










Preview text:
14:37, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
Chapter 3: The Z – Transform and its Application
the Analysis of LTI System
he z-transform of the discrete-time system x(n) is efined as the power series
Where z - complex variable.
sometimes called the direct z-transform.
he inverse procedure is called the inverse z-transfo X(z) ≡ Z { x(n) } (3.1.2) z x(n) ↔ X(z) (3.1.3)
he region of convergence ( ROC) of X(z) is the se
l values z for which X(z) attains a finite value .
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu 3.1 The z-transform
Let us express the complex variable z in polar form z = r ejθ (3.1.4)
r = |z| and θ = z , Then
In the ROC of X(z), | x (z) | < ∞ , then
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform
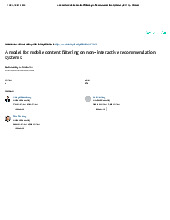
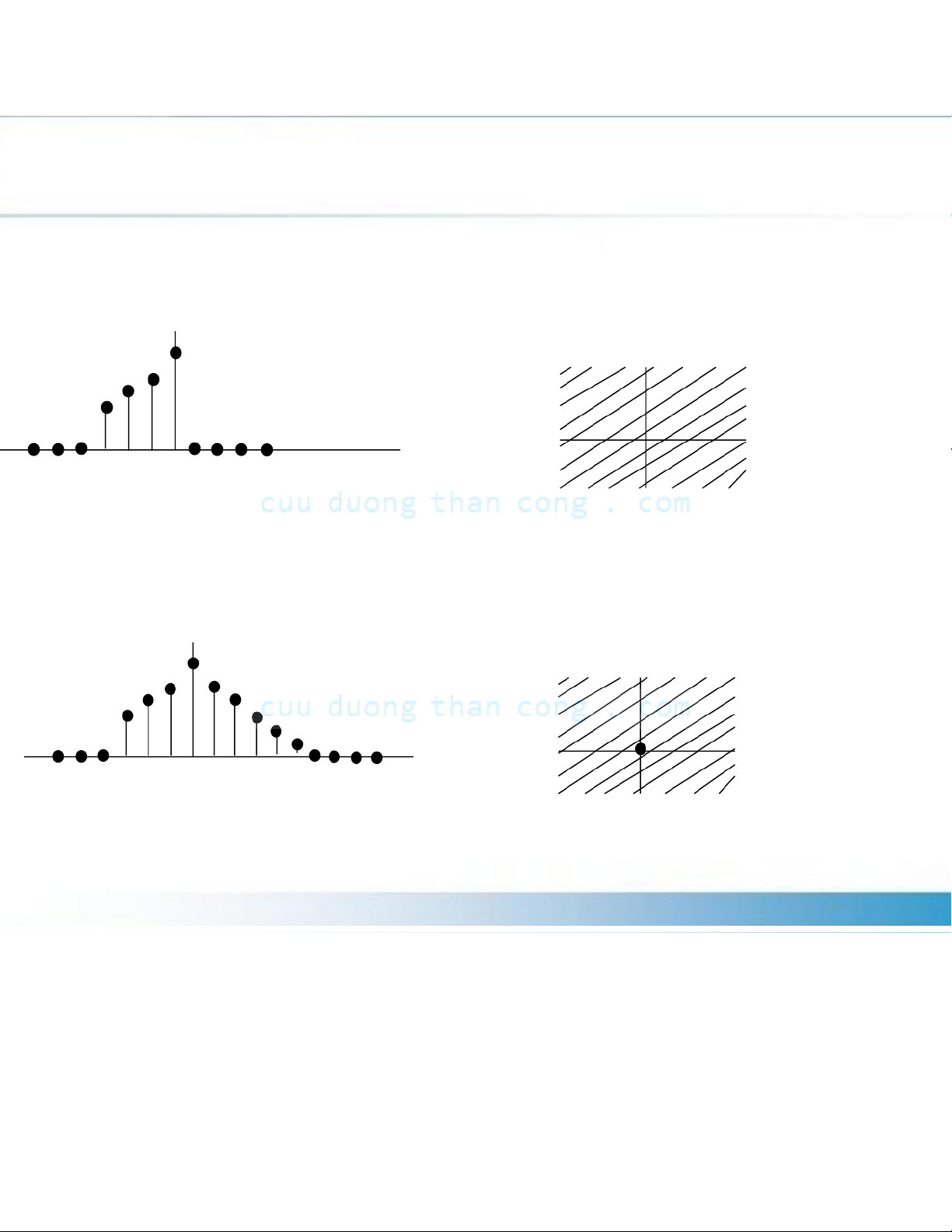
gure 3.1 Region of convergence for X(z) and its correspond
causal and anticausal components.
