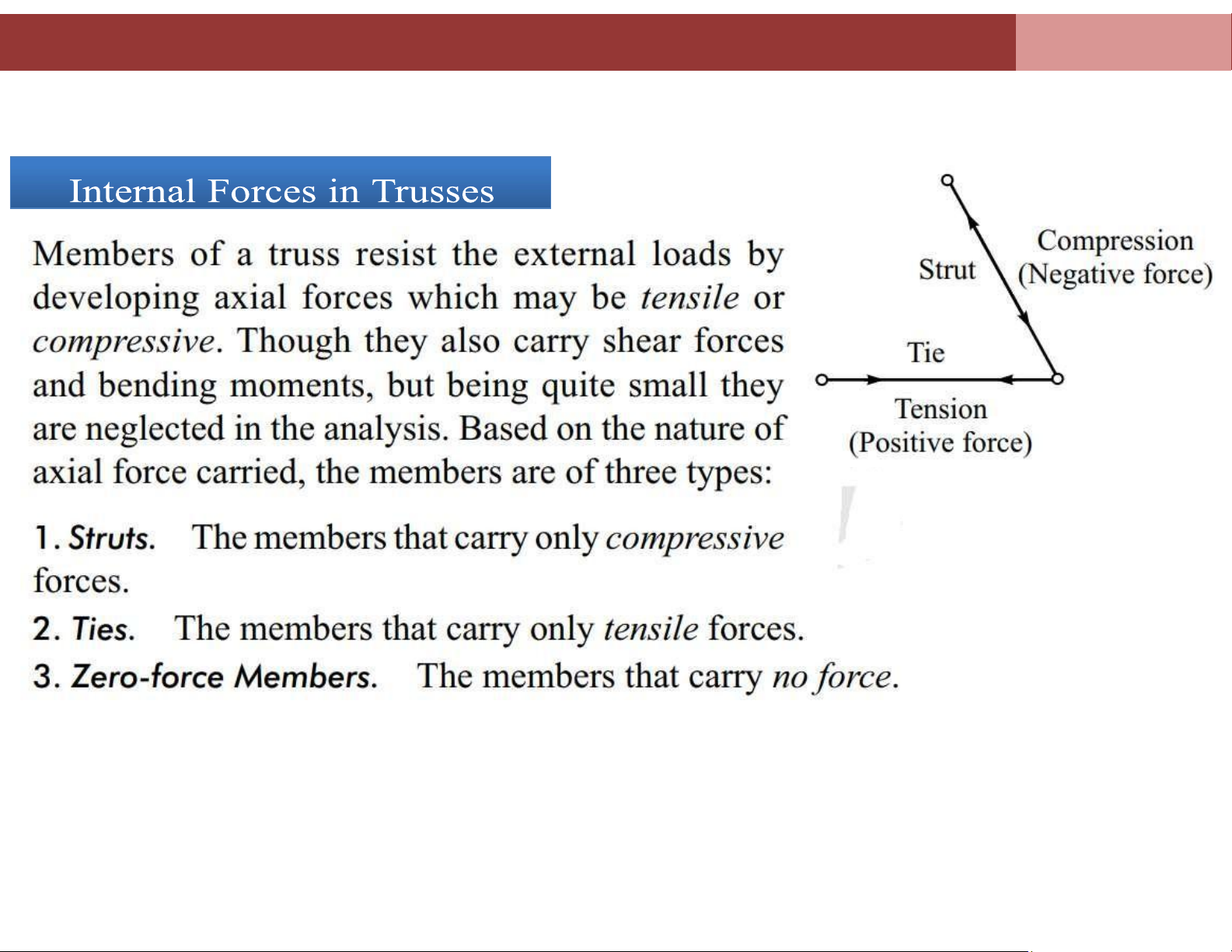
The major forces produced in members are axial forces (compressive or tensile) lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems
4.1. Introduction to the plane trus problem and assumptions
The tensile force is taken as positive and compressive force as negative.
