


Preview text:
lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115
CHAPTER 4: SOLUTION DEVELOPMENT
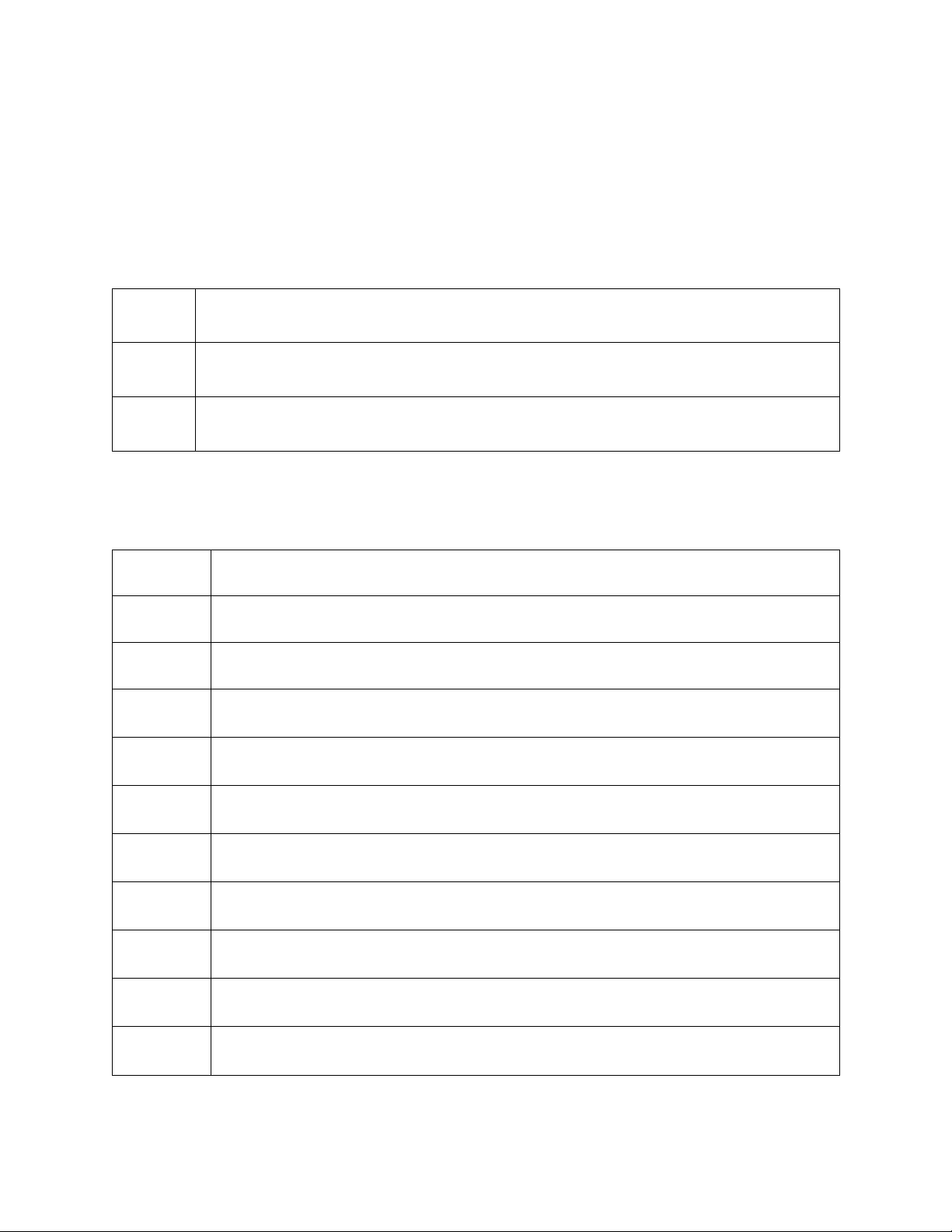
4.1. Mathematical formulation 4.1.1. Index i Index of factories j
Index of continential warehouse k Index of regional warehouse
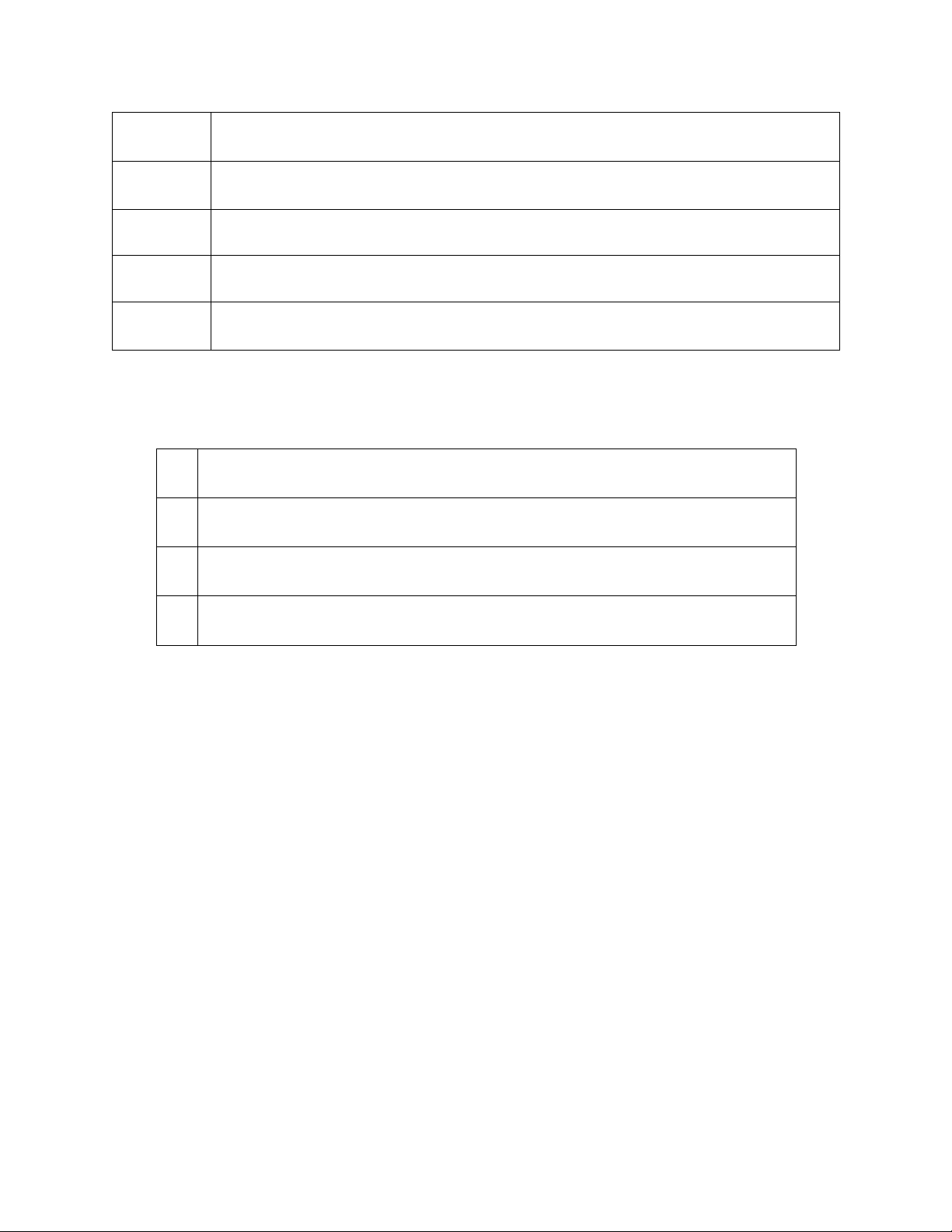
Table 4.1: Table of indexs 4.1.2. Parameters S Set of factories i W
Set of continental warehouses j D
Set of regional warehouses k C
Inbound transportation cost from factory i to warehouse j ij C
Outbound transportation cost from warehouse j to RWH k jk f
Fixed cost per period related to factory i i f
Fixed cost per period related to CWH j j M
Manufacturing cost per unit at the factory i i H
Handling cost per unit at warehouse j j S Capacity of factory i i W
Capacity of warehouse j j lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 FP
Maximum number of factories allowed to open max FP
Minimum number of factories allowed to open min ℘
Maximum number of warehouses allowed to open max ℘
Minimum number of warehouses allowed to open min D
Demand of distribution center k k
Table 4.2: Table of parameters
4.1.3. Decision variables X
Total number of products flowing from factory i to warehouse j ij X
Total number of products flowing from warehouse j to regional warehouse k jk Y
Binary variable for factory i i Y
Binary variable for warehouse j j
Table 4.3: Table of decision variables
4.1.4. Objective function:
MinZ=∑∑Cij∗X ij+∑∑C jk∗X jk +∑ f i∗Y i+∑ f j∗Y j+¿∑∑ Mi∗Xij+∑∑ H j∗X jk ¿ i j j k i j i j j k 4.1.5. Constraints
Capacity constraint of the factory. It implies that the level of product shipped from each factory to warehouses cannot exceed that factory's capacity.
∑ Xij ≤Si, ∀i∈S (2) j lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115
