
Preview text:
Cauchy Index of Tangent of the Phase Angle Ang Man Shun October 10, 2012
1 Review of Related Mathematics 1.1 Complex Algebra - Polar Form
∀z : z = x + jy ∈C , this rectangular form can be represented by polar form :
z = ρejθ where ρ =
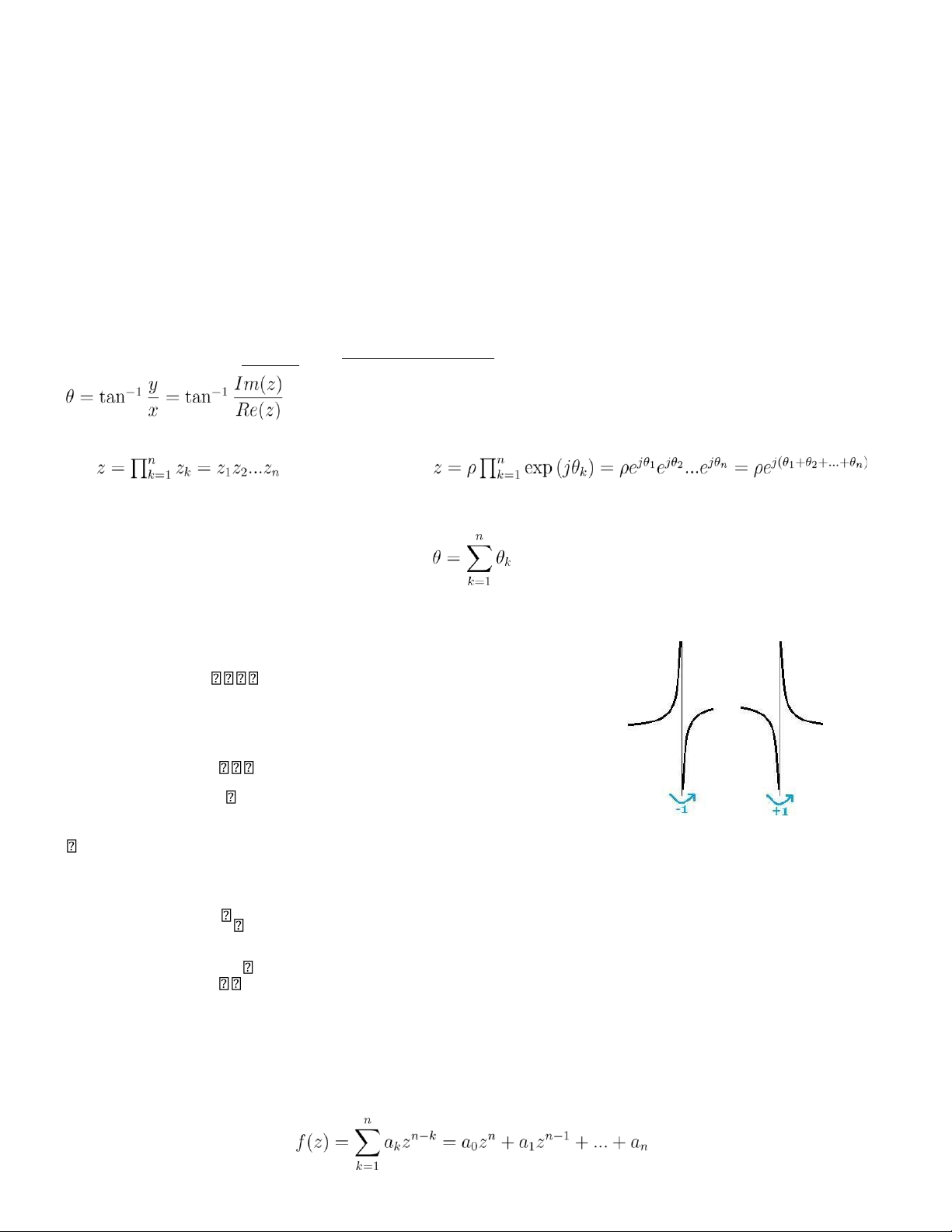
√x2 + y2 = √[Re(z)]2 + [Im(z)]2 and For , their polar form is i.e. 1.2 Cauchy Index +1 −∞→ +∞ Cauchy Index = −1 +∞→−∞ 0 else +1
lim f(x) = −∞ ∩ lim f(x) = +∞ x→a− x→a+ ⇐⇒ −1
lim→ −f(x) = +∞ ∩ lim→ +f(x) = −∞ x a x a 0 else 2
The Cauchy Index of Tangent of Phase Angle