4.1. Introduction to the plane trus problem and assumptions lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems Sign Convention
Tensile member: Internal force has positive value (>0)
Compressive member: Internal force has negative value (<0) lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
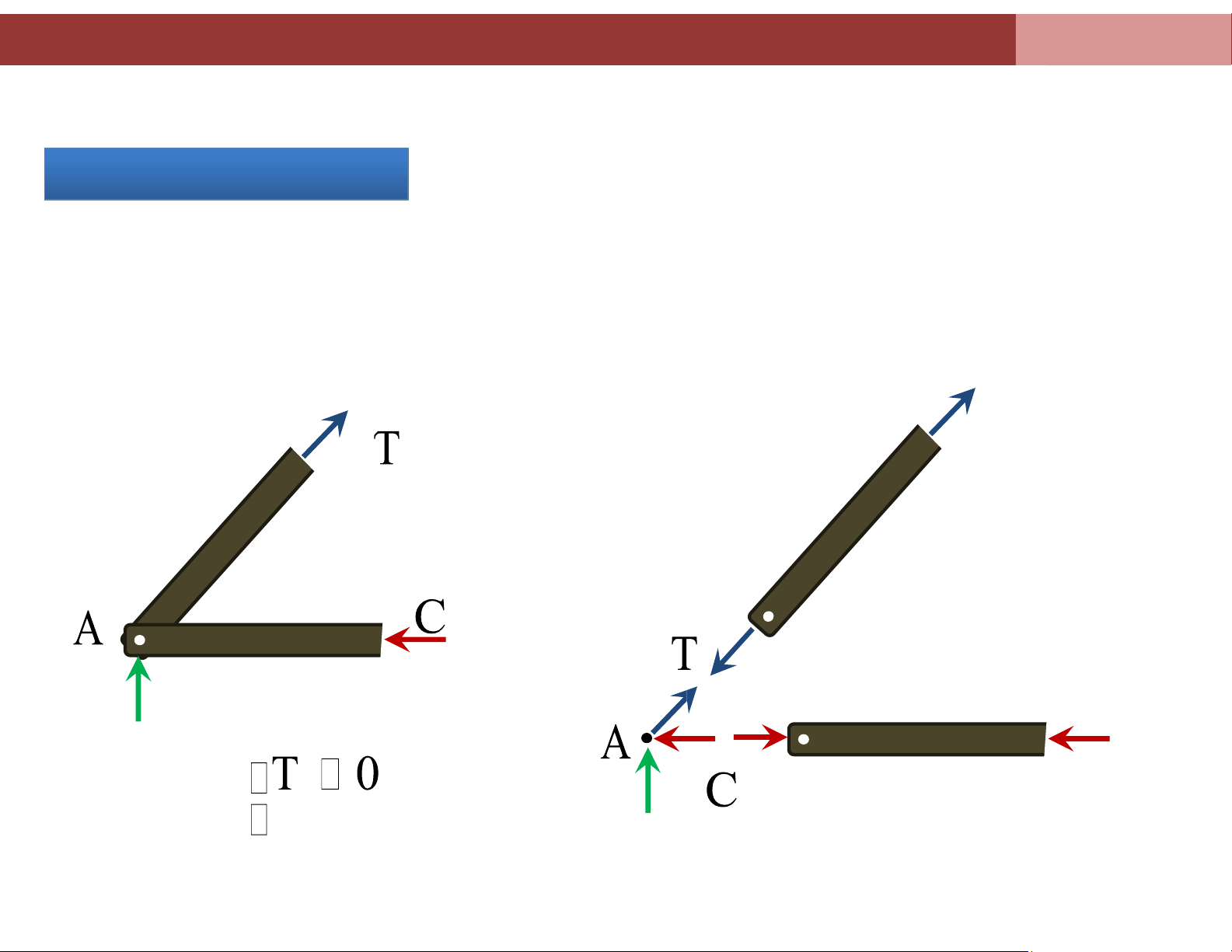
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems C 0