The warehouse capacity constraint. It implies that the level of product transferred from each warehouse to the distribution center cannot exceed the capacity of that warehouse.
∑ X jk ≤W j ,∀ j∈W (3) k
The total number of open factories cannot be greater than the maximum and cannot be less than the minimum allowable number of factories that need to be opened.
F Pmin≤∑Y i ≤F Pmax (4) i
The total number of open warehouses cannot be greater than the maximum and cannot be less than the minimum allowable number of warehouses that need to be opened.
W Pmin≤∑ Y j ≤W Pmax (5) j
The amount of product distributed from factories to a warehouse is equal to the
amount of product distributed from that warehouse to the distribution centers, for all warehouses.
∑ Xij−¿∑ X jk=0,∀ j∈W ¿ (6) i k
The number of products delivered from warehouses to a distribution center cannot be less than the quantity demanded by that distribution center, for all distribution centers. lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115
∑ X jk ≥ Dk ,∀ k∈ D (7) j
Any product cannot be delivered from a factory unless the factory is open.
Xij Mij Y i≤0,∀i∈S,∀ j∈W (8)
Any product cannot be delivered from a warehouse unless the warehouse is open.
X jk M jk Y j ≤0, ∀ j∈W ,∀ k∈S (9) /
The value of Y i Y j is 1 if the factories/warehouses are open or the value is 0 otherwise.
Y i ,Y j={0,1}, ∀i∈S, ∀ j∈W (10)
The product quantity delivered from factories to distribution centers cannot be negative.
Xij , X jh≥0, ∀i∈S, ∀ j∈W ,∀ k ∈S (11) 4.1.6. Service level Averagedistance=∑ Xjk j,k djk∑∗D k k
Percentageof demandthat iswithin1300 kilometers=∑j,k ajk∑∗DXjkk lOMoAR cPSD| 23136115 k Where:
djk is the distance from continential warehouses to regional warehouses. The estimated distance is shown in the Appendix.
ajk=1 if the djk>1300, otherwise, ajk=0.