ROC for the first sum consists of all points in a circle of som radius r1 < . ∞ Im*(z) z"#plane r1 Re(z) Region#of#convergence#for# (a)
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform
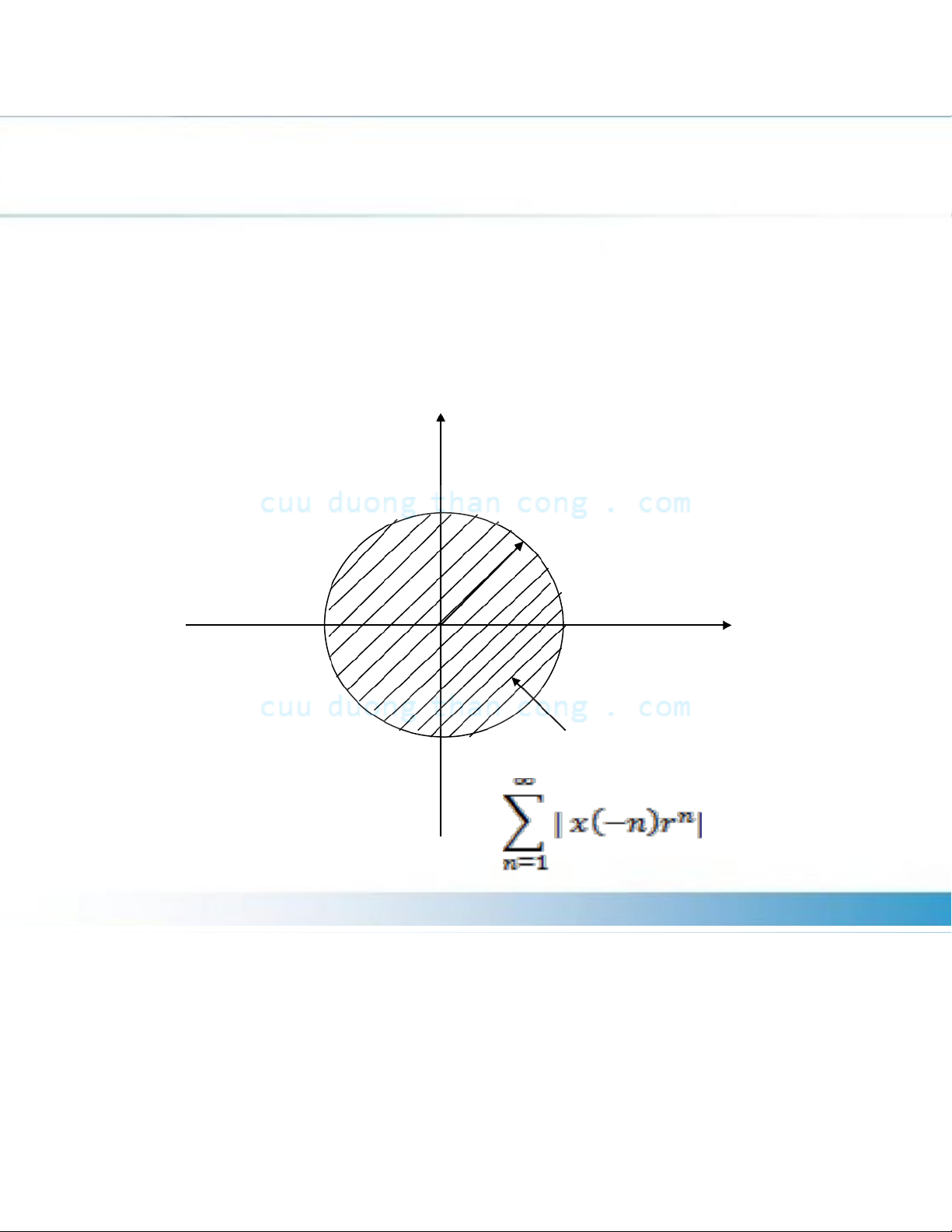
ROC for the second sum consists of all points outside a
circle of radius r > r2 Im(z)
r2 z%&plane Re(z) Region#of#convergence#for# (b)
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform
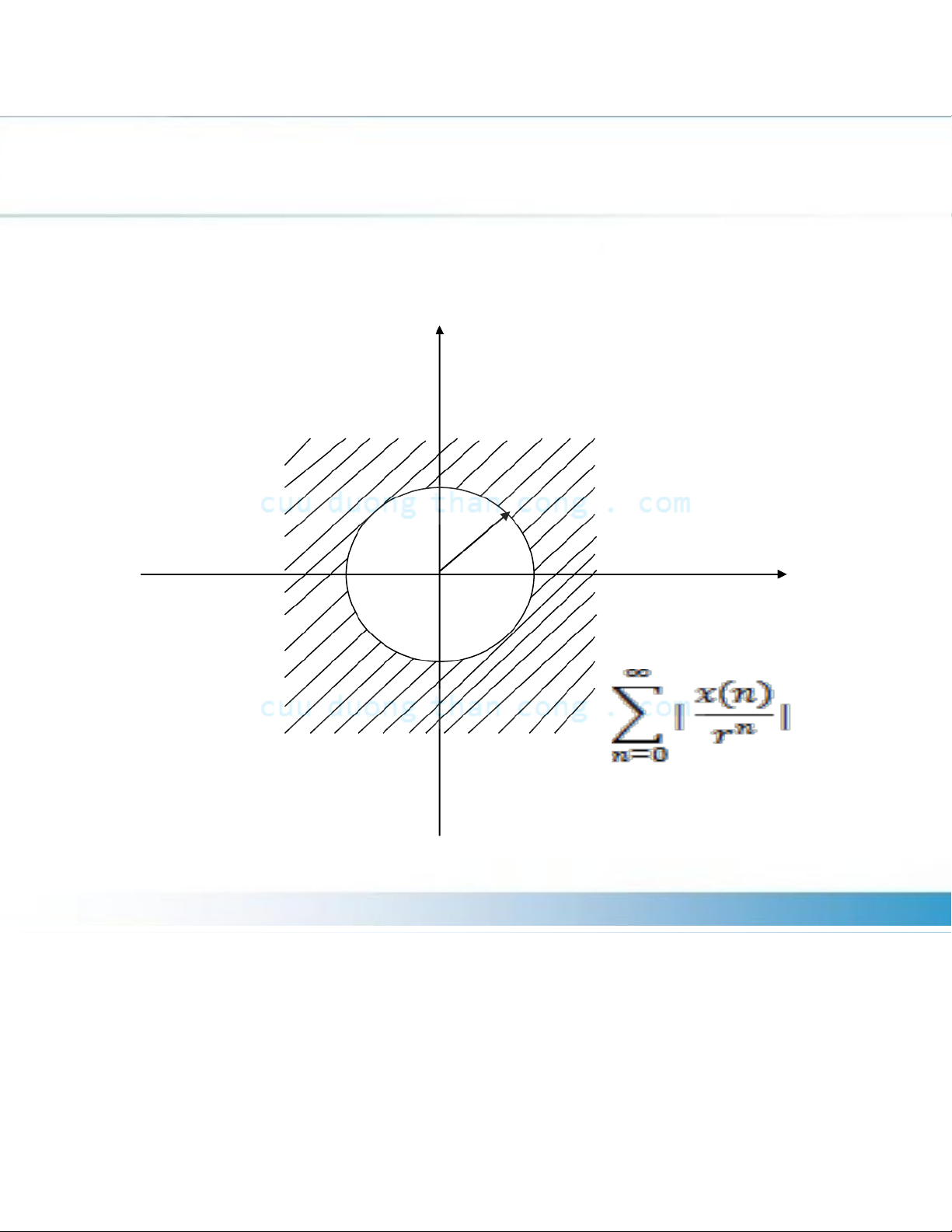