4.1. Introduction to the plane trus problem and assumptions Solution methods lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 1. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 2. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
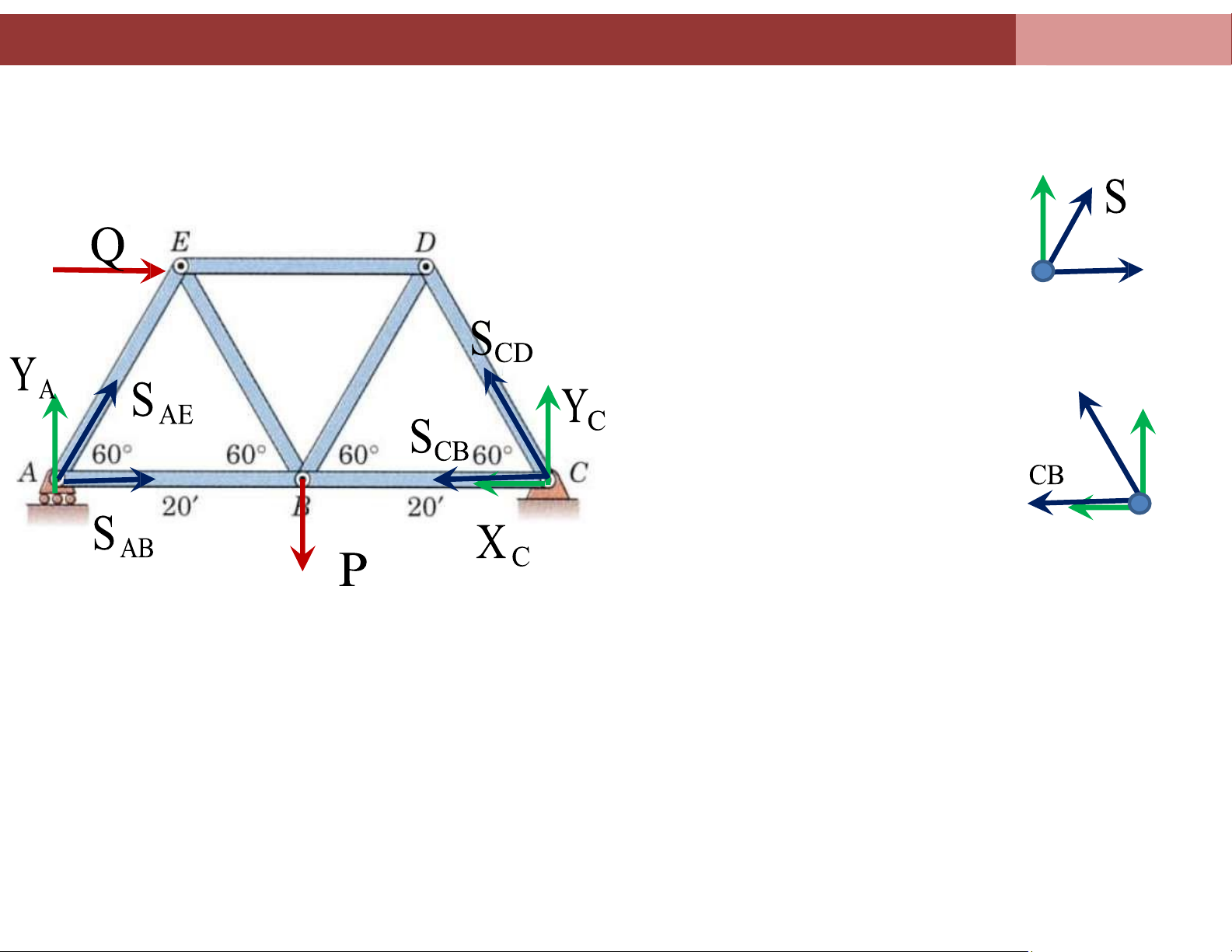
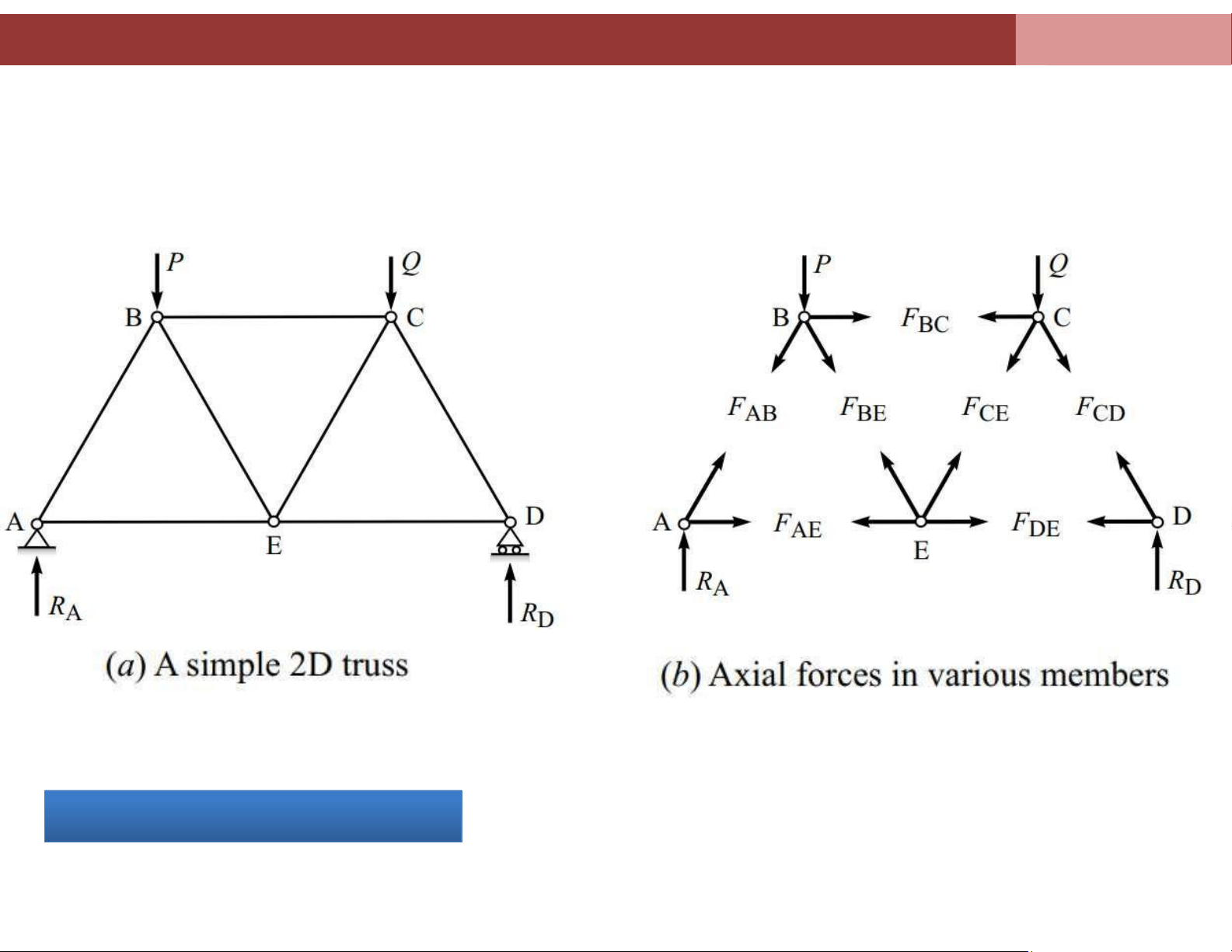
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints Method off Joints
The following steps describe the method of joint: 1.