For a function f(z) = Re[f(z)] + Im[f(z)]
By Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
Degree n equation has exactly n roots ∴
Assume no roots of f(z) = 0 lie on imaginary axis Let
N = number of roots of f(z) = 0 with negative real parts
P = number of roots of f(z) = 0 with positive real parts And thus
N + P = n
As f(z) is complex, express f(z) in polar form
f(z) = ρ(z)ejθ(z) Where
ρ(z) = √Re2 [f(z)] + Im2 [f(z)] Since , therefore Where
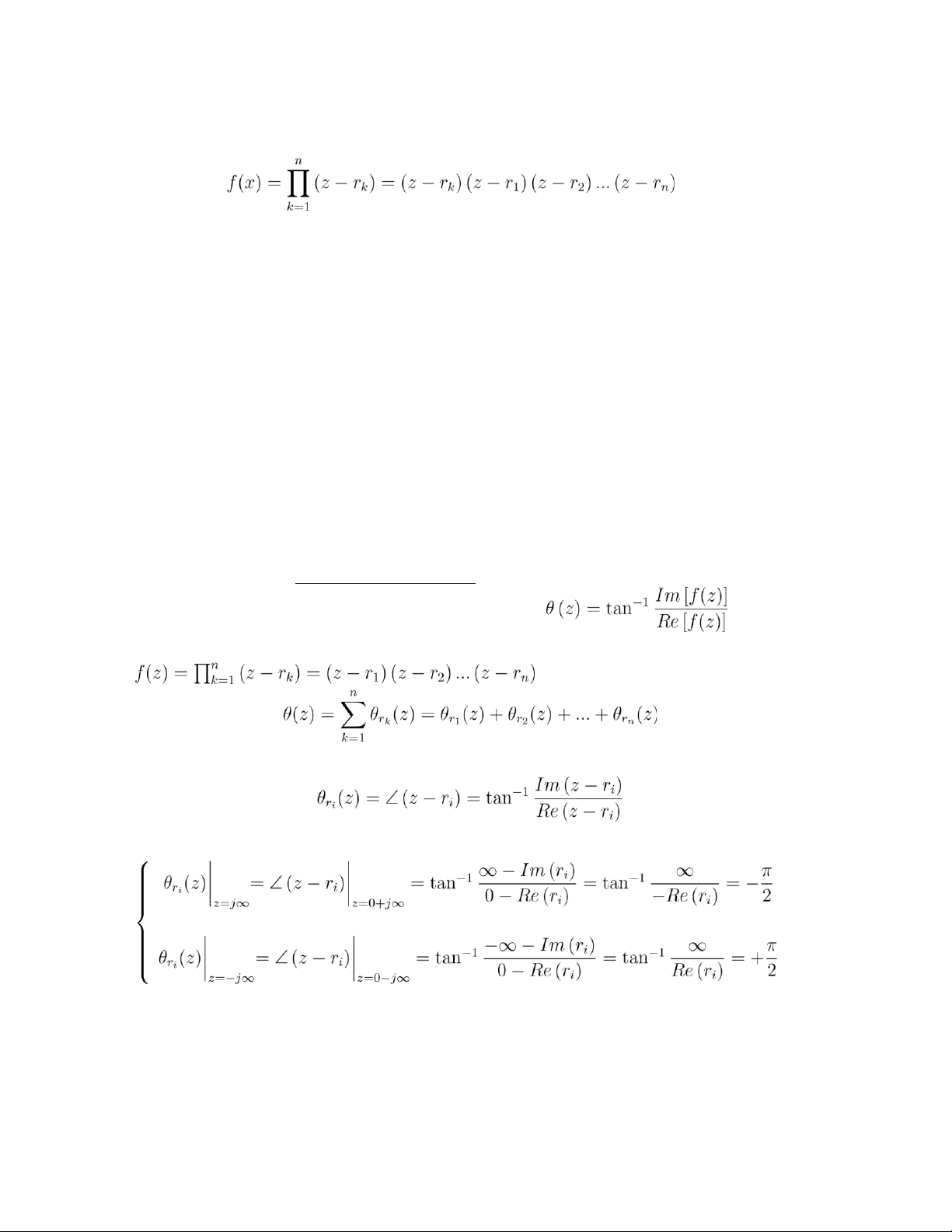
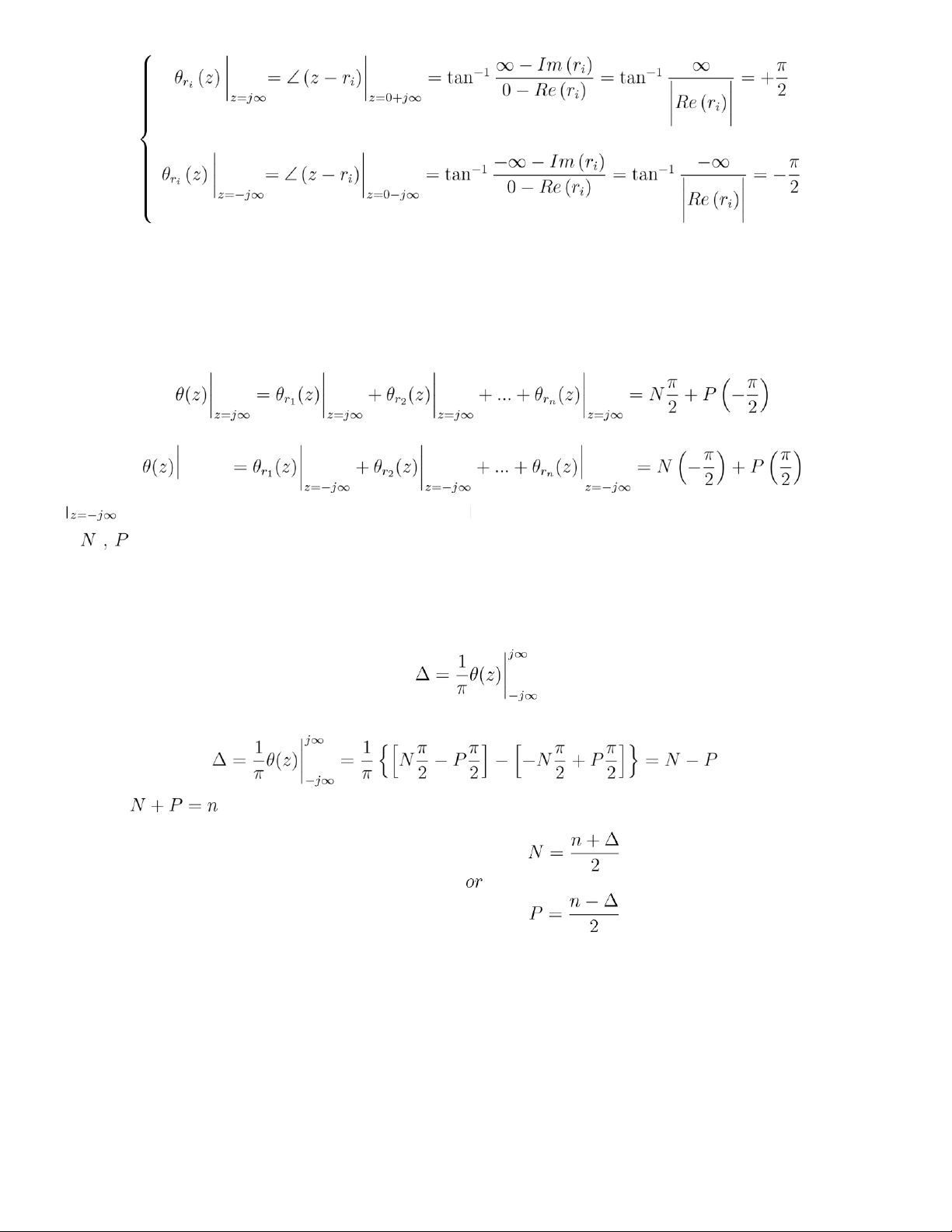
Case 1 . For the ith root of f(z) , it it has a positive real part, i.e. Re(ri) > 0 then
Case 2. For the ith root of f(z) , it it has a negative real part , i.e. Re(ri) < 0 then 2 Therefore, Recall that,
are the number of roots that has negative real part and positive real parts, and
N + P = n. Now let Then With 2N = n + ∆ 2P = n − ∆
Thus, given a polynomial function f(z) with degree n , N , P can be found by evalute ∆
And the value ∆ is the Cauchy Index for the function θ(z)
i.e. , the value for the Tangent of the Phase Angle of a function f(z) −END− 3