ROC of X(z) is generally specified as the annular region in th
plane , r2 < r < r1, Im*(z) z"#plane r2 Re(z) r1
Region#of#convergence#for#|
X(z)|*r2*<*r*<*r1 (c)
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform
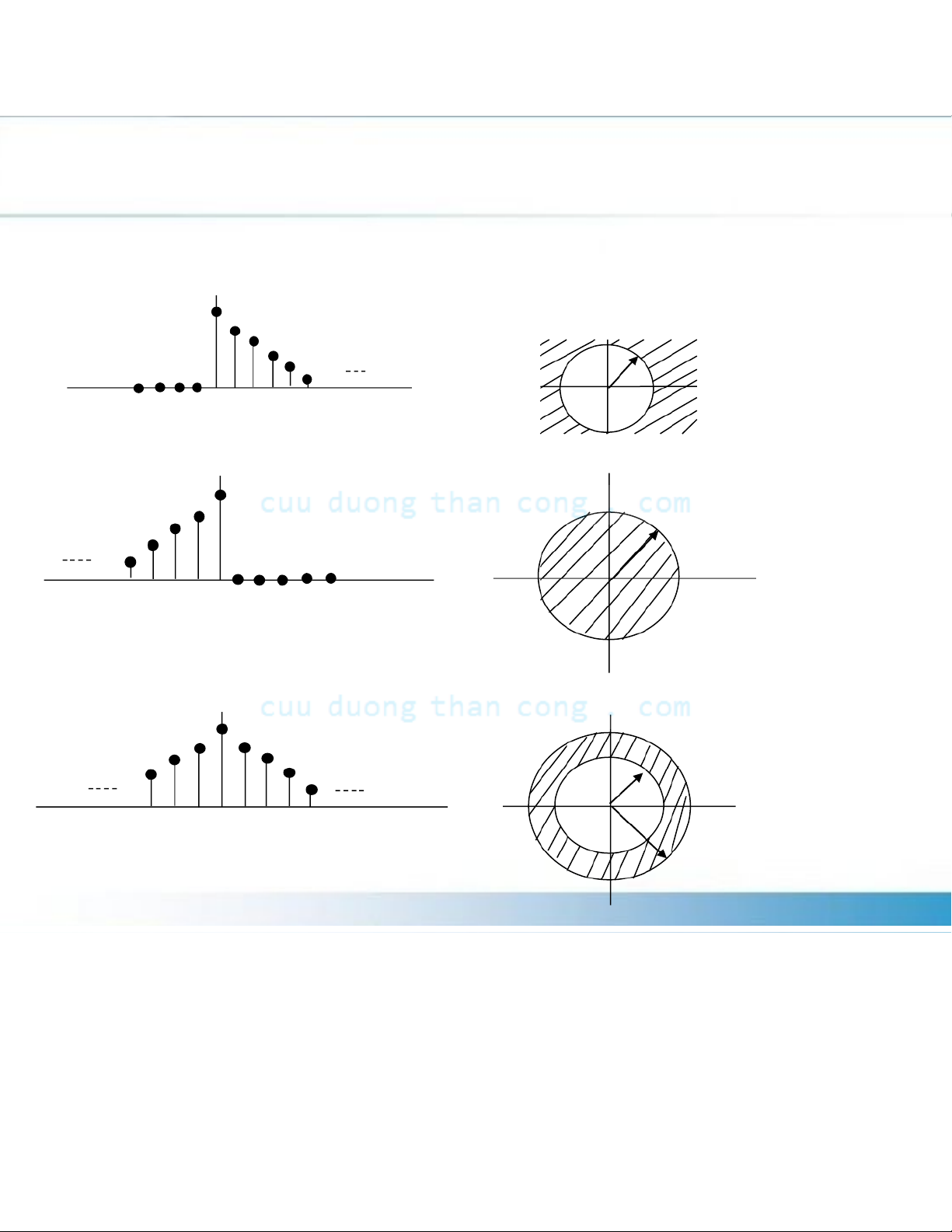
A discrete–time x(n) is uniquely determined by its
transform x(z) and the region of convergence of x(z
Table 3.1 Characteristic Families of signal with their corresponding ROC. Signal# ROC
Finite%&Dura3on&Signal& Causal# En3re&z%plane except&z=0 0 n
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform An3causal En3re&z%plane&&
except&&z&=&∞ 0 n Two%sided En3re&z%plane&&
except&z&=&0&&
and&&z&=&∞ 0 n
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform
Infinite&–&Dura3on&Signals Causal r2 |z|*>*r2 0 n An3causal r1 |z|*<*r1 0 n Two&%sided r2
r2&<&|z|&<&r1 0 n r1
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.1 The direct z-transform
These types of signal are called right-sided
left-sided, and finite-duration two-sided, signals.