Draw FBD, find the support reations by considering equilibrium lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems Y 2. Consider joint A, and find AAE internal forces SAE and SAB A SAB S 3. Consider joint C , CD Y find SCD and SCB SC C lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems XC
4. Consider the remaining joints 4.2. Method of Joints Method off Joints lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints
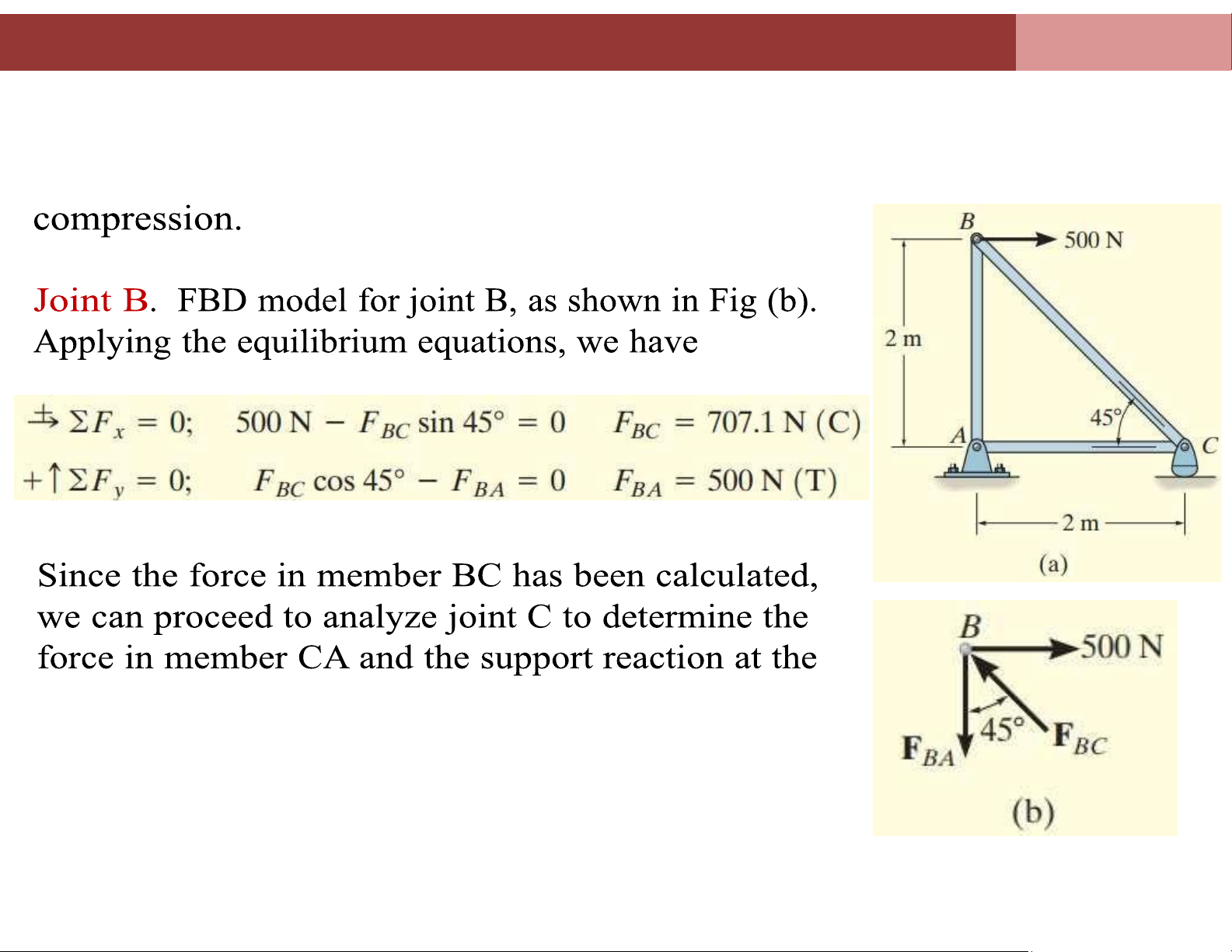
Example 1: Determine the force in each member of the truss shown in
Figure a and indicate whether the members are in tension or lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
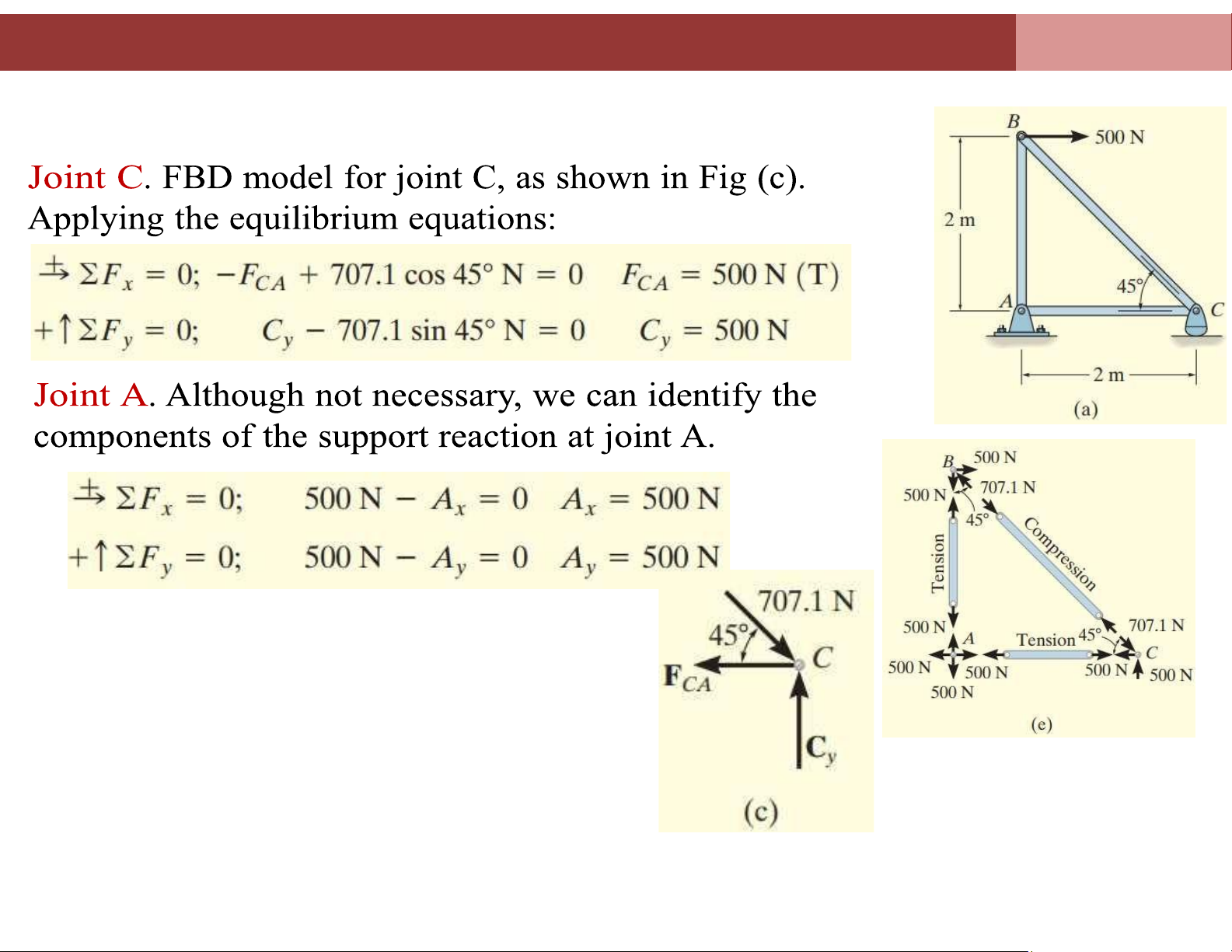
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints joint. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints
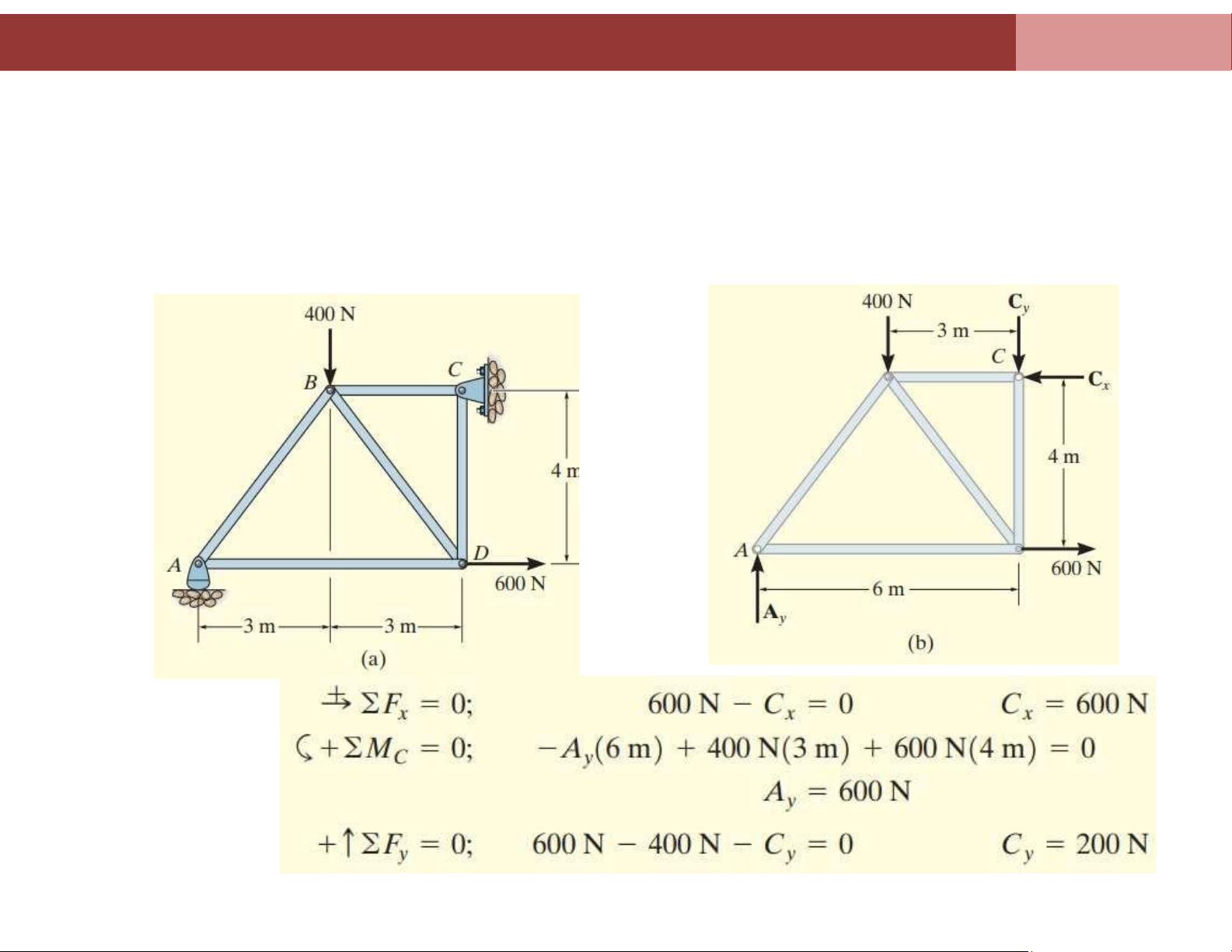
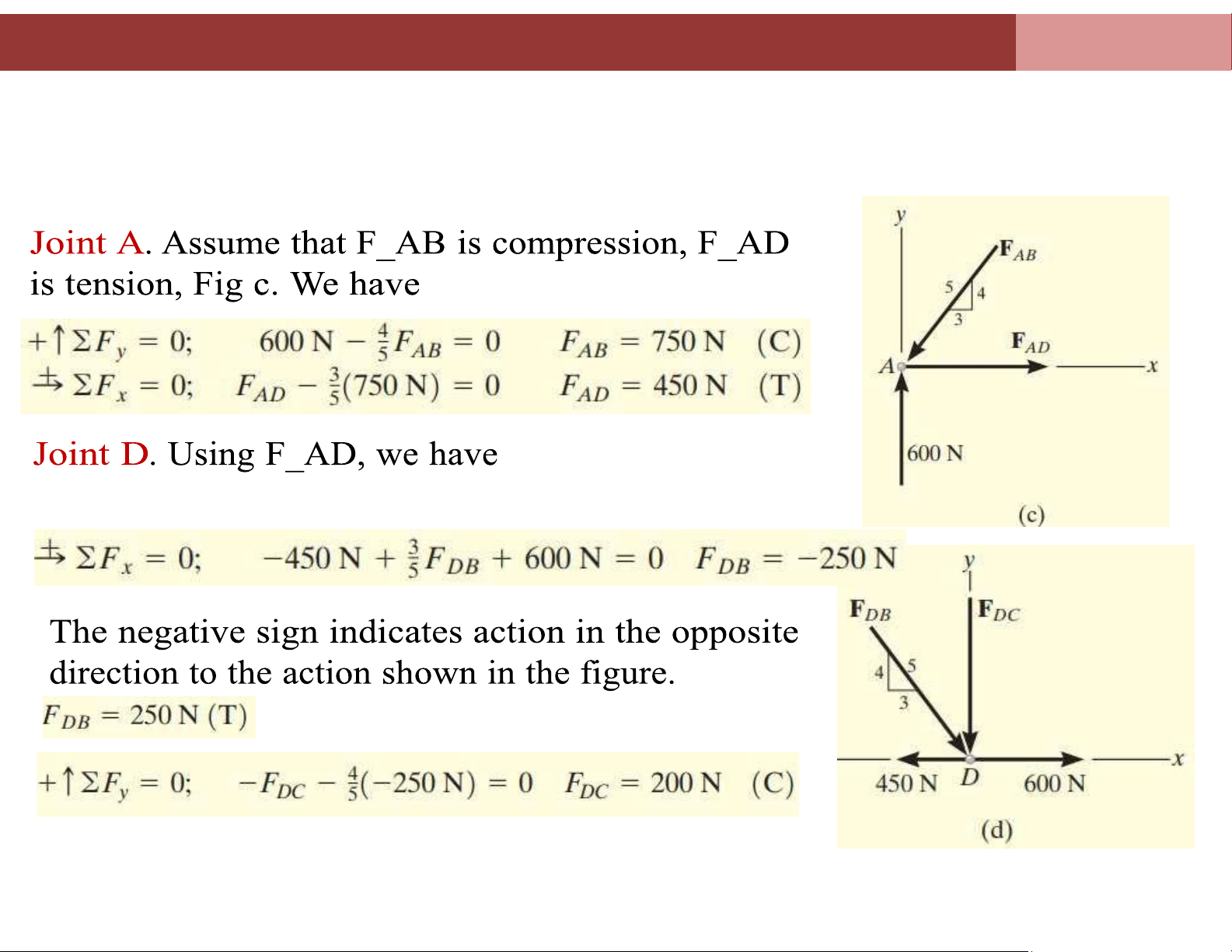