If there is a ROC for an infinite duration two-
sided signal, it is a ring (annular region) in the z-plane.
The one-sided or unilateral z-transform given by
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Department 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.1.2 The Inverse z-Transform
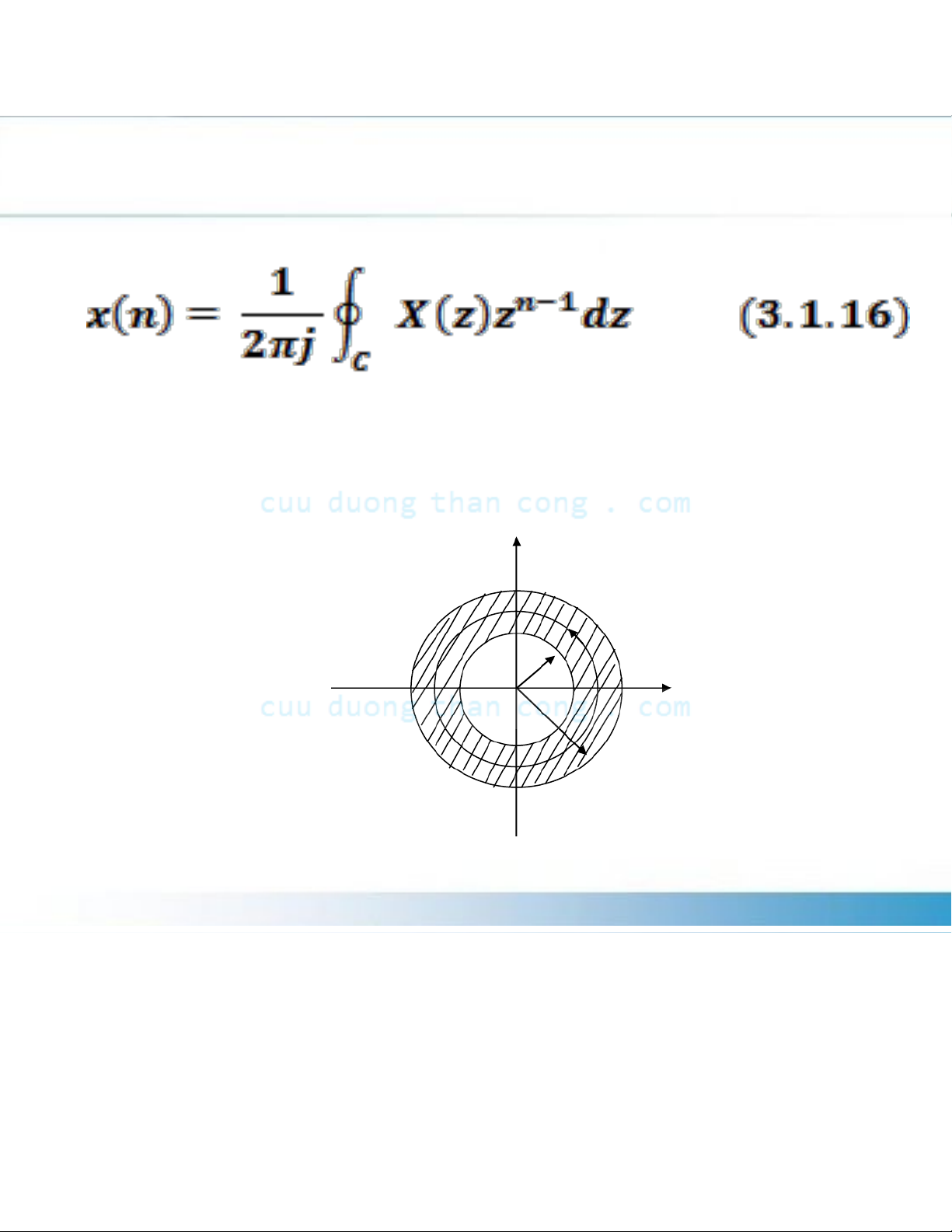
The procedure for transform from the z-dom
to the time domain is called the inversion z- transform.