Example 2: Determine the force in each member of the truss shown in figure a
and indicate whether the members are in tension or lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
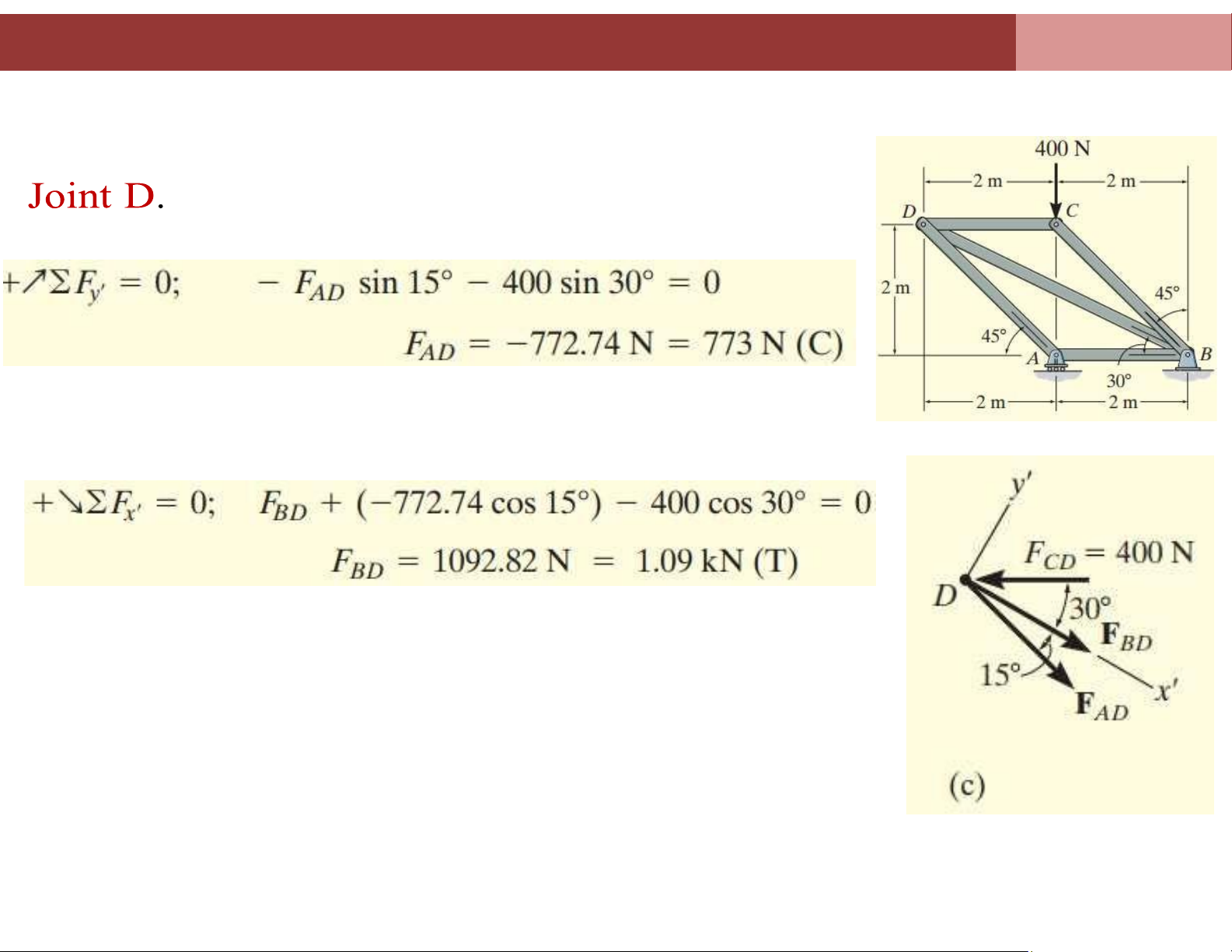
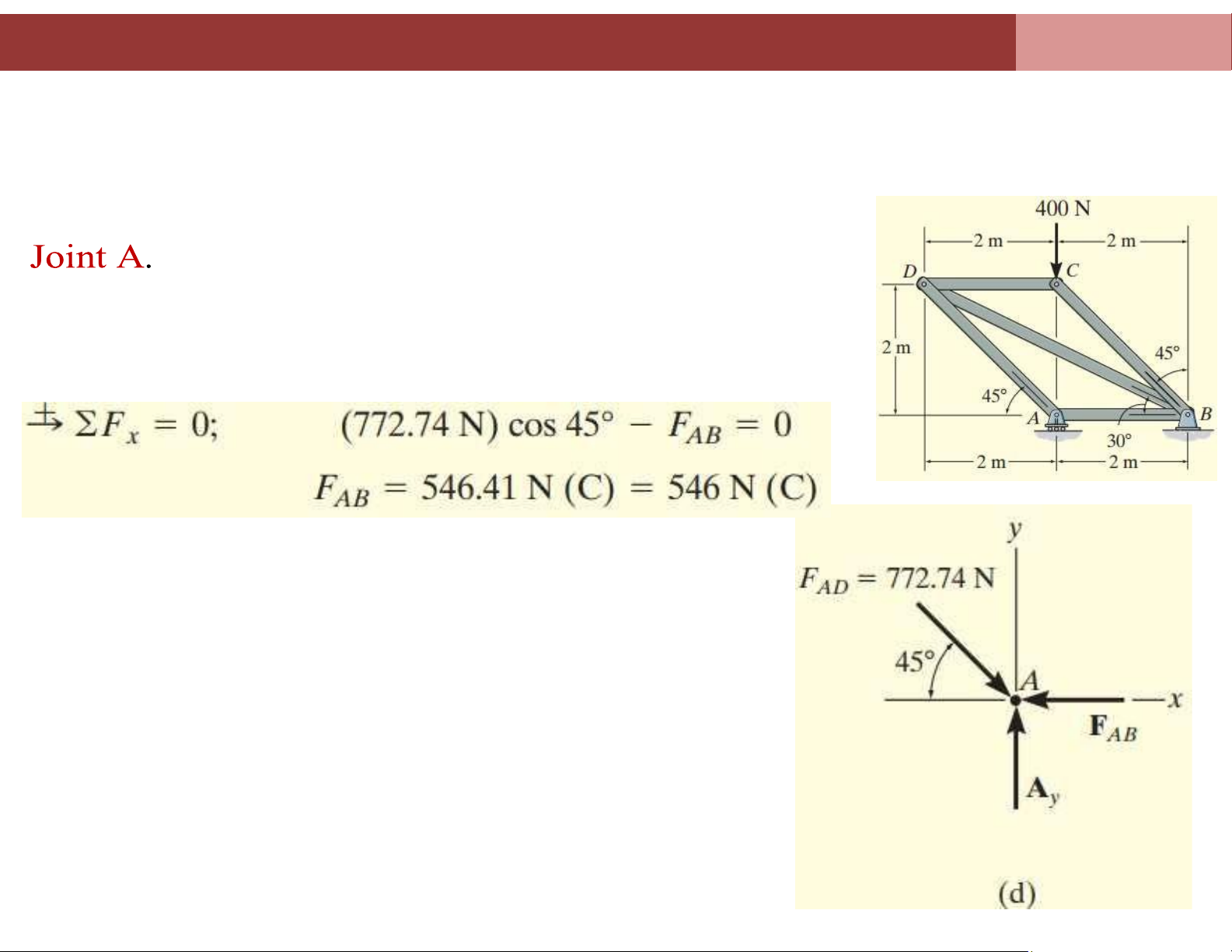
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints
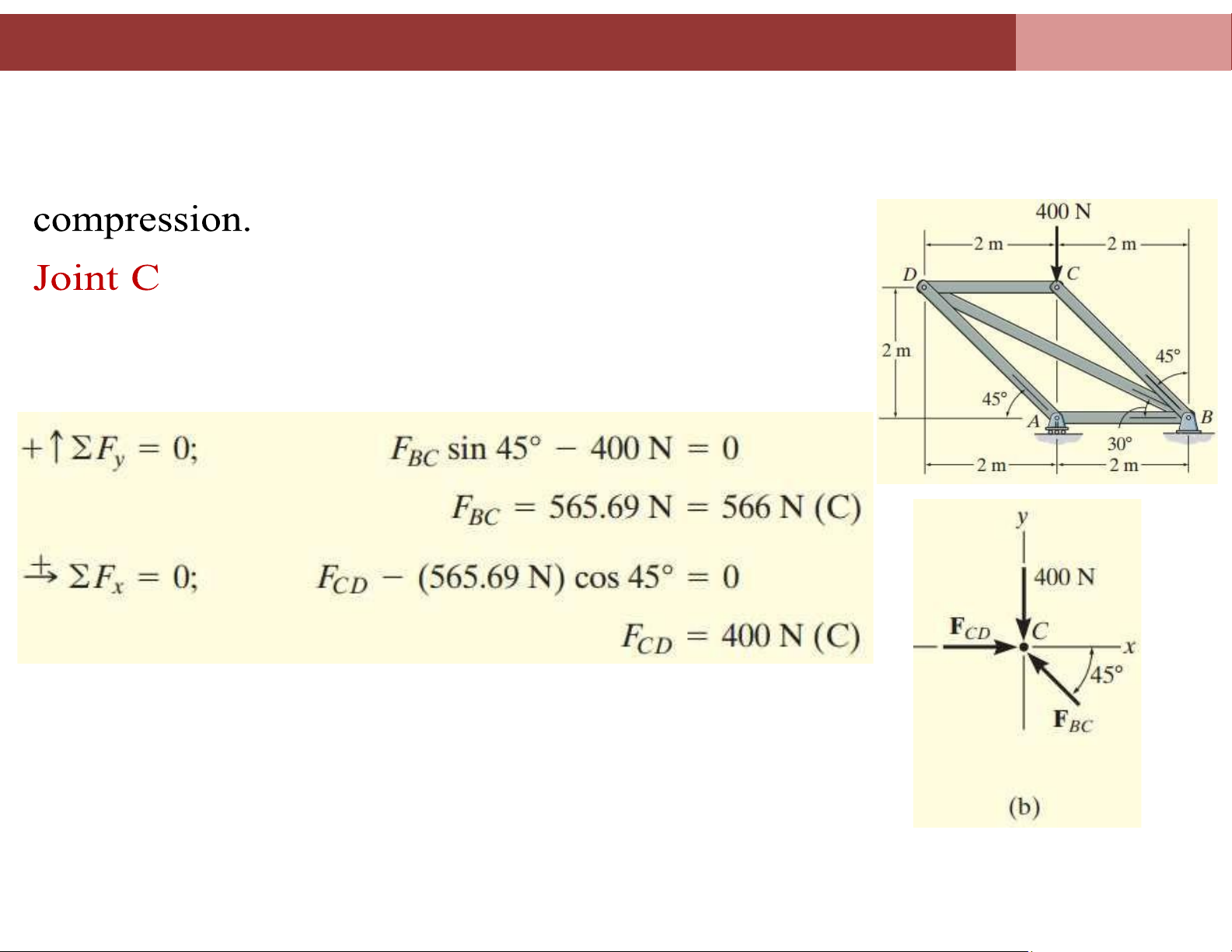
Example 3: Determine the force in each member of the truss shown in figure a
and indicate whether the members are in tension or compression. lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints lOMoAR cPSD| 58675420
Chapter 4. Analysis of plane truss systems 4.2. Method of Joints Joint C