Cauchy integral theorem. We have then
Where C the closed contour in the ROC of X(z
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt 2013, CE Department 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
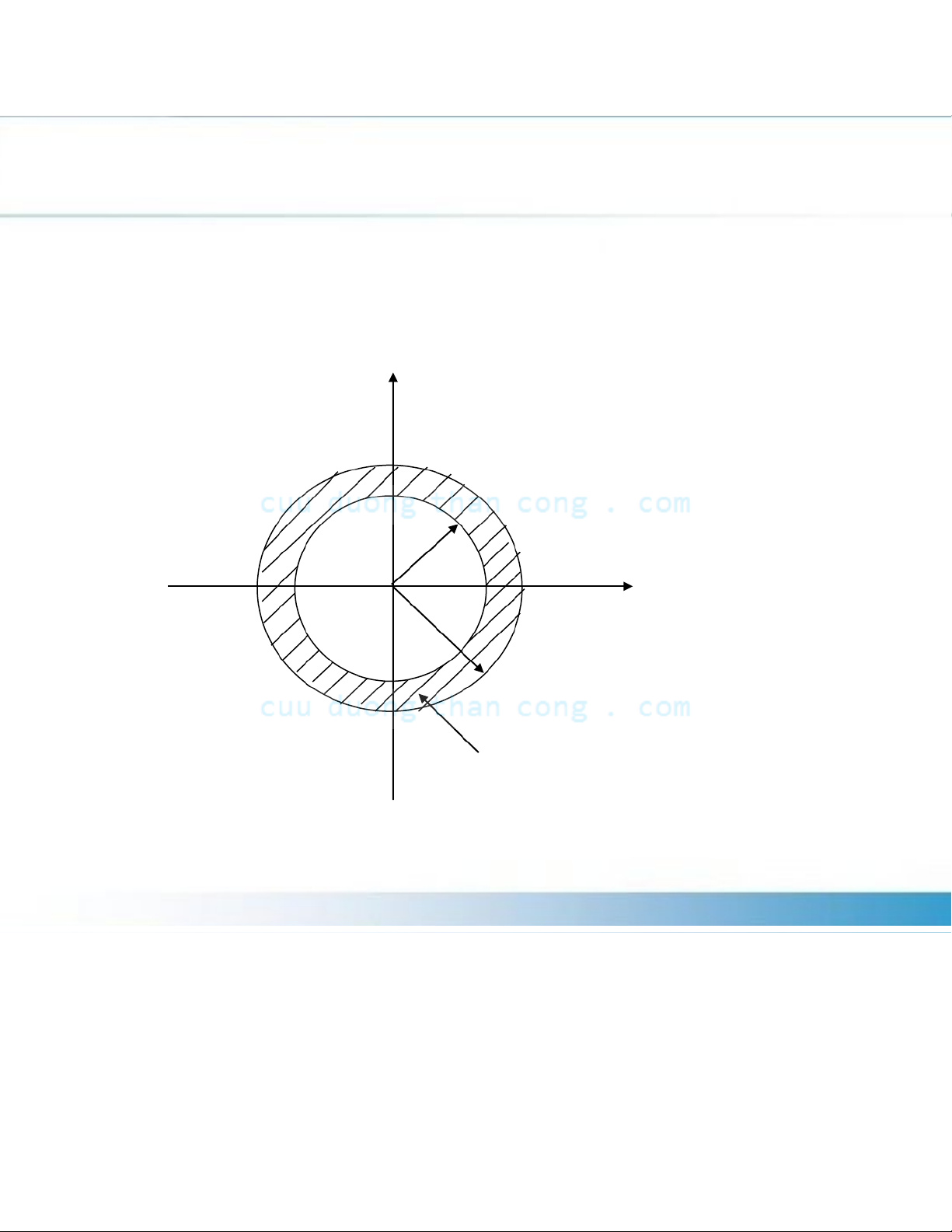
3.1.2 The Inverse z-Transform or
Figure 3.1.5 Contour C for integral in (3.1.13) Im*(z) r C 2 r1 Re*(z)
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform + Linearity z z if x1(n) X ↔ 1(z) and x2(n) X ↔ 2(z) then z
x(n) = a1x1(n) + a2x2(n) X(z) = a ↔
1X1(z) + a2X2(z) (3 + Time shifting z if x(n) ↔ X(z)
then x(n-k) ↔ z z -k X(z) (3.2.5)
+ Scaling in the z-domain z If
x(n) ↔ X(z),
ROC: r1 < |z| < r2 then a z n x(n) X(a ↔
-1z), ROC: | a|r1 < |z| < |a|r2 (3.2.9
or any constant a, real or complex.
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform ime reversal z x(n) X(z), ↔
ROC: r1 < |z| < r2 hen x(-n) ↔ z X (z-1),
ROC: 1/r2 < |z| < 1/r1 (3.2
ifferentiation in the z-domain z x(n) ↔ X(z) z hen nx(n) -z dX(z) ⁄ dz ↔ (3.2.14)
onvolution of two sequences z z
x1(n) ↔ X1(z), x2(n) X ↔ 2(z), z
hen x(n) = x1(n) * x2(n) X(z) = X ↔ 1(z) X2(z) (3.2
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt , CE Department 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform
orrelation of two sequences z z x1(n) X ↔
1(z), and x2(n) X ↔ 2(z) en
ultiplication of two sequences z z x1(n) X ↔ 1(z), x2(n) X ↔ 2(z) en
closed contour that encloses the origin and lies within th
gion of convergence common to both X1(v) and X2(1/v)
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform
Parseval’s relation
f x1(n) and x2(n) are complex-valued sequences , th
provided that r1lr2l < 1 < r1ur2u,
where r1l < lzl < r1u and r2l < lzl < r2u are the ROC of
X1(z) and X2 (z).
The initial value theorem
f x(n) is causal then
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform
+ Table 3.2 Properties of the z-transform
Property Time#Domain# z"#Domain## ROC
Nota=on######x"(n)#############X"(z)###ROC:#r2"<"|z|"<"r1
"""x1"(n)# ############X1"(z)###ROC1 x2"(n)##
#######X2"(z)"##############ROC2
Linearity#""""""""""a1x1"(n)+########a1X1"(z)"+a2X2"(z)""""""At#least#intersec=on#of################ ############a2x2"(n)### ##########ROC#1#and#ROC2
Time#shiDing#############x"(n/k)"#########z/k"X(z)###That#of#X#(z),#except#z=0#if########### ### ######
k=0#and#z"="∞"if#k"<"0
Scaling#in#the##an"x"(n)#########X""(a/1"z)###|a|r2"<"|z|"<|a|"r1" #"domain
Time#reversal####x"(/n)###########X""(z/1)###1/r1"<"|z|"<"1/r2"""
Conjuga=on####x*"(n)#########################X*"(z*)####ROC
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform
eal#part#####Re{x"(n)} #1/2[X"(z)+X*(z*)] Includes#ROC
aginary#part#####Im{x"(n)} 1/2j[X"(z)"/"X*(z*)] Includes#ROC
fferen=a=on#in#####nx"(n) r2 ## "<"|z|"<"r1
onvolu=on##############x1"(n)"*x2"(n)########X1#(z)#X2(z)#########################At#least,#the##interse ####### of##ROC#1#and#ROC2
orrela=on###############rx1x2"(l)"=########Rx1x2"(z)="X1"(z)"X2"(z/1)""""""At#least,#the##intersec=o
###########x1"(l)"*"x2"(/l) "####################################ROC#1#of#X1#(z)#and#X2(z"1)
=al#value############If#x"(n)#causal#"x"(0)"=""lim"X(z)" eorem##### ##### ##
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform
Table 3.3 Some common z-transform pairs
Signal,#x(n) z"#transform,#x(z) ROC 1#####δ"(n) 1# "
#################All#z###############
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.2 Properties of the z–Transform
Signal,#x(n) z"#transform,#x(z) ROC
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm 14:38, 10/01/2026
Chương 3: Z-Transform và Ứng Dụng trong Phân Tích Hệ LTI - CNTT 101 - Studocu
3.3 Rational z- transforms + Poles and Zeros
The zeros of a z-transform X(z) are the values of for which z X(z) = 0
The pole of a z-transform are value of for z
which X(z) = ∞
+ If X(z) is a rational function, then
CuuDuongThanCong.com https://fb.com/tailieudientucntt ©2013, CE Departm